Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 4 - R-C R-L Circuit in Series PDF
Uploaded by
Trần Ngọc HảiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 4 - R-C R-L Circuit in Series PDF
Uploaded by
Trần Ngọc HảiCopyright:
Available Formats
AC SIGNALS ACTION TO R-C, R- L CIRCUITS
I.Learning Objectives:
a. Define equivalent resistance of RC circuit
b. Define equivalent resistance of RL circuit
c. Calculate the phase difference of 2 signals.
II.Theory:
Current I(t) and potential difference U(t) in an AC circuits are defined by using Oscilloscope in 2
channel mode. A function generator S
12
is used as a voltage source which has U
0
amplitude and variable
frequency f. Measurements are used to calculate average value of equivelent resistor follow expression:
Z =U
0
/ I
0
and the phase difference between current and potential difference.
Alternating-current circuit (AC) theory:
- If circuit has only resistor, current and potential difference between 2 terminal of resistor have
the same phase
- If AC circuit has only inductions, currents phase is t/2 later than potential difference s phase
- If AC circuit has only capacitor, currents phase is t/2 sooner than potential difference s phase
2.1. AC Circuits have resistor and capacitor in series
RC circuit in series:
- Use current as a origin.
- Potential difference between 2 terminal of resistor and current the same phase
- Potential difference between 2 terminal of capacitor is t/2 later than current .
AC current : i =I
0
. Sin(et)
Potential difference on R : u
R
=U
0RSin
(et)
Potential difference on C : u
C
=U
0CSin
(et - t/2)
Potential difference on RC : u =U
0
Sin (et +)
- With: is the phase difference between potential difference and currents amplitude in circuit.
can be calculated from phase diagram
Potential difference on RC : u =U
0
Sin (et +)
- With: is the phase difference between potential difference and currents amplitude in circuit.
can be calculated from phase diagram.
In series RC circuit: u =u
R
+u
C
RC circuit in series
Gin pha ca
mch RL ni tip
Phase diagram of RC
circuit in series
And U
2
=U
2
r
+U
2
c
U
2
=I
2
(R
2
+1/(e.c)
2
)
So that, we can definde summary resistance of RC circuits in series:
( )
2
2 2
.
1
C
R Z
+ =
Phase difference between potential difference and currents amplitude in circuit is
tg () =
L R U
U
R
C
. .
1
=
Summary: if we know U
R
, U
C ,
and phase difference , we can find current and equivalent resistance in
circuit..
2.2. AC Circuits have resistor and inductor in series
RL circuit in series:
- Use current as a origin.
- Potential difference between 2 terminal of resistor and current the same phase
- Potential difference between 2 terminal of inductor is t/2 sooner than current .
RL circuit in series
AC current : i =I
0
. Sin(et)
Potential difference on R : u
R
=U
0RSin
(et)
Potential difference on L : u
L
=U
0LSin
(et +t/2)
Potential difference on RL circuits : u =U
0
Sin (et +)
- With: is the phase difference between potential difference and currents amplitude in circuit.
can be calculated from phase diagram
With RL sreial circuit: u =uR +u
L
And U
2
=U
2
r
+U
2
L
U
2
=I
2
(R
2
+(e.L)
2
)
So that, we can definde summary resistance of RL circuits in series:
( )
2 2 2
. L R Z + =
Phase difference between potential difference and currents amplitude in circuit is
tg () =
R
L
U
U
R
L
.
=
Summary: if we know U
R
, U
L ,
and phase difference , we can find current and equivalent of resistor in
circuit..
2.3. AC Circuits have inductor and capacitor in series
Phase diagram of RL
circuit in series
- Use current as a origin.
- Potential difference between 2 terminal of capacitor is t/2 later than current .
- Potential difference between 2 terminal of inductor is t/2 sooner than current
AC current : i =I
0
. Sin(et)
Potential difference on L : u
L
=U
0LSin
(et +t/2)
Potential difference on C : u
C
=U
0CSin
(et - t/2)
Potential difference on RL circuit : u =U
0
Sin (et +)
So that: U =U
L
U
C
Summary: The phase difference is t/2 if UL
is greater than UC. And
phase difference is =-t/2 if UL
is smaller than UC.
