Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TUTORIAL+CHAPTER+1 Solution
Uploaded by
Nilofer NisaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIAL+CHAPTER+1 Solution
Uploaded by
Nilofer NisaCopyright:
Available Formats
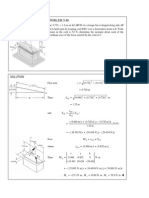
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
Solution Q1
Kinematics:
and
(
()
Answer
(
()
Answer
Solution Q2
(a) Determine the position and the velocity of the particle when t=14 s
Split into three parts: A, B and C
Part A ( 0<t<6) constant deceleration
When t=6s, 8 V
A
= m/s
When t=0s; t a V V
A A A
+ =
O
) (
) )( ( ) ( 6 4 V 8
A o
+ =
16 V
A
=
O
) ( m/s
When 0 V
A
= , 4 t = s
When t=0s, s=0
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
When t=6s; ( ) ( )
2
A A A o A
t a
2
1
t V S S + + =
O
) )( ( ) (
2
A
6 4
2
1
6 16 0 S + + =
24 S
A
= m
When t=4s; ( ) 32 S
A 4 t
=
=
m
Part B ( 6<t<10) zero acceleration, a =0
When t=6s, ( ) 8 V V
B A
= =
O
m/s
When t=10s, 8 V
B
= m/s
When t=6s, ( ) 24 S S
B A
= =
O
m
When t=10s, ( ) ( )
2
B B B o B
t a
2
1
t V S S + + =
O
56 S
B
= m
Part C ( 10<t<14) constant acceleration
When t=10s, ( ) 8 V V
C B
= =
O
m/s
When t=14s, t a V V
C C C
+ =
O
) (
) )( ( 4 4 8 V
C
+ =
8 V
C
= m/s Answer
When 0 V
C
= , 12 t = s
When t=10s, ( ) 56 S S
C B
= =
O
m/s
When t=14s, ( )
2
C C C C
t a
2
1
t V S S + + =
O O
) (
56 S
C
= m Answer
When t=12s; ( ) 64 S
C 12 t
=
=
m
(b) Determine the total distance traveled by the particle when t=14 s
Total distance = 32+(32-24)+24+56+(64-56)+(64-56)=136 m Answer
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
Solution Q3
graph: For the time interval , the condition is when
(
When
(
For the interval , the initial condition is
when .
(
( )
Thus, when
Answer
Also, the change in velocity is equal to the area under the graph. Thus
()() (
The graph is shown as
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
graph: For the time interval , the initial condition is when
(
)
When ,
(
)
For the time interval
, the initial condition is when
(
( )
)
When
,
()
()
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
The graph is shown as
Solution Q4
Horizontal motion: ( ) 228 0 5 t 30 v t v x . cos cos = = =
O O
o
=
O
30 v
772 4
t
cos
.
Vertical motion: ( ) ( ) ( )
2 2
t 81 9
2
1
t 30 v 2 at
2
1
t v y y . sin sin + = + + =
O O O
o
( )
( )
2
t 81 9
2
1 772 4
2 048 3 .
cos
sin .
. + =
o
o
s 59 0 t . =
Therefore; 34 9 v . =
O
m/s Answer
Solution Q5
Coordinate system: The coordinate system will be set so that its origin coincides with
point A.
-motion: Here, (
and . Thus
(
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
()
(1)
-motion: Here, (
and
. Thus
()
()
()(
(2)
Solving Eqs. (1) and (2) yields
Answer
Solution Q6
(a) At point A
Given 50 v
A
= m/s
89 8 25 81 9 25 a a
N
. cos . cos = = = m/s
2
Then 89 8
r
50
r
v
a
2 2
N
. = = =
281 r = m Answer
(a) At highest point 0 v
y
= and v 25 v v
A x
= = cos
Then 81 9 a
N
. = m/s
2
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
Therefore
( )
81 9
r
25 50
r
v
a
2 2
N
.
cos
=
= =
209 r = m Answer
Solution Q7
, therefore
( )
,
( )
( )
|
( )
For
()
( )
Answer
( )
Answer
()
()
()
()
Answer
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
Solution Q8
Position coordinates: By referring to Fig. (a), the length of the two ropes written in terms of
the position coordinates
and
are
(1)
and
(2)
Eliminating
from Eqs. (1) and (2)
(3)
Time derivative: Taking the time derivative of Eq. (3)
()
Here,
. Hence,
Answer
Solution Q9
Take positive if downward.
