Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch24 Answer Key
Uploaded by
mrmr92Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch24 Answer Key
Uploaded by
mrmr92Copyright:
Available Formats
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10
th
ed. Chapter !: "eneti#s and "enomi#s
Chapter 24: Genetics and Genomics
I. The Emerging Role of Genetics and Genomics in Medicine
A. "eneti#s is the study o$ inheritan#e o$ #hara#teristi#s.
B. "enes are se%uen#es o$ nu#leotides o$ the nu#lei# a#id &'A.
C. Chromosomes are rod shaped stru#tures that #arry genes.
&. A genes nu#leotide se%uen#e tells a #ell how to lin( a #ertain se%uen#e o$
amino a#ids together to #onstru#t a spe#i$i# protein mole#ule.
). A genome is the #omplete set o$ geneti# instru#tions in a human #ell.
*. Somati# #ells ha+e two sets o$ #hromosomes.
". &iploid means ha+ing two sets o$ #hromosomes or !, #hromosomes.
H. Se- #ells ha+e one set o$ #hromosomes.
.. Haploid means ha+ing one set o$ #hromosomes or / #hromosomes.
0. "enomi#s is the study o$ the human 1ody in terms o$ multiple, intera#ting
genes.
2. Proteonomi#s $o#uses on the spe#trum o$ proteins that spe#i$i# #ell types
produ#e.
L. )n+ironmental $a#tors that a$$e#t how genes are e-pressed are #hemi#al,
physi#al, so#ial, and 1iologi#al.
II. Modes of Inheritance
A. .ntrodu#tion
1. 3he pro1a1ility that a #ertain trait will o##ur in the o$$spring o$ two
indi+iduals #an 1e determined 1y (nowing how genes are distri1uted in
meiosis and the #om1inations in whi#h they #an #ome together at
$ertili4ation.
B. Chromosomes and "enes Come in Pairs
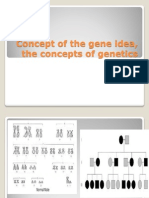
1. 2aryotypes are #hromosome #harts that display the / #hromosome
pairs in si4e order.
. Autosomes are #hromosome pairs 1 through and do not #arry genes
that determine se-.
/. Se- #hromosomes are #hromosome pair / and determine se-.
!. 5ost #hromosomes #ontain hundreds o$ thousands o$ genes.
6. Alleles are +ariant $orms o$ genes.
,. Homo4ygous alleles are identi#al.
7. Hetero4ygous alleles are di$$erent.
8. "enotype is the parti#ular #om1ination o$ genes in a persons genome.
9. Phenotype is the appearan#e or health #ondition o$ the indi+idual that
de+elops as a result o$ the ways the genes are e-pressed.
10. A wild type allele is asso#iated with the most #ommon or normal
phenotype.
11. A mutant allele is a #hange $rom the wild type.
C. &ominant and :e#essi+e .nheritan#e
1. A dominant allele is one that mas(s that o$ another allele.
. A re#essi+e allele is one that is mas(ed 1y a dominant allele.
/. An autosomal gene is lo#ated on a nonse- #hromosome.
!. An ;<lin(ed gene is lo#ated on an ; #hromosome.
6. A =<lin(ed gene is lo#ated on a = #hromosome.
,. 5ode o$ inheritan#e re$ers to whether a trait is dominant or re#essi+e,
autosomal or #arried on a se- #hromosome.
7. An autosomal #ondition is e%ually li(ely to a$$e#t either se-.
8. ;<lin(ed #hara#teristi#s a$$e#t males mu#h more than $emales.
9. :e#essi+e #onditions #an s(ip a generation 1e#ause a person most
li(ely inherits a re#essi+e #ondition $rom two healthy parents who are ea#h
hetero4ygotes.
10. &ominant #onditions do not s(ip generations 1e#ause a person who
inherits the #ondition has at least one a$$e#ted parent.
11. 3he disease #ysti# $i1rosis is an e-ample o$ an autosomal re#essi+e
disorder.
