Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 12 Cbse Political Science Syllabus 2014
Uploaded by
Sunaina RawatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 12 Cbse Political Science Syllabus 2014
Uploaded by
Sunaina RawatCopyright:
Available Formats
248
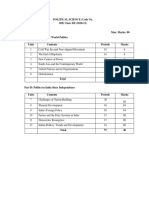
Class XII
One Paper Time : 3 Hours Marks 100
Content Periods Marks
Part A: Contemporary World-Politics
Units
1. Cold War Era 14
2. The End of bipolarity 12 14
3. US Hegemony in World Politics 12
4. Alternative centres of Power 10 16
5. Contemporary South Asia 12
6. International Organizations 12 10
7. Security in Contemporary World 10
8. Environment and Natural Resources 10 10
9. Globalisation 12
104 50
Part B: Politics in India since independence
10. Challenges of Nation-Building 12
11. Era of One-Party Dominance 12 16
12. Politics of Planned Development 10
13. Indias External relations 12 6
14. Challenges to the Congress System 12 12
15. Crisis of the Democratic order 12
16. Rise of Popular Movements 10
17. Regional aspirations 10 16
18. Recent Developments in Indian Politics 12
102 50
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
249
COURSE CONTENTS Periods
Part A: Contemporary World Politics
1. Cold War Era 14
Emergence of two power blocs after the second world war. Arenas of the cold war.
Challenges to Bipolarity: Non Aligned Movement, quest for new international economic
order. India and the cold war.
2. The End of Bipolarity 12
New entities in world politics: Russia, Balkan states and Central Asian states, Introduction
of democratic politics and capitalism in post-communist regimes. Indias relations with
Russia and other post-communist countries.
3. US Hegemony in World Politics 12
Growth of unilateralism: Afghanistan, first Gulf War, response to 9/11 and attack on Iraq.
Dominance and challenge to the US in economy and ideology. Indias renegotiation of its
relationship with the USA.
4. Alternative Centres of Power 10
Rise of China as an economic power in post-Mao era, creation and expansion of European
Union, ASEAN. Indias changing relations with China.
5. Contemporary South Asia in the Post-Cold War Era 12
Democratisation and its reversals in Pakistan and Nepal. Ethnic conflict in Sri Lanka,
Impact of economic globalization on the region. Conflicts and efforts for peace in South
Asia. Indias relations with its neighbours.
6. International Organizations 12
Restructuring and the future of the UN. Indias position in the restructured UN. Rise of
new international actors: new international economic organisations, NGOs. How
democratic and accountable are the new institutions of global governance?
7. Security in Contemporary World 10
Traditional concerns of security and politics of disarmament. Non-traditional or human
security: global poverty, health and education. Issues of human rights and migration.
8. Environment and Natural Resources 10
Environment movement and evolution of global environmental norms. Conflicts over
traditional and common property resources. Rights of indigenous people. India's stand in
global environmental debates.
9. Globalisation 12
Economic, cultural and political manifestations. Debates on the nature of consequences of
globalisation. Anti-globalisation movements. India as an arena of globalization and struggle
against it.
250
Part B: Politics in India Since Independence
10. Challanges of Nation-Building 12
Nehrus approach to nation-building: Legacy of partition: challenge of refugee resettlement,
the Kashmir problem. Organisation and reorganization of states; Political conflicts
over language.
11. Era of One-Party Dominance 12
First three general elections, nature of Congress dominance at the national level, uneven
dominance at the state level, coalitional nature of Congress. Major opposition parties.
12. Politics of Planned Development 10
Five year plans, expansion of state sector and the rise of new economic interests. Famine
and suspension of five year plans. Green revolution and its political fallouts.
13. Indias External Relations 12
Nehrus foreign policy. Sino-Indian war of 1962, Indo-Pak war of 1965 and 1971. Indias
nuclear programme and shifting alliances in world politics.
14. Challenges to the Congress System 12
Political succession after Nehru. Non-Congressism and electoral upset of 1967, Congress
split and reconstitution, Congress victory in 1971 elections, politics of garibi hatao.
15. Crisis of the Democratic Order 12
Search for committed bureaucracy and judiciary. Navnirman movement in Gujarat and
the Bihar movement. Emergency: context, constitutional and extra-constitutional dimensions,
resistance to emergency. 1977 elections and the formation of Janata Party. Rise of civil
liberties organisations.
16. Rise of New Social Movements 10
Farmers movements, Womens movement, Environment and Development-affected peoples
movements. Implementation of Mandal Commission report and its aftermath.
17. Regional Aspirations 10
Rise of regional parties. Punjab crisis and the anti-Sikh riots of 1984. The Kashmir situation.
Challenges and responses in the North East.
