Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision F4 C8 Dynamic Ecosystem
Uploaded by
Muhammad NaquibCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision F4 C8 Dynamic Ecosystem
Uploaded by
Muhammad NaquibCopyright:
Available Formats
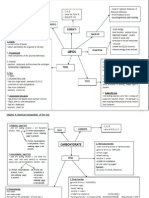
FORM 4 CHAPTER 8 Dynamic Ecosystem
STUDY TIPS
For paper 2, commonly asked include:
1. What is the importance of biodiversity?
2. Paper 3:
The effect of different **light intensity on the population growth of ***LEMNA species.
** Light intensities is the abiotic factors. It can be **pH, Temperature, nutrients too !!
What is ***Lemna? Please check the revision notes.
3. Interaction between organism.
To EXPLAIN HOW, or EXPLAIN WHY means include FACTS + EXPLANATION
4. Succession in Mangrove swamp.
5. Explain the problems and the adaptive structures of EACH mangrove plant species.
6. Quadrat sampling TECHNIQUE.
7. Capture, mark, release, recapture TECHNIQUE (CMRR).
8. You must know very well about YEAST, the microorganism which is often used in LAB
experiments.. It appears in this chapter, apart from Chapter 7 (Respiration) !
9.Harmful microorganisms~ focusing on diseases which are transmitted via:
* food/water
* direct contact
* vectors
* air
Diseases required to know: Malaria, Dengue fever, cholera, AIDS, food poisoning, SARS, Hepatitis.
10. What is Antibiotics, vaccines, antiseptics and disinfectant!
11. Uses of microorganisms in biotech:
* production of antibiotic and vaccines . [ 3m]
* waste treatment. [4m]
* food processing.[4m]
* production of bioplastic.[3m]
* production of energy from biomass.[3m]
REVISIONS
Biotic and Abiotic Components of the environment
Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and interactions between organisms and their
environment.
Biotic components: the living organisms: producers, consumers, decomposers.
Abiotic components: Non living factors such as temperature, pH, humidity, microclimate, topography
and light intensity
Abiotic Components :
a) Topography
a region
**Experiment to investigate effect of aspect on the distribution and growth of Pleurococcus(see #) !!!!
b) pH value
Effect on the distribution of organisms (in the habitat)
**Experiment to investigate the effect of pH on the activity of yeast OR Lemna (see ## below) !!
c) Light intensity
ution & growth of plants & animals
different type of plants
**Experiment to investigate the effect of light intensity on the distribution and growth of
Pleurococcus.
d) Temperature
Affects the physiological activities of plants & animals
decreases of metabolic activity in living organisms
e) Humidity
water evaporates from the moist surfaces at the faster rate
f) Microclimate
ts the population & distribution of organisms
* Take note of the definitions...
# Pleurococcus sp
(i) On a rock (ii) On a tree trunk
## What is Lemna sp?
Please find out a little about about Lemna sp.. please be aware of the significance of this species in
Bio SPM syllabus !!
When you talk about Lemna sp..the aquatic green small plant which is found growing in the pond..it
is often used in studies related to abiotic factors affecting its population distribution / GROWTH..
Common name for Lemna sp is duckweed.
For example:
Design an experiment to study the effect of pH on the population growth of Lemna sp OR
...Other factors which possibly be asked are: temperature, light intensity, humidity and topography...
..But in the Lab, the factors such as light intensity, pH and temperature could be investigated easier.
Sample Questions:
Tips: . Identify all the three Variables first!!
To investigate the effect of light intensity on the population growth rate of Lemna sp
Manipulated Variable : Light intensities
(How are you going to operate this??...perhaps by using different power of the bulbs : 20W, 40W,
60W and 80W???)
Responding Variable: Number of Lemna sp.
(Because Lemna leaves/plants can be counted one by one!!!..)
(The more the number of Lemna means the more growth..)
Fixed variable : ..any suitable parameters such as, pH of water..or even temperature.
To investigate the effect of pH on the population growth rate of Lemna sp
Manipulated Variable : pH
(How to operate manipulated variable?? By using different pH medium of Knop Solution: maybe
pH 2, pH6, pH8...and Lemna best growth in neutral medium..Both acidic and alkali are not suitable
for Lemna sp )
To investigate the effect of temperature on the population growth rate of Lemna sp
Manipulated Variable: Temperature
(..manipulate the temperature by using different temperature of water where Lemna is
growing..Maybe at 10, 20, 40,60
0
C.).
So guys..go and read about Lemna sp.. It might come out for Paper 3 SPM, Question 1 or even
Question 2...
Food chain, food web and trophic levels
Food chain :
- shows the feeding relationship of biotic components in an
ecosystem
- shows how energy is transferred from one organism to another.
- as one organism feeds on another, energy is transferred from one
trophic level to another.
- about 90% of the energy is lost to the environment
- while only 10% is passed on energy is lost through processes
such as respiration, excretion and
defaecation
Example: The Marine Food Chain
- Phytoplankton is the first level of the
food chain,
- followed by the zooplankton, which
feeds on the phytoplankton.
- The zooplankton are then eaten by
krill, fish and other crustaceans,
- which all go on to be eaten by big fish,
penguins, seals, walruses and whales.
- The food chain continues when these
are eaten by mammals like polar bears.
If you think about the food chain
logically it is easy to understand how,
without plankton, all of the oceans
animals would die :-
- Without phytoplankton, zooplankton
would not have food and die.
- Without zooplankton, krill, smaller
fish and other crustaceans would have
nothing to eat and they
would die, etc, etc.
- Until finally you get all the way out to
large mammals like whales, dolphins, and manatees.
- All animals in the ocean depend on plankton for survival.
# see sample question 2 , 3 and 4
Useful tips:
..And please take note of all Diagrams/pictures in your Text Book and also in
your reference books...which show the interactions between organisms...
You should be able to explain their interactions: Either Win-Win or Win-Lose
You should be able to differentiate between food chain and food web.
Question might want you to draw /construct Food Chain...or may be Food
Web..So please response to the question!!
Use the organisms given in the question...unless the questions ask you to
construct with others examples...
Always start with The Producer!! Apart from plants, phytoplanktons are
producers too...and algae!!! ( or any photosynthetic organism...)
Interaction between organism.
What is this Interaction?
Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiosis is a close ecological relationship between the
individuals of two (or more) different species. Sometimes a
symbiotic relationship benefits both species, sometimes one
species benefits at the other's expanse and in other cases
neither species benefits.
Ecologists use a different term for each type of symbiotic relationship:
Mutualism -- both species benefit
Commensalism -- one species benefits, the other is unaffected # see sample question 9
Parasitism -- one species benefits, the other is harmed
Competition
that are limited (strong organisms will survive , weak organisms will migrate or die)
Competition -- neither species benefits
Intraspecific competition: competition that occurs between members of the same species of plants
& animals to obtain common basic needs
Interspecific competition: competition that occurs between members of the different species of
plants & animals to obtain common basic needs
# see sample question 6 and 7
Prey-predator Relationship:
If graph is produced, you should be able to explain the relationship.