Constraint of cable on left: constant = +
B A
x 3 x 2
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
0 = +
B A
v 3 v 2
A B
v
3
2
v =
Then
A B
a
3
2
a =
Constraint of cable on right: constant = +
C B
x 2 x
0 = +
C B
v 2 v
Hence
B c
v
2
1
v =
Then
B C
a
2
1
a =
Constraint of point D on cable:
constant = +
D A
x x 2
Hence
B A D
v 3 v 2 v = =
B D
a 3 a =
(a) Given 200 a
B
=
mm/s
2
( ) 300 200
2
3
a
A
= = mm/s
2
@ ( ) |
2
300mm/s
( ) 100 200
2
1
a
c
= = mm/s
2
@ ( ) |
2
100mm/s
( ) 600 200 3 a
D
= = mm/s
2
@ ( ) +
2
600mm/s
(b) Given ( ) ( ) ( ) 0 v v v
D C A
= = =
o o o
When t = 10 s; ( ) t a v v
A A A
+ =
( )( ) 3000 10 300 0 v
A
= + = mm/s @ ( ) | mm/s 3000
( )( ) 2610 10 200 610 v
B
= + = mm/s @ ( ) + mm/s 2610
( )( ) 1000 10 100 0 v
C
= + = mm/s @ ( ) | mm/s 1000
( )( ) 6000 10 600 0 v
D
= + = mm/s @ ( ) + mm/s 6000
(c) Relative velocity D to B: ( ) + = = = mm/s
/
3390 2610 6000 v v v
B D B D
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
Solution Q10
A B A B
v v v
/
+ =
A B A B
v v v =
/
From x-axis:
( ) ( ) ( )
x A x B x A B
v v v =
/
( ) 30 43 0 30 50 v
x A B
. cos
/
= = km/h
From y-axis:
( ) ( ) ( )
y A y B y A B
v v v =
/
( ) ( ) 0 65 40 30 50 v
y A B
. sin
/
= = km/h
Magnitude 1 78 v
A B
.
/
= km/h Answer
Angle = 3 56
A B
.
/
u
Answer
Solution Q11
Relative Velocity:
Equating and component, we have
(1)
(2)
Solving Eqs. (1) and (2) yields
CHAPTER 1: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE
Answer
Thus, the time required by the boat to travel from point A to B is
Answer
You might also like
- PC235W13 Assignment5 SolutionsDocument10 pagesPC235W13 Assignment5 SolutionskwokNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Riley Dynamics PDFDocument253 pagesSolucionario Riley Dynamics PDFElsa Vasquez VargasNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsDocument14 pagesWBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Dinamica de RileyDocument253 pagesSolucionario Dinamica de RileyTiAGO100% (1)
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Solution For Problem 1Document7 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Solution For Problem 1Jeniffer OngNo ratings yet
- NEET SHM and Oscillations Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesNEET SHM and Oscillations Important Questionssapnasingh19951No ratings yet
- Examples - PhysicsDocument8 pagesExamples - Physicslaila1001No ratings yet
- NJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 AnsDocument7 pagesNJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 AnsYong JieNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: MOCK GATE (2012) - 2Document12 pagesEngineering Academy: MOCK GATE (2012) - 2shrish9999No ratings yet
- WBJEE 2010 Question Paper With SolutionDocument50 pagesWBJEE 2010 Question Paper With SolutionLokesh Kumar67% (3)
- On The Darboux Vector Belonging To Involute Curve A Different ViewDocument8 pagesOn The Darboux Vector Belonging To Involute Curve A Different ViewMia AmaliaNo ratings yet
- 2021 20 JulyDocument37 pages2021 20 JulyDeeepakNo ratings yet
- Calculator Techniques 2Document101 pagesCalculator Techniques 2Gilbert Gbing BeloNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems From Solving Dynamics Problems in Mathcad: by Brian D. Harper Ohio State UniversityDocument9 pagesSample Problems From Solving Dynamics Problems in Mathcad: by Brian D. Harper Ohio State UniversityMario Jucharo LaymeNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-26-02-2021-Shift-2 (Memory Based) PhysicsDocument35 pagesJEE-Main-26-02-2021-Shift-2 (Memory Based) PhysicsReddy TejNo ratings yet
- Neet Question Paper 2021 Code O1Document71 pagesNeet Question Paper 2021 Code O1Deev SoniNo ratings yet
- Wbjee 2009 Paper With SolutionsDocument53 pagesWbjee 2009 Paper With SolutionsMichelle RobertsNo ratings yet
- Iit-Jee/Aieee/Pmt Combined Test Series by Atc - Test - 01 - Physics+Maths+Chemistry+BiologyDocument7 pagesIit-Jee/Aieee/Pmt Combined Test Series by Atc - Test - 01 - Physics+Maths+Chemistry+BiologyShubham RankaNo ratings yet
- MST207 04Document6 pagesMST207 04pigcowdogNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-16-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) Physics: Question: Heat and Work Are: OptionsDocument42 pagesJEE-Main-16-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) Physics: Question: Heat and Work Are: OptionsHNo ratings yet