1. .$ 1oth parents are hetero4ygotes $or the trait that #auses #ysti#
$i1rosis, there is a 6> #han#e that their o$$spring will 1e homo4ygous
dominant, a 60> #han#e their o$$spring will 1e hetero4ygous, and a 6>
#han#e their o$$spring will 1e homo4ygous re#essi+e.
1/. A Punnet s%uare is a ta1le used to predi#t the pro1a1ilities o$
parti#ular genotypes o##urring in o$$spring.
1!. A pedigree is a diagram that depi#ts $amily relationships and
genotypes and phenotypes when they are (nown.
16. An e-ample o$ an autosomal dominant disorder is Huntington disease.
&. &i$$erent &ominan#e :elationships
1. .n#omplete dominan#e is a type o$ inheritan#e in whi#h the
hetero4ygous phenotype is intermediate 1etween that o$ either
homo4ygote.
. An e-ample o$ a trait inherited through in#omplete dominan#e is
$amilial hyper#holesterolemia.
/. Codominant means di$$erent alleles are 1oth e-pressed in a
hetero4ygotes.
!. 3he genotypes o$ indi+iduals with the $ollowing 1lood types are:
type A ? .
A
.
A
or .
A
i
type B ? .
B
.
B
or .
B
i
type AB < .
A
.
B
type @ < ii
III. Gene Expression
A. .ntrodu#tion
1. 3he same allele #om1ination #an produ#e di$$erent phenotypes 1e#ause
o$ the in$luen#es o$ nutrition, to-ins, illnesses or the a#ti+ities o$ other
genes.
. A maAor goal o$ genomi#s is to identi$y and understand the intera#tions
o$ alleles, nutrition, en+ironmental $a#tors, illnesses, and a#ti+ities o$ other
genes.
B. Penetran#e and )-pressi+ity
1. Completely penetrant means that e+eryone who inherits it has some
symptoms.
. .n#ompletely penetrant means some indi+iduals do not e-press the
phenotype.
/. A phenotype is +aria1ly e-pressi+e i$ the symptoms +ary in intensity in
di$$erent people.
C. Pleiotropy
1. Pleiotropy is a single geneti# disorder that #an produ#e se+eral
symptoms.
. An e-ample o$ a disease that e-hi1its pleiotropy is 5ar$an syndrome.
&. "eneti# Heterogeneity
1. "eneti# heterogeneity is when the same phenotype may result $rom the
a#tions o$ di$$erent genes.
. An e-ample o$ a #ondition that e-hi1its geneti# heterogeneity is
hereditary dea$ness.
IV. Complex Traits
A. 5onogeni# means the traits are determined 1y a single gene and their
e-pression is not greatly in$luen#ed 1y the en+ironment.
B. Polygeni# means the traits are determined 1y more than one gene.
C. Bariations in height are due to multiple genes.
&. Bariations in s(in #olor are due to three or more genes with two alleles ea#h.
). Bariations in eye #olor are due to two genes, with two alleles ea#h.
*. Comple- traits are traits molded 1y one or more genes plus the en+ironment.
". )-amples o$ #omple- traits are height, s(in #olor, and #ertain illnesses.
V. Matters of Sex
A. .ntrodu#tion
1. A human $emale is termed homogameti# 1e#ause she has two o$ the
same type o$ se- #hromosome.
. A human male is termed heterogameti# 1e#ause his two se-
#hromosomes are di$$erent.
B. Se- &etermination
1. A male is #on#ei+ed when a sperm #ontaining a = #hromosome
$ertili4es and egg Cwhi#h has an ; #hromosomeD.
. A $emale is #on#ei+ed when a sperm #ontaining an ; #hromosome
$ertili4es and egg.
/. 3he gene responsi1le $or 1eing male is the S:= gene.
C. Se- Chromosomes and 3heir "enes
1. 3he ; #hromosome has more than 1000 genes.
. 3he = #hromosome has only a $ew do4en genes.