18. Recent Developments in Indian politics: 12
Participatory upsurge in 1990s. Rise of the JD and the BJP. Increasing role of regional
parties and coalition politics. UF and NDA governments. Elections 2004 and UPA
government.
Recommended text books:
1. Indian Constitution at Work, Class XI, Published by NCERT
2. Political Theory, Class XI, Published by NCERT
3. Contemporary World Politics, Class XII, Published by NCERT
3. Politics in India Since Independence, Class XII, Published by NCERT
Note : The above textbooks are also available in Hindi and Urdu versions.
You might also like
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus For Political Science 2014-2015Document5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Syllabus For Political Science 2014-2015cbsesamplepaperNo ratings yet
- 323 PoliticalscienceDocument4 pages323 Politicalscienceprernamehra906No ratings yet
- 323 Politicalscience PDFDocument4 pages323 Politicalscience PDFSayan Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- Political Science-323: Syllabus For Class 12Document4 pagesPolitical Science-323: Syllabus For Class 12saumya bargotiNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument4 pagesPolitical ScienceSuhail AnsariNo ratings yet
- Political ScienceDocument4 pagesPolitical Scienceyashrajsinghhh10No ratings yet
- Cbse Board Sample Papers For Political ScienceDocument3 pagesCbse Board Sample Papers For Political Scienceapi-139761950No ratings yet
- 323 PoliticalscienceDocument2 pages323 PoliticalscienceKhushali PooniaNo ratings yet
- CUET Political Science Syllabus 2024 in Detail - HitbullseyeDocument3 pagesCUET Political Science Syllabus 2024 in Detail - HitbullseyeBalaji RamamurtiNo ratings yet
- Sample Papers For Political Science Cbse BoardDocument4 pagesSample Papers For Political Science Cbse Boardapi-139761950No ratings yet
- Term-Wise Syllabus: 2019-20 Class - XII Subject - Political ScienceDocument5 pagesTerm-Wise Syllabus: 2019-20 Class - XII Subject - Political ScienceADARSH pandeyNo ratings yet
- Sample Papers Pol Sci Q PaperDocument151 pagesSample Papers Pol Sci Q PaperSachin MishraNo ratings yet
- Political Science Sample Paper of Cbse BoardDocument4 pagesPolitical Science Sample Paper of Cbse Boardapi-139761950No ratings yet
- Pol Science XII Final 2Document127 pagesPol Science XII Final 2Game LoverNo ratings yet
- Political Science IGNOUDocument52 pagesPolitical Science IGNOUswarajcha100% (1)
- Political Science Syll - 2nd YearDocument4 pagesPolitical Science Syll - 2nd YearMansur AlomNo ratings yet
- Political Science and International RelationsDocument4 pagesPolitical Science and International RelationsNeha PatilNo ratings yet
- Material List: GeographyDocument5 pagesMaterial List: GeographyPtb4docNo ratings yet
- V 4 Ynr Ow IIG76 MT N6 CC HKDocument15 pagesV 4 Ynr Ow IIG76 MT N6 CC HKgauravyadav06092006No ratings yet
- Revised CBSE Class 12 Political Science Syllabus 2020-21Document22 pagesRevised CBSE Class 12 Political Science Syllabus 2020-21Shrija SinghNo ratings yet
- Classroom Material List: Geography S.N. TopicDocument6 pagesClassroom Material List: Geography S.N. TopicMahesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Vision Material ListDocument6 pagesVision Material ListShubham PadwalNo ratings yet
- Biographies of the Second 23 American Presidents - Volume IIFrom EverandBiographies of the Second 23 American Presidents - Volume IINo ratings yet
- Political Theory and Indian Politics:hasDocument4 pagesPolitical Theory and Indian Politics:haspriya3793No ratings yet
- Political Theory and Indian PoliticsDocument2 pagesPolitical Theory and Indian Politicsanon-135403100% (1)
- UPSC Political Science Syllabus PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesUPSC Political Science Syllabus PDF DownloadABHI PIMNo ratings yet
- The Political Logic of Economic Reform in ChinaFrom EverandThe Political Logic of Economic Reform in ChinaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Janata Interludes: Democracy, Plurality and Social Change in IndiaFrom EverandThe Janata Interludes: Democracy, Plurality and Social Change in IndiaNo ratings yet
- China Ascendant: Its Rise and ImplicationsFrom EverandChina Ascendant: Its Rise and ImplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- MPSC Political Science SyllabusDocument3 pagesMPSC Political Science SyllabusYumkhaibam PamchaNo ratings yet
- Baps Dse-3 Block-4Document54 pagesBaps Dse-3 Block-4kartikbag67No ratings yet
- The China Questions: Critical Insights into a Rising PowerFrom EverandThe China Questions: Critical Insights into a Rising PowerNo ratings yet
- Socialstudies Class XDocument9 pagesSocialstudies Class XMohammed Amjad AliNo ratings yet
- Political Science SyllabusDocument3 pagesPolitical Science Syllabusarif9kNo ratings yet
- PSIR Optional SyllabusDocument4 pagesPSIR Optional SyllabusJeevan BennyNo ratings yet
- Red Revolution, Green Revolution: Scientific Farming in Socialist ChinaFrom EverandRed Revolution, Green Revolution: Scientific Farming in Socialist ChinaNo ratings yet
- OooDocument3 pagesOooAbhinandanNo ratings yet
- Most Expected Css QuestionsDocument7 pagesMost Expected Css QuestionsMůṥāwwir Abbāś AttāriNo ratings yet
- National University: SyllabusDocument10 pagesNational University: SyllabusHOSSAINAHMED BANGLADESHNo ratings yet
- How China Is Governed: An Inside Look at the Politics of the World’s Economic PowerhouseFrom EverandHow China Is Governed: An Inside Look at the Politics of the World’s Economic PowerhouseNo ratings yet
- Young India: An interpretation and a history of the nationalist movement from withinFrom EverandYoung India: An interpretation and a history of the nationalist movement from withinNo ratings yet
