Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Malaysia Technical-Notes-on-SI - Good PDF
Uploaded by
gahsoon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views11 pagesSI
Original Title
Malaysia Technical-Notes-on-SI - good.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views11 pagesMalaysia Technical-Notes-on-SI - Good PDF
Uploaded by
gahsoonSI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
GENERAL TECHNICAL NOTES
FOR SITE INVESTIGATION WORKS
MALAYSIAN SITE INVESTIGATORS ASSOCIATION
Compiled by MSIA
From references and contributors
APPENDIX A GEOTECHNICAL DESIGN CRITERIA FOR ROAD WORKS
APPENDIX B - LIST OF LABORATORY & INSITU TESTS
APPENDIX C LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS / SYMBOLS
APPENDIX D - APPLICABILITY OF COMMON FIELD OR INSITU TESTS
APPENDIX D1- SCOPE OF SI AND SI METHODS
APPENDIX E COMMON SAMPLERS
APPENDIX F - LIST OF STANDARD SIZES OF DRILLING RODS. CORE BITS & CASING
APPENDIX G QUALITY OF SAMPLES (AFTER ROWE)
APPENDIX H - GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION OF SUMMARY OF SCOPE OF SI WORKS
(DESIGN OF SCOPE OF SI FOR ROAD PROJECTS)
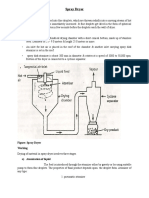
Figure 1 - FLOW-CHART FOR SI WORKS
APPENDIX A
GEOTECHNICAL DESIGN CRITERIA FOR ROAD WORKS
DESIGN COMPONENT
MODE OF FAILURE
MINIMUM
FACTOR OF
SAFETY
DESIGN
LIFE
(durability
of materials)
MAXIMUM PERMISSIBLE MOVEMENTS
VERTICAL
LATERAL
DIFFERENTIAL
1. Unreinforced Slopes
1.1 Local & global stability
(cut & fill slopes)
1.2 Bearing (fill)
1.20
2.0
75 yrs
2. Reinforced or treated
slopes (not on soft
ground)
2.1 Local & global stability
(cut & fill slopes)
2.2 Bearing (fill)
1.50
1.5
75 yrs
Analysis should be according to GEOTECHNICAL MANUAL FOR SLOPES
(1984), GEO Hong Kong
3. Permanent Anchors
3.1 Tensile Resistance
3.2 Resistance at Soil
Grout Interface
3.3 Creep/corrosion
2.0
3.0
75 yrs
Geo Spec 1 (1989), GEO Hong Kong
BS 8081
4. Rigid Retaining
Structures
4.1 Overturning
4.2 Sliding
4.3 Overall Stability
4.4 Bearing
1.8
1.6
1.5
2.0
75 yrs
15 mm along
face of wall
Geoguide 1 (1983), GEO Hong Kong
15 mm along
face of wall
1:150
along face of wall
5. Reinforced fill walls/
structures
External Stability
120 yrs
5mm per metre height
15mm from reference alignment
1:100
along face of wall
Internal Stability
BS 8006
6. Individual Foundation
Piles (mainly under axial
loads)
6.1 Shaft Resistance
2.0
75 yrs
12 mm along axis of pile
at pile head at design load.
38 mm or 10% pile size
at pile head at twice design load.
6.2 Base Resistance
2.0
BS 8004
7. Individual Foundation
loads (mainly under lateral &
bending loads perpendi-
cular to axist of pile)
Ultimate lateral
Resistance
2.5
75 yrs
12 mm along axis of pile
at pile head at design load
BS 8004
12 mm perpendicular to axis of
pile at design load
8. Pile group
Block Bearing Capacity
2.0
75 yrs
12 mm at Working Load
BS 8004
10 mm
9. Piles as retaining
structures
As for 4, 6 & 7 above
As for
individual
foundation
piles
75 yrs
As 4 above for rigid retaining structures
BS 8004
10. Embankment on Soft
Ground
11.1 Bearing (short term)
11.2 Local & global slope
stability (long term)
1.4
1.2
75 yrs
- Total post construction settlement < 400 mm
- 5 years post construction settlement < 100 mm (or 10% of estimated ultimate settlement)
(For embankment within 10 m from bridge abutment, the above settlement criteria should be reduced to 15%).