/. 3he three groups o$ =<lin(ed genes are genes at the tips o$ the =
#hromosome that ha+e #ounterparts on the ; #hromosome, genes that are
+ery similar in &'A se%uen#e to #ertain genes on the ; #hromosome, and
genes that are uni%ue to the = #hromosome.
!. =<lin(ed genes are transmitted $rom $ather to sons.
6. Any gene on the ; #hromosome o$ a male is e-pressed in his
phenotype 1e#ause he has no se#ond allele on a se#ond ; #hromosome to
mas( its e-pression.
,. An allele on an ; #hromosome o$ a $emale may or may not 1e
e-pressed 1e#ause it depends on whether it is dominant or re#essi+e and
upon the nature o$ the allele on the se#ond ; #hromosome.
7. 3he male is said to 1e hemi4ygous $or ;<lin(ed traits 1e#ause he has
hal$ the num1er o$ genes on the ; #hromosome that the $emale has.
8. )-amples o$ ;<lin(ed re#essi+e traits are red<green #olor 1lindness and
hemophilia.
9. .$ a mother is hetero4ygous $or a parti#ular ;<lin(ed gene, her son has
a 60> #han#e o$ inheriting either allele $rom her.
10. ;<lin(ed genes are passed on $rom mother to son.
11. A daughter #an inherit an ;<lin(ed disorder only i$ her $ather is
a$$e#ted and her mother is a #arrier.
&. "ender )$$e#ts and Phenotypes
1. A se-<lin(ed trait is one that a$$e#ts a stru#ture or $un#tion o$ the 1ody
that is present in only males or only $emales.
. Se-<in$luen#ed inheritan#e is a type o$ inheritan#e in whi#h an allele is
dominant in one se- 1ut re#essi+e in another.
/. A hetero4ygous male is 1ald and a hetero4ygous $emale is not 1ald
1e#ause the 1aldness allele is dominant in males 1ut re#essi+e in $emales.
!. "enomi# imprinting is an e$$e#t in whi#h the e-pression o$ a disorder
di$$ers depending upon whi#h parent transmits the disease<#ausing gene.
VII. Chromosome isorders
A. Polyploidy
1. Polyploidy is the #ondition o$ ha+ing an e-tra set o$ #hromosomes.
. Polyploidy results $rom $ormation o$ a diploid gamete.
/. 3he $ate o$ a polyploid human is death as an em1ryo or $etus.
B. Aneuploidy
1. Aneuploid means a #ondition o$ missing a #hromosome or ha+ing an
e-tra one.
. )uploid means a normal #hromosome num1er.
/. Anueploidy results $rom nondisAun#tion.
!. 'ondisAun#tion is meioti# error in whi#h a #hromosomal pair $ails to
separate, produ#ing a sperm or egg that has two #opies o$ a parti#ular
#hromosome or none.
6. Autosomal aneuploidy o$ten results in mental retardation.
6. 3risomy is the #ondition o$ ha+ing one e-tra #hromosome.
,. 5onosomy is the #ondition o$ missing one #hromosome.
7. 3ranslo#ation is a type o$ a1erration in whi#h one #opy o$ a
#hromosome e-#hanges parts with a di$$erent #hromosome.
8. 3risomy 1 is (nown as &own syndrome.
9. @ther #ommon autosomal trisomies are trisomy 1/ and trisomy 18.
10. 3urner syndrome results $rom missing one ; #hromosome.
11. 2line$elter syndrome results $rom ha+ing an e-tra ; #hromosome.
1. 0a#o1s syndrome results $rom ha+ing an e-tra = #hromosome.
C. Prenatal 3ests
1. An ultrasound #an dete#t growth rate, head si4e, and si4e and lo#ation
o$ organs.
. Amnio#entesis is a pro#edure in whi#h a needle is inserted into the
amnioti# sa# to draw amnioti# $luid and #an dete#t #hromosomal
a1normalities.