- Handout For China and GlobalizationDocument8 pagesHandout For China and GlobalizationGeorgi PagolaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus JamiaDocument24 pagesSyllabus JamiaAnadi GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Sydney Globalist Vol VIII Issue I - "Shifting Seats: Transitions of Power in National Leadership"Document44 pagesThe Sydney Globalist Vol VIII Issue I - "Shifting Seats: Transitions of Power in National Leadership"thesydneyglobalistNo ratings yet
- China's Megatrends: The 8 Pillars of a New SocietyFrom EverandChina's Megatrends: The 8 Pillars of a New SocietyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- A Companion to the Gilded Age and Progressive EraFrom EverandA Companion to the Gilded Age and Progressive EraChristopher M. NicholsNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Reflective QuestionsDocument24 pagesLast Minute Reflective QuestionsJo BaabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture PL Faysal Hayat - CSS2020 Qualifier - CSS MentorDocument5 pagesLecture PL Faysal Hayat - CSS2020 Qualifier - CSS MentorArsalan Khan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Political Theory and Indian PoliticsDocument4 pagesPolitical Theory and Indian PoliticsDhiraj MeenaNo ratings yet
- India Is Broken: A People Betrayed, Independence to TodayFrom EverandIndia Is Broken: A People Betrayed, Independence to TodayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PSIR Basic Kit Tushar GupthaDocument64 pagesPSIR Basic Kit Tushar GupthaNaniNo ratings yet
- OptionalDocument3 pagesOptionalPankajNo ratings yet
- Towards a New World Order: Uniting for a More Peaceful, Just and Equitable SocietyFrom EverandTowards a New World Order: Uniting for a More Peaceful, Just and Equitable SocietyNo ratings yet
- Class 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Document2 pagesClass 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Geography Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Document2 pagesClass 6 ICSE Geography Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina Rawat100% (1)
- Class 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Document3 pagesClass 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 7 ICSE English Sample PaperDocument2 pagesClass 7 ICSE English Sample PaperSunaina Rawat100% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Document2 pagesClass 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Sunaina Rawat100% (3)
- Class 6 ICSE Geography Term 2 Model 1Document2 pagesClass 6 ICSE Geography Term 2 Model 1Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE History Civics SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 6 ICSE History Civics SyllabusSunaina Rawat0% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Document2 pagesClass 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina Rawat100% (7)
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 3Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 3Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Maths SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 6 ICSE Maths SyllabusSunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Geography SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 6 ICSE Geography SyllabusSunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 3Document2 pagesClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 3Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Sunaina Rawat67% (3)
- Class 6 ICSE English Sample PaperDocument3 pagesClass 6 ICSE English Sample PaperSunaina Rawat38% (8)
- Class 6 ICSE English SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 6 ICSE English SyllabusSunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 2Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 2Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 1Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 1Sunaina Rawat100% (2)
- Class 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Document2 pagesClass 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Sunaina Rawat0% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set IDocument2 pagesClass 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set ISunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set IIDocument3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set IISunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set 1Document3 pagesClass 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set 1Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 5 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 2Document2 pagesClass 5 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 2Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Document2 pagesClass 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina Rawat100% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set IIDocument2 pagesClass 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set IISunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 5 ICSE Maths SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 5 ICSE Maths SyllabusSunaina Rawat57% (7)
- Class 4 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 1Document2 pagesClass 4 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 1Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Document2 pagesClass 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Sunaina Rawat100% (5)
- Class 5 ICSE Maths Sample Papers Term 1 Model 2Document2 pagesClass 5 ICSE Maths Sample Papers Term 1 Model 2Sunaina Rawat64% (28)