# see sample question 8
Succession in Mangrove swamp.
(Explain the problems and the adaptive structures of EACH mangrove plant species.)
..Before you go into details about the process of colonisation in mangrove swamp, you have to
understand the meaning of certain terms like
colonisation, pioneer species, successor species, dominant species, succession,
climax community...
* The details about mangrove swamps are not yet asked in SPM.....but there are so many facts about
mangrove swamps which could possibly be asked... ..As the processes of colonisation and succession
in a pond, there was an essay question asked in 2007.... # see sample question 10
Mangrove swamps are found in tropical and subtropical regions where freshwater meets salt water
Their characteristics include:
TAKE NOTE:
1.You should be able to interpret the graphs of competition by giving FACTS and
EXPLANATION/ REASONS.
2. Take note of the given organisms involve in the competition . Eg: If it is between maize and
paddy plant: it is an interspecific competition. If it is between maize and maize, it is an
intraspecific competition.
Please take note of the experiments involved!!
i. soft, muddy soil
ii. higher concentration of salt
iii. very low level of oxygen due to waterlogged condition
iv. exposed to a high intensity of sunlight.
v. strong wind
Their characteristics are THE FACTS and you have to elaborate with EXPLANATION...by asking SO
WHAT?? Example :
....soft, muddy soil....so what??..
....higher concentration of salt...so what???..
And mangrove swamps along tropical bays characteristically show ZONATION...(Refer text book or
any reference book )
Example : Explain the problems faced by mangrove plants and how they overcome it. [10 marks]
Tips: Remember: FACTS and EXPLANATION [ 5+5 Marks]
You may explain according to species or according to its zonation
...and you should be able to identify which species are distributed in different zones...
..and the spelling of each species...and their adaptive characteristics..
Avicennia sp and Sonneratia sp
Avicennia sp (api-api) and Sonneratia sp (Perapat)are pioneer species of mangrove swamp.
Avicennia sp with pneumatophores- the breathing roots which grow vertically upwards from the
mud. Gaseous exchange takes place through the pores in the pneumatophores...The roots are also
long branched cable roots.
Rhizophora sp
Rhizophora sp has prop roots..to give support . It gradually replaced the pioneer sp.
Prop root trap more silt and mud.. Soil then becomes firmer and Drier.. The soil level is raised and
is more fertile with the collection of decaying plants parts..This condition favors Bruguiera sp to
replace..
Bruguiera sp
Bruguiera sp has buttress root..which trap more mud
and silt causing the land structure to change..
Vivoporous Seedling
The seeds of mangroves are especially remarkable because they commonly germinate within their fruit
while still attached to the parent plant, a condition known as "viviparous seeds."
- The viviparous seeds: which attach and germinate at the mother's plant
Having their embryonic root (hypocotyl) already elongated gives them a better chance of establishing
themselves in soft mud during low tide. Called "sea pencils", the cigar-shaped seedlings
(disseminules) of red mangrove may have an elongate taproot up to 10 inches long when they drop
from the parent tree.
The unusual, top-shaped fruit of tea mangrove contains one of the largest seeds in the world
(excluding palms).
It floats with the elongate, embryonic root pointing downward, and readily becomes implanted in soft
mud.
The seedling drops into the water where it is automatically planted in the soft mud or floats away.
- Salt that enters the root from sea water will be excreted through hydathodes.
# see sample question 11, 12, 13
Population Ecology
Population Ecology the study about size population measurement and the factors affecting population
size
Technique to determine size and population density ..
...And the quadrat Formula...and the CMRR Formula too... for Paper 1...
1. The quadrat sampling technique
Conduct an experiment to investigate distribution of plant in school field
number of quadrats containing a species
a) Percentage frequency = -------------------------------------------------- x 100%
number of quadrats sampled
aerial coverage of all quadrats
b) Percentage coverage = ------------------------------------------------------ x 100%
number of quadrats sampled x quadrat area
Total number of individuals of a species in all quadrats
c) Density = ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
number of quadrats sampled x quadrat area
2.Capture, mark, release and recapture technique
Conduct the analogy experiment using soys beans that can be mark by the marker pen
Total number of the first captured x Total number of the second captured
Population = --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of marked individuals from the second captured
..You must be aware of the existance of Pleurococcus sp and Lemna sp
(Which are stated in Bio Syllabus: Indicating that you must know about these two organisms..and
possibly be asked too...)
Biodiversity
Effect of abiotic components on the activity of microorganism
main microorganism is YEAST
the abiotic components mainly are : pH, temperature, light intensity, nutrient or water
For example:
Design an experiment to study the effect of light intensity on the activity of yeast !
Sample Questions:
Tips: . Identify all the three Variables first!!
To investigate the effect of light intensity on the activity of yeast.
Manipulated Variable : Light intensities
(How are you going to operate this? Perhaps by using different power of the bulbs : 20W, 40W,
60W , 80W? or one 60W bulb put at 10cm, 20cm, 30cm, 40cm, 50cm distance from the yeast ?)
Responding Variable: Height of coloured liquid in a manometer
(When yeast active and respires, CO
2
is released and accumulated in the boiling tube)
(.. more CO
2
will cause higher air pressure in boiling tube to push the coloured liquid up the
manometer..)
(The higher the level of the coloured liquid in a manometer means the increase of the yeast
activity)
Fixed variable : any suitable parameters such as, pH, temperature, time taken, amount of yeast
The activity of yeast is higher at a lower intensity of light.
To investigate the effect of pH on the activity of yeast
Manipulated Variable : pH
(How to operate manipulated variable?? By using different pH, maybe pH 2, pH6, pH8 by adding
different drops of hydrochloric acid solution into the yeast suspension. )
The activity of yeast is higher in an acidic medium and lower in an alkaline medium
To investigate the effect of temperature on the activity of yeast
Manipulated Variable: Temperature
(..manipulate the temperature by placing yeast suspension at different temperature of water bath:
10, 20, 40,60
0
C.).
The activity of yeast is optimum at 35
0
C.
To investigate the effect of nutrient on the activity of yeast
Manipulated Variable: concentration of glucose solution (nutrients)
(..manipulate the concentration of glucose by adding yeast suspension with 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%
glucose solution or distilled water).
The activity of yeast is higher at a higher concentration of nutrients
The harmful effects of microorganism spoilage of food/ substance and cause diseases
The Role of Useful Microorganism in the Ecosystem Nitrogen Cycle
The Use of microorganism in Biotechnology
# see sample question 14 ,15, 16, 17 and 18
Sample Question 1 (Objective - for Food Chain/ Food Web/ Energy Trophic)
1. If almost all the snakes in the field are killed because of a disease, which organism in the food chain
will immediately increased in number?