/. Chorioni# +illus sampling is o$ #horioni# +illus #ells and #an dete#t
#hromosomal a1normalities.
!. 5aternal serum mar(ers #an dete#t an underde+eloped $etal li+er that
may indi#ate an in#reased ris( o$ trisomy.
6. *etal #ell sorting is a pro#ess that separates and #an dete#t geneti#
a1normalities.
VIII. Gene Therap!
A. .ntrodu#tion
1. *un#tions o$ gene therapy are to alter, repla#e, silen#e or augment a
genes $un#tion to impro+e or pre+ent symptoms.
. "ene therapy operates at the gene le+el.
B. 3wo Approa#hes to "ene 3herapy
1. 3wo 1asi# types o$ gene therapy are herita1le gene therapy and
nonherita1le gene therapy.
. Herita1le gene therapy is the type that introdu#es the geneti# #hange
into a sperm, egg or $ertili4ed egg, whi#h #orre#ts ea#h #ell o$ the resulting
indi+idual.
/. Herita1le gene therapy is most #ommonly per$ormed in plants.
!. 'onherita1le gene therapy is the type that targets only a$$e#ted #ells
and there$ore #annot 1e transmitted to the ne-t generation.
6. A nonherital1e gene therapy $or #ysti# $i1rosis is an aerosol #ontaining
a +irus that has had its pathogeni# genes remo+ed and a $un#tional human
C*3: gene added.
C. 3ools and 3argets o$ "ene 3herapy
1. .ntrodu#tion
a. Some tools o$ gene therapy are +iruses, liposomes, and na(ed
preparations o$ &'A.
1. 3he #hallenge in nonherita1le gene therapy is to target su$$i#ient
num1ers o$ a$$e#ted #ells $or a long enough time to e-ert a
noti#ea1le e$$e#t.
. Bone 5arrow
a. Bone marrow tissue in#ludes the pre#ursors o$ all mature 1lood
#ells types.
1. 5any new gene therapy targets might 1e rea#hed 1y 1one
marrow 1e#ause stem #ells in 1one marrow #an also tra+el to other
sites, su#h as mus#le, li+er, and the 1rain.
/. S(in
a. .n the la1oratory, s(in #ells grow well.
1. S(in gra$ts #an 1e used to se#rete therapeuti# proteins into a
persons system.
!. 5us#le
a. 3he reasons mus#le tissue is a good target $or gene therapy are
1e#ause it #omprises a1out hal$ o$ the 1odys mass, is easily
a##essi1le, and is near a 1lood supply.
1. 3reatments o$ &u#henne mus#ular dystrophy are deli+ery o$
$un#tional genes to immature mus#le #ell or to dire#t stem #ell
$rom 1one marrow to mus#le tissue where they di$$erentiate and
produ#e needed proteins.
6. )ndothelium
a. )ndothelium is a tissue that $orms #apillaries and lines the
interiors o$ other 1lood +essels.
1. )ndothelium #an 1e altered to se#rete a su1stan#e dire#tly into
the 1loodstream.
,. Li+er
a. 3he li+er is a +ery important $o#us o$ gene therapy 1e#ause it
#ontrols many 1odily $un#tions and it #an regenerate.
1. Li+er #ells that are geneti#ally altered #an relie+e #holesterol
1uildup.
7. Lungs
a. 3he respiratory tra#t is an e-#ellent #andidate $or gene therapy
1e#ause an aerosol #an dire#tly rea#h its lining #ells, ma(ing it
unne#essary to remo+e #ell, alter them, and reimplant them.
1. A $orm o$ gene therapy used to treat emphysema is inhalation o$
alpha<1<antitrypsin.
8. 'er+e 3issue
a. "ene therapy o$ neurons is not $easi1le 1e#ause these #ells do
not di+ide.
1. :outes o$ ner+e #ell gene therapy #ould in#lude altering
neuroglial #ells or sending in a +alua1le gene atta#hed to the
herpes simple- +irus, whi#h remains in ner+e #ells a$ter in$e#tions.
