Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lat Short Pile
Uploaded by
magdyamdbCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lat Short Pile
Uploaded by
magdyamdbCopyright:
Available Formats
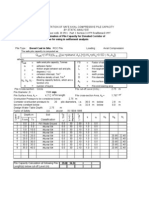
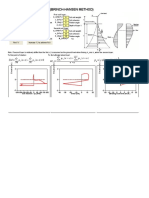
LATERALLY LOADED PILE (BRINCH-HANSEN METHOD)
H (kN) =
e (m) =
40.0
18.30
Lateral working load
Height of load application
B (m) =
L (m) =
Required FoS =
1.05
4.00
1.00
Pile diameter
Initial guess for embedment
Overall factor of safety
Mmax (kN.m) =
1000
Pile moment capacity
n1 =
20
# of elements above x
n2 =
10
2.38
40.7
x (m) =
Hu (kN) =
Find "x"
First soil layer:
g1 (kN/m) = 0
c 1 (kPa) =
f1 (deg) =
d1 (m) =
0
0
0
Soil unit weight
Soil cohesion
Friction angle
Depth of layer 1
Second soil layer:
g2 (kN/m) = 17 Soil unit weight
# of elements below x
Depth to point of rotation
FoS =
1.02
c 2 (kPa) =
40 Soil cohesion
f2 (deg) = 0 Friction angle
Mu (kN.m) = 757
Increase "L" to achieve FoS
Note: If second layer is relatively stiffer than the first, d1 is assumed as the ground level when finding Kq and Kc within the second layer.
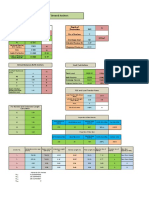
To find point of rotation:
To find ultimate
lateral load:
x
x L
L
M pu e z pu e z 0
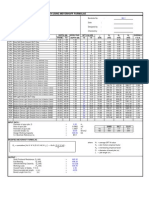
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
-6
-400
zx
Elevation (m)
Elevation (m)
z 0
-200
200
Soil reaction - pz (kPa)
400
z0
z x
p u gzK qz cK cz B
e x
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
-6
-600
Elevation (m)
-400
-200
Shear (kN)
200
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
-6
-1000
L
n
Bending moments (kN.m)
1000
You might also like
- Secant Pile RC Retaining WallDocument6 pagesSecant Pile RC Retaining WallUmesh Chamara100% (2)
- Broms MethodDocument1 pageBroms MethodTemp Temptemp100% (3)
- Lateral Load Pile P-Y MethodDocument2 pagesLateral Load Pile P-Y MethodCarlos Valverde Portilla100% (2)
- Pile Capacity CalculationDocument3 pagesPile Capacity CalculationArnab Sur67% (3)
- Block Foundation DesignDocument1 pageBlock Foundation DesigndantevariasNo ratings yet
- Concrete Cores-Lift Walls DesignDocument10 pagesConcrete Cores-Lift Walls DesignmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- All PileDocument15 pagesAll PileMohd Arman Meohan100% (3)
- Pile SpringDocument6 pagesPile Springkaleswara_tellakula100% (2)
- Retaining Wall With AnchorsDocument11 pagesRetaining Wall With Anchorsmailmaverick8167100% (3)
- Pile Cap DesignDocument228 pagesPile Cap Designraymond80% (5)
- Design of Sanitary Wastewater ManholesDocument5 pagesDesign of Sanitary Wastewater Manholessujith s pNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation and Strengthening of Old Masonry Buildings H. Meireles R. Bento Março de 2013Document27 pagesRehabilitation and Strengthening of Old Masonry Buildings H. Meireles R. Bento Março de 2013magdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Nicira - It Is Time To Virtualize The NetworkDocument9 pagesNicira - It Is Time To Virtualize The Networkcsp_675491No ratings yet
- HSM Info and CommandsDocument17 pagesHSM Info and CommandsapmountNo ratings yet
- ASME B1.16 - B1.16M - 1984 (Reaffirmed 2006) PDFDocument184 pagesASME B1.16 - B1.16M - 1984 (Reaffirmed 2006) PDFKristin Jones100% (1)
- Soil Pile CapacityDocument26 pagesSoil Pile CapacityOmar Najm100% (2)
- Pile Length CalculationDocument3 pagesPile Length CalculationCivilax.comNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity Analysis NewDocument30 pagesBearing Capacity Analysis Newauliyanusyura100% (2)