APPENDIX B
LIST OF LABORATORY & INSITU TESTS
1. Soil Classification Tests: BS 1377: Part 2: 1990
Moisture content, Liquid limit, Plastic limit, Plasticity index, linear shrinkage, particle size distribution.
(These tests are from disturbed samples such as split spoon samplers (SPT), bulk samples, etc.).
2. Chemical & Electro-chemical Tests: BS 1377 Part 3: 1990
Organic matter content, Mass loss on ignition, Sulphate content of soil and ground water, Carbonate
content, Chloride content, Total dissolved solids, pH value, Resistivity and Redox potential.
3. Compaction-related Tests: BS 1377: Part 4
(These tests are from bulk samples)
3.1 Dry density - moisture relationship (2.5 kg/4.5 kg hammer)
- Soil with some coarse gravels
- vibrating method
3.2 Moisture condition value (MCV)
3.3 CBR tests
4.* Compressibility, Permeability and Durability Tests: BS 1377: Part 5
4.1 1-D consolidation test
4.2 Swelling and collapse tests
4.3 Permeability by constant head
4.4 Dispersibility
5.* Consolidation & Permeability Tests in Hydraulic Cells &
with pore pressure measurements: BS 1377: Part 6
5.1 Consolidation Properties using hydraulic cell
5.2 Permeability in hydraulic consolidation cell
5.3 Isotropic consolidated properties using triaxial cell
5.4 Permeability in a triaxial cell
6.* Shear Strength Tests (Total Stress) BS 1377: Part 7
6.1 Lab vane shear
6.2 Direct shear box (small)
6.3 Direct shear box (large)
6.4 Residual strength
6.5 Undrained shear strength (UU)
6.6 Undrained shear strength (multi loading)
7.* Shear Strength Tests (Effective Stress) BS 1377: Part 8
7.1 CIU with pore pressure measurement
7.2 CD with pore pressure measurement
8. Insitu Tests: BS 1377: Part 9
Field Density (cone, sand replacement & balloon), CBR, SPT, Plate Bearing, Vane shear (Acker,
Geonor, cylindrical), DS (Static Dutch Cone), Piezocone Test, etc.
* These tests are from undisturbed samples (thin wall samplers, piston samplers, Mazier samplers, block
samples etc).
APPENDIX C
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS/SYMBOLS
ACEM = Association of Consulting Engineers Malaysia
ASTM = American Society For Testing And Meterials
BS = British Standard
BQ = Bills of Quantities
C
c
= Compression Index
C
v
= Coef. of Consolidation
C
1
= Effective Cohesion
Cu = Cohesion
CBR = California Bearing Ratio
CIDB = Construction Industry Development Board
CU = Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Test
CD = Consolidated Drained Triaxial Test
CIUC = Consolidated Undrained Compression Triaxial Test With Pore Pressure
Measurement (Effective stress)
CIUE = - Ditto - extension
Ck
o
UC = Consolidated Undrained Compression At Ko Conditions
DB = Deep Boring (rotary drilling)
DS = Deep Sounding (Static Dutch Cone Penetrometer)
GL = Ground Level
HA = Hand Auger
HMLC = 65 mm Triple Tube Core Barrel (DCMA)
IEM = Institution of Engineers Malaysia
JKR = Jabatan Kerja Raya
LL = Liquid Limit
M/C = Moisture Content
M
v
= Coef. of Compressibility
MHB = Motorized Hand Boring (Wash Boring/Percussion Drilling)
MS = Malaysian Standard
NW = N Size Casing (101.6 mm diam)
NMLC = 52 mm Triple Tube Core Barrel (DCMA)
P.Eng = Professional Engineer registered with Board of Engineers Malaysia
pH = Acidity Index
PL = Plastic Limit
PI = Plasticity Index
Pc = Effective Preconsolidated Pressure
RL = Reduced Level
RQD = Rock Quality Designation
R/r = Recovery Ratio
SI = Site Investigation
SPT = Standard Penetration Test
TNW = 61 mm Double Tube Core Barrel (Atlas Copco)
UU = Unconsolidated Undrained Test gives undrained shear strength (total stresses)
UCS = Unconfined Compression Strength
WT = Water Table
APPENDIX D
APPLICABILITY OF COMMON FIELD OR INSITU TESTS
FIELD TESTS
Soil
Soil
Rock
SOIL TYPE
SOIL PARAMETERS
type
Profile
H.Rock
S.Rock
Gr
Sand
Silt
Clay
Peat
Cu
Mv
Cv
K
1.
