Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch7 Evans BA1e Case Solution
Uploaded by
yarli7777Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch7 Evans BA1e Case Solution
Uploaded by
yarli7777Copyright:
Available Formats
1 Technically, one should run a two-sample hypothesis test for differences in proportions.
However, Excel does not provide this tool,
and consequently it is not discussed in the book. So what should a student do? Here is a chance to build upon previous knowledge to
apply confidence intervals. Using the concepts from the previous chapter (see page 192 on CIs and decision making), we could construct
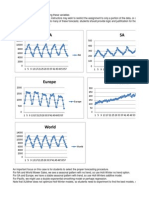
confidence intervals for the data and compare them. For example, for Dealer Satisfaction, all confidence intervals overlap,
For example, for Dealer Satisfaction, all confidence intervals overlap, although the overlap between NA and SA, and SA and China is slight,
suggesting that there might be a significant difference between them.
Similarly, it appears that there is a difference between SA and China in End User Satisfaction also.
Dealer Satisfaction
Survey Scale:
North America
2012
South America
2012
Europe
2012
Pacific Rim
2012
China
2012
End-User Satisfaction
North America
2012
South America
2012
Europe
2012
Pacific Rim
2012
China
2012
15
44
56
125
22
60
5 Sample
Size
90
0.91
0.0300
0.85
0.97
17
30
0.83
0.0680
0.7
0.96
12
0.75
0.1250
0.51
0.99
16
0.63
0.1210
0.39
0.87
0
0
1
2
2
3
3
15
4
31
5 Size
49
100
0.80
0.0400
0.72
0.87
19
37
37
100
0.74
0.0439
0.65
0.83
19
45
33
100
0.78
0.0414
0.7
0.86
19
42
35
100
0.77
0.0421
0.69
0.85
31
14
50
0.90
0.0424
0.82
0.98
Top Box ProportionsStandard error Lower 95% CI Upper 95% CI
0.80
0.0358
0.73
0.87
2
Using ANOVA, we reject the null hypothesis that all ratings are the same; so at least one differs from the rest.
Anova: Single Factor
SUMMARY
Groups
Count
Quality
Ease of Use
Price
Service
Sum
200
200
200
200
Average
879
833
734
828
4.395
4.165
3.67
4.14
55.505
621.65
3
796
18.50167
0.780967
677.155
799
Variance
0.581884
0.610829
1.136784
0.794372
ANOVA
Source of Variation
SS
Between Groups
Within Groups
Total
df
MS
23.6907
P-value
F crit
1.1E-14 2.616089
3
The proportion of on time deliveries in 2008 was 0.9850.
We may test the null hypothesis that the proportion of on time deliveries in 2012 is < 0.985 to determine if it has improved (the alternate hypothesis is p > 0.985)
The sample proportion for 2012 is 0.9907
z = (0.9907 - 0.985)/SQRT(.985*(1-0.985)) =
0.046893
Critical value = 1.645
p-value =
0.48129912
Therefore, we cannot conclude a significant improvement
4 A chart of the average number of defects by year shows a declining trend.
1000
800
600
400
200
0
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
We may test for differences between 2008 and 2012 (assuming the samples are the monthly data since we don't know the actual number of shipments)
t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances
2008
Mean
826.3333333
Variance
135.3333333
Observations
12
Hypothesized Mean Difference
0
df
12
t Stat
20.61894864
P(T<=t) one-tail
4.88441E-11
t Critical one-tail
1.782287556
P(T<=t) two-tail
9.76883E-11
t Critical two-tail
2.17881283
2012
496.25
2940.022727
12
The test clearly shows a significant difference in the mean defect rates.