A Cats C Caterpillars
B Eagles D Rats
2. Which of the following are primary consumers ?
A Decomposers C Herbivors
B Autotrophs D Carnivores
3. The abiotic factors which influence the distribution of organisms in pond include
I the pH
II light intensity
III the presence of predators
IV concentration of carbon dioxide
A I and II C II, III and IV
B I, II and III D I, II and IV
Sample Question 2 (Structured - for Food Chain/ Food Web/ Energy Trophic)
1.Figure 1 shows pond ecosystem.
(a) (i) Based on Figure 1, name TWO factors for each of the following:-
-Biotic factor :
-Abiotic factor : .. [4m]
(ii) Name the abiotic factor that controls the distribution of submerged plants in the pond. [1m]
(iii) State the relationship between the factor you have named in (a)(ii) and the distribution of
submerged plants. [1m]
(b) (i) Based on Figure 1, construct :
- A food web showing the interaction of all the organisms in the figure. [2m]
- A pyramid of numbers consisting of four trophic levels [2m]
(ii) Explain how energy is transferred from the sun to the organisms in food chain. [3m]
(iii) Explain why the amount of energy received by an organism via the food chain gradually
decreases from one trophic level to the other trophic levels. [3m]
(c) (i) Name the organism that is known as the pioneer species in the pond. [1m]
(ii) Most of the pioneer species have adaptations that enable them to live in the bare
habitat. Give TWO adaptations of the pioneer species you have named in (c)(i). [2m]
(iii) Explain how the ecosystem in Figure 1 can turn into a climax ecosystem. [5m]
(d) Vegetables were planted near the pond in Figure 1. A farmer used chemical fertilizers to
enhance the growth of the vegetables. He also used pesticide to control the pests.
Predict the effects arising from those activities to the pond ecosystem after several years. [5m]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 2
1.Figure 1 shows pond ecosystem.
(a) (i) Based on Figure 1, name TWO factors for each of the following:-
-Biotic factor : Producer/ consumer
-Abiotic factor : light intensity/ pH of water / depth of the pond [4m]
(ii) Name the abiotic factor that controls the distribution of submerged plants in the pond.
light intensity [1m]
(iii) State the relationship between the factor you have named in (a)(ii) and the distribution of
submerged plants.
The lower the light intensity in the pond, the lower the population of submerged plant [1m]
(b) (i) Based on Figure 1, construct :
- A food web showing the interaction of all the organisms in the figure. [2m]
Marks given for : all organisms correct- 1 , arrow correct - 1
- A pyramid of numbers consisting of four trophic levels [2m]
(ii) Explain how energy is transferred from the sun to the organisms in food chain. [3m]
P1 - light energy trap by chlorophyll (in producers) and changed to chemical energy in food (via
photosynthesis)
P2 - producer eaten by primary consumer, so energy from producer transfer to the primary
consumer
P3- primary consumer eaten by other consumer, so energy will transfer to that organism via
feeding
(iii) Explain why the amount of energy received by an organism via the food chain gradually
decreases from one trophic level to the other trophic levels. [3m]
F - energy lost directly from organisms to the surrounding through radiation
E1- lost through excretion such as urination, constipation and sweating
E2- lost through respiration
(c) (i) Name the organism that is known as the pioneer species in the pond. [1m]
Hydrilla sp. / Elodea / Cabomba
(ii) Most of the pioneer species have adaptations that enable them to live in the bare
habitat. Give TWO adaptations of the pioneer species you have named in (c)(i). [2m]
P1 - Reproduce asexually
P2 - need only low light intensity to carry out photosynthesis
(iii) Explain how the ecosystem in Figure 1 can turn into a climax ecosystem. [5m]
P1 - submerged plants died and sink at the bottom of the pond, it change the nutrient content and depth
of the pond.
P2 - submerged plants replaced by the floating plants, which at the end covered surface of the water
P3 - light cannot enter the inner part of the pond, so all submerged plants will die and the pond become
more shallow
P4 - now the amphibian plants will replace the floating plant, and the pond become less water
P5 - at the end , terrestrial plants will take over the pond and form the climax community
(d) Vegetables were planted near the pond in Figure 1. A farmer used chemical fertilizers to
enhance the growth of the vegetables. He also used pesticide to control the pests.
Predict the effects arising from those activities to the pond ecosystem after several years. [5m]
Pesticide :-
- the toxic substances accumulate in the organisms via the food chain
- the concentration of toxic become higher as the trophic level increase
- this will cause extinction
Fertilizers :-
- more nitrates and phosphates in the pond
- enhance the growing of floating plants which caused algal bloom
- this will reduce amount of oxygen in the pond; situation known as eutrophication
Sample Question 3 (Essay - for Food Chain/ Food Web/ Energy Trophic)
The diagram shows a terrestrial ecosystem. Explain how energy flows through the food chain and
how it is lost to the environment. [ 8 marks]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 3
F1 - Energy flows through the food chain in one direction [ 1 mark]
E1 - In the food chain, the plant is the producer, the rat is the primary consumer, the snake is the
secondary consumer and the eagle is the tertiary consumer.
// In the food chain, the plant is the producer, the earthworm is the primary consumer, the bird is
the secondary consumer and the snake/ eagle is the tertiary consumer. [ 2 marks]
F2- Each level of food chain is called a trophic level. [ 1 mark ]
- Energy is transferred from one trophic level to another trophic level [ 1 mark ]
E2- When energy is transferred from one trophic level to another level as much as 90% of the
chemical energy in the food consumed by primary consumer is used for its metabolic activities and
lost as heat [ 2 marks ]
E3- Only 10% of the energy in an organism is passed on to the organism at the next trophic level [1m ]
Sample Question 4 (Essay - for Food Chain in a pond)
Diagram below shows an ecosystem in a pond. Discuss the flow of energy in the food chain of the
ecosystem. (10 marks)
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 4:
Diagram below shows an ecosystem in a pond. Discuss the flow of energy in the food chain of the
ecosystem. (10 marks)
P1- In a pond ecosystem, the source of energy is sunlight
P2- Producers such as lotus plants and sedges absorb solar energy from the sun and convert it into
chemical energy stored in food during photosynthesis
P3- Some of this energy is used by the lotus plants for cell division, growth and excretion
P4- When the producers die, the energy becomes available to decomposers such as saprophytic
bacteria
P5- As one organism eats another in the pond, there is a transfer of energy from one consumer to
another
P6- When primary consumers such as mosquito larvae feed on the leaves of the lotus plant, some of
the energy stored in the lotus plant is passed on to the mosquito larvae
P7- About 10% of the plants available energy is passed on to the primary consumers
P8- The primary consumers released energy during respiration , etc and used the energy for growth,
movement
P9- Some of this energy becomes available to the decomposers through excretion and defeacation of
the primary consumers
P10- When the secondary consumers like the small fish eat mosquito larvae, the primary consumers
available energy is passed on to the secondary consumers
P11- The small fish loses energy through respiration, excretion and defeacation
P12- The small fish is then eaten by the big fish. Energy flows through the food chain in the ecosystem
when a consumer eats another organism
P13- When the mosquito larvae, the big fish and the small fish die, they are decomposed by
saprophytic bacteria.
