Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kem Imtiaz Dungun 14 Sekay
Uploaded by
ujiee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views10 pagesaa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views10 pagesKem Imtiaz Dungun 14 Sekay
Uploaded by
ujieeaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
1
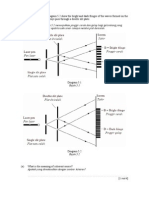
1 Diagram 1 shows an image seen through a lens.
Rajah 1 memmjukkan satu imej yang dilihat menerusi sebuah kanta.
Diagram 1
(a) Name the light phenomenon involved in Diagram 1.
Namakan fenomenon cahaya yang terlibat di Rajah 1.
.
[ 1 mark ]
(b) On Diagram 2, draw a ray diagram to show how the image in Diagram 1 is formed.
Pada Rajah 2, lukis satu rajah sinar untuk menunjukkan bagaimana imej dalam Rajah 1
terbentuk.
Diagram 2
[3 marks]
(c) The focal length of the lens in Diagram 2 is f. Referring to f, suggest a suitable position to
place the object to produce an inverted image.
Panjang fokus kanta dalam Rajah 2 ialah f. Merujuk kepada f cadang satu kedudukan yang
sesuai untuk meletakkan objek bagi menghasilkan imej songsang.
[1 mark]
2
(d) An eye piece of focal length, f
e
= 5 cm, and an objective lens are used to build a simple
astronomical telescope. The objective lens is chosen from Table 1.
Sebuah kanta mata yang mempunyai panjang fokus, f
e
= 5 cm dan sebuah kanta objektif
digunakan untuk membina sebuah teleskop astronomi ringkas. Kanta objektif dipilih dari
Jadual 1.
Lens Kanta Focal length of
lens, f
o
(cm)
Panjang fokus
kanta, f
o
(cm)
Magnification
Pembesaran
Diameter of the objective
lens (cm) Diameter kanta
objektif (cm)
P 10
2.5
Q 10
5.0
R 40
2.5
S 40
5.0
Table 1
(i) Complete Table 1 by writing down the values of M for every lens
Lengkapkan Jadual 1 dengan menulis nilai M bagi setiap kanta itu.
[ 2 marks ]
(ii) Choose the two lenses that produce the largest image.
Pilih dua kanta yang mengghasilkan imej yang paling besar.
[ 1 mark ]
(iii) Give one reason for the answer in 1(d)(ii).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan di 1(d)(ii).
[ 1 mark ]
(iv) Choose the two lenses that produce the brightest image.
Pilih dua kanta yang menghasilkan imej yang paling terang.
...
[ 1 mark ]
(v) Give one reason for the answer in 1(d)(iv).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan di 1(d)(iv).
[ 1 mark ]
(vi) Based on the answers in 1(d)(ii) and 1(d)(iv), choose the most suitable lens as the
objective lens.
Berdasarkan jawapan di 1(d)(ii) dan 1(d)(iv). pilih kanta yang paling sesuai sebagui
kanta objektif.
[ 1 mark ]
3
2 Diagram 2.1 and Diagram 2.2 show two photographs of electrical circuits.
Rajah 2.1 dan Rajah 2.2 menunjukkan dua fotograf litar elektrik.
Diagram 2.1 Diagram 2.2
(a) Which diagram shows a parallel circuit?
Rajah yang manakah menunjukkan litar selari
[ 1 mark ]
(b) Draw an electrical circuit diagram for the photograph in Diagram 2.1.
Lukis rajah litar elekirik bagi folograf dalam Rajah 2.1.
[ 2 marks ]
(c) Diagram 2.3 shows an electric circuit. Assume that the internal resistance of the baterry is
negligible.
Rajah 2.3 menunjukkan satu litarelektrik. Anggap rintangan dalam bagi bateri boleh
diabaikan.
Diagram 2.3
(i) Calculate the effective resistance of the circuit.
Hitung rintangan berkesan bagi litar itu.
4
[ 2 marks ]
(ii) What is the reading of the ammeter?
Berapakah bacaan ammeter itu?
[1 mark]
(iii) One of the 10 resistors is removed from the circuit. What happens to the ammeter
reading?
Satu daripada perintang 10 dikeluarkan dari litar itu Apakah yang berlaku
kepada bacaan ammeter itu?
..
[1 mark]
3 Diagram 7 shows a simple transformer.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan sebuah transformer ringkas.