- Auger FoundationDocument9 pagesAuger Foundationpakbilal1No ratings yet
- Lateral Loads On PilesDocument5 pagesLateral Loads On Pilesandyhr100% (1)
- Pile DesignDocument17 pagesPile DesignTuan Syed100% (4)
- Pile Capacity & SettlementDocument7 pagesPile Capacity & SettlementbonnicoNo ratings yet
- Design of Bored Pile at Abut A & BDocument10 pagesDesign of Bored Pile at Abut A & BLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- BROMS Horiz Loading On Piles (Cohesionless) - LABKOMPUSATDocument1 pageBROMS Horiz Loading On Piles (Cohesionless) - LABKOMPUSATDanny Erlangga Supriyadi100% (1)
- Pile Geotechnical &structural Design Using SPT ValuesDocument12 pagesPile Geotechnical &structural Design Using SPT ValuesCivilax.comNo ratings yet
- Lateral Pile Capacity - BromsDocument2 pagesLateral Pile Capacity - Bromscalky117100% (1)
- Winkler Spring Calculation ForAbutment BoredPileDocument1 pageWinkler Spring Calculation ForAbutment BoredPileVal Beltran100% (2)
- Pile DesignDocument3 pagesPile Designalinawaz91100% (9)
- Pile Design EN1997Document4 pagesPile Design EN1997ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Retaining Wall With PilesDocument7 pagesRetaining Wall With PilesKaosar Alam Rocky100% (3)
- Pile FundationDocument49 pagesPile FundationFranklyn GenoveNo ratings yet
- Tension Design-Reaction Pile Tower BDocument4 pagesTension Design-Reaction Pile Tower BsinthianNo ratings yet
- PILE Analysis - Design 1.4Document99 pagesPILE Analysis - Design 1.4HanafiahHamzahNo ratings yet
- Laterally Loaded Piles BromsDocument3 pagesLaterally Loaded Piles BromsAnonymous AXaLBO4yNo ratings yet
- Calculation Report - C01Document29 pagesCalculation Report - C01francis0511No ratings yet
- Pile CapacityDocument6 pagesPile Capacityhemantkle2u100% (1)
- Bored Pile Calc. SpreedsheetDocument1 pageBored Pile Calc. SpreedsheetandinumailNo ratings yet
- Design Capacity of Bored Pile - by AndypasviDocument10 pagesDesign Capacity of Bored Pile - by AndypasviRamilArtatesNo ratings yet
- Pile Design - Great StuffDocument126 pagesPile Design - Great StuffMaryanne Tana89% (9)
- Pile Capacity - BYWGDocument70 pagesPile Capacity - BYWGHamidAffandyNo ratings yet
- BpileDocument2 pagesBpileAlsonChinNo ratings yet
- Pile Design SheetDocument14 pagesPile Design SheetKhader Abu-dagga71% (7)
- Lateral Capacity of Pile (FEM)Document26 pagesLateral Capacity of Pile (FEM)Civilax.comNo ratings yet
- Project: Pilipinas Kao Inc.: Slope StabilityDocument5 pagesProject: Pilipinas Kao Inc.: Slope StabilityclarkgaguiNo ratings yet
- Design of Ground Anchors For ClaysDocument1 pageDesign of Ground Anchors For ClaysMUHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- Design Calculation For Pile Length Using Meyerhoff FormulaeDocument1 pageDesign Calculation For Pile Length Using Meyerhoff Formulaeezarul fitri83% (6)
- IksaPro en v1.0 Demo 3anchorsDocument20 pagesIksaPro en v1.0 Demo 3anchorsEduardo MarquesNo ratings yet
- (Bore Hole No. 2) : Calculation Spec.: NO. Soil Bearing & Pile Capacity REV. No.: 0Document26 pages(Bore Hole No. 2) : Calculation Spec.: NO. Soil Bearing & Pile Capacity REV. No.: 0mayureshNo ratings yet
- Bored Pile Design - Deep FoundationDocument6 pagesBored Pile Design - Deep Foundationbuffyto5377No ratings yet
- Richart's Formula - Machine FoundationDocument3 pagesRichart's Formula - Machine Foundationdebjyoti_das_6No ratings yet
- Bored Pile FDN - BearingCapacity-450mmDocument16 pagesBored Pile FDN - BearingCapacity-450mm폴로 쥰 차No ratings yet
- Km5 978Document243 pagesKm5 978Nguyen Anh100% (1)
