Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Be PTDC V Sem e & TC PDF
Uploaded by
mahereashish0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
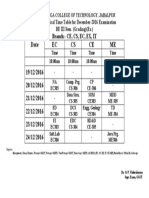
22 views9 pagesBE (PTDC) Sem : FIFTH Branch : ELECTRONICS and TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Code Subject Periods EVALUATION SCHEME Credits L T P SESSIONAL EXAM ESE SUB TOTAL TA CT TOTAL EC-27 Digital Communication Unit-I random processes:Cumulative distribution function, probability density function, Mean, Variance and standard deviations of random variable, Gaussian distribution, Error function, Cor
Original Description:
Original Title
BE PTDC V SEM E & TC.DOC.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBE (PTDC) Sem : FIFTH Branch : ELECTRONICS and TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Code Subject Periods EVALUATION SCHEME Credits L T P SESSIONAL EXAM ESE SUB TOTAL TA CT TOTAL EC-27 Digital Communication Unit-I random processes:Cumulative distribution function, probability density function, Mean, Variance and standard deviations of random variable, Gaussian distribution, Error function, Cor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views9 pagesBe PTDC V Sem e & TC PDF
Uploaded by
mahereashishBE (PTDC) Sem : FIFTH Branch : ELECTRONICS and TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Code Subject Periods EVALUATION SCHEME Credits L T P SESSIONAL EXAM ESE SUB TOTAL TA CT TOTAL EC-27 Digital Communication Unit-I random processes:Cumulative distribution function, probability density function, Mean, Variance and standard deviations of random variable, Gaussian distribution, Error function, Cor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
JABALPUR ENGINEERING COLLEGE, JABALPUR (MP)
(An Autonomous Institute of Govt. of M.P. )
Affiliated to Rajiv Gandhi Technological University, Bhopal (MP)
Scheme of Study and Examination (w.e.f. July 2010)
BE (PTDC) Sem : FIFTH
Branch : ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Course
Code
Subject
Periods EVALUATION SCHEME Credits
L T P
SESSIONAL
EXAM
ESE
SUB
TOTAL
TA CT TOTAL
EC-27 Digital Communication
3 1 - 10 20 30 70 100 4
EC-31 Microwave Engineering
3 1 - 10 20 30 70 100 4
EC-35 VLSI Technology
3 1 - 10 20 30 70 100 4
EC-57
Computer System
Organization
3 1 - 10 20 30 70 100 4
(PRACTICAL/DRAWING/DESIGN)
EC-28L
Digital Communication
Lab
- - 2 20 - 20 30 50 2
EC- 32L
Microwave Engineering
Lab
- - 2 20 - 20 30 50 2
EC- 36L VLSI Technology Lab
- - 2 20 - 20 30 50 2
EC-62L Professional Activity - - 2 50 - 50 - 50 2
Total 12 4 8 150 80 230 370 600 24
T.A. Teachers Assessment, CT- Class Test, ESE - End Semester Examination, Total
Marks 600 Total Periods : 24, Total Credits : 24
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
PTDC
DIGITAL
COMMUNICATION
EC-27
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
Unit-I
Random Processes : Random variables:- Cumulative distribution function, Probability density
function, Mean, Variance and standard deviations of random variable, Gaussian distribution, Error
function, Correlation and autocorrelation, Central-limit theorem, Error probability, Power Spectral
density of digital data.
Unit-II
Pulse Modulation : Analog Signals:- Sampling of Signal, Sampling Theorem for Low Pass and
Band Pass Signals, Aliasing, Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM), Time Division Multiplexing
(TDM), Channel Bandwidth for PAM-TDM Signal, Types of Sampling, Instantaneous, Natural
and Flat Top (Mathematical and Spectral Analysis), Aperture Effect, Introduction to Pulse Position
and Pulse Duration Modulation.
Unit-III
Pulse Code Modulation : Digital Signal:- Quantization, Quantization Error, Pulse Code
Modulation (PCM), Signal-to-Noise Ratio in PCM, Companding, Data Rate and Bandwidth of
Multiplexed PCM Signal, Inter-symbol Interference, Differential PCM (DPCM), Delta Modulation
(DM), and Adaptive Delta Modulation (ADM), Comparison of various system in terms of
Bandwidth and Signal-to-Noise Ratio.
Unit-IV
Digital Modulation Techniques :- Analysis, Generation and Detection (Block Diagram),
Spectrum and Bandwidth of Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK),
Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK), Offset and Non-offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
(QPSK), M-ary PSK, Binary Frequency Shift Keying (BFSK), M-ary FSK, Minimum Shift
Keying, Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), Comparison of digital modulation techniques
on the basis of probability of error, Matched Filter.
