Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leukemia Bone Marrow Cancer
Uploaded by
roonn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesLeukemia is a term derived from the Greek words "leukos" and "heima", meaning "white blood cells" the white blood cells fight infection, while the red blood cells carry oxygen and the platelets help blood to clot. Chronic leukemia means that the cells can still do the work of normal white blodd cells but the cancer is slowly growing.
Original Description:
Original Title
Leukemia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLeukemia is a term derived from the Greek words "leukos" and "heima", meaning "white blood cells" the white blood cells fight infection, while the red blood cells carry oxygen and the platelets help blood to clot. Chronic leukemia means that the cells can still do the work of normal white blodd cells but the cancer is slowly growing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesLeukemia Bone Marrow Cancer
Uploaded by
roonnLeukemia is a term derived from the Greek words "leukos" and "heima", meaning "white blood cells" the white blood cells fight infection, while the red blood cells carry oxygen and the platelets help blood to clot. Chronic leukemia means that the cells can still do the work of normal white blodd cells but the cancer is slowly growing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Leukemia: Cancer of the Bone Marrow
Sep 15, 2014
Leukemia, known as cancer of the blood cells, is an abnormal rise in the number of white blood cells. These white
blood cells crowd out other blood cells like the red blood cells and platelets. Remember that the white blood cells
fight infection, while the red blood cells carry oxygen and the platelets help blood to clot.
Leukemia is a term derived from the Greek words leukos and heima, meaning white blood
cells. Leukemis is the abnormal growing in numbers of the white blood cells in the bone
marrow. Thus, they are unable to fight infection the way which a normal white blood cell should
do. As these combines, they interfere with the functions of vital organs which also includes the
production of healthy blood cells. And when the body does not have enough red blood cell that
will supply oxygen, the enough platelets to ensure proper clotting and enough normal white
blood cells to fight body infections, it will result to being anemic and vulnerable to bleeding and
infection.
Leukemia is grouped by how quickly it develops (acute or chronic), or by the type of blood cell
that is affected (lymphocytes or myelocytes). Chronic leukemia means that the cells can still do
the work of normal white blodd cells but the cancer is slowly growing. While in acute leukemia,
the cells can't do any of the work because the cells increases rapidly which means it worsens
quickly.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)is the most common adult leukemia, affecting people
over the age of 55.
Acute lymphocytic or lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)affects lymphoid cells and
grows quickly. This is the most common type of leukemia among young children, but
also occurs in adults.
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)usually grows slowly at first, and mainly affects
the adults. There will be few or no symptoms for the first few months, but the
leukemia cells grow quickly in a certain phase.
Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)is a common type of leukemia that occurs in
both children and adults. AML is the most common acute leukemia in adults.
Both chronic and acute leukemia include symptoms like the following:
swollen lymph nodes that don't hurt
frequent infections
swelling or discomfort in the abdomen (may be from a swollen spleen or liver)
fevers or night sweats
feeling weak or tired
pain in the bones or joints
bleeding and bruising easily
weight loss or the loss of appetite with no known reason
Though these symptoms may appear, routine blood test will guarantee if one does have
leukemia. Aside from blood test, there are also other test to be done for the doctor to verify the
leukemia, and which type it would be.
Other tests to be done may include:
Physical exam- for swollen lymph nodes, spleen or liver.
Biopsy- wherein the doctor will get a sample of your tissue to know if the leukemia
cells are in your bone marrow already. Bone marrow aspirationis when the doctor
uses thick, hollow needle to get samples of bone marrow. But when the doctor
remove a small piece of bone and bone marrow, it is calledbone marrow biopsy.
Cytogenetics- This type of test looks at the choromosomes of cells from the
samples of blood, bone marrow and lymph nodes. If abnormal cells are found, then
the type of leukemia can be identified.
Spinal tap- It is the removing of the cerebrospinal fluid, which is found in and
around the brain and spinal cord, to check for leukemia cells.
Chest X-ray- Swollen lymph nodes or other signs of disease in the chest usually
shows in an x-ray.