Sample Question 5 (Exercise - forInteraction)
For the Images below, please identify the interaction (examples : Saprophytism, epiphytes, epizoytes,
parasitism..What else) and explain in 2-3 sentences about the 'Interaction'..
commensalism mutualism Prey-predator
commensalism
saprophytism
Parasitism
(plant)
Parasitism
(animal)
Saprophytism
commensalism
saprophytism
Sample Question 6 (Essay - for Competition) :
1. In natural ecosystems, there is competition between members of the same species as well as
between different species.
a) Explain how competition between members of the same species helps to control
population growth. [2m]
b) Crop plants must compete with weeds for the same resources. Farmers control weeds by
spraying herbicides(weedkillers). State two factors that the crop plants and weed may compete
for and explain the importance of each. [2+2 = 4m]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 6:
1. In natural ecosystems, there is competition between members of the same species as well as
between different species.
a) Explain how competition between members of the same species helps to control
population growth. [2m]
F: intraspecific competition
E: Plants which grow quickly, will obtain sufficient light ,thus will survive at the expanse of
others //control other plants population growth.
b) Crop plants must compete with weeds for the same resources. Farmers control weeds by
spraying herbicides(weedkillers). State two factors that the crop plants and weed may compete
for and explain the importance of each. [2+2 = 4m]
F1: light intensity
E1: light is important for photosynthesis that produce energy for a crop plants and weed
F2: water
E2: to replace the water lost caused transpiration
Sample Question 7 (Essay - for Competition) : (SPM 2009, Paper 2 , Q7a)
Name and describe the interaction shown in Diagram 7.1. [ 4 Marks]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 7:
- the interaction is Parasitism..... [ 1 mark]
-the parasite (Rafflesia sp) .. [1mark]
-which will benefit by living and obtaining nutrients from its host which is living ... [ 1 mark ]
- and cause harm and weaken their host in the process [1mark]
Sample Question 8 (Essay - for Prey-predator)
Diagram 8 shows types of interaction between two organisms in an ecosystem.
Explain how the interaction between the two organisms controls each other population. [10 marks]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 8:
- The interaction is Prey-predator interaction ( 1 m)
- The interaction is where an organism which is smaller (rabbit) called prey (1m)
- is hunted and eaten by a stronger animal, the predator ( wolf) (1m)
F1: When the population of a predator (wolf) is high, the population of its prey (rabbit) decreases
E1: because the prey is eaten by the predator
F2: When the population of the prey falls, there is insufficient food for the predator
E2: results in a decline of the predator population
F3: When the population of predator is low, the prey recovers and its population increases
E3: result in an increase in the population of the predator (have enough food)
- The interaction takes place in a cycle that keeps the population of both organisms in a dynamic
equilibrium.
Sample Question 9 (Essay - for Commensalism)
(a) Diagram shows a plant species P with green leaves on a tree trunk.
(i) Describe the relationship between species P and the host plant, Q. [4 marks]
(ii) Explain how species P obtains their needs and adapted to the environment [6 marks]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 9:
(a) Diagram shows a plant species P with green leaves on a tree trunk.
(i) Describe the relationship between species P and the host plant, Q. [4 marks]
- the interaction is ............commensalism [ 1 mark]
-the species P is a commensal / epiphyte .. [1mark]
-which will benefit by living attached to the host (tree) to gain higher canopy level/position to trap
maximum sun light for photosynthesis ... [ 1 mark ]
- and cause no harm to their host in the process [1mark]
(ii) Explain how species P obtains their needs and adapted to the environment [6 marks]
F : adapted structures
E : function of adaptation
F1 : Roots system is occupied by ants
E1 : the ants bring all kinds of rubbish and remnants of food to the roots
E2 : These materials gradually decompose into humus
F2 : Leaf arrangement in the form of a basket
E1 : can collect falling leaves
E2 : the leaves then decomposes into humus
F3 : Corrugated leaves with grooves
E1 : can direct rainwater and dew to the roots
F4 : Leaf with thick cuticle
E1 : to reduce transpiration
Sample Question 10 (Essay - for Colonisation in a pond)- PYQ 2007 Paper2Q9(a)
Diagram shows the process of colonisation and succession in a habitat. (Diagram shows the pond)
What is meant by 'colonisation and succession in a habitat'?
Based on Diagram, explain how colonisation and succesion bring about the formation of primary
forest in a habitat. [10 M]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 10:
- Colonisation is a process whereby a species colonises in a newly formed area/ habitat/pond. [1m]
- Succession is a process whereby one species of organism changes the habitat , then being replaced by
other species which are more adaptable to the habitat. [1 M]
...next 8 points are to explain how colonisation and succesion bring about the formation of primary
forest:
P1- Pioneer species /submerged plants causes a change in the environment
P2-the remains of plants and decayed body deposited to the pond bed
P3-pond becomes shallower
P4-nutrients are added to soil/pond water
P5-lead to the growth of floating plants to replace submerged plants
P6-Floating plants cover the water surface, preventing the light to penetrate water
P7-result in greater rate of plants death which sink to the bottom of the river
P8-making the pond shallower
P9-floating plants are then slowly replaced by amphibious. emergent plants
P10-the successor causes further changes to habitat/pond
P11-finally amphibinas plants are replaced by land community which dominate the area.
[Any 8 marks]
Sample Question 11 (for Colonisation in mangrove swamp)
Diagram below shows a mangrove swamp at a river mouth in 1950 and 2007 respectively. The line
XY shows the position of the beach.
(a) i) What has happened to the mangrove zone in diagram 3. [ 1m]
ii) Name the process that is taking place. [ 1m]
iii) Explain the process mention in (a) ii [3 m]
b) By using suitable keys, sketch the zones of mangrove swamp in diagram 4 ii) in which the
following mangrove trees can be found.
Brugueira sp, Avicennia sp, Rhizophora sp. (3 marks)
c) i) State the type of seedlings produced by the mangrove trees. (1 mark)
ii) Explain how this type of seedling increases the chances of survival of the mangrove trees.(2m)
d) State one problem faced by mangrove trees. Explain how mangrove trees overcome this
problem.( 2 marks )
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 11:
Diagram below shows a mangrove swamp at a river mouth in 1950 and 2007 respectively. The line
XY shows the position of the beach.