9. "ene 3herapy Against Can#er
a. "lioma is a 1rain tumor.
1. A gene therapy approa#h $or glioma is to in$e#t $i1ro1lasts with
a +irus 1earing a gene $rom a herpes +irus that ma(es the #ell
sensiti+e to a drug #alled gan#i#lo+ir. 3he altered $i1ro1lasts are
implanted near the tumor.
#. Another geneti# approa#h to 1attling #an#er is to ena1le tumor
#ells to produ#e immune system 1io#hemi#als or to mar( them so
that the immune system more easily re#ogni4es them.
&. C@&A
1. "ene dis#o+eries ha+e shed light on how the 1ody normally $un#tions.
. "ene produ#ts intera#t with ea#h other and en+ironmental $a#tors in
intri#ate ways to 1uild the 1odies o$ humans and other multi#ellular
organisms.
You might also like
- DSE Biology Chapter 2 - Genetics and Evolution 遺傳與進化Document50 pagesDSE Biology Chapter 2 - Genetics and Evolution 遺傳與進化li100% (1)
- Genetika ZadaciDocument85 pagesGenetika ZadaciAmar ZahirovicNo ratings yet
- Learning Modules For General Biology 2Document24 pagesLearning Modules For General Biology 2Albert Rosete0% (1)
- You Are Unique : An Introduction to Genetics - Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandYou Are Unique : An Introduction to Genetics - Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument47 pagesPatterns of InheritanceFrenche PañaresNo ratings yet
- 1 NCLEX-examDocument28 pages1 NCLEX-exammrmr92No ratings yet
- 1 NCLEX-examDocument28 pages1 NCLEX-exammrmr92No ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-3 (Mtap Notes)Document94 pagesLecture 1-3 (Mtap Notes)Ma. Mecy COMAHIGNo ratings yet
- Feedback Systems in The BodyDocument13 pagesFeedback Systems in The Bodymrmr92No ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument364 pagesPlant BreedingElizabeth Peña Reyes100% (4)
- Chapter 14Document11 pagesChapter 14homamunfatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument4 pagesChapter 14: Mendel and The Gene IdeaBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Week1PodcastTranscript (Updated 1-6)Document3 pagesWeek1PodcastTranscript (Updated 1-6)dulexNo ratings yet
- Adaptasi Dan EvolusiDocument26 pagesAdaptasi Dan EvolusiPoppy Siska IsabellaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Similarity and VariationDocument36 pagesGenetics Similarity and VariationLuisNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument6 pagesBiology ProjectFROST Gaming0% (1)
- Biology Project Pedigree Analysis Class 12Document28 pagesBiology Project Pedigree Analysis Class 12PrateekBansal61% (36)
- Pedigree AnalysisrrrrrDocument16 pagesPedigree AnalysisrrrrrFraizner FenilNo ratings yet
- Directions:: Activity No. 1.2 Essay Name Garcia, Alanah Jane, A. Section BSMT2ADocument3 pagesDirections:: Activity No. 1.2 Essay Name Garcia, Alanah Jane, A. Section BSMT2AAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Nonmendelian AssignmentDocument4 pagesNonmendelian AssignmentAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- Solving Genetics Problems - AnswersDocument11 pagesSolving Genetics Problems - AnswersGonzalo Estrán Buyo0% (1)
- SSRR X Ssrr. Determine The Expected Progeny Phenotypes and What FractionDocument2 pagesSSRR X Ssrr. Determine The Expected Progeny Phenotypes and What FractionJamie SimsNo ratings yet
- Life History PatternsDocument7 pagesLife History PatternshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- BI324 OConnor Linkage Practice (1) JhbjsujduDocument1 pageBI324 OConnor Linkage Practice (1) JhbjsujduMiruna RuseiNo ratings yet
- Mendel and The Gene Idea: Lecture OutlineDocument17 pagesMendel and The Gene Idea: Lecture Outlinehaha_le12No ratings yet
- HeredityDocument72 pagesHereditySein Hla KyawNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Pedigree Analysis Class 12Document21 pagesBiology Project Pedigree Analysis Class 12Anonymous DWvfJuMcQNo ratings yet