You might also like
- Name: Babafemi Bunmi Oluwatosin Reg No. VU-BNS-2001-0049 Course: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Topic: Leukemia (Blood Cancer)Document7 pagesName: Babafemi Bunmi Oluwatosin Reg No. VU-BNS-2001-0049 Course: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Topic: Leukemia (Blood Cancer)Bunmi OluwatosinNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument34 pagesLeukemiaAnnie Lou AbrahamNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia?Document21 pagesWhat Is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia?hawinnurdianaNo ratings yet
- Types and Treatment of LeukemiaDocument14 pagesTypes and Treatment of LeukemiaalirezaNo ratings yet
- Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument6 pagesLymphocytic Leukemiaル シリ100% (1)
- Nursing Assessment of a Client with LeukemiaDocument25 pagesNursing Assessment of a Client with LeukemiaMyLucky DecodeNo ratings yet
- Leukemia NotesDocument22 pagesLeukemia NotesJess NinaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Group 4 - 9 - Einstein Abilene Reglos Danica Cabalmarian Isabel Matampac JP Deveraturda James Guillen PenaflorDocument49 pagesLeukemia: Group 4 - 9 - Einstein Abilene Reglos Danica Cabalmarian Isabel Matampac JP Deveraturda James Guillen PenaflorTheSAmeNonsenseNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR OUTLINE TOPIC leukeDocument6 pagesSEMINAR OUTLINE TOPIC leukemarvellousjulius90No ratings yet
- Leukemia - Topic OverviewDocument5 pagesLeukemia - Topic OverviewPhilipus Putra RaharjoNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIADocument20 pagesLEUKEMIAHafsaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument3 pagesLeukemiacindya13No ratings yet
- Lymphomas and LeukemiasDocument27 pagesLymphomas and LeukemiasgraceNo ratings yet
- What Is LeukemiaDocument13 pagesWhat Is Leukemiazaid505No ratings yet
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument5 pagesAcute Lymphocytic LeukemiaRatna DewiNo ratings yet
- Leukaemia and Lymphoma Whats The DifferenceDocument7 pagesLeukaemia and Lymphoma Whats The Differencepaul_calburean7899No ratings yet
- Leukemia: Neha Srivastava Senior Nursing Tutor PipramsDocument54 pagesLeukemia: Neha Srivastava Senior Nursing Tutor PipramsVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Leukemia Techical Description 1Document5 pagesLeukemia Techical Description 1api-253514816No ratings yet
- Leukemia What Is Leukemia?Document2 pagesLeukemia What Is Leukemia?Ctn ZQNo ratings yet
- Leukemia PDFDocument36 pagesLeukemia PDFOjika OlandaNo ratings yet
- What Is LeukemiaDocument8 pagesWhat Is LeukemiaVicky ShuarNo ratings yet
- Pathway LeukemiaDocument2 pagesPathway LeukemiaAmbar RahmanNo ratings yet
- What Is Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?Document7 pagesWhat Is Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?Marcelina ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and TypesDocument17 pagesAcute Lymphocytic Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and TypesfxkryxieNo ratings yet
- Leukemia ReportDocument5 pagesLeukemia ReportCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About LeukemiaDocument14 pagesEverything You Need to Know About LeukemiaAkmal HamdanNo ratings yet
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionDocument6 pagesProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument58 pagesAcute Myeloid LeukemiaFernando ValenNo ratings yet
- Amity Institute of Biotechnology: Topic-Leukemia (2017-2018)Document23 pagesAmity Institute of Biotechnology: Topic-Leukemia (2017-2018)AkshitaNo ratings yet
- What is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALLDocument43 pagesWhat is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALLCormeus BaltiNo ratings yet
- HND 3Document12 pagesHND 3arham pirachaNo ratings yet
- Blood CancerDocument9 pagesBlood CancerSneha Sinha100% (1)