5 Testing hypotheses that the mean cost has improved for one of the new processes, we cannot conclude a signficant improvement.
t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances
Current
Mean
289.6
Variance
2061.144828
Observations
30
Hypothesized Mean Difference
0
df
52
t Stat
0.283404509
P(T<=t) one-tail
0.388996025
t Critical one-tail
1.674689154
P(T<=t) two-tail
0.77799205
t Critical two-tail
2.006646805
Process A
285.5
4217.637931
30
t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances
Current
Mean
289.6
Variance
2061.144828
Observations
30
Hypothesized Mean Difference
0
df
41
t Stat
-0.968320801
P(T<=t) one-tail
0.169280943
t Critical one-tail
1.682878002
P(T<=t) two-tail
0.338561887
t Critical two-tail
2.01954097
Process B
298.4333333
435.3574713
30
6 Conduct two sample tests on mean years at PLE for each factor.
t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances
Female
Mean
5.530769231
Variance
12.25064103
Observations
13
Hypothesized Mean Difference
0
df
18
t Stat
-0.009174759
P(T<=t) one-tail
0.496390313
t Critical one-tail
1.734063607
P(T<=t) two-tail
0.992780627
t Critical two-tail
2.10092204
Male
5.540740741
6.449430199
27
CONCLUSION: NO SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCE BY GENDER
t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances
College Grad N
Mean
4.892307692
Variance
5.819102564
Observations
13
Hypothesized Mean Difference
0
df
29
t Stat
-1.078815194
P(T<=t) one-tail
0.144780886
t Critical one-tail
1.699127027
P(T<=t) two-tail
0.289561772
t Critical two-tail
2.045229642
College Grad Y
5.848148148
9.10951567
27
CONCLUSION: NO SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCE BY COLLEGE GRAD STATUS
t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances
Local N
Mean
3.629411765
Variance
5.690955882
Observations
17
Hypothesized Mean Difference
0
df
34
t Stat
-4.418641425
P(T<=t) one-tail
4.80512E-05
t Critical one-tail
1.690924255
P(T<=t) two-tail
9.61023E-05
t Critical two-tail
2.032244509
Local Y
6.947826087
5.272608696
23
CONCLUSION: SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCE BY LOCAL AREA
EMPLOYEES FROM THE LOCAL AREA HAVE GREATER RETENTION
You might also like
- Ch11 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument14 pagesCh11 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch10 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument19 pagesCh10 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777100% (1)
- Ch15 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument12 pagesCh15 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777100% (1)
- Ch14 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument21 pagesCh14 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch6 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument30 pagesCh6 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli77770% (1)
- Ch3 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument16 pagesCh3 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch5 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument7 pagesCh5 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Case Assignment 1 2017-8 Sem2Document3 pagesCase Assignment 1 2017-8 Sem2mingzNo ratings yet
- Database - Performance Lawn Equipment Database - DONT - TOUCHDocument56 pagesDatabase - Performance Lawn Equipment Database - DONT - TOUCHziveoNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument56 pagesCh12 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli777750% (2)
- Final Year Project (Main) PDFDocument50 pagesFinal Year Project (Main) PDFPradeep JoraNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument10 pagesCh13 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- BAS121 - Midterm ReportDocument19 pagesBAS121 - Midterm ReportSi WongNo ratings yet
- Performance Lawn EquipmentDocument6 pagesPerformance Lawn Equipmentrddavis3100% (2)
- Report - ResponsesDocument9 pagesReport - ResponsesRiya KhungerNo ratings yet
- DI Made EasyDocument15 pagesDI Made Easyshantnusingh8No ratings yet
- RegressionDocument6 pagesRegressionooveNo ratings yet
