Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDF
Uploaded by
Prasetyo Adi40%(5)40% found this document useful (5 votes)
6K views3 pagesThe modern motorcycle is a complex piece of equipment, capable of extremely high performance in a number of areas, not just in terms of top speed. The modern motorcycle engineer must be able to understand the forces and stresses generated by the extremes of rider expectation and input.
Original Description:
Original Title
MOTORCYCLE-CHASSIS-DESIGN-AND-DYNAMICS.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe modern motorcycle is a complex piece of equipment, capable of extremely high performance in a number of areas, not just in terms of top speed. The modern motorcycle engineer must be able to understand the forces and stresses generated by the extremes of rider expectation and input.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
40%(5)40% found this document useful (5 votes)
6K views3 pagesMotorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDF
Uploaded by
Prasetyo AdiThe modern motorcycle is a complex piece of equipment, capable of extremely high performance in a number of areas, not just in terms of top speed. The modern motorcycle engineer must be able to understand the forces and stresses generated by the extremes of rider expectation and input.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Module Title MOTORCYCLE CHASSIS DESIGN AND DYNAMICS
Module Code 6MV501 Pre-requisite
(where
appropriate)
Motorcycle
Chassis
Engineering or
Equivalent
Date of Approval March 2012
Module Level 6
Credit value 20
Total Number of
Learning Hours
200
Key Words
(10 words
maximum)
Chassis Performance, Dynamics and Analysis, Tyre
Modelling, Innovation Aspects.
Module Delivery Online/Distance Blended/Face to
face
Work-based
learning
Mode (Please tick
as appropriate)
Module
Description
(200 words max)
The modern motorcycle is a complex piece of equipment,
capable of extremely high performance in a number of areas,
not just in terms of top speed.
The modern motorcycle engineer must be able to understand
the forces and stresses generated by the extremes of rider
expectation and input, coupled with the power and torque
outputs developed.
Module Learning
Outcomes
On successful completion of the module, students will be able
to:
1. Critically review, consolidate and extend the application
and analysis of motorcycle dynamics concepts.
2. Design and critically evaluate chassis concepts and use
analytical methods in the investigation of the installation of
drive-train components and the stresses generated.
3. Design and critically analyse the operation of motorcycle
suspension systems and predict ride behaviour and
handling performance.
4. Critically review and analyse the innovative approach to
motorcycle chassis and suspension design at the cutting
edge of chassis technology and systems
Module Content
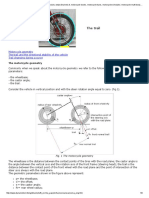
Vehicle Ride
Kinematics and dynamic analysis of suspension systems;
suspension modelling, measurement of suspension forces;
gyroscopic effects, procession, interaction with engine
rotational forces.
Vehicle Handling
Analytical models for cornering and braking at a range of
speeds and on a variety of surfaces, counter-steering effects,
acceleration and braking, braking stability; steering systems;
effects of geometrical changes, effects of weight transfer and
cornering forces
Stress Analysis
Torsional chassis stress, suspension stresses under cornering,
braking and acceleration conditions; Chassis flex and lateral
stiffness considerations
Tyre modelling
Tyre properties and behaviour; tyre forces and moments,
contact velocity and displacement; tyre models, discussion of
coefficients of friction; on and off-road design principles.
Innovation aspects
Modern technologies, manufacturing and machining
techniques, composite / extruded / cast / tubular chassis
systems. Joining methods and structural considerations.
Module Learning
and Teaching
Methods
Learning & Teaching Methods (as defined in the QAA
indicative list See Guidance Notes):
The module will be delivered through lectures, group tutorials
and supervised demonstrations.
Lectures 24 hours
Tutorials 12 hours
Demonstration 12 hours
Guided independent study 152 hours
Total 200 hours
Activity Type Percentage Category
Scheduled learning and
teaching activities
24% 1
Guided independent study 76% 2
Placement/study abroad 0% 3
Total 100%
Module
Assessment
Method
Formative Assessment (0%):
This is designed to give students some indication of their
progress and levels of understanding and will be used
throughout the module. It will be achieved by setting students
time constrained tutorial tasks followed by individual feedback
Summative Assessment (100%):
CW: 70% : Learning outcomes 1, 2 and 4 to be assessed
An assignment of nominal length 3000 words which covers
aspects of chassis design and innovation, power-train
installation considerations and chassis dynamics.
