Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro About Solar Radiation
Uploaded by
Akshay DeshpandeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro About Solar Radiation
Uploaded by
Akshay DeshpandeCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Notes No:1
Title : The sun and the Earth
The Sun:
- is basically a sphere in shape.
- Contains intensely hot gases matter within it.
- It has a diameter of 1.39x10
9
m or 13.9x10
5
km.
- Distance between the earth and sun is around 1.5x10
11
m
- It rotates its own axis about 4 weeks.
- Its black body temperature is in the order of 5762 K
- Temperature of the inner core of the sun is estimated between
8x10
6
to 40x10
6
K
- Density is 1000 times than the water (Plasma).
- It contains 80% of hydrogen (H2)and 19% of the helium (He).
- Remaining may be 100 plus observed elements makesup the tiny
fraction of this composition of the sun.
- The source of the sun energy may be due to hydrogen to helium in
the thermonuclear fusion reaction.
Anatomy of the sun:
Core:
- 90% of the sun energy generated from this region
- It distance range is 0 to 0.23 R (where R is the radius of the sun).
- It temperature range is around 8 to 40 x10
6
K.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solar wind
Corona
Chromosphere
Photosphere
Convective shell
Radioactive shell
Core
- Pressure is around 10
9
atm.
- Its density is around 100 g/cc or 1,00,000 kg/m
3
.
- It contains 40% of the mass of the sun.
- It occupies around 15% of the volume of the sun.
Radioactive shell:
- it is at a distance of 0.7 R from the centre of the sun.
- the temperature across this region is around 1,30,000 K.
- its density drop across this region is around 70 kg/m
3
.
- After this region, (ie) the outer layer of this region is starts with
convective shell.
Convective Shell:
- it is very important region of the sun.
- The convection process begins from this region.
- It range is 0.7 R to 1R.
- Within this region, the temperature drop is around 5000 K.
- The density drop across this region is about 10
-5
kg/m
3
.
- Usually the sunspots are appeared in this region only.
- The outer most layer of this region is photosphere.
Sunspots:
- it is a temporary phenomenon on the photosphere of the sun.
- this appears visibly as dark compared to its surrounding areas,
- these are caused by the inverse magnetic activity which inhibits
convection by an effect comparable to eddy current brake, forming
the area of the reduced surface temperature.
- The temperature of this spot is around 3000 to 4000 K whereas
surrounding temperature is around adiabatic flame temperature is
about 5780 K.
- If the sunspot is isolated from the surrounding materials, it would
be brighter than the electric arc.
- It can expands or contracts as they move across the surface of the
sun.
- Max sunspot identified appears and viewed from the earth is
around 80,000 km.
- Its relative speed of its travel is few hundred miles per second.
Photopshere:
- The edge of the photosphere is sharply defined.
- It is in the range of 1.015 R.
- The temperature across this region is around 5000 K to 10
6
K.
- It density of the gases in this layer are in the range of 10
-8
to 10
-4
g/cc.
- It is composed of the gases are strongly ionized and able to absorb
and emit a continuous spectrum of radiation.
- It is the source of the most of the solar radiation.
- The outer most layer of the photosphere is called chromosphere.
Chromosphere:
- it is more or less transparent atmosphere.
- It can be observed during the solar eclipse or by instrumental that
obscure the solar disk.
- Above the photosphere, there is layer of cooler gases for several
hundred kilometers deep, called the reversing layer.
- It temperature are in the region is 10
6
K.
- This temperature range prevails upto the layer of corona.
- It density across this layer is very low (10
-4
to 10
-6
g/cc).
- It distance depth about 10,000 km.
- The outer lost layer of this region is corona.
Corona:
- it is of very low density.
- Its temperature is in the high range of about 10
6
K.
- This corona can be seen only during the solar eclipse.
The Earth:
- it shaped as an oblate spheroid. (ie) a sphere flattened at the poles
and bulging in the plane normal to the poles.
- It can be assumed as sphere for many practical purposes.
- It diameter is about 12,800 km at the equatorial plane.