Penetrometer
1.1 JKR Probe
1.2 SPT
1.3 DS (CPT)
1.4 Piezocone (CPTU)
1.5 Flat Dilatometer
1.6 Resistivity Probe
X
A
B
A
B
C
C
B
A
A
A
C
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
B
X
X
X
X
C
B
B
A
C
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
X
B
C
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
C
X
X
C
A
C
X
X
X
C
A
C
X
X
X
X
B
X
X
2
3
4
5.
Vane Shear
PB Pressuremeter
SB Pressuremeter
Continuous Soil Sampling
B
B
B
A
C
B
B
A
X
C
C
X
X
A
B
B
X
B
B
B
X
B
B
A
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
A
X
X
B
C
A
B
B
B
X
B
B
B
X
C
B
B
X
X
B
C
Legends:-
A = suitable/useful = effective frictional angle K = coef. of permeability
B = moderate Cu = undrained strength
C = doubtful Mv = coef. of volume compressibility
X = not suitable Cv = coef. of consolidation
SCOPE OF SI & SI METHODS
Geophysical Geophysical Sounding Boring and Sampling Ground Loading
survey Logging water Test
Boring and Rock-core
SI Method Seismic Electric soil sampling boring
Scope & purpose of SI
by type of road structure
Identify soil & rock weathering profile A A B A B B B A B A B
suitability of construction material survey A B B B B B A A A
subgrade investigation rock B B
(after excavation) soil B B B A B A
Stability rock A B B A B B B B A B
soil A B B B B B B B A B B B A B B A B B B B A B
Identify soil & rock weathering profile A B B B B B A B B A B
suitability of construction material survey A B B B B A A B A B
surface deposit A A B B B B A A B B A B B B B
rock property (strength, etc) A A B A A A B B A A B A B B A
geologic strata (fault, etc) A A B B B A A A A A B B A A A B B B A
see-page B B A A B B A B B A B B A B A
tulus B B A B B
mountainous sand gravel B B A B B
sandy soil B B B A B B
clayey soil B B B A B B B B
rolling/flat sandy soil B B B B B A B B
clayey soil B B B B B B A A B B
sandy soil A A A B A B B B A B
flat (soft) clayey soil A A A B A A B A A A B
peat A A A B A B B A A A B
foundation for pipe culvert, retaining wall (toe wall <2m) A B B B B A B A B B B B
structures with mountainous/rolling B B A B B B A B A
small-medium flat (general) B A B B A B B A B B A
scale flat (soft) B A B ** A B A A A
supporting strata B B A B A B B B A B A A
mountainous excavation B B A B A B A A A
structures /rolling large scale excavation B B A B A B A B A A A
with supporting strata B B B B A B B A B A B B A B A
large flat (general) excavation B B B B A B B A B A B B A B A A
scale excavation below water level B B B B A B B A B A A A A
supporting strata B A A A B A A B A B A
flat (soft) excavation B A A B B A A A B A A
excavation below water level A A B B A A A A B A
A : applicable
B : supplementary or may be applicable
APPENDIX D1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
m
e
t
e
r
T
e
s
t
H
o
r
i
z
o
n
t
a
l
B
o
r
i
n
g
P
a
c
k
e
r
T
e
s
t
/
S
e
e
p
a
g
e
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
P
u
m
p
i
n
g
o
r
P
e
r
m
e
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
T
e
s
t
V
a
r
i
a
t
i
o
n
i
n
G
r
o
u
n
d
W
a
t
e
r
L
e
v
e
l
P
l
a
t
e
/
L
o
a
d
i
n
g
T
e
s
t
T
e
s
t
P
i
t
/
T
r
e
n
c
h
H
o
r
i
z
o
n
t
a
l
I
n
c
l
i
n
e
d
V
e
r
t
i
c
a
l
H
a
n
d
A
u
g
e
r
i
n
g
T
h
i
n
W
a
l
l
T
u
b
e
D
o
u
b
l
e
o
r
T
r
i
p
l
e
T
u
b
e
C
o
n
t
i
n
u
o
u
s
F
o
i
l
S
a
m
p
l
i
n
g
I
n
S
i
t
u
V
a
n
e
T
e
s
t
S
P
T
D
u
t
c
h
C
o
n
e
P
e
n
e
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
T
e
s
t
(
D
S
)
J
K
R
P
r
o
b
e
F
l
a
t
D
i
l
a
t
o
m
e
t
e
r
T
e
s
t
P
i
e
z
o
c
o
n
P
S
W
a
v
e
R
e
f
l
e
c
t
i
o
n
E
l
e
c
t
r
i
c
N
u
c
l
e
o
n
i
c
H
o
r
i
z
o
n
t
a
l
V
e
r
t
i
c
a
l
S
.