EX: 30%: Learning outcome 3 to be assessed
A time constrained 3 hour exam covering aspects of
suspension design, analysis and behaviour
Reading list Link to ASPIRE
Cocco, G. (2005) Motorcycle design and technology -
how and why. Nada
Cossalter, V. (2006) Motorcycle Dynamics. 2
nd
Ed.
Lulu.com
Robinson, J. (1993) Motorcycle tuning chassis.
Butterworth Heinemann
Noakes, K (2007) Motorcycle Road and Racing Chassis
Designs: A Modern Review of the Best
Independents Veloce publishing ltd
Foale, T (1988) Motorcycle Chassis Design: theory and
Practice Osprey
You might also like
- Distance Learning - Motorsport - Chassis DynamicsDocument4 pagesDistance Learning - Motorsport - Chassis Dynamicsrudey18No ratings yet
- The Multibody Systems Approach to Vehicle DynamicsFrom EverandThe Multibody Systems Approach to Vehicle DynamicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Motorcycle FramesDocument10 pagesMotorcycle FramesNeagoie SergiuNo ratings yet
- Tony Foale Designs - Vyrus Suspension HistoryDocument7 pagesTony Foale Designs - Vyrus Suspension HistoryStuart CouttsNo ratings yet
- Comparing Tubular Frame and Alu Frame of Motorcycle Complete AnalysisDocument112 pagesComparing Tubular Frame and Alu Frame of Motorcycle Complete AnalysisDastagir Shaikh100% (2)
- Motorcycle Design Guide March 2009Document32 pagesMotorcycle Design Guide March 2009Anonymous EfZxcqNJp2No ratings yet
- Build Your Own Race Car on a BudgetDocument5 pagesBuild Your Own Race Car on a BudgetBalaji AeroNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Cornering Behavior Modeling - PaperDocument14 pagesMotorcycle Cornering Behavior Modeling - PaperRafael DonadioNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Dynamics LibraryDocument10 pagesMotorcycle Dynamics LibrarySaufiy SarminNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Modeling and ControlDocument72 pagesMotorcycle Modeling and ControlkeeblerkhanNo ratings yet
- FSAEDocument81 pagesFSAE69x4No ratings yet
- Data Acquisition To Analyze The Driver and His Race CarDocument188 pagesData Acquisition To Analyze The Driver and His Race CarKelvin NyeNo ratings yet
- The Summary of Race Car Chassis DesignDocument2 pagesThe Summary of Race Car Chassis Designmohamed elbakryNo ratings yet
- Optimization of ATV Chassis Frame for Improved PerformanceDocument3 pagesOptimization of ATV Chassis Frame for Improved PerformanceSuraj AminNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis of The Lotus Seven S4 (Type 60) PDFDocument18 pagesDesign Analysis of The Lotus Seven S4 (Type 60) PDFChristian Villa100% (4)
- Sus KinematicsDocument46 pagesSus KinematicsTony Foale100% (4)
- Car Chassis Basics and WorkingDocument11 pagesCar Chassis Basics and WorkingRuthvikNo ratings yet
- Designing Efficient Commuter Vehicle Using Finite Element Analysis and Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument6 pagesDesigning Efficient Commuter Vehicle Using Finite Element Analysis and Computational Fluid DynamicsSyed Anas SohailNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Body EngineeringDocument21 pagesVehicle Body Engineeringjittume69% (13)
- Applied Vehicle Dynamics Seminar April 2017Document2 pagesApplied Vehicle Dynamics Seminar April 2017PRAVEEN REDDY100% (1)
- Racing Simulation Tuning GuideDocument15 pagesRacing Simulation Tuning GuideVyssion100% (1)
- Motorcycle Dynamics PDFDocument9 pagesMotorcycle Dynamics PDFTiago Camargo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Racecar DynamicsDocument14 pagesRacecar Dynamicsnemanjatopalovic1992No ratings yet
- Design Optimization of Two Wheeler (Bike) ChassisDocument5 pagesDesign Optimization of Two Wheeler (Bike) ChassisPrakash KatdareNo ratings yet
- Advances in The Modelling of Motorcycle Dynamics: Multibody System Dynamics October 2004Document34 pagesAdvances in The Modelling of Motorcycle Dynamics: Multibody System Dynamics October 2004Tyrone BerryNo ratings yet
- Chassis: by Naveen KDocument56 pagesChassis: by Naveen KNaveen KandasamyNo ratings yet