- 28 36Document10 pages28 36Carlos Moran CepedaNo ratings yet
- Supch09 PDFDocument12 pagesSupch09 PDFvampakkNo ratings yet
- Phys1122 202200Document8 pagesPhys1122 202200Amritraj DashNo ratings yet
- PHYS 151 Homework 6Document7 pagesPHYS 151 Homework 6QuinnNgo100% (1)
- 10 - SHM, Springs, DampingDocument4 pages10 - SHM, Springs, DampingBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 2022 26 July Morning Shift Question Paper With Solutions PDFDocument26 pagesJee Main 2022 26 July Morning Shift Question Paper With Solutions PDFALEKHYA KANCHIBHATLANo ratings yet
- KVPY Paper Solution XI 04-11-12Document23 pagesKVPY Paper Solution XI 04-11-12muley_jayNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2012 Physics and Chemistry Question Paper With SolutionDocument53 pagesWBJEE 2012 Physics and Chemistry Question Paper With SolutionPremKumarKalikiri100% (1)
- School of Computing, Engineering and Mathematics Semester 2 Examinations 2011/2012Document9 pagesSchool of Computing, Engineering and Mathematics Semester 2 Examinations 2011/2012Kish ShenoyNo ratings yet
- 46 55Document10 pages46 55Carlos Moran CepedaNo ratings yet
- Particle Kinematics: Part II. Curvilinear MotionDocument24 pagesParticle Kinematics: Part II. Curvilinear MotionTony KaoNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 January 29 Evening Shift Question Paper With SolutionsDocument27 pagesJEE Main 2023 January 29 Evening Shift Question Paper With SolutionsShruti bajajNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Dinamica de RileyDocument253 pagesSolucionario Dinamica de RileyRoberto MongeNo ratings yet
- 41 50Document13 pages41 50Roger MendozaNo ratings yet
- Solution:: V 105m S S 62m T 0Document50 pagesSolution:: V 105m S S 62m T 0Yousif AL Ayoubi100% (1)
- Wbjee 2010 Paper 7Document1 pageWbjee 2010 Paper 7subhadip728No ratings yet
- 163003723825) JEE Main 2021 March 17 Shift 2 Question Paper With SolutionDocument36 pages163003723825) JEE Main 2021 March 17 Shift 2 Question Paper With SolutionChaitanya NitaweNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2 PCM CombinedDocument25 pagesJEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2 PCM CombinedVeda Vikas DNo ratings yet
- Control Systems 2Document18 pagesControl Systems 2Sengottu VelusamyNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument18 pagesControl SystemsSengottu VelusamyNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion (6 Hours)Document87 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion (6 Hours)aNo ratings yet
- NCESQ 2015 Answer KeyDocument10 pagesNCESQ 2015 Answer KeyKenneth Joy SorianoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry - Tutorial SheetDocument8 pagesTrigonometry - Tutorial SheetmNo ratings yet
- EE-EC - RIB (W) - Control Sys - 13-08-16 - SK1-sol - 1391Document9 pagesEE-EC - RIB (W) - Control Sys - 13-08-16 - SK1-sol - 1391arunNo ratings yet
- 10 Jan Slot 2 SolutionsDocument40 pages10 Jan Slot 2 SolutionsBabita MishraNo ratings yet
- MJC 2010 H2 Physics Prelim Solutions To Paper 1 and 2xDocument23 pagesMJC 2010 H2 Physics Prelim Solutions To Paper 1 and 2xcjcsucksNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-17-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsDocument40 pagesJEE-Main-17-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsSuvigya YadavNo ratings yet
- Ultimo 16 Supch09 PDFDocument12 pagesUltimo 16 Supch09 PDFmri_leonNo ratings yet
- Example Sheet 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesExample Sheet 1 SolutionsDominic Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Solving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2DFrom EverandSolving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2DNo ratings yet
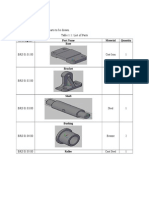
- Table 1.1 Shows The List of Parts To Be Drawn. Table 1.1: List of PartsDocument3 pagesTable 1.1 Shows The List of Parts To Be Drawn. Table 1.1: List of PartsNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Boilers and ThermicFluidHeatersDocument42 pagesBoilers and ThermicFluidHeatersvallamreddyNo ratings yet