W
a
v
e
R
e
f
r
a
c
t
i
o
n
V
e
l
o
c
i
t
y
S
t
r
u
c
t
u
r
e
F
i
l
l
I
n
s
p
e
c
t
i
o
n
/
W
a
l
k
-
O
v
e
r
S
u
r
v
e
y
P
.
W
a
v
e
R
e
f
r
a
c
t
i
o
n
C
u
t
B
o
r
r
o
w
P
i
t
T
u
n
n
e
l
F
i
l
l
APPENDIX E
COMMON SAMPLERS
TYPE OF SAMPLERS
REMARKS
1. OPEN DRIVE SAMPLERS
1.1 Split-spoon for SPT
1.2 Thin-wall sampler
1.3 Thick wall sampler
(50mm, 75mm, 100mm, 150mm).
2. THIN-WALL SAMPLER WITH
STATIONARY PISTON
(50mm, 75mm, 100mm, 150mm)
3. DENISON SAMPLER
(Double tube with thin wall tube)
4. MAZIER SAMPLER
(74mm)
5. FOIL CONTINUOUS SAMPLERS
(DELFT 29mm, 66mm OR SWEDISH
SAMPLER 68mm diam)
6. BLOCK SAMPLING
7. ROTARY ROCK CORE SAMPLERS
1. No piston; penetration by static thrust or
dynamic impact; suitable for almost all
types of soils except gravelly soils or
hard/dense materials.
2. The most reliable sampler to procure
undisturbe soft to stiff cohesive soils; area
ratio is usually about 10%. The inside
clearance ratio shall be 0.5 to 1%. Mainly
for shear strength & consolidation tests.
3. No piston; suitable for stiff to very stiff
cohesive soil and sandy soil (SPT = 4-20);
open drive sampler
4. Triple tube sampler; usual core size 74mm
diam & PW casing is required; air foam
drilling technique is preferred to procure
high quality undisturbed samples from
residual soils. Not suitable for gravelly
soils.
5. With stationary piston; suitable for minor
stratification ie sand seams because of
continuous samples of 5 to 8m can be
procured.
Continuous samples for soil fabrics &
stratigraphical or profiling evaluation etc.
6. Blocks of soil (200 to 350mm cubes) cut
from test pits; Need careful sealing and
handling. Mainly for triaxial, shear box &
permeability tests.
7. Double tube core barrels for strong rock
(Grade 1 or 2): 30mm; 42mm; 54mm;
TNW, 61mm; T2-76, 62mm.
Triple tube core barrels for fractured rock;
HMLC, 52mm; HMLC, 64mm
Notes:
1. Std. sampler size (UK): 50, 75, 100, 150, 250 mm diam
Std. sampler size (US): 1 1/2, 2, 2 1/2, 3, 4, 5 inches diam
2. Samples should be labeled, handled, transported and extruded carefully in accordance with BS 5930.
APPENDIX F
LIST OF STANDARD SIZES OF DRILLING RODS.