- 6AN8 Aerodynamics Lab: Aerodynamics of Racing CarsDocument30 pages6AN8 Aerodynamics Lab: Aerodynamics of Racing CarsAnshul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- FSAE SuspensionDocument37 pagesFSAE SuspensionDonald MuchemwaNo ratings yet
- KTM Design and ResearchDocument31 pagesKTM Design and ResearchNandan NandyNo ratings yet
- Toyota Motorsport GMBH - The Home of High PerformanceDocument27 pagesToyota Motorsport GMBH - The Home of High PerformanceMarcos SoarNo ratings yet
- Chassis, Aerodynamics and FeaDocument25 pagesChassis, Aerodynamics and FeaSivaPrasad Chekri100% (1)
- Motorcycle Frame DesignDocument5 pagesMotorcycle Frame DesignKomang Priatna SuardiNo ratings yet
- Suspension Design and Calculations For A Motor CycleDocument2 pagesSuspension Design and Calculations For A Motor Cyclevicky danNo ratings yet
- Project Charger: The Step-By-Step Restoration of a Popular Vintage CarFrom EverandProject Charger: The Step-By-Step Restoration of a Popular Vintage CarNo ratings yet
- Rouelle PPTDocument36 pagesRouelle PPTA Van DiNo ratings yet
- FS 2014 Digimag WebDocument32 pagesFS 2014 Digimag WebVyssionNo ratings yet
- Riding Skills: "Essential Skills For Building Rock Solid Track Riding Foundations"Document47 pagesRiding Skills: "Essential Skills For Building Rock Solid Track Riding Foundations"Sargento AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Fiberglassing - Moldless CompositesDocument5 pagesFiberglassing - Moldless CompositesMata Bana NajouNo ratings yet
- The Modern Chassis: A Practical Manual of Automotive Chassis and Suspension DesignFrom EverandThe Modern Chassis: A Practical Manual of Automotive Chassis and Suspension DesignRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Aerodynamics Low Speed Race Car (FSAE)Document38 pagesAerodynamics Low Speed Race Car (FSAE)Paul Bruneau100% (5)
- Leading-Edge Motorsport Technology Since 1990Document22 pagesLeading-Edge Motorsport Technology Since 1990tushar girotra100% (1)
- Thomas Ramsay to Explain Race Car Aerodynamics at Feb 18 MeetingDocument4 pagesThomas Ramsay to Explain Race Car Aerodynamics at Feb 18 MeetingKarthik ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Diagrams of Racing MotorcycleDocument6 pagesDiagrams of Racing MotorcycleRenan AlvesNo ratings yet
- Designing and Manufacturing of A Hand-Made Electric MotorcycleDocument6 pagesDesigning and Manufacturing of A Hand-Made Electric MotorcycleArash0% (1)
- Hub Centres SteeringDocument29 pagesHub Centres SteeringSudheesh Kumar ENo ratings yet
- Grand Prix Motorcycle Engine Development Over 60 YearsDocument35 pagesGrand Prix Motorcycle Engine Development Over 60 YearsShaswata Panja100% (1)
- 2019-10-01 Racecar Engineering 2Document100 pages2019-10-01 Racecar Engineering 2Can not Formula NingNo ratings yet
- Affects of Alignment, Chain Tension and Tire PressureDocument2 pagesAffects of Alignment, Chain Tension and Tire PressurePrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Super Mastercam + Rra BRT 2017Document1 pageSuper Mastercam + Rra BRT 2017Prasetyo Adi85% (26)
- Moto3 - Honda Nsf250rDocument2 pagesMoto3 - Honda Nsf250rPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Miniature InductiveDocument5 pagesMiniature InductivePrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Tech110 PDFDocument4 pagesTech110 PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head Design and Modification - Getting StartedDocument4 pagesCylinder Head Design and Modification - Getting StartedBruno BambinetiNo ratings yet
- Us20080168859a1 PDFDocument7 pagesUs20080168859a1 PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Gts Dyno Form PDFDocument4 pagesGts Dyno Form PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- E Catalogue of MIKUNI INDONESIA PT PDFDocument1 pageE Catalogue of MIKUNI INDONESIA PT PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDFDocument3 pagesMotorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDFPrasetyo Adi40% (5)