III.Apparatus
3.1 Define equivalent resistance of RL circuit
Order Equipments Quantity
1 A4 Test board 1
2 Resistor STE 1O, 2W 1
3 Resistor STE 100O, 2W 1
4 Resistor STE 10kO, 0.5W 1
5 500 turns coil 1
6 1000 turns coil 1
7 Funtions Generator S12 1
8 Oscilloscope 303 1
9 Jack 2
10 Wire 1
11 Multimeter 2
3.2. Define equivalent resistance of LC circuit
Order Equipments Quantity
1 A4 test board 1
2 Resistor STE 10O, 2W 1
3 Resistor STE 100O, 2W 1
4 Capacitor STE 1F, 100V 1
5 Capacitor STE 4.7F, 63V 1
6 500 turns coil 1
7 1000 turns coil 1
8 Funtions Generator S12 1
9 Oscilloscope 303, 1
10 Jack 2
11 Wire 1
12 Multimeter 2
IV. Experimenting
4.1 Define standard for Oscilloscope in 2 channel mode.
4.1.1. Function Generator.
- Connect Multimeter to the output port of function Generator for measuring different potential and
frequency.
- Adjust amplitude and frequency in function generator to get the signal with 5000Hz frequecy and
2V different potential at out put ports.
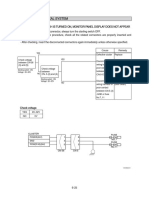
4.1.2. OCR HM 303-6.
Hnh 5.1: Function buttons of OCR HM 303-6
Follow steps:
a. Connect instrument to power outlet, depress red POWER button. LED indicates
operating condition.
b. Depressed the Calibrator pushbutton, the CRO will out put the standard pulse with
1kHz frequency (T=1ms), amplitude 0,2Vpp (V peak to peak: the different potential
between 2 peak of signal.
c. Put the channel I probe to Test Socket (39). Adjust the Volt/Div rotate switch (13) to
0.1 Volt/Div ( mean the length of 0,1 volt is 1 grid line), adjust the Cal button (14)
until the length of peak to peak of the square wave is 2 grid line.
d. Adjust Time/Div rotate switch to 0.2 ms/Div (mean 0,2 ms length is 1 grid line),
adjust Cal (25) to have the lenghth period of signal is 5 grid line. (Standard time/Div)
e. Do all steps above with Channel II
4.2. Define equivalent resistance of RC circuit
Hnh 5.2: Mch RC ni tip
4.2.1. Use OCR to define U
R
on resistor
- The general volt meter and ampere meter can only measure effective value (rms), and can not measure
phase difference so we must use an OCR for measuring them. In OCR we can see the sin signal, measure
the effective voltage Urms by dividing peak to peak voltage Upp to 2 2 .
- Make a circuit like image 5.2 with R =10O, C =0.22F, U(t) is the AC source which get from Function
Generator.
- Use 1 channel of OCR to define potential difference on resistor. OCR must be set to single channel
mode.
- Adjust Volt/ Div, Time/Div button in OCR for the clearest wave in OCRs screen
- Measure the distance between peaks of 2 sequential signals in OCR. Define Upp.
- Calculate effective voltage from Upp
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
4.2.2. Use OCR to define U
C
on capacitor
- Make a circuit like image 5.2. Use 1 channel of OCR to define potential difference on capacitor. OCR
must be set to single channel mode.
- Adjust Volt/ Div, Time/Div button in OCR for the clearest wave in OCRs screen
- Measure the distance between peaks of 2 sequential signals in OCR. Define Upp.
- Calculate effective voltage from Upp
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
4.2.3. Define phase difference between current and potential
- Make a circuit like image 5.2.
- OCR is set to dual channel mode. Put the probe CHI to B point, mass probe to A to measure potential
difference on R. Put the probe CHII to C point, mass probe to A to measure potential difference on RC
circuit.
Note: in dual channel mode, 2 channel must have common mass point.
- Adjust Volt/ Div, Time/Div button in OCR for the clearest wave in OCRs screen
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
- Measure the phase difference in 2 way:
Measure t ( phase difference time of 2 signal) and T ( signals period) in OCR which likes image below.
Calculate these measurements by Time/Div in CRO
Image 5.3: Phase difference of 2 signals
So that: =360
0
. t/T (degree)
Or =2t. t/T (rad)
4.3 Define equivalent resistance on RL circuit
4.3.1. Use OCR to define U
R
on resistor
Image 5.4: RL circuit
- Make the circuit like image 5.4: with R =200O, L is a 1000 turns coil.