- RVC Assignment 1Document10 pagesRVC Assignment 1ynegiNo ratings yet
- Base Case Financial ModelDocument4 pagesBase Case Financial ModelAbdul KhaderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Solutions Develop Your Skills 9.1: Production Before and After Music Is Played in The PlantDocument40 pagesChapter 9 Solutions Develop Your Skills 9.1: Production Before and After Music Is Played in The PlantgainesboroNo ratings yet
- Econometrics 3A Supplementary Examination MemoDocument9 pagesEconometrics 3A Supplementary Examination MemomunaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Strategy Planning and Operation 7th Edition Chopra Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesSupply Chain Management Strategy Planning and Operation 7th Edition Chopra Solutions Manualmoriskledgeusud100% (22)
- International Institute For Higher Education in MoroccoDocument7 pagesInternational Institute For Higher Education in MoroccoNakonoaNo ratings yet
- Empirical Project Assignment 1Document6 pagesEmpirical Project Assignment 1ehitNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Special Issue International Journal of Pure and Applied MathematicsDocument13 pagesInternational Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Special Issue International Journal of Pure and Applied MathematicsShiva ParmarNo ratings yet
- Session 03 and 04-2021 (2021 - 10 - 19 04 - 03 - 36 UTC)Document38 pagesSession 03 and 04-2021 (2021 - 10 - 19 04 - 03 - 36 UTC)Della DillinghamNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business Forecasting 1St Edition Ord Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Business Forecasting 1St Edition Ord Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFyuyen1ty6100% (9)
- Unit 8Document14 pagesUnit 8ravicluoNo ratings yet
- Session 05-2021 (2021 - 10 - 19 04 - 03 - 36 UTC)Document18 pagesSession 05-2021 (2021 - 10 - 19 04 - 03 - 36 UTC)Della DillinghamNo ratings yet
- Assign 2Document10 pagesAssign 2wuehendhsueNo ratings yet
- A Note On Saaty'S Random Indexes: CI RIDocument3 pagesA Note On Saaty'S Random Indexes: CI RIcovid19 bebasNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Level 3: LCCI International QualificationsDocument19 pagesBusiness Statistics Level 3: LCCI International QualificationsHein Linn Kyaw100% (1)
- Operations Manager For Excel (C) 1997-2003, User Solutions, IncDocument18 pagesOperations Manager For Excel (C) 1997-2003, User Solutions, IncRabih DarwishNo ratings yet
- 20 MASTER Exercise Answers MBADocument38 pages20 MASTER Exercise Answers MBASimbarashe Stewart KamwendoNo ratings yet
- Levine Smume7 Bonus Ch08Document11 pagesLevine Smume7 Bonus Ch08Kiran SoniNo ratings yet
- BB0010 Quantitative Techniques in Business 2Document18 pagesBB0010 Quantitative Techniques in Business 2Ashraf HussainNo ratings yet
- HW5 For Financial MathameticsDocument9 pagesHW5 For Financial MathameticsshihuiNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 5 T TEST MBA With Solution November 5 2022Document3 pagesACTIVITY 5 T TEST MBA With Solution November 5 2022Violets n' DaisiesNo ratings yet
- 15.S24 Fundamentals of Financial Mathematics Problem Set 5 Shihui Chen ID: 913599770Document12 pages15.S24 Fundamentals of Financial Mathematics Problem Set 5 Shihui Chen ID: 913599770shihuiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4-5 Cashless Policy Data AnalysisDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 4-5 Cashless Policy Data AnalysisDiiyor LawsonNo ratings yet
- Article Rev Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesArticle Rev Cost AccountingFikir GebregziabherNo ratings yet
- Capstone Interim Report - HR CTC PredictionDocument16 pagesCapstone Interim Report - HR CTC Predictionchinudash86% (7)
- QMT 3001 Business Forecasting Term ProjectDocument30 pagesQMT 3001 Business Forecasting Term ProjectEKREM ÇAMURLUNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods: SKASSI Alexandra Penmatsa Ramya BOUTROS Ghassan WANG KankanDocument18 pagesQuantitative Methods: SKASSI Alexandra Penmatsa Ramya BOUTROS Ghassan WANG Kankanramya penmatsaNo ratings yet