(a) i) What has happened to the mangrove zone in diagram 3
They have been moved from their original position. [ 1m]
ii) Name the process that is taking place. Succession [ 1m]
iii) Explain the process mention in (a) ii [3 m]
-The roots of the pioneer species trap the mud, causing the soil to become more compact
- At the same time the soil level increases, thereby exposing its exposure to the tides and this
makes the soil unsuitable for the pioneer species .
- The species in zone U are the successors , which take over the area of zone T
- Slowly, succession of the species in zone W takes place.
b) By using suitable keys, sketch the zones of mangrove swamp in diagram 4 ii) in which the
following mangrove trees can be found.
Brugueira sp, Avicennia sp, Rhizophora sp. (3 marks)
c) i) State the type of seedlings produced by the mangrove trees. Viviparous seedling (1 mark)
ii) Explain how this type of seedling increases the chances of survival of the mangrove trees.(2m)
. - The seedling are able to germinate while still being attached to the parent plant.
- As the seedling fall into the water , they can float horizontally and, subsequently, get washed up
on mudflats where they settle and grow into new plants
d) State one problem faced by mangrove trees. Explain how mangrove trees overcome this
problem.( 2 marks )
. - The mangrove trees are exposed to direct sunlight which results in a high rate of transpiration.
- This problem is overcome by the thick and succulent leaves of mangrove trees which can store
water
Sample Question 12 (Essay - for Colonisation in mangrove swamp)
Diagram shows a transect through a mangrove swamps ecosystem.
a. Based on Diagram , explain succession in mangrove swamps. [10 marks]
b. Explain the adaptive characteristics of mangrove plants to ensure its survival.[10 marks]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 12:
Diagram shows a transect through a mangrove swamps ecosystem
(a).Based on Diagram , explain succession in mangrove swamps. [10 marks]
P1 Pioneer species in mangrove swamps are Avicennia and Sonneratia..
P2 Extensive root systems of these trees collect sediments, including organic matter from
decaying plants.
P3 As time passes, soil become more compact and firm.
P4 This condition favours growth of successor species , Rhizophora.
P5 Arching prop roots of Rhizophora trap silt and mud.
P6 Creating a firmer soil and over time.
P7 Ground becomes higher and soil becomes drier.
P8 Condition now becomes more suitable for second successor species , Brugueira.
P9 Buttress root of Brugueira form loops which protrude from soil to trap more silt and mud.
P10- Modifies soil structure gradually.
P11- Over time, terrestrial plants begin to replace Brugueira.
P12- Terrestrial forest eventually become tropical rainforest, which is the climax community.
(b) Explain the adaptive characteristics of mangrove plants to ensure its survival.[10 marks]
F1 Avicennia has long underground cable roots
P1 give support in soft muddy soil and protect from strong coastal wind.
F2 pneumatophores
P2 breathing roots that allow gaseous exchange during low tide.
F3 present of hydatodes
P3 pores in the epidermis of leaves which excretes excess salts.
F4 Leaves with thick cuticles.
P4 reduce rate of transpiration during hot weather.
F5 succulent leaves
P5 able to store water to prevent dehydaration.
F6 root cells have higher osmotic pressure than surrounding salt water.
P6 prevent cell sap of roots lose water by osmosis.
F7 viviparous seeds.
P7 increase the chance of survival of the seedlings as they can float on water.
Sample Question 13 (Structured - for Colonisation in mangrove swamp)
Diagram 2 shows the shoreline profile of a mangrove swamp and its plants.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan profil pesisir pantai paya bakau dan tumbuhan yang tumbuh.
(a) State the type of seedlings produced by the mangrove trees . Explain how this type of this seedling
increases the chances of survival of the mangrove trees. [2m]
Nyatakan jenis biji benih yang dihasilkan oleh tumbuhan paya bakau. Terangkan bagaimana jenis biji
benih menambahkan peluang kemandirian pokok paya bakau.
(b)State a species of mangrove tree found in zone A [1m]
Nyatakan spesies pokok bakau yang didapati di zone A
(c)Name the root system possessed by the mangrove tree in zone A [1m]
Namakan sistem akar yang dipunyai oleh pokok bakau di zone A
(d)Name the structure found in the root system of mangrove trees that inhabit zone A.[1m]
Namakan struktur yang terdapat pada sistem akar pokok paya bakau yang mendiami zon A.
(e)State three reasons why the mangroves swamp is not colonized by many plant.[3m]
Nyatakan tiga alasan mengapa paya bakau tidak di tumbuhi oleh banyak jenis tumbuhan
(f) Explain how the mangrove trees adapt to the salty habitat. [2m]
Terangkan bagaimana pokok paya bakau menyesuaikan diri dengan habitat yang masin.
(g)State the importance of the mangrove swamp in the food web of aquatic living things. [1m]
Nyatakan kepentingan paya bakau dalam rantaian makanan hidupan haiwan akuatik
(h)Name the type of forest formed when succession in mangrove swamp areas reaches its climax?
Namakan jenis hutan yang akan terbentuk apabila penyesaran di dalam kawasan paya bakau
mencapai klimaks?
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 13:
Diagram 2 shows the shoreline profile of a mangrove swamp and its plants.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan profil pesisir pantai paya bakau dan tumbuhan yang tumbuh.
(a) State the type of seedlings produced by the mangrove trees . Explain how this type of this seedling
increases the chances of survival of the mangrove trees. [2m]
Nyatakan jenis biji benih yang dihasilkan oleh tumbuhan paya bakau. Terangkan bagaimana jenis biji
benih menambahkan peluang kemandirian pokok paya bakau.
Viviparous seedling
E1 -the seedling germinates while still attach to the parent plant ensure the sufficient supply of
nutrients and oxygen for the process
E2 the elongated radical/taproot (cigar-shaped seedlings) point downward make it readily
implanted in the soft mud
(b)State a species of mangrove tree found in zone A - Avicennia sp , Sonneratia sp [1m]
Nyatakan spesies pokok bakau yang didapati di zone A
(c)Name the root system possessed by the mangrove tree in zone A Pneumatophores [1m]
Namakan sistem akar yang dipunyai oleh pokok bakau di zone A
(d)Name the structure found in the root system of mangrove trees that inhabit zone A.[1m]
Namakan struktur yang terdapat pada sistem akar pokok paya bakau yang mendiami zon A.
Have openings known as lenticels for breathing
(e)State three reasons why the mangroves swamp is not colonized by many plant.[3m]
Nyatakan tiga alasan mengapa paya bakau tidak di tumbuhi oleh banyak jenis tumbuhan
- Muddy soft soil
- Very low level of Oxygen
- Very high concentration of salt
- Exposed to very high intensities of sunlight
- Strong winds [any three]
(f) Explain how the mangrove trees adapt to the salty habitat. [2m]
Terangkan bagaimana pokok paya bakau menyesuaikan diri dengan habitat yang masin.