UnitV
Spread Spectrum Modulation : Introduction to Spread Spectrum modulation, Generation and
Characteristics of p-n Sequences, Direct sequence Spread Spectrum System, Spread Spectrum with
Code division Multiple Access (CDMA), Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum.
References:
1. Taub and Schilling: Principles of Communication System, TMH
2. Simon Haykins: Communication Systems, 4th Edition, John Wiley.
3. Singh and Sapre: Communication System, TMH
4. B.P. Lathi: Modern Analog and Digital Communication System, Oxford University Press
5. Tomasi: Advanced Electronics Communication Systems, 6th Edition, PHI
6. Couch: Digital and Analog Communication, Pearson Education.
7. David Smith : Digital Transmission Systems, Springer- Macmillan India Ltd
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
B.E/PTDC
Microwave
Engineering
EC-31
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
Microwave Engineering
1 Introduction to Microwaves and Mathematical model of Microwave Transmission. .
History of Microwaves, Microwave Frequency bands. Applications of Microwaves: Civil and
Military,Medical, EMI/ EMC, Concept of Mode ,Characteristics of TEM, TE and TM Modes,
Losses associated with microwave transmission, Concept of Impedance in Microwave transmission
.
2. Analysis of RF and Microwave Transmission Lines. Coaxial Line, Rectangular Waveguide,
Circular waveguide, Stripline,Microstrip Line,Microwave Network Analysis: Equivalent
Voltages and currents for non-TEM lines, Network parameters for microwave Circuits, Scattering
Parameters.
3. Passive and Active microwave Devices: Microwave Passive components: Directional Coupler,
Power Divider, Microwave Passive components: Magic Tee,attenuator, resonator, Microwave
Active components: Diodes, Transistors, Microwave Active components: oscillators,
mixers.Microwave Semiconductor Devices: Gunn Diodes, IMPATT diodes, Schottky Barrier
diodes, PIN diodes. Microwave tubes: Klystron, TWT, Magnetron.
4.Microwave Design Principles. Impedance transformation, Impedance Matching, Microwave
Filter Design, RF and Microwave Amplifier Design, Microwave Power amplifier Design. Low
Noise Amplifier Design, Microwave Mixer Design, Microwave Oscillator Design.
5. Microwave Measurements and Modern Trends in Microwaves Engineering .Power,
Frequency and impedance measurement atmicrowave frequency.Network Analyser and
measurement of scattering
parameters.Spectrum Analyser and measurement of spectrum of a microwave signal. Noise at
microwave frequency and measurement of noise figure. Measurement of Microwave antenna
parameters. Effect of Microwaves on human body. Medical and Civil applications of
microwaves.Electromagnetic interference / Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMI / EMC).
Monolithic Microwave IC fabrication. RFMEMS for microwave components. Microwave Imaging.
References:
1. David M. Pozar, "Microwave Engineering", Third Edition, Wiley India.
2. Samuel Y.Lio, Microwave Devices andCircuits ,PHI India
2. S. Ramo, J.R.Whinnery and T.V.Duzer, "Fields and Waves in
Communication
Electronics", Third Edition, Wiley India.
3. R.E.Collin, "Foundations for Microwave Engineering", Second edition,
IEEE Press.
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
PTDC
VLSI
TECHNOLOGY
EC-35
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
VLSI TECHNOLOGY
Unit - I
Introduction to cmos circuits, circuits & system representation Behavioral representation, structural
representation. Physical representation MOS transistor theory. NMOS and PMOS enhancement
transistor. Threshold voltage body effect. Mos device design equation. Basic DC equation. Second
order effect, MOS models.
Unit - II
The complementary cmos inverter DC character, Static load MOS inverters. The differential
inverter Tristate inverter. Bipolar devices, diodes, transistors, BICMOS inverters.
Unit - III
Review of silicon semiconductor technology and basic CMOS technology-n- well and p-well
process. Interconnect and circuit Twin-tub process layout design rules and latch-up, latch-up
triggering and prevention.
Unit - IV
Circuit characterization and performance estimation resistance and capacitance estimation,
Switching characteristics, CMOS gate transistor sizing, power dissipation. Basic physical design of
simple logic gates. CMOS logic structure.
Unit - V
CMOS design methods. Design strategies. Programmable logic, programmable logic structure,
reprogrammable gate arrays. Exiling programmable gate array. Algotonix, concurrent logic, sea of
gate and gate array design VHDL as a tool.
Reference Books:
1. Neil, H.E. Wesdte, Kamran Eshraghian, Principles of CMOS VLSI design, Pearson
Education.
2. Wyne wolf, Modern VLSI design-system on silicon, Prentics Hall of india
3. Phillip E. Allen and Douglas R holding, CMOS analog Circuit Design, 2
nd
edition, Oxford
University press.