- Students Tutorial Answers Week2Document10 pagesStudents Tutorial Answers Week2HeoHamHốNo ratings yet
- Think Pair Share Team G1 - 7Document8 pagesThink Pair Share Team G1 - 7Akash Kashyap100% (1)
- Extra Exercises - Introductory StatisticsDocument8 pagesExtra Exercises - Introductory Statisticsworks.aliaazmiNo ratings yet
- Basic Data Analysis in Action Research With ComputerDocument43 pagesBasic Data Analysis in Action Research With ComputerIroal Joanne Narag PersonNo ratings yet
- Percentages Short Cut MethodsDocument17 pagesPercentages Short Cut Methodsshaan02040% (2)
- Question #1: Ms FinanceDocument5 pagesQuestion #1: Ms Financezungetsu100% (1)
- 2 Assignment For Data Analysis For Decision Making: Dipanwita GhoshDocument13 pages2 Assignment For Data Analysis For Decision Making: Dipanwita GhoshDipanwita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Homework Panel DataDocument2 pagesHomework Panel DataCitra WiduriNo ratings yet
- BB0010 - Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDocument15 pagesBB0010 - Quantitative Techniques in BusinessYoubarajsharmaNo ratings yet
- STAT 1043 Homework 9Document3 pagesSTAT 1043 Homework 9mapletonNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 2 - SolutionsDocument13 pagesPractice Paper 2 - SolutionsMarcel JonathanNo ratings yet
- Reduce The Failure Rate of The Screwing Process With Six Sigma ApproachDocument8 pagesReduce The Failure Rate of The Screwing Process With Six Sigma ApproachLe ProfesseurNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics Using Microsoft ExcelDocument5 pagesDescriptive Statistics Using Microsoft ExcelVasant bhoknalNo ratings yet
- The Measurement ImperativeDocument10 pagesThe Measurement ImperativeAnonymous PKVCsG0% (1)
- L-Data Analysis For Accountants Assessment 2Document10 pagesL-Data Analysis For Accountants Assessment 2gatunemosesNo ratings yet
- The Art of PD Curve Calibration: Dirk Tasche December 15, 2012Document36 pagesThe Art of PD Curve Calibration: Dirk Tasche December 15, 2012karasa1No ratings yet
- Ch18 Evans BA1eDocument878 pagesCh18 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch17 Part2 Evans BA1eDocument18 pagesCh17 Part2 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch16 Evans BA1eDocument38 pagesCh16 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch17 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument12 pagesCh17 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch17 Part1 Evans BA1eDocument17 pagesCh17 Part1 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch18 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument5 pagesCh18 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch16 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument23 pagesCh16 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch14 Evans BA1eDocument65 pagesCh14 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch13 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument10 pagesCh13 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch15 Evans BA1eDocument41 pagesCh15 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch13 Evans BA1eDocument35 pagesCh13 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch11 Part2 Evans BA1eDocument25 pagesCh11 Part2 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch9 Evans BA1eDocument136 pagesCh9 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch12 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument56 pagesCh12 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli777750% (2)
- Ch11 Part1 Evans BA1eDocument24 pagesCh11 Part1 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch7 Evans BA1eDocument107 pagesCh7 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch12 Evans BA1eDocument256 pagesCh12 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch8 Evans BA1eDocument32,767 pagesCh8 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch9 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument5 pagesCh9 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch8 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument32,767 pagesCh8 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch5 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument7 pagesCh5 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch5 Evans BA1eDocument91 pagesCh5 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch6 Evans BA1eDocument74 pagesCh6 Evans BA1eyarli7777No ratings yet