- It has circumferential distances at:
Equatorial plane is 40,075.17 km
Meridionial plane is 40,007.86 km
- the surface area of the earth is:
total area is about 510,072,000 km
2
land area is about 148,292,000 km
2
- 29.2%
water area is about 361, 780,000 km
2
70.8%.
- it makes one rotation about its own axis in every 24 hours.
- It completes a revolution around the sun in a period of approx.
365.25 days.
- The mean density of the earth is 5.517 g/cm
3
.
- It has a central core of about 2,560 km in diameter which is more
rigid than steel.
- Beyond this core, there is mantle, which forms about 70% of the
earths mass.
- Beyond this is the outer layer of the earth is so called crust, which
forms about 1% of the earths mass.
- The earth revolves the sun in an elliptic orbit with latter at one of
its foci of the ellipse.
- The apparent path of the sun s seen from the earth is known as
ecliptic.
- The eccentricity of the earths orbit is such that the distance
between the sun and earth varies by 1.7%.
- The mean sun-earth distance is 1.495x10
11
km.
Sun-earth distance:
SUN
1.495 X 10
11
m 1.7%
1.39x10
9
m
1.27x10
7
m
32
EARTH
Black body Radiation:
- The energy density of the radiation emitted at a given wave length
(monochromatic) by a perfect radiations, usually called a black
body.
- 2 5 ) T / C (
1
b
n ) 1 e (
C
E
2
- Where,
Eb = Monochromotaic emissive power of the black
body.
C1 = 3.74 x 10
8
W. m
4
/m
2
C2 = 1.44 x 10
4
m K
n = Refractive index of the medium
For vacuum n=1:
For air taken to be n=1.
- Monochromotic emissive power means energy emitted by a perfect
radiator per unit wave length at the specified wave length per unit area
per unit time at the temperature T.
- Now, the total energy emitted by the black body is integrating the
above equation over wavelengths,
d E E
0
b b
Where,
Eb = total emissive power of the black body in W/m
2
The total Energy emitted by the sun from its outer surface is given by,
4
s s b
T * A * * E
Where,
= Stefan Boltzmanns constant = 5.67x10
-8
W/m
2
K
4
T = Suns outer surface absolute temperature in K.
= Emissivity of the sun
A = Surface Area of the sun in m
2
Why do we need the solar energy?
Ans:
- is the worlds most abundant permanent source of the energy.
- Amount of this energy intercepted by the earth is about 5,000
times greater than the sum of the other forms of energy sources
(like nuclear, geothermal, gravitational energies, lunar gravitational
energy etc.,)
- Out of this energy intercepted,
30% of the energy is reflected back to space.
47% is converted to low temperature heat and again
reradiated back to space.
23% is used for evaporation and precipitation of
biosphere.
Less than 0.5% is represented in the KE of the wind
and waves
Remaining amount are stored in the forms of
photosynthesis in plants.
- The total terrestrial radiation is only about one third of the
extraterrestrial radiation total during a year.
- 70% of the energy falls on the ocean
- Only 1.5x10
17
kW hr falls on the land =
= Which is equal to 6,000 times the total energy usage
of USA IN 2000.
