Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Borrow Pit Volumes
Uploaded by
Shafiullah Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views10 pagesborrow-pits
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentborrow-pits
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views10 pagesBorrow Pit Volumes
Uploaded by
Shafiullah Khanborrow-pits
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
When trying to figure out Borrow Pit Problems you need to understand a few things.
1. Water can be added or removed from soil
2. The MASS of the SOLIDS CAN NOT be changed
3. Need to know phase relationships in soil.which I will show you next
Phase relationship in Soil
This represents the soil that you take from a
borrow pit. It is made up of AIR, WATER, and
SOLIDS.
So if you separated the soil into its components
it would look like this. It is referred to as a Soil
Phase Diagram.
When looking at a Soil Phase Diagram you
think of it two ways, 1. Volume, 2. Mass.
AIR
WATER
SOIL
AIR
WATER
SOIL
Volume
V
a
V
w
V
s
Mass
M
a
= 0
M
w
M
s
V
a
= Volume Air
V
w
= Volume Water
V
s
= Volume Solid
M
a
= Mass Air = 0
M
w
= Mass Water
M
s
= Mass Solid
V
t
= Volume Total = V
a
+ V
w
+ V
s
M
t
= Mass Total = M
w
+ M
s
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
Basic Terms/Formulas to know Soil Phase relationship
Density of Water = !
water
= M
w
/V
w
English Units = 62.42 pounds per CF(pcf)
SI Units = 1,000 g/liter = 1,000kg/m
3
Specific Gravity = G
s
= !
solids
/!
water
=M
s
/(V
s
* !
water
)
Moisture Content (w) = M
w
/M
s
Porosity (n) = V
v
/V
t
V
v
= Volume of Voids = V
w
+ V
a
V
t
= Total Volume = V
s
+V
w
+ V
a
Degree of Saturation (S) = V
w
/V
v
V
w
= Volume of Water
V
v
= Total Volume of Voids
Void Ratio (e) = V
v
/V
s
V
v
= Total Volume of Voids
V
s
= Volume of Solid
Total or Wet Density of Soil (!
wet
) = M/V
M
= M
w
+ M
s
V = V
w
+ V
s
+ V
a
Dry Density of Soil (!
dry
) = M
s
/V
V = V
w
+ V
s
+ V
a
Density of Solids = M
s
/V
s
Specific Gravity = the density of the solids divided by the density of Water
Moisture Content = Mass of Water divided by the Mass of Solids
Void Ratio = Volume of Voids divided by the Volume of Solids
Porosity = Volume of Voids divided by the Total Volume,
Higher porosity = higher permeability
Specific Gravity = S
* e = G
s
* w
Porosity (n) = e/(1+e)
Void Ratio (e) = n/(1-n)
Total or Wet Density of Soil (!
wet
) =
!
wet
= ((!
water
* G
s
( 1+w))/(1+e)
Dry Density of Soil (!
dry
) = !
wet
/(1+w)
(!
dry
) = (!
water
* G
s
)/(1+(w/S)*G
s
)
(!
dry
) = (!
water
* G
s
)/(1+e)
Relationships to know
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
Load and Shrinkage Factors
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
AIR
WATER
SOIL
AIR
WATER
SOIL
AIR
WATER
SOIL
1.0BCY
1.25LCY
.90CCY
V
B
V
L
= V
B
(1+SWELL)
V
L
= V
B
x SWELL FACTOR(or Load factor)
V
C
= V
B
(1 - SHRINKAGE)
V
C
= V
B
x SHRINKAGE FACTOR
DL = Dry Loose Unit Weight (!
DL
)
DC = Dry Compacted Unit Weight (!
DC
)
DB = Dry Bank Unit Weight (!
DB
)
Important Volume Change Relationships:
In excavation, 1+Swell is called Swell Factor
LCY to CCY:
CCY to BCY:
Borrow-Pit Method
! Another important concept to know is the Borrow Pit Method in order to calculate the
volume of the borrow pit. It is also called the unit-area method.
! The Volume is determined based on a predetermined grid pattern. The site is divided
into equal squares of sides 20,50, or a 100 ft. Elevations are then measured at the corners
of the grid, which are given titles that correspond to the coordinates of the corner in the
grid, ex: 3-D, 4-A,..