- the root cells of mangrove trees have a higher osmotic pressure than the surrounding salt water.
- the leaves are succulent and able to store water.
(g)State the importance of the mangrove swamp in the food web of aquatic living things. [1m]
Nyatakan kepentingan paya bakau dalam rantaian makanan hidupan haiwan akuatik
Mangrove swamps are the confluence of mud and silt and become a source of food for living thing
of sea
(h)Name the type of forest formed when succession in mangrove swamp areas reaches its climax?
Namakan jenis hutan yang akan terbentuk apabila penyesaran di dalam kawasan paya bakau
mencapai klimaks?
Tropical rainforest
Sample Question 14 (Structured - for Biodiversity: harmful microorganism)
Diagram 5.1 shows microorganism P that attack a bacterium.
(a) (i) What is microorganism P? [1 mark ]
(ii) What type of interaction between P and the bacterium? [ 1 m]
(iii) Explain the interaction that you mentioned in (a) (ii). [2m ]
(b)State one characteristics of organism P. [1m]
Siti lives in a flat area with clogged drainage and poor sanitary system. Unluckily last week she was
down with fever. She had severe body pain and rashes over the body. She also experienced severe
headaches and vomiting.The doctor discovered that she had been infected by microorganism Q that
carried by the vector R as shown in Diagram 5.2.
(c) i. Name the microorganism Q. [1 m]
ii. Why the antibiotic cannot treat this disease? [2 m]
iii. After one week rest, Siti is recovered. State the type of immunity she obtained. [1m]
iv. Explain the immunity you mentioned in (b) (ii). [2 m]
(d)State one similarity between microorganism P and Q.
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 14:
Diagram 5.1 shows microorganism P that attack a bacterium.
(a) (i) What is microorganism P? Bacteriophage [1 mark ]
(ii) What type of interaction between P and the bacterium? Parasitism [ 1 m]
(iii) Explain the interaction that you mentioned in (a) (ii). [2m ]
F: It is a relationship in which virus (parasite) benefits while the bacteria (host) is harmed
E: because virus will destroy the bacteria at the end
(b)State one characteristics of organism P. [1m]
-virus is a non-living cell , cannot survive or reproduce on its own outside the cells of its host
// all viruses are infectious; they must infect living cells to reproduce.
Siti lives in a flat area with clogged drainage and poor sanitary system. Unluckily last week she was
down with fever. She had severe body pain and rashes over the body. She also experienced severe
headaches and vomiting.The doctor discovered that she had been infected by microorganism Q that
carried by the vector R as shown in Diagram 5.2.
(c) i. Name the microorganism Q. Dengue virus [1 m]
ii. Why the antibiotic cannot treat this disease? [2 m]
F: Antibiotic function by interrupt the metabolism process in a microb
E: Antibiotic cannot treat this disease because the dengue virus did not have the metabolism that
can interrupted by antibiotic
iii. After one week rest, Siti is recovered. State the type of immunity she obtained. [1m]
naturally acquired active immunity
iv. Explain the immunity you mentioned in (b) (ii). [2 m]
F: this immunity is obtained after a person is exposed to a pathogen
E: the pathogen stimulate an immune response that produces antibodies in her body.
(d)State one similarity between microorganism P and Q.
-Both are virus / pathogenic / infectious / can cause disease.
Sample Question 15 (Structured - for Biodiversity: microorganism)
1.(a) State the difference between bacteria and virus in the following aspect : [3m]
i. Structure
ii .Method of reproduction
iii.Nutrition.
(b) (i) Parasites can cause diseases. State 3 main ways how parasitic diseases can be transmitted in a
community . [3m]
(ii) Ringworm is a disease caused by fungus. Explain how transmission of this pathogen can be
stopped. [3m]
(c) Microorganisms can be useful to human. Explain the importance of microorganisms :
(i) In food industry. [3m]
(ii) In Nitrogen cycle [3m]
(iii) Production of insulin [3m]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 15 (Structured - for Biodiversity: microorganism):
1.(a) State the difference between bacteria and virus in the following aspect : [3m]
i. Structure
- Bacteria enclosed by cell wall made of glycoprotein, but virus only have protein coat
// Bacteria have nucleus but virus only contain RNA / DNA
ii .Method of reproduction
- Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission , but virus only replicate the DNA/RNA in the
host
iii.Nutrition.
- Bacteria can be synthesis organic substances via chemosynthesis (autotroph) or feed organic
substances from other organisms (heterotroph) but viruses are strickly parasit (absorp
nutrient from the host)
(b) (i) Parasites can cause diseases. State 3 main ways how parasitic diseases can be transmitted in a
community . [3m]
- by vector such as rat, housefly or others
- by food / water
- by droplet transmission
(ii) Ringworm is a skin disease caused by fungus. Explain how transmission of this pathogen can
be stopped. [3m]
- do not share clothes with others
- wash / clean all part of your body and make sure it dry
- use anti-fungus cream
- take vitamin
(c) Microorganisms can be useful to human. Explain the importance of microorganisms :
(i) In food industry. [3m]
- Yeast used in cake industry / wine industry
- bacteria used in chocolate / dairy product industry
- fungus used as a food
(ii) In Nitrogen cycle [3m]
- Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert the nitrogen gas to nitrates in the soil
(example Rhizobium sp and Nostoc)
- Bacteria and fungi decompose dead organisms to form ammonia
- Nitrosomonas and nitrobacter convert ammonia to nitrites and nitrites to nitrates.
(iii) Production of insulin [3m]
- Fragment of DNA which control the formation of insulin from pancreas was inserted in the
DNA of bacteria
- then the bacteria will be cultured in a specific medium.
-the bacteria now has the ability to produce insulin in big amount and faster.
Sample Question 16 (Essay - for Biodiversity: harmful microorganism)
Some bacteria and other microorganisms are harmful to human beings as they cause diseases.
EXPLAIN HOW diseases are transmitted and SUGGEST ways to control the spread of diseases. [10
marks]
Tips:
1. Command words : EXPLAIN HOW and SUGGEST
2.Total Marks 10
3. It is 6 + 4
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 16 (Essay - for Biodiversity: harmful microorganism)
Some bacteria and other microorganisms are harmful to human beings as they cause diseases.
EXPLAIN HOW diseases are transmitted and SUGGEST ways to control the spread of diseases. [10
marks]
1. Method of transmitting disease [6 marks are allocated]
2. Ways to control [ 4 marks allocated]
Disease such as cholera can be transmitted through contaminated food and water . Microorganisms
such as bacteria or virus will attached to the dirty hands of the infected person when they touch the
food.