You might also like
- Raw Material Specification Sheet - Petroflo 20Y3437 NewDocument2 pagesRaw Material Specification Sheet - Petroflo 20Y3437 NewBasty Tejano67% (3)
- Basic of Hvac: Prepared By: Engr. Mark Ivan C. EspinosaDocument26 pagesBasic of Hvac: Prepared By: Engr. Mark Ivan C. EspinosaMark Ivan EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Solar EnergyDocument238 pagesFundamental of Solar EnergyAvnish Narula95% (19)
- Fundamental of Solar EnergyDocument238 pagesFundamental of Solar EnergyDreamer_ShopnoNo ratings yet
- Earth AstroDocument55 pagesEarth AstroBel Esguerra CabillonNo ratings yet
- The SunDocument43 pagesThe SunRahman BimantaraNo ratings yet
- SunDocument18 pagesSunDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy EC339 Unit 1 Google ClassroomDocument26 pagesSolar Energy EC339 Unit 1 Google ClassroomZohaib Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Phy301 Energy 02 SunDocument16 pagesPhy301 Energy 02 SunPrikshit HoodaNo ratings yet
- The Sun: Motion and Location Within The MWDocument10 pagesThe Sun: Motion and Location Within The MWVictor De Paula VilaNo ratings yet
- Note SN Form 3Document10 pagesNote SN Form 3nozel77No ratings yet
- The Sun: A Presentation Prepared by Riana Therese F. GolinganDocument45 pagesThe Sun: A Presentation Prepared by Riana Therese F. GolinganTrinna AbrigoNo ratings yet
- The SunDocument39 pagesThe SunAnonymous 6iv9eQTP6No ratings yet
- Solar Science and Technology 2020Document6 pagesSolar Science and Technology 2020Richard Simon KisituNo ratings yet
- Space StructureDocument1 pageSpace StructureNaman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 02Document69 pagesUnit 02adeebNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Basics OneDocument46 pagesRenewable Energy Basics OneqiTNo ratings yet
- CH-1003 L-T-P: 1-0-0: Dept. of Chemistry School of Applied Sciences KIIT UniversityDocument47 pagesCH-1003 L-T-P: 1-0-0: Dept. of Chemistry School of Applied Sciences KIIT UniversityDaisy FlowerNo ratings yet
- Book1 1Document6 pagesBook1 1DrCNo ratings yet
- Afsdfadfawefewf: Alpha ParticlesDocument10 pagesAfsdfadfawefewf: Alpha ParticlesMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- The SunDocument7 pagesThe SunCY BokNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-3 Solar EnergyDocument53 pagesCHAPTER-3 Solar Energyaman jainNo ratings yet
- Explosion of Sun: Alexander Bolonkin, Joseph FriedlanderDocument14 pagesExplosion of Sun: Alexander Bolonkin, Joseph FriedlanderRamón Elías Cerrada MontoyaNo ratings yet
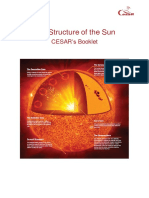
- The Structure of The Sun: Cesar 'S BookletDocument9 pagesThe Structure of The Sun: Cesar 'S BookletAlondra Joan MararacNo ratings yet
- AST191 CH 10 HomeworkDocument2 pagesAST191 CH 10 HomeworkErik SikoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Solar Radiation at The Top of The AtmosphereDocument19 pagesChapter One: Solar Radiation at The Top of The AtmosphereuunsyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Solar RadiationDocument78 pagesLesson 2-Solar RadiationZyra Yvonne MangligotNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Atmosphere & Magnetic Field: Activity 2Document49 pagesThe Earth's Atmosphere & Magnetic Field: Activity 2Maynard SonidoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy: AfdsfaawefaweDocument9 pagesThermal Energy: AfdsfaawefaweMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 04 Lecture Notesfirst lastNo ratings yet
- Our Active SunDocument14 pagesOur Active SunJames BradleyNo ratings yet
- Solar Cooker and Water HeaterDocument59 pagesSolar Cooker and Water HeaterDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (5)
- Insolation, Atmospheric Temperature and Heat Budget of The EarthDocument31 pagesInsolation, Atmospheric Temperature and Heat Budget of The Earthbirudulavinod1No ratings yet
- Solar Energy: Role and Potential of Solar Energy in INDIADocument12 pagesSolar Energy: Role and Potential of Solar Energy in INDIAsuresh270No ratings yet
- Spacecraft Design EnvironmentDocument21 pagesSpacecraft Design EnvironmentKeerthana NageshNo ratings yet
- All Document Reader 1702874093129Document6 pagesAll Document Reader 170287409312961 SURAJ KUMAR TIRKINo ratings yet