CORE BITS & CASING
ASTMD2113
DCMA
E,A,B,N,H,P = 1 1/2", 2", 3", 4", 5"
TABLE 1 Core Bit Sizes
__________________________________________________
Outside Diameter Inside Diameter
_______________ _______________
Size Designation in mm In mm
__________________________________________________
Core size RWT 1.16 29.5 0.375 18.7 WF series (BS4019)
(mm) EWT 1.47 37.3 0.905 22.9 WT series (CDDA)
T2-76 62 EWG, EWM 1.47 37.3 0.845 21.4 WM series (DCMA)
Double TNW 61 AWT 1.88 47.6 1.282 32.5 Craelius T or K series
Tube T2-101 84 AWG, AWM 1.88 47.6 1.185 30.0 (Atlas Copco)
T6-101 79 BWT 2.35 59.5 1.750 44.5
BWG, BWM 2.35 59.5 1.655 42.0
NMLC 52 NWT 2.97 75.3 2.313 58.7
Triple HMLC 64 NWG, NWM 2.97 75.3 2.155 54.7
Tube 3C-MLC 76 2 3/4 x 3 7/8 3.84 97.5 2.69 68.3
C-MLC 102 HWT 3.89 98.8 3.187 80.9
HWG, ... 3.89 98.8 3.000 76.2
4 x 5 1/2 5.44 138.0 3.97 100.8
6 x 7 3/4 7.66 194.4 5.97 151.6
__________________________________________________
K3 - 76 48
Tb - 76 57
K3 - 86 58
TABLE 2 Casing Sizes
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Size Designation Outside Diameter Inside Diameter Will Fit Hole Drilled with
_______________ _______________ Threads per in. Core Bit Size
in mm in mm
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
RW 1.144 36.5 1.19 30.1 5 EWT, EWG, EWM
EW 1.81 46.0 1.50 38.1 4 AWT, AWG, AWM
AW 2.25 57.1 1.91 48.4 4 BWT, BWG, BWM
BW 2.88 73.0 2.38 60.3 4 NWT, NWG, NWM
NW 3.50 88.9 3.00 76.2 4 HWT, HWG
HW 4.50 114.3 4.00 101.6 4 4 x 5 1/2
PW 5.50 139.7 5.00 127.0 3 6 x 7 3/4
SW 6.63 168.2 6.00 152.4 3 6 x 7 3/4
UM 7.63 193.6 7.00 177.8 2 ...
ZW 8.63 219.0 8.00 203.2 2 ...
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
TABLE 3 Drill Rods
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Size Designation Rod and Coupling Outside Rod Inside Diameter Coupling Bore, Threads
______________________ ______________________ ____________________________
in mm in mm in mm per in
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
RW 1.09 27.7 0.72 18.2 0.41 10.3 4
EW 1.38 34.9 1.00 25.4 0.44 11.1 3
AW 1.72 43.6 1.34 34.1 0.63 15.8 3
BW 2.13 53.9 1.75 44.4 0.75 19.0 3
NW 2.63 66.6 2.25 57.1 1.38 34.9 3
HW 3.50 88.9 3.06 77.7 2.38 60.3 3
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
APPENDIX G
QUALITY OF SAMPLES (AFTER ROWE)
Quality
Class
Properties
Purpose
Typical Sampling
Procedure
1
- Remoulded properties
- Fabric
- Water content
- Density and porosity
- Compressibility & deformation
- Effective strength parameters
- Total strength parameters
- Permeability*
- Consolidation*
Laboratory data on
in situ soils
(classification tests
& engineering
properties)
Piston thin walled
sampler with water
balance
Mazier sampler with
foam drilling
Block samples
2
- Remoulded properties
- Fabric
- Water content
- Density and porosity
- Compressibility and
deformation*
- Effective strength parameters*
- Total strength parameters*
Laboratory data on
in situ insensitive
soils
Pressed or driven
thin
or thick walled
sampler with water
balance
Mazier sampler
3
- Remoulded properties
- Fabric A * 100% recovery.
Continuous
B * 90% recovery.
Consecutive
Fabric examination
and laboratory data
on remoulded soils
Pressed or driven
thin or thick walled
samplers. Water
balance in highly
permeable soils.
4
- Remoulded properties
Laboratory data on
remoulded soils.
Sequence of strata
Bulk and jar samples
(from SPT split
samplers)
5
None
Aproximate
sequence
of strata only
Washings (washed
samples)
* Items changed from original German classification (7th. Int. Conf. Soil Mech. Foundn.
Engng. Mexico 1969).