! Then for simplicity of calculations, the points are connected to the corners
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
WWW.LEARNCIVILENGINEERING.COM
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
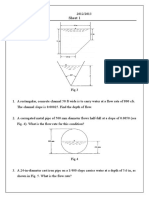
Question #1: After surveying a borrow pit, the surveyor produced the
following borrow pit grid below. If you consider 0.0, the elevation that you
can cut to. What is the total cut volume (cy) available?
a. 250 cy
b. 232 cy
c. 201 cy
d. 343 cy
A
B
C
D
E
G
F
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.5
3.3
3.1
2.1
2.4
2.8
1.8
1.6
1.3
20 feet
20 feet
20 feet
20 feet
20 feet
Question # 2: 120cy of bank soil is excavated and stockpiled before being
trucked and then compacted. The soil has a swell of 25% and a shrinkage of
15%.
What is the final volume of the compacted soil?
a. 68 cy
b. 102 cy
c. 150 cy
d. 128 cy
Question #3. A 10 ft wide, 500 ft long, 2 ft thick road is being constructed. The soil
density after compaction was found to be 112.1 pcf at an optimum moisture content
of 10.5%. The soil from the borrow pit has a total density of 105pcf and a moisture
content of 8.5%
What is the total volume(cf) of soil that needs to be hauled from the borrow pit?
a. 45,395 cf
b. 12,856 cf
c. 11,584 cf
d. 5,260 cf
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
Question # 4. Soil borings at a proposed Borrow Pit indicate that the soil is
primarily a sandy clay. Cores taken of the soil in the pit indicates an average
dry density of 88pcf at a moisture content of 22%.
The volume of the contained soil in the fill when constructed is 20,000 cy.
Based on the average results of a Standard Proctor compaction test the soil
will be compacted to a density of 95 pcf at a moisture content of 25%.
Dump trucks with a capacity of 15cy will be used to transport the soil from the
borrow pit to the proposed road bed.
1. Assuming that the soil in the dump truck has a dry density of 69 pcf at a
moisture content of 22% estimate the number of loads that will be necessary.
2. Compute the volume of the hole at the borrow pit after the soil is removed
a. 68 trucks
b. 12,856 trucks
c. 658 trucks
d. 1,836 trucks
a. 36,568 cy
b. 21,591 cy
c. 24,564 cy
d. 19,836 cy
WWW.LEARNCIVILENGINEERING.COM
Answer #1:
Step 1: Setup a chart to get the volume under each square; Then sum up all
the volumes.
Step 2: Find Volume in Cubic yards
! V
total
= 6260 cf / (27cf/cy) = 232 cy
EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION AND LAYOUT
**BORROW PIT VOLUMES**
Grid Area (sf) Average depth (ft) Volume (cf)
A 400 (2.4+3.5+2.8+3.3)/4 = 3.0 1200
B 200 (3.5+3.3+2.1)/3 = 2.97 594
C 400 (2.8+3.3+3.2+3.1)/4 = 3.1 1240
D 400 (3.3+2.1+3.1+2.4)/4 = 2.7 1080
E 400 (2.1+1.8+2.4+1.6)/4 = 1.98 792
F 200 (3.1+2.4+2.8)/3 = 2.77 554
G 400 (2.4+2.8+1.6+1.3)/4 = 2.0 800
V
total
= 6260cf
Answer #2:
The shrinkage factor is taken with respect to the bank volume condition.
- so, V
compacted fill
=(1-.15)(120cy) = 102cy
For your information the swell is taken with respect to the bank volume
condition too.