- 12 Air Sea InteractionsDocument47 pages12 Air Sea InteractionsNaga LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Nafeesah Azmi 3 Fatimah Az-Zahra Cikgu AzlezanDocument14 pagesNafeesah Azmi 3 Fatimah Az-Zahra Cikgu AzlezanYanafeesabila AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesThe Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat Transferkaushik baruahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7, Factors Affecting Insolation On EarthDocument19 pagesChapter 7, Factors Affecting Insolation On EarthPrachi AshmiNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document21 pagesLec 3Harinath CNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Quenifel B. BustilloDocument32 pagesPrepared By: Quenifel B. Bustilloguardianp8245No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthDocument65 pagesChapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthClydeNo ratings yet
- Rse Final 2023Document138 pagesRse Final 2023Rupesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - EN671Document19 pagesLecture 3 - EN671Faltu Ka jhamlqNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument37 pagesSolar RadiationMarshet MulatNo ratings yet
- Ambastha MsDocument20 pagesAmbastha MsNitin YadavNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Technology: Lecture # 4Document52 pagesRenewable Energy Technology: Lecture # 4Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sandip MondalDocument75 pagesDr. Sandip Mondalsignal jammerNo ratings yet
- 2nd WeekDocument46 pages2nd WeekNIKHIL SAJI (RA1811027010052)No ratings yet
- The SunDocument13 pagesThe SunJamil Md TasrifNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument12 pagesAtmospherelovemhiz431No ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument77 pagesSolar Energychetanya soniNo ratings yet
- Earth and Its FeaturesDocument20 pagesEarth and Its FeaturesZemran Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- TachoclineDocument8 pagesTachoclineMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- 9.1 The Sun: CharacteristicsDocument9 pages9.1 The Sun: CharacteristicsAina AzNo ratings yet
- Vertical Structure of The Atmosphere: Introduction To Meteorology Leila CarvalhoDocument31 pagesVertical Structure of The Atmosphere: Introduction To Meteorology Leila CarvalhoAfsheen ZafarNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation - 1Document27 pagesSolar Radiation - 1Vyshnav vNo ratings yet
- SolarangDocument14 pagesSolarangDennis KasaboNo ratings yet
- Layers of SunDocument2 pagesLayers of Sunjhustineghail153218No ratings yet
- 14 Fun Facts About the Sun: A 15-Minute BookFrom Everand14 Fun Facts About the Sun: A 15-Minute BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 18.335 Problem Set 2 SolutionsDocument7 pages18.335 Problem Set 2 SolutionsAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Boiling: Change of Phase of A Fluid From Liquid To Gaseous State When Heated Is Called BoilingDocument27 pagesBoiling: Change of Phase of A Fluid From Liquid To Gaseous State When Heated Is Called BoilingAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Structure of A Plane Shock Layer: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument13 pagesStructure of A Plane Shock Layer: Articles You May Be Interested inAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Blacs Install - PsDocument20 pagesBlacs Install - PsAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review of Recent Results in Vortex Induced VibrationsDocument23 pagesA Brief Review of Recent Results in Vortex Induced VibrationsAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Circle Method For Isolated AirfoilsDocument8 pagesCircle Method For Isolated AirfoilsAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Solar Flat Plate CollectorsDocument7 pagesSolar Flat Plate CollectorsAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Solar TimeDocument3 pagesSolar TimeAkshay Deshpande0% (1)
- ) tan * tan (cos 15 2 S: Incidence angle (θ)Document3 pages) tan * tan (cos 15 2 S: Incidence angle (θ)Akshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Sun AnglesDocument7 pagesSun AnglesAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- The Fuel of The FutureDocument21 pagesThe Fuel of The FutureAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Axial, Radial TurbinesDocument91 pagesAxial, Radial TurbinesAkshay Deshpande100% (2)