Disease such as AIDS can be transmitted by direct contact with an infected person. This is through
sexual contact with infected person. Disease like ringworm can be infected by using personal things
of infected person.
Vectors such as flies and cochroaches can transmit microorganism/pathogen from faeces or
contaminated food while mosquito inject the infected person when it bites the body of another
person and it pass the microorganisms
Airborne diseases like TB is transmitted via liquid droplets which contains pathogen and enter to the
other persons body via respiratory system. The liquid droplets produced when a person sneezes,
cough or spit.
In order to control the spread of diseases: the use of antibiotics may kill and inhibit the growth of the
pathogen. Examples of antibiotics are penicillin and streptomycin.
The use of vaccine to stimulate the body to produce antibody to built up the body immune system also
can control the spread of diseases. Examples of such vaccine are the Sabine vaccine and the BCG.
Antiseptics can applied on wounds or cuts to kill or inhibit growth of microorganism Examples are
acriflavin and iodine solution
And lastly is the use of disinfectant can inhibit the growth of microorganisms on the surface of floors,
building, furniture, rooms and surgical equipment. Examples are phenol, formaldehyde and carbolic
acid
Sample Question 17 (Essay- for Biodiversity: useful microorganism)
Most microorganisms are harmless and useful to humans. Yeast and bacteria are microorganisms.
Discuss the benefits of using this two microorganisms to produce useful products for humans. [ 10
marks]
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 17 (Essay- for Biodiversity: useful microorganism)
Most microorganisms are harmless and useful to humans. Yeast and bacteria are microorganisms.
Discuss the benefits of using this two microorganisms to produce useful products for humans. [ 10
marks]
Medical Purpose :
F1: Antibiotic (4 marks)
E1: Antibiotic are chemicals which either inhibit the growth of or kill other microorganisms,
especially disease-causing bacteria
E2: Example : streptomycin is produced by Streptomycin sp.
E3: penicillin is produced by the fungus Penicillium chrysogenum sp.
E4: The microorganism/bacteria/fungus is grown in large fermenters, and the antibiotic produced
is then isolated and purified
F2: Immunisation ( 1 mark)
E5: The vaccine that contains weakened or dead microorganism which stimulates the body to
produce antibodies.
Food Processing Industry
F3: Wine ( 2 marks)
E6: Wine is made by adding yeast to fruit sugar (glucose) from grapes.
E7: The yeast converts glucose in grapes into alcohol during anaerobic respiration / fermentation
F4: Bread ( 2 marks)
E8: Bread is made from yeast, flour,sugar and water. The most commonly used species of yeast is
Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
E9: Fermentation by yeast produces ethanol and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide causes the
dough to rise
F5: Soya Sauce ( 1mark)
E10: Soya sauce is made from fermented soya beans caused by the action of fungi.
**Or any other suitable answer
Sample Question 18 (Essay- for Biodiversity: useful microorganism PYQ 2009, P2 No 7)
Suggested Answer For Sample Question 18 (Essay- for Biodiversity: useful microorganism)
-Nitrogen fixing bacteria (Rhizobium sp) in root nodules of leguminous plants or those living freely in
the soil (Nostoc sp) use nitrogen in the air to make nitrates. This process is called nitrogen fixation.
-Nitrates then are absorbed by plants to make protein
-When animals eat plants the protein is transferred to animals
-When plants and animals die, and excretory nitrogenous substances are decomposed by decaying
saprophytic bacteria and fungi (decomposers). They break the proteins down to ammonium
compound
-Nitrifying bacteria (Nitrosomonas sp) converts/oxidize ammonia into nitrite (nitrification process)
-Nitrifying bacteria (Nitrobacter sp) converts/oxidize nitrite into nitrate (nitrification process)
-Denitrifying bacteria converts nitrates back to nitrogen gas (denitrification process)
You might also like
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Form 2 June 2010Document9 pagesIntegrated Science Form 2 June 2010asjawolverine0% (2)
- Sains Form1 Final ExamDocument10 pagesSains Form1 Final ExamNOR SUAKMA BT JAAFARNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 2Document2 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2Ng Imm Khuan100% (1)
- Science Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsDocument16 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsLouis Lim0% (1)
- Modul F2 Science Chapter 1Document21 pagesModul F2 Science Chapter 1NorelyanaAli95% (21)
- Exam Question Bi Form2Document11 pagesExam Question Bi Form2Princess DyanaNo ratings yet
- IT Bio F5 Final Year Examination (BL)Document13 pagesIT Bio F5 Final Year Examination (BL)Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Document8 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Form 1 - Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesTopical Test Form 1 - Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeMei Yun LiewNo ratings yet
- Human Sensory Organs and SensesDocument19 pagesHuman Sensory Organs and SensesAngie Kong Su Mei100% (2)
- Form 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5Document4 pagesForm 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5KelvinNo ratings yet
- Linear Inequalities in Two Unknowns (A)Document78 pagesLinear Inequalities in Two Unknowns (A)Jason LauNo ratings yet
- Determine EMF and internal resistance of a dry cellDocument3 pagesDetermine EMF and internal resistance of a dry cellmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Model Pt3Document30 pagesModel Pt3Sean Larson100% (4)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaDocument14 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Surfaces, Areas and VolumesDocument12 pagesSurfaces, Areas and Volumesamms_110011No ratings yet
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFDocument22 pagesSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFIsmaliza Ishak0% (1)
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatDocument10 pagesSkema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatSitinorsyahidah JantanNo ratings yet
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Document11 pagesAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433No ratings yet
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07Document21 pagesChemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07hudazzakiNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY FORM 4 SUMMARYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY FORM 4 SUMMARYNora MnNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science WorksheetDocument6 pagesForm 2 Science WorksheetBathma SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 BerjawapanDocument15 pagesSPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition Oft He CellDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition Oft He CellAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFDocument70 pagesKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 2Document15 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 2Cikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Document14 pagesTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 5Document5 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 5Nur Syazwani Khodir100% (1)