Diagram 7
(a) (i) Name the type of the transformer.
Namakan jenis transformer itu.
..
[1 mark]
(ii) State why soft iron is used as the transformer core.
Nyatakan mengapa besi lemhut digunakan sebagai teras transformer.
.
[1 mark]
5
(b) The number of turns on the primary coil in Diagram 7 is 1 000. Calculate the number of
turns on the secondary coil.
Bilangan Milan pada gegelung primer pada Rajah 7 ialah I 000.Hitung bilangan lilitan
pada gegelung sekunder.
[2 marks ]
(c) The transformer in Diagram 7 is used to switch on an electrical appliance.
The current in the primary coil is 0.1 A and the efficiency is 75%.
Transformer dalam Rajah 7 digunakan untuk menghidupkan sebuah alat elektrik.
Arus yang mengalir dalam gegelung primer ialah 0.1 A dan kecekapannya ialah 15%.
(i) Calculate the output power of the transformer.
Hitung kuasa output transformer itu.
[2 marks ]
(ii) An electrical appliance which needs 20 W of power is connected to the transformer
output.
Suggest a modification to the transformer that enables the appliance to functu
correctly.
Satu alat elektrik yang memerlukan kuasa 20 W disambung inula output transformer
itu.
Cadangkan satu pengubahsuaian pada transformer itu supaya alat itu boleh
berfungsi dengan betul.
.
[1 mark]
(d) A student connects a television which uses direct current to the output of the transforme in
Diagram 7.
When the television is switched on, it does not function.
Seorang murid menyambungkan sebuah televisyen yang menggunakan bekalan arus teru
kepada output transformer pada Rajah7.
Apabila suis televisyen dihidupkan, didapati televisyen itu tidak berfungsi.
6
(i) Why the television does not function?
Mengapakah televisyen itu tidak berfungsi?
.
[1 mark]
(ii) An electrical component is connected to the output of the transformer so that the
television functions.
Name the electrical component and state how the connection is made.
Satu komponen elektrik disambung kepada output transformer itu supaya televisyen
itu berfungsi.
Namakan komponen elektrik itu dan nyatakan bagaimana sambungan itu dilakukan.
..
.
.
[2 marks]
4 Diagram 4.1 shows a bright spot, P, formed on the screen of a cathode-ray oscilloscope, C.R.O.,
when it is switched on.
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan satu tompok cerah, P, terbentuk pada skrin osiloskop sinar katnd. O.S.K..
apabila suis dihidupkan.
Diagram 4.1
(a) What is the meaning of cathode ray?
Apakah maksud sinar katod?
............................................................................
[ 1 mark]
(b) Explain how the bright spot is formed on the screen of the C.R.O.
Terangkan bagaimana tompok cerah itu terbentuk pada skrin O.S.K. itu.
[ 2 marks]
(c) Diagram 4.2 shows the bright spot is displaced to Q when a direct current, d.c. supply, is
connected to the Y-input of the C.R.O.
Rajah 4.2 menunjukkan tompok cerah itu disesarkan kepada Q apabila bekalan arus terns,
a.t., disambungkan kepada input-Y bagi O.S.K. itu.
7
Diagram 4.2
(d) Diagram 4.3 shows an alternating current, a.c. supply, is connected to the C.R.O. The Y-gain
of the C.R.O. remains at 2 V /division.
Rajah 4.3 memmjukkan bekalan ariis ulang-alik, a.u., disambungkan kepada O.S.K. itu.
Gandaan-Y bagi O.S.K. itu kekal pada 2 V /bahagian.
Diagram 4.3
Draw the output signal on the screen in Diagram 4.3 when the peak voltage of the a.c. supply
is 6 V and the time base is switched off.
Lukis isyarat output pada skrin di Rajah 4.3 apabila voltan puncak bekalan a.u. ialah 6 V
dan dasar masa dimatikan.
[2 marks]
5 Diagram 4 shows a circuit with a transistor that acts as an automatic switch.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan satu litar bertransistoryang bertindak sebagai suis automatik.
Diagram 4
Resistor X has high resistance in the dark and low resistance in the bright.
8
Perintang X berintangan tinggi dalam keadaan gelap dan berintangan rendah dalam keadaan
cerah.
(a) Name resistor X.
Namakan perintang X.