- so, V
stockpile
=(1+.25)(120cy) = 150cy
Answer #3:
Step 1: Find the mass of solids (M
s
) required for the controlled fill:
- Volume of Compacted soil = (500ft)(10ft)(2ft) = 10,000 cf
- dry density of the compacted soil is given = 112.1 pcf
- using Dry Density of Soil (!
dry
) = M
s
/V = 112.1pcf = M
s
/10,000cf, so M
s
=
1,121,000 lbs
Step 2: Find total volume of soil that needs to be hauled from the borrow pit:
- using Moisture Content (w) = M
w
/M
s
, .085 = M
w
/1,121,000lbs = M
w
= 95,285
lbs
- Total Mass at borrow pit = 1,121,000lbs + 95,285lbs = 1,216,285 lbs
- using Total or Wet Density of Soil (!
wet
) =
M/V = 105pcf = 1,216,285 lbs/V, V = 11,583.7 cf
FYI ----to figure out the Mass of water in compacted soil
- Moisture content in compacted soil given at 10.5% = .105
- using Moisture Content (w) = M
w
/M
s
, .105 = M
w
/1,121,000lbs = M
w
=
117,705 lbs
Answer #4:
Step 1: Find the mass of solids (M
s
) required for the controlled fill:
- Volume of Compacted soil = 20,000 cy * 27cf/cy = 540,000 cf
- dry density of the compacted soil is given = 95 pcf
- using Dry Density of Soil (!
dry
) = M
s
/V = 95 pcf = M
s
/540,000 cf, so M
s
=
51,300,000 lbs
Step 2: Find the # of Trucks required to haul Soil.
- M
s
= 51,300,000 lbs, and the dry density of the soil to be hauled is 69 pcf
- so, 51,300,000 lbs/69pcf = 743,478 cf / 27cf/cy = 27,536 cy
- so the number of trucks needed is 27,536cy/15cy/truck = 1836 trucks
Step 3: Find the Volume at the borrow pit
- dry density of the compacted soil is given = 88 pcf
- (!
dry
) = M
s
/V, 88pcf = 51,300,000 lbs/V, V= 51,300,000lbs/88pcf = 582,955cf
- convert to cy, 582,955cf/(27cf/cy) = 21,591cy
You might also like
- Material Schedule of Two Storey BuildingDocument1 pageMaterial Schedule of Two Storey BuildingOreoluwaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For TrafficDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank For TrafficjananiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Footing DesignDocument30 pagesReinforced Concrete Footing DesignAizuddinNo ratings yet
- CE 408 Transportation Engineering: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument119 pagesCE 408 Transportation Engineering: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesThony CayNo ratings yet
- Final Requirement On Ce 523: Situation IDocument4 pagesFinal Requirement On Ce 523: Situation ICzindy MoradosNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering DesignDocument20 pagesTransportation Engineering DesignSesay AlieuNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure of Double Storey BungalowDocument2 pagesWork Breakdown Structure of Double Storey BungalowDavidNo ratings yet
- Research (Design of Water Tank-Ch 3)Document15 pagesResearch (Design of Water Tank-Ch 3)Alyssa Mae GomezNo ratings yet
- Factor of Safety Against Sliding Refresher CourseDocument3 pagesFactor of Safety Against Sliding Refresher CourseKim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- DR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 7Document41 pagesDR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 7Engr.Towhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFimran5705074No ratings yet
- PERMEABILITYDocument26 pagesPERMEABILITYChristian Felix MapilesNo ratings yet
- Mock Quiz Solution Key PDFDocument20 pagesMock Quiz Solution Key PDFLong Live TauNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 NewDocument6 pagesAssignment 4 Newmohamed younisNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Deck for 5.77m SpanDocument2 pagesDesign of Steel Deck for 5.77m Spanrmrv valdez0% (1)
- Profile Leveling NotesDocument2 pagesProfile Leveling Notessunleon310% (1)
- Item 1018Document5 pagesItem 1018Ester MarianNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesDocument18 pagesMODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Geothecnical Engg 4 - SOIL COMPACTIONDocument56 pagesGeothecnical Engg 4 - SOIL COMPACTIONRenderizzah FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Level 1 Lab Report Front PageDocument7 pagesLevel 1 Lab Report Front PageNora NorazisahNo ratings yet