APPENDIX H
GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION OF SUMMARY OF SCOPE OF SI WORKS
(DESIGN OF SCOPE OF SI FOR ROAD PROJECTS)
Summary of Scope of SI Works with the following details should be given to the SI
Contractor:
1. Brief project description and objectives of SI.
2. SI Methods & Locations (Scope of SI Works)
- Types & methods SI & the brief quantities should be summarized & indicated
- Locations of SI shown on Drawings should be indicated
3. Criteria of Terminating Boreholes
Criteria of terminating boreholes or other SI methods should be clearly indicated, eg,
in Cut Areas, in fill areas (in soft ground/swamp and residual soil areas) and in
structure areas.
4. Field testing & sampling criteria
Types & frequency of various field testing & sampling should be specified.
5. Laboratory Testing
Types of lab testing & the selection criteria of samples should be specified.
6. Special requirements
Special requirements about SI methods, testing & sampling if any should be clearly
mentioned. Method Statement for SI methods & tests plus works programme shall be
submitted to the Designer at least 3 working days before commencement of SI works.
* Example of Scope of SI Works for road project is enclosed.
* Scope of SI works are based on Guidelines for planning SI works for Road Projects
OK
Detail Geotechnical Design
Prepare factual SI interpretative report by Designer
End
Prepare factual SI report (SI Contractor)
NO
Additional SI ?
Execute SI works programme
Determine scope of Lab tests
Direct, supervise and monitor SI Works by Designer
Yes
OK
NOT
OK
NOT
OK
Identify likely geotechnical issues & problems
Determine design parameters required
Prepare SI programme & budget
Preliminary Project Appraisal
Desk Studies
Site reconnaissance
Preliminary SI
Preliminary Engineering Assessment
Project Brief
Scope of Works
Design Criteria
Define Project Work Plan
Project Initiation
Audit by Expert
Design or determine scope of SI in detail (see Appendix H)
Preparation of tender/contract documents, BQ & Spec.
Send SI proposal to client for
approval
Fig 1: Flow-chart for SI works
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Klang Standard Drain DrawingDocument1 pageKlang Standard Drain DrawinggahsoonNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Qi GongDocument83 pagesQi GonggahsoonNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Perspec Prime Daily Earthwork RecordsDocument1 pagePerspec Prime Daily Earthwork RecordsgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Dip Forms 019Document2 pagesDip Forms 019gahsoonNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Extract Page 1Document4 pagesExtract Page 1gahsoonNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- ELECTRIFIED RAIL PROJECT RAWANG-IPOHDocument1 pageELECTRIFIED RAIL PROJECT RAWANG-IPOHgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Site Concreting Record: Date: RI NoDocument1 pageSite Concreting Record: Date: RI NogahsoonNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Rebar SplicingDocument12 pagesRebar SplicinggahsoonNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Rawang-Ipoh Electrified Double Track Reinforced Inspection FormDocument1 pageRawang-Ipoh Electrified Double Track Reinforced Inspection FormgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Electrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh: Zone / Package: Chainage/StructureDocument2 pagesElectrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh: Zone / Package: Chainage/StructuregahsoonNo ratings yet
- Embankment Cutting Checklist 013Document1 pageEmbankment Cutting Checklist 013gahsoonNo ratings yet
- Embankment Cutting Checklist 013Document1 pageEmbankment Cutting Checklist 013gahsoonNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Qi GongDocument83 pagesQi GonggahsoonNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Liquid & Plastic Limits 035Document1 pageLiquid & Plastic Limits 035gahsoonNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- An0401 Metro InstrumentationDocument20 pagesAn0401 Metro InstrumentationAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- CON21Document65 pagesCON21jonlabuNo ratings yet
- An 11001 Diaphragm WallDocument20 pagesAn 11001 Diaphragm Wallgahsoon100% (4)
- RC Work Typical Detailing 2010Document2 pagesRC Work Typical Detailing 2010gahsoonNo ratings yet
- Deep Excavation via Soil Nailing Saves CostsDocument19 pagesDeep Excavation via Soil Nailing Saves CostsgahsoonNo ratings yet