- Ch4 Evans BA1e Case SolutionDocument33 pagesCh4 Evans BA1e Case Solutionyarli7777No ratings yet
- How Google WorksDocument9 pagesHow Google WorksHoangDuongNo ratings yet
- Al Madad-Yusuf Khattar MuhammadDocument12 pagesAl Madad-Yusuf Khattar MuhammadMujahid Asaadullah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Documented Essay About EmojisDocument8 pagesDocumented Essay About EmojisSweet MulanNo ratings yet
- Anticipating Strategy DecayDocument14 pagesAnticipating Strategy DecayRoshela KhanNo ratings yet
- Hicks Community & Nation-State in East TimorDocument4 pagesHicks Community & Nation-State in East TimorDaniel De LuccaNo ratings yet
- Comfort For Grieving ParentsDocument9 pagesComfort For Grieving Parentsapi-26605500No ratings yet
- Vajra Songs of The Indian SiddhasDocument21 pagesVajra Songs of The Indian SiddhasHeruka108100% (1)
- The Portrait of A Lady - NotesDocument5 pagesThe Portrait of A Lady - NotesQudsiyah AdvaniNo ratings yet
- English Model Paper 3 emDocument15 pagesEnglish Model Paper 3 emReddy GmdNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Knowledge by Niccolo TucciDocument5 pagesThe Evolution of Knowledge by Niccolo TucciPaulo RodriguesNo ratings yet
- A Discussion On The Names and Attributes of AllahDocument3 pagesA Discussion On The Names and Attributes of AllahmaryamNo ratings yet
- Apprentice Manual FinalDocument112 pagesApprentice Manual FinalshsnaNo ratings yet
- Opinion ParagraphDocument1 pageOpinion Paragraphapi-273326408No ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument10 pagesSimple Past TenseEka FitriNo ratings yet
- G.C.E. (Advanced Level) General EnglishDocument147 pagesG.C.E. (Advanced Level) General EnglishMaliNo ratings yet
- Tinder and Humanitarian Hook-Ups: The Erotics of Social Media RacismDocument4 pagesTinder and Humanitarian Hook-Ups: The Erotics of Social Media RacismMartaNo ratings yet
- Slac Eval MayDocument36 pagesSlac Eval MayJMAR ALMAZANNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Dropout Rate at Secondary School Level in Private Schools of Punjab, PakistanDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Dropout Rate at Secondary School Level in Private Schools of Punjab, PakistanImran Malik ImranNo ratings yet
- Traditional Public Administration Versus The New Public Management: Accountability Versus Efficiency James P. PfiffnerDocument10 pagesTraditional Public Administration Versus The New Public Management: Accountability Versus Efficiency James P. PfiffnerChantal FoleriNo ratings yet
- RPT KSSMPK BMDocument11 pagesRPT KSSMPK BMSITI NABILA AISHAHNo ratings yet
- Assessing Reading. (2000) - J. Charles Alderson. Cambridge: CambridgeDocument4 pagesAssessing Reading. (2000) - J. Charles Alderson. Cambridge: CambridgeThariq Al FalahNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Axioms: The Question of Objectivity in MathematicsDocument19 pagesBeyond The Axioms: The Question of Objectivity in Mathematicscpeter9No ratings yet
- Jaimini KarakasDocument3 pagesJaimini KarakasnmremalaNo ratings yet
- Iich 13Document21 pagesIich 13elisha89261No ratings yet
- Lab Report: Rocket Experiment 2017Document20 pagesLab Report: Rocket Experiment 2017api-343596257No ratings yet
- Academic Word List Generalizing/ Hedging Practice: Downloaded FromDocument2 pagesAcademic Word List Generalizing/ Hedging Practice: Downloaded FromLindsey CottleNo ratings yet
- BK00906 Interior Pages 26Document2 pagesBK00906 Interior Pages 26Tatu RrowyoNo ratings yet
- Lakshmi Mantras To Chant For Success, Prosperity and WealthDocument5 pagesLakshmi Mantras To Chant For Success, Prosperity and WealthDurgaNo ratings yet
- Commit30 - Goal Getting GuideDocument4 pagesCommit30 - Goal Getting GuidePongnateeNo ratings yet
- Air Properties Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAir Properties Lesson Planapi-489169715No ratings yet