- FW#7 (Ce121 F)Document24 pagesFW#7 (Ce121 F)Alyssa Atienza67% (3)
- Hydraulics Refersher Module PDFDocument4 pagesHydraulics Refersher Module PDFKim SomeraNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Beam Design ProblemsDocument4 pagesReinforced Concrete Beam Design ProblemsRaine ZaficoNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Analysis of PrecipitationDocument43 pagesLec 6 Analysis of PrecipitationumairNo ratings yet
- Soil mechanics homework solutionsDocument5 pagesSoil mechanics homework solutionsMyca QuizaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics New ProblemsDocument5 pagesHydraulics New ProblemsEugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- CEng 152 Correlation Exam 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCEng 152 Correlation Exam 1 SolutionsMICHAEL CORETICONo ratings yet
- Permeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsDocument16 pagesPermeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsGed CudiamatNo ratings yet
- Textbook For CMT (Asphalt, Wood, & Steel)Document15 pagesTextbook For CMT (Asphalt, Wood, & Steel)vincelordNo ratings yet
- Ce Laws, Contracts and SpecificationsDocument20 pagesCe Laws, Contracts and SpecificationsMIKE ARTHUR DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Module 3 SW5Document13 pagesModule 3 SW5hgfhfghfghgNo ratings yet
- Pre1 1Document43 pagesPre1 1Tooty FrootyNo ratings yet
- Geotech1Lab-Laboratory Work No. 2 PDFDocument4 pagesGeotech1Lab-Laboratory Work No. 2 PDFMarc Carlo IbañezNo ratings yet
- Geometry 100-200Document14 pagesGeometry 100-200Franz Anfernee Felipe GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Ce161p A88 q1 MakeupDocument1 pageCe161p A88 q1 MakeupRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- TRADE-OFF 1 Context 2Document7 pagesTRADE-OFF 1 Context 2jerico habitanNo ratings yet
- 15 Ciap Doc 102 Section 1-5 RobinDocument53 pages15 Ciap Doc 102 Section 1-5 RobinJoshua Ian Aban0% (1)
- Ce 411 MeDocument1 pageCe 411 MeJames Llamera ArgenteNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. Liquid Limit of Soil by Satic Cone PenetrometerDocument2 pagesExperiment No. Liquid Limit of Soil by Satic Cone PenetrometerOpu DebnathNo ratings yet
- Upang Cea 4bsce Cie095 P3Document51 pagesUpang Cea 4bsce Cie095 P3Wheng JNo ratings yet
- Hydrology in Civil EngineeringDocument5 pagesHydrology in Civil EngineeringAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Quantity SurveyingDocument16 pages01 Introduction To Quantity SurveyingNelson Tapsirul0% (1)
- Calculating volumes of earthworks for road constructionDocument3 pagesCalculating volumes of earthworks for road constructionfrancessichNo ratings yet
- Determine Concrete Slump with Slump TestDocument7 pagesDetermine Concrete Slump with Slump Testayat1234No ratings yet
- Level 4 Practice ModuleDocument8 pagesLevel 4 Practice ModuleJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Lec #19 (Permeability Thru Stratified Soils)Document24 pagesLec #19 (Permeability Thru Stratified Soils)Muhammad Irfan100% (1)
- Manual - Laboratory Experiment No. 3 - Measurement of Coefficients of An OrificeDocument11 pagesManual - Laboratory Experiment No. 3 - Measurement of Coefficients of An OrificeDarwin LeeNo ratings yet
- CTPaperII PDFDocument118 pagesCTPaperII PDFindian royal0% (2)
- EarthworkDocument26 pagesEarthworkWan MahiramNo ratings yet
- Areal Precipitation Data AnalysisDocument46 pagesAreal Precipitation Data AnalysisAsjad Ullah100% (1)
- CE408 Environmental Engineering AssignmentDocument1 pageCE408 Environmental Engineering AssignmentmarkhanNo ratings yet
- Preboard Set ADocument6 pagesPreboard Set AJames Bryan Garcia SolimanNo ratings yet
- Electrical-Communication-Security-Fire-Building Service SystemsDocument2 pagesElectrical-Communication-Security-Fire-Building Service SystemsPrincess Morales TyNo ratings yet
- Cebep Reviewer Set 1Document33 pagesCebep Reviewer Set 1Loysa Agtarap MataNo ratings yet