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
B.E/PTDC
COMPUTER
SYSTEM
ORGANIZATION
EC-57
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
COMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANIZATION
Unit - I
Von newmann model-CPU, Memory, I/O, System Bus, Memory address register, Memory data
register, program Counter, Accumulator, Instruction register, Micro operations, Register Transfer
Language, Instruction Fetch, decode and execution, Instruction formats and addressing modes.
Unit - II
Control Unit Organization, Hardwired control Unit, Micro programmed Control Unit, Control
Memory, Address Sequencing, Micro instruction formats, Micro program sequencer,
Microprogramming
Unit - III
Arithmetic Processor design, Addition and subtraction algorithms, Multiplication algorithm,
Division algorithm, Floating point arithmetic, Decimal Arithmetic Unit.
Unit - IV
Input Output Organization, I/O interface, Asynchronous data transfer, Programmed I/O, Interrupt
initiated I/O, DMA, I/O processor, Priority Interrupts.
Unit - V
Memory Organization RAM, ROM, Memory Maps, Memory Hierarchy, Cache Memory
Organization and mapping. Associative memory, Virtual memory, Memory Management
Hardware. Introduction to parallel processing, Instruction and Arithmetic Pipeline.
Reference Books:
1. Morris Mano, Computer System Architecture, PHI.
2. William Stalling, Computer Organization and Architecture, PHI.
3. Kain, Advance Computer Architecture a system design approach, Prentice Hall of India ,
New Delhi.
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
PTDC
DIGITAL
COMMUNICATION
LAB
EC-28L
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LAB
(Suggested Exercise)
List of Experiments (Expandable):
Simulation of different modulation techniques using Scilab (Freeware-Downloadable from
www.Scilab.org) /Matlab/Any Similar Software. Plotting of signal constellation diagrams and
signals
(modulated/ unmodulated). Calculation of Bit error rates BER and comparison of various
modulation
techniques.
1. Study of Sampling Process and Signal Reconstruction and Aliasing.
2. Study of PAM, PPM and PDM.
3. Study of PCM Transmitter and Receiver.
4. Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Demultiplexing.
5. Study of ASK, PSK and FSK Transmitter and Receiver.
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
B.E/PTDC
Microwave
Engineering LAB
EC-32L
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
Microwave Engineering LAB
List of Experiments (Expandable):
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
B.E/PTDC
VLSI
TECHNOLOGY LAB
EC-36L
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
VLSI TECHNOLOGY LAB
(Suggested Exercise)
List of Experiments
1. Design of MOS Generator Using any Electronic Design Automation (EDA)- eg. Microwind
/ Cadence /Sylvaco / Tanner silicon HiPer / Xilinx ISE 9i or any similar software
2. DC MOSFET Curves using EDA.
3. Design of CMOS Logic Gates using EDA.
4. Draw the following CMOS circuits using 0.12 m and 65 ntechnology and simulate for
transfer characteristics along with 2D and 3D view from 450 angles. Compare power
consumption and rise/fall delays
in both technologies:
a. CMOS Inverter with 0.1pF and 0.1fF capacitance loads, in both cases with equal rise and
fall times.Plot output eye diagram also.
b. CMOS NAND and NOR gates with 0.01pF load and equal rise and fall times. Comment on
area requirement of both gates.
5. To design Current Mirror using CMOS 0.18 micron Technology.
6. Design a basic differential amplifier circuit using current mirror logic. Show gain of
amplifier and comment on bandwidth.
7. Design the Schmitt trigger circuit with UTP= 4.5 V and LTP = 2.0 V. Plot transfer curve
analysis (with hysteresis effect) VO versus VI.
8. Design a 2-bit parallel adder from schematic and its CMOS layout. List global delay of all
nodes. Identify the critical path and comment on its optimization.