- Working - With Mooring ForceDocument14 pagesWorking - With Mooring ForceJack DoverNo ratings yet
- Laterally Loaded Pile (Brinch-Hansen Method) : First Soil LayerDocument2 pagesLaterally Loaded Pile (Brinch-Hansen Method) : First Soil LayerLucas Ziliotto VieroNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional 2011 - NoteDocument6 pagesAutodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional 2011 - Note01oscar1977100% (1)
- Shallow FoundationDocument15 pagesShallow FoundationRiskiawan ErtantoNo ratings yet
- Concentric Foundation Revised 2.15Document5 pagesConcentric Foundation Revised 2.15Eldho GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument5 pagesPile DesignKanu PreiyaNo ratings yet
- Boundary Wall Design - Final For RFCDocument10 pagesBoundary Wall Design - Final For RFCShubham KhareNo ratings yet
- Ground Slab Design (Zone-4)Document769 pagesGround Slab Design (Zone-4)AbhiNo ratings yet
- L-Footing Design ProgramDocument31 pagesL-Footing Design ProgramMesfin DerbewNo ratings yet
- L Footing Design ProgramDocument5 pagesL Footing Design ProgramTariku DessuNo ratings yet
- Foundations PDFDocument5 pagesFoundations PDFrajiuaeNo ratings yet
- Wind Pressure CalculationDocument20 pagesWind Pressure CalculationARUN RAWATNo ratings yet
- 1 Level:: 2.1 Material PropertiesDocument7 pages1 Level:: 2.1 Material Properties144990No ratings yet
- DR Fixit General Repair Remedial Waterproofing Guide PDFDocument40 pagesDR Fixit General Repair Remedial Waterproofing Guide PDFandrealeger755774No ratings yet
- DR Fixit Waterproofing ReckonerDocument40 pagesDR Fixit Waterproofing ReckonerSusheel TalrejaNo ratings yet
- ENERCALC Biaxial Concrete Solver BasisDocument11 pagesENERCALC Biaxial Concrete Solver BasismagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Research On Property Property of Steel-Encased Concrete On Property of Steel - Encased Concrete Composite Beam With Superior PerformanceDocument4 pagesResearch On Property Property of Steel-Encased Concrete On Property of Steel - Encased Concrete Composite Beam With Superior PerformanceseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- The Wet-Seal System Waterproofing Membrane: ProductDocument4 pagesThe Wet-Seal System Waterproofing Membrane: ProductmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Ductility of Prefabricated Cage Reinforced Concrete Beams: Analytical StudyDocument9 pagesDuctility of Prefabricated Cage Reinforced Concrete Beams: Analytical StudymagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Confined Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument5 pagesConfined Reinforced Concrete BeammagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Pilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramDocument24 pagesPilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramBabacar NIANGNo ratings yet
- LatPilePY - 2 SAP EXAMPLEDocument38 pagesLatPilePY - 2 SAP EXAMPLEmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Pilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramDocument24 pagesPilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramBabacar NIANGNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap Design 26102009Document136 pagesPile Cap Design 26102009magdyamdb100% (1)
- Pilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramDocument24 pagesPilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramBabacar NIANGNo ratings yet
- BROMS Horiz Loading On Piles (Cohesionless) - LABKOMPUSATDocument1 pageBROMS Horiz Loading On Piles (Cohesionless) - LABKOMPUSATDanny Erlangga Supriyadi100% (1)