- To Estimate Manning's Roughness Coefficient (N) and Chezy's Coefficient (C) For Open Channel Flow.Document6 pagesTo Estimate Manning's Roughness Coefficient (N) and Chezy's Coefficient (C) For Open Channel Flow.Shaheer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Earthwork Construction Layout Borrow Pit VolumesDocument10 pagesEarthwork Construction Layout Borrow Pit VolumesmovilaNo ratings yet
- Soil Compaction Earthworks Borrow-Pit-Volumes1 PDFDocument9 pagesSoil Compaction Earthworks Borrow-Pit-Volumes1 PDFGnabBangNo ratings yet
- Borrow Pit VolumesDocument10 pagesBorrow Pit VolumesJanaka Ruwan100% (1)
- CE2251 Soil QBDocument29 pagesCE2251 Soil QBShane RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Planning Engineer: Company Namealmajal Alarabi HoldingDocument6 pagesPlanning Engineer: Company Namealmajal Alarabi HoldingShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- NEW (2015) Water Resources and Environmental Breath (Morning) Civil Exam SpecificationsDocument2 pagesNEW (2015) Water Resources and Environmental Breath (Morning) Civil Exam SpecificationsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Figure 303.12. Discharge Through A Triangular Weir.: 303.19.3. Broad-Crested WeirsDocument2 pagesFigure 303.12. Discharge Through A Triangular Weir.: 303.19.3. Broad-Crested WeirsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric pressure and temperature at different elevationsDocument1 pageAtmospheric pressure and temperature at different elevationsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- ENGI6705 StructuralAnalysis ClassNotes3Document39 pagesENGI6705 StructuralAnalysis ClassNotes3s149653No ratings yet
- Mobilization SpecsDocument8 pagesMobilization SpecsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- RatesDocument1 pageRatesShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Foundations: Shallow Foundation Deep FoundationDocument28 pagesTypes of Foundations: Shallow Foundation Deep FoundationLeung Wai YipNo ratings yet
- 303.5. Friction Loss in Open Channels: H LS LDocument2 pages303.5. Friction Loss in Open Channels: H LS LShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- (Merrill Y. Van Wagoner) Spoken Arabic Saudi (Bookos - Org) TextDocument157 pages(Merrill Y. Van Wagoner) Spoken Arabic Saudi (Bookos - Org) TextShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- EquipmentproductivityDocument2 pagesEquipmentproductivityShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- List of Long Lead Items Rev C 11 Oct 2016Document2 pagesList of Long Lead Items Rev C 11 Oct 2016Shafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- RatesDocument1 pageRatesShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Ext 153 Fax No.: 0112154500 2015Document1 pageExt 153 Fax No.: 0112154500 2015Shafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Civ WRE April 2015 - Combined PDFDocument4 pagesCiv WRE April 2015 - Combined PDFShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Sieve Openings PDFDocument3 pagesSieve Openings PDFShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- PE Exam Review - Geotechnical: Demonstration Problem SolutionsDocument34 pagesPE Exam Review - Geotechnical: Demonstration Problem SolutionsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Points, Lines, and Conic SectionsDocument26 pagesPoints, Lines, and Conic SectionsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 06 InfluenceLineBeamsDocument59 pages06 InfluenceLineBeamsPlant MechanicsNo ratings yet
- ENGI6705 StructuralAnalysis ClassNotes3Document39 pagesENGI6705 StructuralAnalysis ClassNotes3s149653No ratings yet
- Aci 2014Document66 pagesAci 2014Shafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- US Standard Sieve Openings: Sieve Number Opening, MM Wire Diameter, MMDocument3 pagesUS Standard Sieve Openings: Sieve Number Opening, MM Wire Diameter, MMShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- STAAD Foundation Advanced ManualDocument456 pagesSTAAD Foundation Advanced ManualMarius Rizea100% (8)
- Pep Rep Geo Technical SolutionsDocument34 pagesPep Rep Geo Technical SolutionsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Test Masters Educational ServicesDocument43 pagesTest Masters Educational ServicesShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 - 001Document26 pagesExam 1 - 001Jose Carlos ArgeñalNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1Shafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro TutorialDocument572 pagesStaad Pro TutorialSammish8383% (12)