- 7 Science Workbook - HeredityDocument27 pages7 Science Workbook - HeredityJorge SanchezNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Vayu Sena Nagar: Arindam Mishra Class Xii-CDocument28 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Vayu Sena Nagar: Arindam Mishra Class Xii-CPippi DasNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Evolution: How Are DNA and Comparative Anatomy Used To Show Relatedness?Document5 pagesEvidence For Evolution: How Are DNA and Comparative Anatomy Used To Show Relatedness?Brionna SmithNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument6 pagesGenetics and HeredityRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Chendi's GeneDocument10 pagesChendi's GeneGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 Lec 10 NotesDocument20 pagesBio 101 Lec 10 NotesAmrin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - BiologyDocument34 pagesChapter 9 - BiologyNikhil ChettyarNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument2 pagesUCSPKaye Celyn Fetilo NooraNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument25 pagesGenetics and HeredityMariam HishamNo ratings yet
- Population GeneticsDocument48 pagesPopulation GeneticsSumaya FarheenNo ratings yet
- CH 5 BIODocument9 pagesCH 5 BIOKrish YadavNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument27 pagesGeneticsKatherine CampillosNo ratings yet
- Class - X Chapter - 9 Notes (Heredity)Document5 pagesClass - X Chapter - 9 Notes (Heredity)Muskan DhingraNo ratings yet
- X-Linked Inheritance: ChromosomeDocument5 pagesX-Linked Inheritance: ChromosomeFebbyNo ratings yet
- 4 Minutes Presentation (AutoRecovered)Document2 pages4 Minutes Presentation (AutoRecovered)moraraNo ratings yet
- Making Babies 16Document4 pagesMaking Babies 16dana.ashraf2193No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 9 Heredity and EvolutionDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolutiondrphysics256No ratings yet
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank 1Document36 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank 1kristygonzalezqsizobcfrj100% (22)
- Why Are My Eyes Brown?: A. IntroductionDocument6 pagesWhy Are My Eyes Brown?: A. Introductionmind4nameNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Evolution ModelsDocument6 pagesEvidence For Evolution ModelsAmber ByronNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Revision NotesDocument9 pagesClass 12 Biology Chapter 5 Revision NotesAnkur YadavNo ratings yet
- BBLR 1Document26 pagesBBLR 1novriliakumalasariNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument22 pagesBiology Projectshruti verma100% (3)
- 2a Inheritance CDocument9 pages2a Inheritance Capi-238529408No ratings yet
- CL 12 Bio Chapter-5 Principle of Inheritance and VariationDocument53 pagesCL 12 Bio Chapter-5 Principle of Inheritance and Variationjackieaj093No ratings yet
- Applying Mendel's Principles: Lesson ObjectivesDocument4 pagesApplying Mendel's Principles: Lesson ObjectivesTae McLoughlinNo ratings yet
- Learning Modules For General Biology 2Document12 pagesLearning Modules For General Biology 2Albert Rosete0% (1)
- Lesson Note For jss3 First TermDocument26 pagesLesson Note For jss3 First TermlepnaandabugatNo ratings yet
- Science Notes PDFDocument7 pagesScience Notes PDFakidelavega19No ratings yet
- Chapter 17, Section 1Document22 pagesChapter 17, Section 1XxClarityAftonxXNo ratings yet
- Genotype Examples: 1. Eye ColorDocument2 pagesGenotype Examples: 1. Eye ColorMishelle DayagNo ratings yet
- KineticDocument8 pagesKineticOchee De Guzman CorpusNo ratings yet
- Heredity NotesDocument6 pagesHeredity Notesbaldevsingh1235151No ratings yet
- City College of Health Sciences and Technology Suleja (CCHSTZ)Document60 pagesCity College of Health Sciences and Technology Suleja (CCHSTZ)Daniel DendaNo ratings yet
- Final Project DirectionsDocument1 pageFinal Project Directionsapi-259739449No ratings yet