- Use 1 channel of OCR to define potential difference on resistor. OCR must be set to single channel
mode. Put signal probe to A point, mass probe to B point.
- Adjust Volt/ Div, Time/Div button in OCR for the clearest wave in OCRs screen
- Measure the distance between peaks of 2 sequential signals in OCR. Define Upp.
- Calculate effective voltage from Upp from Upp and Volt/Div value.
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
4.3.2. Use OCR to define U
L
on inductor
- Make the circuit like image 5.4
- Use 1 channel of OCR to define potential difference on inductor L. OCR must be set to single channel
mode. Put signal probe to B point, mass probe to C point.
- Adjust Volt/ Div, Time/Div button in OCR for the clearest wave in OCRs screen
- Measure the distance between peaks of 2 sequential signals in OCR. Define Upp.
- Calculate effective voltage from Upp from Upp and Volt/Div value.
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
4.3.3. .Define phase difference between current and potential
- Make the circuit like image 5.4.
- OCR is set to dual channel mode. Put the probe CHI to B point, mass probe to A to measure potential
difference on R. Put the probe CHII to C point, mass probe to A to measure potential difference on RL
circuit.
Note: in dual channel mode, 2 channel must have common mass point.
- Adjust Volt/ Div, Time/Div button in OCR for the clearest wave in OCRs screen
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
- Calculate the phase difference of 2 signals like part 4.2
V. Results, calculate
- Source voltage U
0
=...V
5.1. Define equivalent resistance on RC circuit
- Resistor R =....O
- Capacitor C =........F
a. U
R
on resistor.
- Peak to peak potential difference U
Rpp
=(V)
- Effective voltage
......
2 2
= =
Rpp
Rrms
U
U (V)
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper.
b. U
C
on capacitor.
- Peak to peak potential difference U
Cpp
=..... V
- Effective voltage
....
2 2
U
U
Cpp
Crms
= = V
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper
c. Phase difference between current and potential
- Source frequency f =5000 Hz
- Source period .....
f
1
T = = ms
- Phase differences time t =..ms
- Phase difference ....... * 360 = =
T
t
degree ; ...... * 2 = =
T
t
rad
5.2. Define equivalent resistance on RL circuit
- Resistor R =....O
- 1000 turns coil.
a. U
R
on resistor.
- Peak to peak potential difference U
Rpp
=..... (V)
- Effective voltage
....
2 2
U
U
Rpp
Rrms
= = (V)
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper
b. U
L
on inductor.
- Peak to peak potential difference U
Lpp
=...... (V)
- Effective voltage ....
2 2
U
U
Lpp
Lrms
= = (V)
- Draw signal graph in OCR to paper
c. Phase difference between current and potential
- Source frequency f =5000 Hz
t /ms
U /mV
- Source period ....
f
1
T = = ms
- Phase differences time t =.....ms
- Phase difference .....
T
t
* 360 = = degree ; ....