- Chapter 5: A Simple E-N Analysis MSC Fatigue 2005 Quickstart GuideDocument26 pagesChapter 5: A Simple E-N Analysis MSC Fatigue 2005 Quickstart Guidesuhas110No ratings yet
- PhotonsDocument56 pagesPhotonsbob jizzleNo ratings yet
- Closed Conduit Hydraulics DesignDocument44 pagesClosed Conduit Hydraulics DesignRaje kNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems Chapter Provides Accurate Physics PracticeDocument4 pagesDaily Practice Problems Chapter Provides Accurate Physics PracticePritam kumar100% (1)
- Links Eng Prod CederjDocument6 pagesLinks Eng Prod CederjHugo CostaNo ratings yet
- Tpas 1965 4766177 PDFDocument7 pagesTpas 1965 4766177 PDFpedramNo ratings yet
- Geometric:Clifford Algebra For PhysicsDocument25 pagesGeometric:Clifford Algebra For PhysicsBho Bho0% (1)
- Refrigeration Unit: Muhammad Tarmizi Bin Abdul Murad (2019883632)Document18 pagesRefrigeration Unit: Muhammad Tarmizi Bin Abdul Murad (2019883632)Lehbron JemsNo ratings yet
- Autumn Break Home Work Class 9Document4 pagesAutumn Break Home Work Class 9nashjrodrigues709No ratings yet
- UNIT 1, Laser, Book NotesDocument12 pagesUNIT 1, Laser, Book NotesPranoy MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- HPLC Heat Exchanger Design PhilosophyDocument28 pagesHPLC Heat Exchanger Design Philosophyagarwalashwin320% (1)
- MV Cables Data Sheet - SampleDocument5 pagesMV Cables Data Sheet - SampleAvoor KhanNo ratings yet
- StewartCalcET8 14 04Document18 pagesStewartCalcET8 14 04OhoodKAlesayiNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication Past Questions and SolutionsDocument25 pagesOptical Communication Past Questions and SolutionsMelsougly BryceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument40 pagesChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsSricharanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays - 1-10Document10 pagesFundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays - 1-10Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Power Grid Earthing CertificatesDocument40 pagesPower Grid Earthing Certificatesshanmugam.sNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment: Viscosity and Density: September 18, 2018Document15 pagesLab Experiment: Viscosity and Density: September 18, 2018Luqman HakimNo ratings yet
- 18 MN216 Fluid Mechanics IDocument2 pages18 MN216 Fluid Mechanics Ijorge luisNo ratings yet
- Force Between Two Parallel Current Carrying Conductors and Definition of Ampere PDFDocument2 pagesForce Between Two Parallel Current Carrying Conductors and Definition of Ampere PDFPrabhuNo ratings yet
- Chipman TransmissionLines TextDocument244 pagesChipman TransmissionLines TextMau Gar Ec83% (6)
- Solar Radiation GeometryDocument8 pagesSolar Radiation GeometryIshant JagotraNo ratings yet
- YZ250F Matlab DocumentationDocument12 pagesYZ250F Matlab DocumentationvivekpattniNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Circular Micro-TubeDocument14 pagesHeat Transfer of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Circular Micro-TubeGaurav KhamesraNo ratings yet
- LPX M930aDocument39 pagesLPX M930aJhonatan CastroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Solution Density & ViscosityDocument18 pagesChemical Solution Density & ViscosityLee JianNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics III (8.06) - Spring 2016 Term Paper 1 Project SummaryDocument12 pagesQuantum Physics III (8.06) - Spring 2016 Term Paper 1 Project Summarybahadoor22i5583No ratings yet
- Electric Power Engineering Lecture NotesDocument209 pagesElectric Power Engineering Lecture NotesRaj Boda0% (1)
- Improved Reactive Power Capability With Grid Connected Doubly Fed Induction GeneratorDocument14 pagesImproved Reactive Power Capability With Grid Connected Doubly Fed Induction GeneratorUday Wankar100% (2)
- Pair-Ion Plasma Generation Using FullerenesDocument5 pagesPair-Ion Plasma Generation Using FullerenesAhmad Imran KhanNo ratings yet