- Teks LeukemiaDocument6 pagesTeks LeukemiaDewi FOrtyunaNo ratings yet
- Blood Clinical CorellaionsDocument12 pagesBlood Clinical Corellaionssinte beyuNo ratings yet
- 32 - Kesar Patil-Biology ProjectDocument16 pages32 - Kesar Patil-Biology ProjectKesarNo ratings yet
- What Is LeukemiaDocument11 pagesWhat Is LeukemiaNazneen RagasaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: What You Need To Know AboutDocument36 pagesLeukemia: What You Need To Know AboutOsama AlrawabNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii - Discussion of The DiseaseDocument13 pagesChapter Iii - Discussion of The DiseaseJemima LaigoNo ratings yet
- Blood CancerDocument3 pagesBlood CancerReshma kumari100% (1)
- What Is LeukopeniaDocument8 pagesWhat Is LeukopeniaMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- Blood Diseases ProjectDocument31 pagesBlood Diseases ProjectRomyn MoazNo ratings yet
- Bio CompleteDocument20 pagesBio Completeeshani0706No ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument13 pagesLeukemiaWasan JalalNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Leukemia in ChildrenDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Leukemia in ChildrenKenia Isabel PavónNo ratings yet
- Leukemia-Chronic Myeloid (Myelogenous) Overview: What Is Cancer?Document28 pagesLeukemia-Chronic Myeloid (Myelogenous) Overview: What Is Cancer?Glenda GalanganNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument16 pagesLeukemiaclaudespeed047No ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument10 pagesLeukemiaEslam El HaddadNo ratings yet
- Blood CancerDocument8 pagesBlood Cancergoranshamil62No ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument6 pagesChronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaJhannNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Apolonio, Leizel, R. Corpuz Rolyn Mañalac Joelle Anne Señeres Loui AnneDocument33 pagesGroup 1 Apolonio, Leizel, R. Corpuz Rolyn Mañalac Joelle Anne Señeres Loui AnneLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument17 pagesLeukemiaThe Visista EnterpreneursNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument7 pagesAcute Lymphocytic LeukemiaKim Enrico JumarangNo ratings yet
- ALL Case PresentationDocument43 pagesALL Case PresentationMonica MoralesNo ratings yet
- Leukaemia: Image Description. Better Health Channel Logo End of Image DescriptionDocument4 pagesLeukaemia: Image Description. Better Health Channel Logo End of Image DescriptionkapczukNo ratings yet
- About Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Overview of CMLDocument10 pagesAbout Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Overview of CMLthainaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic AnemiaDocument43 pagesChronic Lymphocytic Anemiashobekai30No ratings yet
- Surviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsFrom EverandSurviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSickle Cell Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Math: Vianca M. Estabillo Grade V Ruby Jennilyn Pagdanganan AdviserDocument2 pagesWorksheet in Math: Vianca M. Estabillo Grade V Ruby Jennilyn Pagdanganan AdviserroonnNo ratings yet
- 5 Simple Steps To Do When Iqama Got LostDocument1 page5 Simple Steps To Do When Iqama Got LostroonnNo ratings yet
- The Medical Surgical NurseDocument2 pagesThe Medical Surgical Nurseroonn100% (3)
- Bernadeth P. Solomon BSN Lll-A The Effectiveness of Motorised Lumbar Traction in The Management of LBP With Lumbo Sacral Nerve Root Involvement: A Feasibility Study Annette A Harte1Document5 pagesBernadeth P. Solomon BSN Lll-A The Effectiveness of Motorised Lumbar Traction in The Management of LBP With Lumbo Sacral Nerve Root Involvement: A Feasibility Study Annette A Harte1roonnNo ratings yet