[ 1 mark ]
(b) The resistance of resistor X is 40 k when it is in the dark.
Rintangan perintang X adalah 40 k apabila berada dalam gelap.
Calculate:
Hitung:
(i) The potential difference between T and U
Beza keupayaan di antara T dengan U
[2 marks]
(ii) The current flows through resistor X
Arus yang mengalir melalui perintang X
[2 marks]
(c) Explain why the light emitting diode (LED) lights up when resistor X is in the dark.
Terangkan mengapa diod pemancar cahaya (LED) menyala apabi/a perintang X berada
dalam gelap.
..
..
..
[2 marks]
6 As a researcher, you are assigned to investigate the characteristics of a certain radioactive isotope
that could be used to detect the thickness of paper in a paper factory.
Sebagai seorang penyelidik, anda ditugaskan untuk mengkaji ciri-ciri bagi beberapa isotop
radioaktif untuk digunakan sebagai bahan pengesan ketebalan kertas di sebuah kilang kertas.
9
(a) What does the term isotope mean?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan isotop?
[1 mark]
(b) Table 12 shows the characteristics of five isotopes.
Jadual 12 menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi lima jenis isotop
Isotope
Isotop
Characteristics of isotope
Ciri-ciri isotop
State of
matter
Keadaan
jirim
Emmite
d
radiatio
n
Sinaran
dipanca
rkan
Half-life
Separuh
hayat
Penetrating
power
Kuasa
penembusan
Strontium-90
Strontium-90
Solid
Pepejal
Beta
Beta
28
years
28 tahun
Medium
Sederhana
Cobalt-60
Kobalt-60
Solid
Pepejal
Gamma
Gama
5
years
5
tahun
High
Tinggi
Xenon-133
Xenon-133
Gas
Gas
Beta
Beta
5 days
5 hari
High
Tinggi
Water containing
H-3
Air mengandungi H-
3
Liquid
Cecair
Beta
Beta
12
years
12 tahun
Medium
Sederhana
Polonium-210
Polonium-210
Solid
Pepejal
Alpha
Alfa
140 days
140
hari
Low
Rendah
Table 12
Based on the table above;
Berdasarkan jadual di atas;
(i) Explain the suitable characteristics of the isotopes so that it can be used to measure
the thickness of paper in a paper industry.
10
Terangkan kesesuaian ciri-ciri isotop untuk digunakan sebagai bahan pengesan
ketebalan kertas di sebuah kilang kertas.
(ii) Select the most suitable isotope to be used in detecting the thickness of paper in the
factory and give your reasons.
Tentukan isotop yang paling sesuai digunakan sebagai bahan pengesan ketebalan
kertas di kilang itu dan berikan sebab.
[ 10 marks ]
(c) Suggest briefly the arrangement of the paper thickness detector apparatus and state how
radioactivity is used to detect the thickness of the paper.
Cadangkan secara ringkas satu susunan alat radas pengesan ketebalan kertas dan nyatakan
bagaimana radioaktif digunakan untuk mengesan ketebalan kertas.
[3 marks]
(d) Sketch a graph of activity against time to illustrate how radioactive materials decay.
Use your graph to explain how the half-life is determined.
Lakarkan satu graf aktiviti melawan masa bagi menunjukkan pereputan suatu bahan
radioaktif. Gunakan graf anda untuk menerangkan bagaimana separuh hayat bahan itu
dapat ditentukan
[4 marks]
(e) The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5 years.
Calculate the time taken for the activity of this isotope to decay to 12.5% of its initial value.
Separuh hayat bagi kobalt-60 ialah 5 tahun.
Hitungkan masa yang diambil oleh isotop ini untuk mereput mcnjadi 12.5% daripada nilai
aktiviti asalnya
[2 marks]
You might also like
- Latihan GelombangDocument10 pagesLatihan GelombangujieeNo ratings yet
- Ahli Keluarga - Bahasa ArabDocument8 pagesAhli Keluarga - Bahasa ArabujieeNo ratings yet
- Peta Minda Bicara BeriramaDocument1 pagePeta Minda Bicara BeriramaujieeNo ratings yet
- Pelan Taktikal Bilik BBMDocument3 pagesPelan Taktikal Bilik BBMujieeNo ratings yet
- Borang Permarkahan PertandinganDocument3 pagesBorang Permarkahan PertandinganujieeNo ratings yet