- f2 Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesf2 Chapter 2 PDFNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Teknik Jawab Soalan Bio SPMDocument5 pagesTeknik Jawab Soalan Bio SPMpin21880% (1)
- Instructions: Each Question Is Followed by Four Alternative Answers, A, B, C and D. Circle The Correct AnswerDocument11 pagesInstructions: Each Question Is Followed by Four Alternative Answers, A, B, C and D. Circle The Correct AnswerrosyaNo ratings yet
- Tingkatan 4Document22 pagesTingkatan 4jaaizahkamal100% (1)
- Chem Test 1 2018 SECTION BDocument7 pagesChem Test 1 2018 SECTION BAmirah Noor AffandiNo ratings yet
- (A) (I) Period 0.02 S 1M Frequency 50 HZ 1A (Ii) I 5 A 1A (Iii) Effective Value I 1M 3.54 A 1A (B) (I) P I 1M 5 5 125 W 1ADocument11 pages(A) (I) Period 0.02 S 1M Frequency 50 HZ 1A (Ii) I 5 A 1A (Iii) Effective Value I 1M 3.54 A 1A (B) (I) P I 1M 5 5 125 W 1AVincent haNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Form 1 2004Document13 pagesMid Term Form 1 2004Ct HusnaNo ratings yet
- PT3 C7Document16 pagesPT3 C7MilkNo ratings yet
- HCF LCMDocument7 pagesHCF LCMBunga NoionlaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseDocument7 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Food and Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesCh5 Food and Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsYing Hei NgNo ratings yet
- Modul SC Chapter 2 - f1Document14 pagesModul SC Chapter 2 - f1Raja InaNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology Perlis 2010Document0 pagesSPM Biology Perlis 2010Clement TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Linear InequalitiesDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Linear InequalitiesROSMAWATI BINTI MOHAMED -No ratings yet
- Rational Cloze ExerciseDocument44 pagesRational Cloze ExercisePang Fui ShihNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction GuideDocument23 pagesSexual and Asexual Reproduction GuideHazira HaidzirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MatterDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- Bio Modul U6 2010-3Document66 pagesBio Modul U6 2010-3Thuran Nathan100% (1)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document17 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol67% (3)
- Add Math Indices & LogaritmsDocument11 pagesAdd Math Indices & Logaritmskamil muhammadNo ratings yet
- f4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011Document12 pagesf4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011matleNo ratings yet
- Our - Environment - Notes - Class 10 - CbseDocument3 pagesOur - Environment - Notes - Class 10 - CbseVarshini PeraNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument4 pagesEnvironmentARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities: Group of Organisms That Can Interbreed To Produce Fertile OffspringDocument5 pagesEssential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities: Group of Organisms That Can Interbreed To Produce Fertile OffspringChloe Troulan100% (1)
- Yacomine - Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems - 181110Document5 pagesYacomine - Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems - 181110joeyacomineNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarter 2 Week 6 Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument8 pagesScience 7 Quarter 2 Week 6 Living Things and Their EnvironmentAveCorpuz BioCornerNo ratings yet
- Ecology, Bio Geo Chemical CylesDocument15 pagesEcology, Bio Geo Chemical CylesArkan AliNo ratings yet
- PEE M1 and M2Document13 pagesPEE M1 and M2Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (2)
- Ecology final test questionsDocument7 pagesEcology final test questionssitimeilviNo ratings yet
- Does Grazing Induce Intraspecific Trait Variation in Plants From A Sub-Humid Mountain EcosystemDocument11 pagesDoes Grazing Induce Intraspecific Trait Variation in Plants From A Sub-Humid Mountain EcosystemHarry MeyasNo ratings yet
- Faunal Taxonomy Book (Sri Lanka)Document321 pagesFaunal Taxonomy Book (Sri Lanka)D.M.S. Suranjan Karunarathna100% (1)
- Philippines PDFDocument49 pagesPhilippines PDFMau AntallanNo ratings yet
- Engineers and The EnvironmentDocument20 pagesEngineers and The Environmentbhuvanesh85No ratings yet
- 11 Đề Thi Trắc Nghiệm Công Chức Tiếng AnhDocument59 pages11 Đề Thi Trắc Nghiệm Công Chức Tiếng Anhtổng hợp mọi thứNo ratings yet
- 2014 Spring NewsletterDocument8 pages2014 Spring NewsletterMerryspring Nature CenterNo ratings yet
- Roman Mosaics British MuseumDocument3 pagesRoman Mosaics British Museumsegu82No ratings yet
- The Global EnvironmentDocument2 pagesThe Global EnvironmentJuan Antonio Palacios QuirozNo ratings yet
- Biological Control Without AnimationDocument15 pagesBiological Control Without AnimationElly Chan Wei BeeNo ratings yet
- Barbados' Green Economy Scoping StudyDocument244 pagesBarbados' Green Economy Scoping StudyUnited Nations Environment Programme100% (1)
- Importance Of National Parks And Wildlife SanctuariesDocument3 pagesImportance Of National Parks And Wildlife SanctuariessupriyasakatNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Jyotirao Govindrao PhuleDocument12 pagesMahatma Jyotirao Govindrao PhuleSagar V. ThakkarNo ratings yet
- RIZAL TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Glossary of Key Environmental Engineering TermsDocument6 pagesRIZAL TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Glossary of Key Environmental Engineering TermsMica GiananNo ratings yet
- The Ancestral Domain Belonging To The Higaunon of Agtulawon Mintapod Higaunon Cumadon (AGMIHICU)Document8 pagesThe Ancestral Domain Belonging To The Higaunon of Agtulawon Mintapod Higaunon Cumadon (AGMIHICU)Rosbert Cabug TulodNo ratings yet
- Protecting Our Planet: Lesson Plan SectionsDocument3 pagesProtecting Our Planet: Lesson Plan SectionsMerimaHalilovicKalacNo ratings yet
- Myers Worm 2003Document4 pagesMyers Worm 2003Sandra RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Techniques and Secrets of Beautiful Glass Painting - LetteringDocument6 pagesTechniques and Secrets of Beautiful Glass Painting - LetteringsuryaNo ratings yet
- FEIS Volume IIDocument491 pagesFEIS Volume IISud HaldarNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Climate ChangeDani Carbajal71% (14)
- National Forest Policy Review-BhutanDocument46 pagesNational Forest Policy Review-BhutanSaravorn50% (2)
- Second Planetary Congress of Biospheric RightsDocument63 pagesSecond Planetary Congress of Biospheric RightsBoris Petrovic100% (2)
- Animal Discoveries 2015Document152 pagesAnimal Discoveries 2015prashantNo ratings yet
- The Hudson River Comprehensive Restoration Plan For The Hudson River EstuaryDocument84 pagesThe Hudson River Comprehensive Restoration Plan For The Hudson River EstuaryDaily FreemanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesClimate Change and The PhilippinesJed MendozaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term Test 1as ScientificDocument2 pages3rd Term Test 1as ScientificMis MesbahNo ratings yet
- PLT Activities With The LoraxDocument23 pagesPLT Activities With The LoraxDave KagariseNo ratings yet
- KudzuDocument6 pagesKudzuDonovan WagnerNo ratings yet
- Linking the SDGs to Uganda's Vision 2040 and NDP11Document29 pagesLinking the SDGs to Uganda's Vision 2040 and NDP11opio felix100% (1)
- Research Proposal Contribution of Povert PDFDocument16 pagesResearch Proposal Contribution of Povert PDFYusufNo ratings yet
- DSR Vol. 2Document230 pagesDSR Vol. 2Charan ElectricalsNo ratings yet