- Bernadeth P. Solomon BSN Lll-A The Effectiveness of Motorised Lumbar Traction in The Management of LBP With Lumbo Sacral Nerve Root Involvement: A Feasibility Study Annette A Harte1Document5 pagesBernadeth P. Solomon BSN Lll-A The Effectiveness of Motorised Lumbar Traction in The Management of LBP With Lumbo Sacral Nerve Root Involvement: A Feasibility Study Annette A Harte1roonnNo ratings yet
- YouDocument1 pageYouroonnNo ratings yet
- Print This JournalDocument4 pagesPrint This JournalroonnNo ratings yet
- BSP ProvincialDocument1 pageBSP ProvincialroonnNo ratings yet
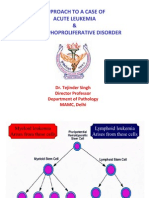
- 01 Approach To A Case Leukemia and Lymphoproliferative DisorDocument49 pages01 Approach To A Case Leukemia and Lymphoproliferative DisorcandiddreamsNo ratings yet
- Biomed TrackerDocument30 pagesBiomed TrackerBarath R BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Robbins Pathology Chapter 13 - White Blood CellsDocument7 pagesRobbins Pathology Chapter 13 - White Blood Cellsscorpiosphinx7980% (5)
- Clasificacion de Linfomas BDocument25 pagesClasificacion de Linfomas BFiorella SalvatNo ratings yet
- Questions - Hematology IndiaDocument22 pagesQuestions - Hematology Indiaamba100% (1)
- Step 2 CK Review - HematologyDocument18 pagesStep 2 CK Review - Hematologyrsmd1986No ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument12 pagesLeukemiaDingdong-didiNo ratings yet
- Hematology & Oncology - Passmedicine 2012Document64 pagesHematology & Oncology - Passmedicine 2012dheajst100% (1)
- Hematologic (Blood) Diseases GuideDocument24 pagesHematologic (Blood) Diseases GuideMasha FloreaNo ratings yet
- Updates For Haploidentical Hematopoietic Transplantation OutcomesDocument46 pagesUpdates For Haploidentical Hematopoietic Transplantation OutcomesaymenNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument8 pagesLeukemiapriscillaNo ratings yet
- Hematology QuestionsDocument13 pagesHematology QuestionsGlazel TulaganNo ratings yet
- Clinical Haematology 201 256Document38 pagesClinical Haematology 201 256Ahmed El AlfyNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C Virus: 1. Exposure DataDocument34 pagesHepatitis C Virus: 1. Exposure DataMagopet RobertNo ratings yet
- IGHV Mutation AnalysisDocument2 pagesIGHV Mutation AnalysisCGIdocsNo ratings yet
- Why Does My Patient Limphadenopathy or Splenomegaly?Document14 pagesWhy Does My Patient Limphadenopathy or Splenomegaly?lacmftcNo ratings yet
- First Aid Haematology Key PointsDocument9 pagesFirst Aid Haematology Key Pointsnaeem2009No ratings yet
- 2017 10Document200 pages2017 10Eduardo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Non-Hodgkin's LymphomasDocument23 pagesNon-Hodgkin's LymphomasshevmyrNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Document38 pagesChronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Vikkineshwaran Siva Subramaniam100% (2)
- Leukemia ReportDocument5 pagesLeukemia ReportCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- A Pattern Approach To Lymph Node Diagnosis - A. Leong (Springer, 2011) WWDocument432 pagesA Pattern Approach To Lymph Node Diagnosis - A. Leong (Springer, 2011) WWAdrian TirlaNo ratings yet
- Oral PathologyDocument184 pagesOral Pathologyyalahopa100% (1)
- Malignant LymphomaDocument3 pagesMalignant LymphomaKakaa KakaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Leukaemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Leukaemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentArnab Ghosh100% (1)
- Peripheral Blood SmearDocument3 pagesPeripheral Blood SmearJosephine Armanne AluyenNo ratings yet
- Non Hodgkin LymphomaDocument9 pagesNon Hodgkin LymphomaAhmad SaifulNo ratings yet
- Hematologic/Blood Cancers: Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia AdultDocument13 pagesHematologic/Blood Cancers: Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Adulthoney bunnyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Leukemia: Causes, Types, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument38 pagesUnderstanding Leukemia: Causes, Types, Symptoms and TreatmentAlvinCandraNo ratings yet