- DS10113 Atc 0312aDocument2 pagesDS10113 Atc 0312aNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4 - QuestionDocument5 pagesTutorial Chapter 4 - QuestionNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 1 Questionstupidscribd41234123No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (B) : Submit Date: 6 November 2012Document5 pagesAssignment 1 (B) : Submit Date: 6 November 2012Nilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Professional Rights and ConductDocument1 pageAssignment 1: Professional Rights and ConductNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Presentation PneumaticDocument29 pagesPresentation PneumaticNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Technology Makes Human LazyDocument1 pageTechnology Makes Human LazyNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Field Trip ReportDocument4 pagesField Trip ReportNilofer Nisa100% (1)
- Schott Optical Glass Collection Datasheets English 17012017Document128 pagesSchott Optical Glass Collection Datasheets English 17012017Fernando CardenasNo ratings yet
- Density, Viscosity, and Refractive Index of Formamide, Three Carboxylic Acis and FormaamideDocument4 pagesDensity, Viscosity, and Refractive Index of Formamide, Three Carboxylic Acis and Formaamidehameed1966No ratings yet
- Poly StyreneDocument7 pagesPoly StyreneH PT MistryNo ratings yet
- Water ChemistryDocument13 pagesWater ChemistrynivasssvNo ratings yet
- Chapter EnzymesDocument2 pagesChapter EnzymesJaved SohawonNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument51 pagesSolutionsSaad MazharNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method ValidationDocument19 pagesAnalytical Method ValidationManasa SgrNo ratings yet
- Class 12 (SYLLABUS 2023-2024)Document4 pagesClass 12 (SYLLABUS 2023-2024)Husain AalaNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Converted - by - AbcdpdfDocument3 pagesLAB REPORT CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Converted - by - AbcdpdfZIAJIANo ratings yet
- Pick Up The Most Appropriate Statement of The Multiple-Choice Answers by Comment On The Correct AnswersDocument9 pagesPick Up The Most Appropriate Statement of The Multiple-Choice Answers by Comment On The Correct Answersأحمد إبراهيم شواربNo ratings yet
- Classification of PoisonDocument4 pagesClassification of PoisonVivekanand PatilNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics: Central Force MotionDocument6 pagesClassical Mechanics: Central Force MotionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Management of Environmental Quality: An International JournalDocument13 pagesManagement of Environmental Quality: An International JournalJosé Antonio MaquénNo ratings yet
- TriboElectric SeriesDocument3 pagesTriboElectric SeriesApurwand JfrNo ratings yet
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Xi (Electromagnetic Waves)Document2 pagesSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Xi (Electromagnetic Waves)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project For Class 12Document13 pagesChemistry Project For Class 12gauravkhanna1996No ratings yet
- PB Arang Aktif 11032020 BDocument2 pagesPB Arang Aktif 11032020 BSiti Sarifa YusuffNo ratings yet
- MCNPDocument35 pagesMCNPFahdila RahmaNo ratings yet
- GPSA Propiedades Termodinamicas 24 PDFDocument42 pagesGPSA Propiedades Termodinamicas 24 PDFDavid Cortez PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Substitution Versus EleiminationDocument20 pagesSubstitution Versus EleiminationmihikaNo ratings yet
- Le Chatelier's Principle WorksheetDocument3 pagesLe Chatelier's Principle WorksheetGerald AlbasinNo ratings yet
- Determination of Polydextrose in Foods by Ion ChroDocument8 pagesDetermination of Polydextrose in Foods by Ion ChrodiegoNo ratings yet
- Physics Project C-12thDocument18 pagesPhysics Project C-12thPratyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot) 25 - 12 - 2023 - SR - IIT - STAR - CO - S (@HeyitsyashXD)Document22 pages(@bohring - Bot) 25 - 12 - 2023 - SR - IIT - STAR - CO - S (@HeyitsyashXD)Idhant SinghNo ratings yet
- RPG One 1.5 2.5Document2 pagesRPG One 1.5 2.5YJ JangNo ratings yet
- Terragen 2 Water GuideDocument24 pagesTerragen 2 Water Guidejon2002No ratings yet
- MSDS - Text Spin H (E)Document4 pagesMSDS - Text Spin H (E)Athiphap SrisupareerathNo ratings yet
- Short ProgramDocument32 pagesShort Programperete69No ratings yet
- 2022 AQA A Level Chemistry Paper 1 MSDocument39 pages2022 AQA A Level Chemistry Paper 1 MSzombie bossNo ratings yet