- Starter MotorDocument2 pagesStarter MotorAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Nozzles and DiffusersDocument45 pagesNozzles and DiffusersAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Turbines and CompressorsDocument70 pagesTurbines and CompressorsAkshay Deshpande100% (1)
- Axial Fans and CompressorsDocument32 pagesAxial Fans and CompressorsAkshay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Theory of Valency &bondingDocument12 pagesElectronic Theory of Valency &bondingshivakafle039No ratings yet
- 1955 - Inhibition of HyaluronidaseDocument22 pages1955 - Inhibition of HyaluronidasekamilNo ratings yet
- The - J-Factor of Chilton and Colburn: Unit OperationDocument6 pagesThe - J-Factor of Chilton and Colburn: Unit OperationGhazy alshyal100% (1)
- Introduction To Physical ElectronicsDocument369 pagesIntroduction To Physical ElectronicsAbhishek yadavNo ratings yet
- CHEM 221/PHY 335 - Molecular Symmetry IDocument34 pagesCHEM 221/PHY 335 - Molecular Symmetry Ipaul javed0% (1)
- 1 - Basic Concepts For Simple and Complex FluidsDocument3 pages1 - Basic Concepts For Simple and Complex FluidszhangNo ratings yet
- BCE 314 - First Exam PDFDocument3 pagesBCE 314 - First Exam PDFCristian SereñoNo ratings yet
- Operator Guide: Cycle Chemistry: Volume 1: Once-Through Oxygenated TreatmentDocument32 pagesOperator Guide: Cycle Chemistry: Volume 1: Once-Through Oxygenated TreatmentAbdul BokhariNo ratings yet
- HK I TermodinamikaDocument21 pagesHK I TermodinamikaPutri Desty AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Waterflooding/EOR Applications: Waterflood - Course DescriptionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Waterflooding/EOR Applications: Waterflood - Course DescriptionKonul AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes of Allen Kota BatchDocument143 pagesElectrostatics Notes of Allen Kota BatchAbhijeet ThakurNo ratings yet
- GTCDocument80 pagesGTCmehul10941No ratings yet
- Schematic For A Typical Natural Gas Sweetening Unit Using A Reversible Chemical Reaction ProcessDocument8 pagesSchematic For A Typical Natural Gas Sweetening Unit Using A Reversible Chemical Reaction ProcessHussamNo ratings yet
- Serway PSE Quick Ch37Document13 pagesSerway PSE Quick Ch37GJ BadenasNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument37 pagesLaserNatnael TamirateNo ratings yet
- Membrane Distillation: BY K.Balvanna Vignesh 2016303507Document16 pagesMembrane Distillation: BY K.Balvanna Vignesh 2016303507Vicky DrackNo ratings yet
- J Phys Condens Matter 18 (2006) 165Document16 pagesJ Phys Condens Matter 18 (2006) 165Balakrishnaiah RNo ratings yet
- LPHX Serie 4500 SIHIDocument11 pagesLPHX Serie 4500 SIHIJorge FernandezNo ratings yet
- PERFORM - Nodal Analysis by ExampleDocument2 pagesPERFORM - Nodal Analysis by ExampleAlfonso R. ReyesNo ratings yet
- HHO Gas Generation in Hydrogen Generator Using EleDocument9 pagesHHO Gas Generation in Hydrogen Generator Using EleNishanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Coolants PDFDocument57 pagesAn Introduction To Coolants PDFPETER ADAMNo ratings yet
- Water Chemistry: CHM 001 Chemistry For EngineersDocument33 pagesWater Chemistry: CHM 001 Chemistry For EngineersEjay CabangcalaNo ratings yet
- ESE - Miscellaneous Treatments of WaterDocument13 pagesESE - Miscellaneous Treatments of WaterRoshan NayakNo ratings yet
- Production of MEKDocument91 pagesProduction of MEKNavdeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Studied Refrigerants: 7 IIR Gustav Lorentzen Conference On Natural Working Fluids, Trondheim, Norway, May 28-31, 2006Document1 pageStudied Refrigerants: 7 IIR Gustav Lorentzen Conference On Natural Working Fluids, Trondheim, Norway, May 28-31, 2006amogmhetreNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Lesson Plan Saturated - Unsaturated SolutionDocument9 pagesScience 7 Lesson Plan Saturated - Unsaturated SolutionKresha Lluisma100% (1)
- Reaction MechanismDocument21 pagesReaction MechanismJayvee GayosoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science SNC2D Review Unit 4 PhysicsDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Science SNC2D Review Unit 4 PhysicsRiazNo ratings yet