- Us20080168859a1 PDFDocument7 pagesUs20080168859a1 PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- B862 PDFDocument2 pagesB862 PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Suspension Setup PDFDocument11 pagesSuspension Setup PDFPrasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- BOOK Karnopp Dean C. - Vehicle Dynamics, Stability, and Control, Second EditionDocument320 pagesBOOK Karnopp Dean C. - Vehicle Dynamics, Stability, and Control, Second EditionJulian GenovNo ratings yet
- HP Velotechnik Scorpion Brochure en EURDocument72 pagesHP Velotechnik Scorpion Brochure en EURAntonio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Final Report - Design of A Pedestrian Bridge - Fall 2009 PDFDocument119 pagesFinal Report - Design of A Pedestrian Bridge - Fall 2009 PDFAbdul Salam100% (1)
- Motorcycle HandbookDocument80 pagesMotorcycle HandbookReev SnerNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle DynamicsDocument181 pagesMotorcycle Dynamicsananth95nandu100% (5)
- Squeeze Film Damper Effect On Vibration of An Unbalanced Exible Rotor Using Harmonic Balance MethodDocument20 pagesSqueeze Film Damper Effect On Vibration of An Unbalanced Exible Rotor Using Harmonic Balance MethodMyleru SNo ratings yet
- CDR 07 NIT Rourkela HPVC 2022Document38 pagesCDR 07 NIT Rourkela HPVC 2022VIPIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Mitas motorcycle tyre guide for on-road bikesDocument15 pagesMitas motorcycle tyre guide for on-road bikessmsudan256371No ratings yet
- 2008 - 05 How A Rear Steering System May Improve Motorcycle Dynamics IJ Vehicle Design MaggioDocument19 pages2008 - 05 How A Rear Steering System May Improve Motorcycle Dynamics IJ Vehicle Design MaggioekmedzicNo ratings yet
- Caster, Camber, ToeDocument6 pagesCaster, Camber, ToeASHUTOSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- CG Measurement of MotorcycleDocument9 pagesCG Measurement of MotorcyclePrasanna MahendiranNo ratings yet
- Cornering skills for descending on a bicycleDocument4 pagesCornering skills for descending on a bicycleBJ MadzNo ratings yet
- FH Vorarlberg Vorarlberg University of Applied Sciences: Master's in MechatronicsDocument208 pagesFH Vorarlberg Vorarlberg University of Applied Sciences: Master's in MechatronicsĆosić AsimNo ratings yet
- Dinamica Del Veicolo IDocument87 pagesDinamica Del Veicolo ILe Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- MZ TuningDocument19 pagesMZ TuningLeo MenonNo ratings yet
- Essential Riding SkillsDocument38 pagesEssential Riding SkillsBob LoblawNo ratings yet
- Steering EffortDocument5 pagesSteering Effortsaran kumarNo ratings yet
- Bike Talk KTH 2006Document66 pagesBike Talk KTH 2006jdpatel28No ratings yet
- Propierties of Lateral-Pendulum Controlled Unicycle Robot in States of Balance and MotionDocument6 pagesPropierties of Lateral-Pendulum Controlled Unicycle Robot in States of Balance and MotionDaniela RochaNo ratings yet
- Caster, Cambercaster, ToeDocument6 pagesCaster, Cambercaster, ToeRajat GiteNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Front Suspension for an Off-Road VehicleDocument6 pagesDesign and Development of Front Suspension for an Off-Road VehicleRodrigo bolaNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument6 pagesProgress ReportBablu KumarNo ratings yet
- Bicycle and Motorcycle DynamicsDocument36 pagesBicycle and Motorcycle DynamicsChanakya ChNo ratings yet
- Study effects of camber, caster, toe angles auto suspensionDocument4 pagesStudy effects of camber, caster, toe angles auto suspensionsai ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalDocument42 pagesImplementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalRenan AlvesNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Maths PapadopoulosDocument3 pagesBicycle Maths PapadopoulosHua Hidari YangNo ratings yet
- Self-Balancing Bicycle For Kids Learning SynopsisDocument8 pagesSelf-Balancing Bicycle For Kids Learning SynopsisAditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Dynamics PDFDocument9 pagesMotorcycle Dynamics PDFTiago Camargo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Motor GraderDocument24 pagesMotor GraderRafael OtuboguatiaNo ratings yet
- Tire Catalog Dunlop Sportmax Roadsmart 2Document3 pagesTire Catalog Dunlop Sportmax Roadsmart 2Exclusivo1No ratings yet