COURSE CONTENT & GRADE (w.e.f. July 2010)
Course Subject Title
Subject
Code
Grade for End
Sem
CGPA at the end of
every even semester
T P
PTDC
PROFESSIONAL
ACTIVITY
EC- 62L
Min
D
Min
D
5.0
Objective The aim of professional activity is to impart training in developing capabilities of
students in expressing views on technical topics. Students can choose any topics related to
electronics & communication branch theoretically or can fabricate practical working models on
which lecture could be delivered . Practical working model demonstration in group is also
permitted. Model fabrication under the professional activity shall be encouraged. Students who
have visited, some technical places can also write & present report on it.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Efficient Internet Searches For ChemistsDocument10 pagesEfficient Internet Searches For ChemistsAnonymous 44wb1YMQVyNo ratings yet
- Practical Time Table VIII Dec.2016 ExDocument1 pagePractical Time Table VIII Dec.2016 ExmahereashishNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BE 21 SEPTDocument43 pagesSyllabus BE 21 SEPTDrAmit Kumar ChandananNo ratings yet
- Gyan Ganga College of Technology Center Code 0208 List of Electives Sem Vii With Student StrengthDocument1 pageGyan Ganga College of Technology Center Code 0208 List of Electives Sem Vii With Student StrengthmahereashishNo ratings yet
- Gyan Ganga College seating plan for BEIII/I CBGS examDocument4 pagesGyan Ganga College seating plan for BEIII/I CBGS exammahereashishNo ratings yet
- 02 MechenicalDocument184 pages02 MechenicalmahereashishNo ratings yet
- CDN PubContent Advertisement Prop080916024228Document4 pagesCDN PubContent Advertisement Prop080916024228mahereashishNo ratings yet
- IT 7 &8 Sem RGPV SyllabusDocument29 pagesIT 7 &8 Sem RGPV SyllabusVijayendra SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Important instructions for degree certificateDocument2 pagesImportant instructions for degree certificatemr_piyush5No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Use NotesDocument25 pagesBasic Computer Use NotesmahereashishNo ratings yet
- 0208 BE 1 Sem NotificationDocument7 pages0208 BE 1 Sem NotificationmahereashishNo ratings yet
- A Concise History of Early ComputersDocument8 pagesA Concise History of Early ComputersRicky RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Electives 2010Document1 pageElectives 2010mahereashishNo ratings yet
- 0208 Centre Expenses Dec 2010Document1 page0208 Centre Expenses Dec 2010mahereashishNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Apostles CreedDocument141 pagesApostles Creedjerome mecca0% (2)
- ArenavirusDocument29 pagesArenavirusRamirez GiovarNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument5 pagesLife and Works of Jose Rizalnjdc1402No ratings yet
- The Story of Babri MasjidDocument54 pagesThe Story of Babri MasjidKiran Penumala100% (1)
- Ashe v. Swenson, 397 U.S. 436 (1970)Document25 pagesAshe v. Swenson, 397 U.S. 436 (1970)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- 2 NDDocument52 pages2 NDgal02lautNo ratings yet
- H-1 Nationalism in Europe NotesDocument5 pagesH-1 Nationalism in Europe Noteskanishk kumarNo ratings yet
- New Democracy June-August 2017Document32 pagesNew Democracy June-August 2017Communist Party of India - Marxist Leninist - New DemocracyNo ratings yet
- The Road To Privatization: TQM and Business Planning: Bennington, Lynne Cummane, JamesDocument11 pagesThe Road To Privatization: TQM and Business Planning: Bennington, Lynne Cummane, JamesBojan KovacevicNo ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Shear Explains Shear Cracks 45 DegDocument15 pagesShear Explains Shear Cracks 45 DegHieu Huy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sustainability of A Beach Resort A Case Study-1Document6 pagesSustainability of A Beach Resort A Case Study-1abhinavsathishkumarNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment K12Document88 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment K12Jardo de la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Acute Care Handbook For Physical Therapists 5Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesAcute Care Handbook For Physical Therapists 5Th Edition Full Chaptergloria.goodwin463100% (20)
- DirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideDocument5 pagesDirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideTempest JannaNo ratings yet
- 6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLDocument11 pages6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLManav100% (2)
- Are Moral Principles Determined by SocietyDocument2 pagesAre Moral Principles Determined by SocietyKeye HiterozaNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Text DocumentDhaniNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2Document33 pagesMock Exam 2Althea Karmylle M. BonitaNo ratings yet
- Dwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&5Document4 pagesDwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&521Dwi Athaya SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RUBRIC PHY110 (For Student)Document3 pages2 - RUBRIC PHY110 (For Student)Puteri AaliyyaNo ratings yet
- Science of Happiness Paper 1Document5 pagesScience of Happiness Paper 1Palak PatelNo ratings yet
- ASBMR 14 Onsite Program Book FINALDocument362 pagesASBMR 14 Onsite Program Book FINALm419703No ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument58 pagesConic SectionNailah Sakinah100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION Quali Observation ReportDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION Quali Observation Reportmira hamzahNo ratings yet
- Al-Rimawi Et Al-2019-Clinical Oral Implants ResearchDocument7 pagesAl-Rimawi Et Al-2019-Clinical Oral Implants ResearchSohaib ShujaatNo ratings yet
- Thin Layer Chromatograph1Document25 pagesThin Layer Chromatograph12581974No ratings yet
- 2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidenceDocument16 pages2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidencebaridinoNo ratings yet
- Telesure Mock 8Document13 pagesTelesure Mock 8Letlhogonolo RatselaneNo ratings yet
- Functional Appliances 2018Document45 pagesFunctional Appliances 2018tonhanrhmNo ratings yet