T
t
* 2 = t = rad
VI. Review Question
1. What is the experiments process?
2. How do frequency effect to resistor, capacitor, inductor ?
3. Is phase difference the same with theory ? Explain it.
You might also like
- (High Performance Integer Arithmetic Circuit Design On FPGA - Architecture, ImplementationDocument125 pages(High Performance Integer Arithmetic Circuit Design On FPGA - Architecture, ImplementationTrần Ngọc HảiNo ratings yet
- M H×NH Tham Chiõu OsiDocument13 pagesM H×NH Tham Chiõu OsingocthieuNo ratings yet
- EE471 Group#11 Lab#1Document17 pagesEE471 Group#11 Lab#1Trần Ngọc HảiNo ratings yet
- Reliable Data Transfer: Transport Layer 3-1Document31 pagesReliable Data Transfer: Transport Layer 3-1Trần Ngọc HảiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Standing Wave PDFDocument6 pagesLab 5 - Standing Wave PDFTrần Ngọc HảiNo ratings yet
- Lab3 - Mach Cau Wheatstone PDFDocument4 pagesLab3 - Mach Cau Wheatstone PDFTrần Ngọc HảiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Dinh Luat Ohm - Ohm Law PDFDocument5 pagesLab 1 - Dinh Luat Ohm - Ohm Law PDFTrần Ngọc HảiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Ats 01 Manual enDocument30 pagesAts 01 Manual enccorrea130% (1)
- 7 Steps To Publishing in A Scientific JournalDocument53 pages7 Steps To Publishing in A Scientific JournalZAHID HUSSAIN AMEERNo ratings yet
- RE18301-91 - Cartridge Valves - NloDocument12 pagesRE18301-91 - Cartridge Valves - NloTaller PahrNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Electrical SystemDocument16 pagesGroup 3 Electrical SystemTaha RdmanNo ratings yet
- Thermo OrionDocument2 pagesThermo Orionhdabc123No ratings yet
- Owner S and Operator S Manual: Vertical, Water-Cooled 4-Cycle Diesel EngineDocument48 pagesOwner S and Operator S Manual: Vertical, Water-Cooled 4-Cycle Diesel EnginethuanNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsRaghuNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Instructions To CandidatesDocument4 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Instructions To CandidatesTomorrow PavingNo ratings yet
- Maytag Catalog Full SpecificationsDocument14 pagesMaytag Catalog Full Specificationsmairimsp2003No ratings yet
- Synchronous AlternatorDocument228 pagesSynchronous AlternatorSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Usf 73 A1Document2 pagesUsf 73 A1A.HassanNo ratings yet
- Lister Peter Running Manual ENITELDocument16 pagesLister Peter Running Manual ENITELRommel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Speech Recognition System Using Ic Hm2007Document21 pagesSpeech Recognition System Using Ic Hm2007Nitin Rawat100% (1)
- Vicinity Map: Waterline, Plumbing and Storm Drainage Layout SCALE: 1:100 MTSDocument1 pageVicinity Map: Waterline, Plumbing and Storm Drainage Layout SCALE: 1:100 MTSLou PotesNo ratings yet
- Configuracion Convertidor Encore Network Sp201Document23 pagesConfiguracion Convertidor Encore Network Sp201Humberto Ochoa MendezNo ratings yet
- Section 26 51 00-Interior Lighting PDFDocument10 pagesSection 26 51 00-Interior Lighting PDFmasoodaeNo ratings yet
- Endress KatalogDocument72 pagesEndress KatalogpnsanatNo ratings yet
- RMF4616B O.M.P. Manual PDFDocument34 pagesRMF4616B O.M.P. Manual PDFcruz TobillaNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Low-Power Differential ISFET/REFET Readout CircuitDocument3 pagesUltra-Low-Power Differential ISFET/REFET Readout CircuitAhmedNo ratings yet
- Mid 185 - Pid 84 - Fmi 2Document3 pagesMid 185 - Pid 84 - Fmi 2AkbarNo ratings yet
- 6 - Transportation ElectrificationDocument98 pages6 - Transportation ElectrificationNamiraNo ratings yet
- Sandvik RD285 TY280 PartsListDocument3 pagesSandvik RD285 TY280 PartsListGiovanni Aliaga MariscalNo ratings yet
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument12 pagesSCR Triggering Methodsbangs34No ratings yet
- XMT 350 Vs PDFDocument36 pagesXMT 350 Vs PDFgerman gualavisiNo ratings yet
- Live Tank Circuit Breakers (MODELO - LTB123D1B) PDFDocument152 pagesLive Tank Circuit Breakers (MODELO - LTB123D1B) PDFclaudia tarattiniNo ratings yet
- Service Interval Parts and Volumes / Compact Wheel Loaders / First Generation ModelsDocument1 pageService Interval Parts and Volumes / Compact Wheel Loaders / First Generation ModelsМ РNo ratings yet
- Diagnostico y Test 9750 Sts PDFDocument2,528 pagesDiagnostico y Test 9750 Sts PDFAlejandro Dho100% (2)
- GX2-RX200BX4-R Quad Return Path Optical Receiver Installation and Operation ManualDocument60 pagesGX2-RX200BX4-R Quad Return Path Optical Receiver Installation and Operation ManualauancasaNo ratings yet
- Arduino 2 Axis Servo Solar TrackerDocument10 pagesArduino 2 Axis Servo Solar TrackerMarius DanilaNo ratings yet
- 88-02 Cummins Exhaust BrakeDocument24 pages88-02 Cummins Exhaust Brakemark_dayNo ratings yet