- Genetics EverydayDocument7 pagesGenetics EverydayRando ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice Problems PDFDocument9 pagesGenetics Practice Problems PDFanaphade5No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planmrmr92No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Middle Adulthood Chapter SummaryDocument1 pageChapter 8: Middle Adulthood Chapter Summarymrmr92No ratings yet
- Jaundice: (Yellowing of Skin)Document4 pagesJaundice: (Yellowing of Skin)mrmr92No ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: (Encephalopathy, Hepatic Portal-Systemic Encephalopathy Encephalopathy, Portal-Systemic)Document4 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy: (Encephalopathy, Hepatic Portal-Systemic Encephalopathy Encephalopathy, Portal-Systemic)mrmr92No ratings yet
- Table 3 PDFDocument5 pagesTable 3 PDFmrmr92No ratings yet
- Study Guide Example PDFDocument18 pagesStudy Guide Example PDFmrmr92No ratings yet
- Study Guide Example PDFDocument18 pagesStudy Guide Example PDFmrmr92No ratings yet
- Broderick and Blewitt 2006Document31 pagesBroderick and Blewitt 2006mousumideNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Genetics Combined PowerpointsDocument49 pagesMeiosis and Genetics Combined Powerpointsapi-242405009No ratings yet
- Create A Face Genetics Lab ActivityDocument3 pagesCreate A Face Genetics Lab Activityapi-2571879770% (1)
- Genetic SymbolsDocument3 pagesGenetic SymbolsHoney McRueloNo ratings yet
- 23 Lecture Presentation PCDocument75 pages23 Lecture Presentation PCSinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Genetics Complete NotesDocument71 pagesGenetics Complete NotesSmritiNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems in Genetics Plus Solutions Problems Involving One GeneDocument20 pagesPractice Problems in Genetics Plus Solutions Problems Involving One GeneGiovanni TorresNo ratings yet
- Perlis Biologi Skema K2 SPM 09Document15 pagesPerlis Biologi Skema K2 SPM 09kanmanikandaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Biology Set 3Document6 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Biology Set 3PARAMASIVAN AKNo ratings yet
- Genes, Environments and Interactions Evolutionary and QuantitativeDocument236 pagesGenes, Environments and Interactions Evolutionary and QuantitativefannylamasgiganteNo ratings yet
- Bloodtype 706816347548628Document17 pagesBloodtype 706816347548628Daniel Del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Mysterio OfficiallyNo ratings yet
- Genetics MCQ 1Document12 pagesGenetics MCQ 1Riya BNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument29 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation Multiple Choice QuestionsPamuletiNo ratings yet
- Lab Topic 13 Paternity TestingDocument1 pageLab Topic 13 Paternity TestingNatasha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Keystone Biology ReviewDocument53 pagesKeystone Biology ReviewTalia GelmanNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesMobCrush Anxiety100% (1)
- Genetics Study Guide 2013 - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesGenetics Study Guide 2013 - Answer Keyapi-211201625No ratings yet
- Bio EvolutionDocument18 pagesBio EvolutionPaula JenNo ratings yet
- 5090 s10 QP 11Document20 pages5090 s10 QP 11DKFBNo ratings yet
- Two Alleles Are Expressed (Multiple Alleles) in Heterozygous IndividualsDocument2 pagesTwo Alleles Are Expressed (Multiple Alleles) in Heterozygous IndividualsBrooke GoodingNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5,6,7Document18 pagesExperiment 5,6,7imenmezhoud1122No ratings yet
- Bar Gene LocusDocument3 pagesBar Gene LocusHasan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Science 9Document3 pagesSummative Test in Science 9Arthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- G9 Science Q1 Week 3 4 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanDocument26 pagesG9 Science Q1 Week 3 4 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanSandra Lee LigsaNo ratings yet