- GEO GEOGUIDE 7 - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Construction (2008)Document100 pagesGEO GEOGUIDE 7 - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Construction (2008)aescarameiaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RE500 With RebarDocument6 pagesRE500 With RebargahsoonNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- 200 Limestones of Jurong Formation Engineering ExperienceDocument9 pages200 Limestones of Jurong Formation Engineering ExperiencegahsoonNo ratings yet
- Encardio CatalogDocument36 pagesEncardio CataloggahsoonNo ratings yet
- GEO GEOGUIDE 7 - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Construction (2008)Document100 pagesGEO GEOGUIDE 7 - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Construction (2008)aescarameiaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Engineering Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesEngineering Properties of Materialspapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Uk Calibration StandardDocument29 pagesUk Calibration Standardgahsoon100% (1)
- RC DesignDocument72 pagesRC DesigngahsoonNo ratings yet
- Samm CertificateDocument7 pagesSamm CertificategahsoonNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Custom Declaration Process FlowDocument1 pageCustom Declaration Process FlowgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Defining Public RelationsDocument4 pagesDefining Public RelationsKARTAVYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Echt Er Nacht 2014Document8 pagesEcht Er Nacht 2014JamesNo ratings yet
- Direction: Read The Questions Carefully. Write The Letters of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesDirection: Read The Questions Carefully. Write The Letters of The Correct AnswerRomyross JavierNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6Document226 pagesManual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6rsp filmes100% (1)
- SAP SD Course Content PDFDocument4 pagesSAP SD Course Content PDFshuku03No ratings yet
- Dryers in Word FileDocument5 pagesDryers in Word FileHaroon RahimNo ratings yet
- Ifatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesIfatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFCondor GuatonNo ratings yet
- Canopen-Lift Shaft Installation: W+W W+WDocument20 pagesCanopen-Lift Shaft Installation: W+W W+WFERNSNo ratings yet
- User Manual LCD Signature Pad Signotec SigmaDocument15 pagesUser Manual LCD Signature Pad Signotec SigmaGael OmgbaNo ratings yet
- The Clàsh The 0nly Band That MatteredDocument255 pagesThe Clàsh The 0nly Band That MatteredNikos VaxevanidisNo ratings yet
- Youre The Inspiration CRDDocument3 pagesYoure The Inspiration CRDjonjammyNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Teaching TrigonometryDocument20 pagesTeaching Trigonometryapi-21940065No ratings yet
- Connection Between Academic and Professional IntegrityDocument3 pagesConnection Between Academic and Professional IntegrityJoshua NyabindaNo ratings yet
- 740 (Q50, V40, Awa 4Document10 pages740 (Q50, V40, Awa 4rawat2583No ratings yet
- Canterburytales-No Fear PrologueDocument10 pagesCanterburytales-No Fear Prologueapi-261452312No ratings yet
- 09 Chapter TeyyamDocument48 pages09 Chapter TeyyamABNo ratings yet
- Sample of Accident Notification & Investigation ProcedureDocument2 pagesSample of Accident Notification & Investigation Procedurerajendhar100% (1)
- Potato Peroxidase LabDocument2 pagesPotato Peroxidase LabKarla GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Italian Painters 02 MoreDocument450 pagesItalian Painters 02 Moregkavvadias2010No ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesMechanical EngineeringSamuel WozabNo ratings yet
- Litz Wire Termination GuideDocument5 pagesLitz Wire Termination GuideBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- CE ProblemDocument5 pagesCE ProblemJho FNo ratings yet
- Elements of Ayurveda Daily Routine GuideDocument1 pageElements of Ayurveda Daily Routine GuideShivani GargNo ratings yet
- Pmls 1 Final Exam Reviewer: Clinical Chemistry ContDocument14 pagesPmls 1 Final Exam Reviewer: Clinical Chemistry ContPlant in a PotNo ratings yet
- Quality Management - QuestionDocument4 pagesQuality Management - QuestionLawzy Elsadig SeddigNo ratings yet
- IntuitionDocument10 pagesIntuitionmailsonNo ratings yet
- Test Fibrain RespuestasDocument2 pagesTest Fibrain Respuestasth3moltresNo ratings yet
- Moment Influence Line LabsheetDocument12 pagesMoment Influence Line LabsheetZAXNo ratings yet
- Fictional Narrative: The Case of Alan and His FamilyDocument4 pagesFictional Narrative: The Case of Alan and His Familydominique babisNo ratings yet
- Indian ChronologyDocument467 pagesIndian ChronologyModa Sattva100% (4)