- Alcocer Recent Experimental Evidence On The Seismic Performance of Rehabilitation Techniques in MexicoDocument37 pagesAlcocer Recent Experimental Evidence On The Seismic Performance of Rehabilitation Techniques in MexicomagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- LatPilePY - 2 SAP EXAMPLEDocument38 pagesLatPilePY - 2 SAP EXAMPLEmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Pilegroup-Stiffpilecap VERY GOOD MahfuzDocument1 pagePilegroup-Stiffpilecap VERY GOOD MahfuzmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Case Studies of Remedial Waterproofing and Repair of BasementsDocument5 pagesCase Studies of Remedial Waterproofing and Repair of BasementsmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Horiz Loading On Piles CohesiveDocument1 pageHoriz Loading On Piles CohesivemagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Pilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramDocument24 pagesPilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramBabacar NIANGNo ratings yet
- Alcocer Recent Experimental Evidence On The Seismic Performance of Rehabilitation Techniques in MexicoDocument37 pagesAlcocer Recent Experimental Evidence On The Seismic Performance of Rehabilitation Techniques in MexicomagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Repair and Strengthening of Bridge SubstructuresDocument292 pagesRepair and Strengthening of Bridge SubstructuresLuis Alberto Riquelme VidalNo ratings yet
- Seismic Vulnerability of The Himalayan Half-Dressed Rubble Stone Masonry Structures, Experimental and Analytical StudiesDocument14 pagesSeismic Vulnerability of The Himalayan Half-Dressed Rubble Stone Masonry Structures, Experimental and Analytical StudiesmagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Flexural-Shear Failure of A Full Scale Tested RC Bridge Strengthened With NSM CFRP. Shear Capacity AnalysisDocument18 pagesFlexural-Shear Failure of A Full Scale Tested RC Bridge Strengthened With NSM CFRP. Shear Capacity AnalysismagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Pilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramDocument24 pagesPilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramBabacar NIANGNo ratings yet
- EQ31 Seismic Behavior of Beam Column Joints-LibreDocument29 pagesEQ31 Seismic Behavior of Beam Column Joints-LibremagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Plandoc 4 3763Document6 pagesPlandoc 4 3763magdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Concrete Tanks Conical BaseDocument10 pagesCylindrical Concrete Tanks Conical BaseWilman Barrera GradosNo ratings yet
- EARTHSCIENCE ppt2Document8 pagesEARTHSCIENCE ppt2Rommel DominguezNo ratings yet
- 591 Useful Unix Commands PDFDocument1 page591 Useful Unix Commands PDFrohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 EnglishDocument53 pagesChapter 9 Englishhoda melhemNo ratings yet
- Boakye Danquah Mphil Analytical Chemistry PG 1: THE 'Heart'' of Electronic Noses ' Chemosensors''Document21 pagesBoakye Danquah Mphil Analytical Chemistry PG 1: THE 'Heart'' of Electronic Noses ' Chemosensors''Alexander Appiah-KubiNo ratings yet
- AmdDocument14 pagesAmdObed Andalis100% (1)
- Interpretations of The IMO Gas Code: International Association of Classification SocietiesDocument53 pagesInterpretations of The IMO Gas Code: International Association of Classification SocietiesAlkaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Wing Design Parameter Selection Rev 3 PDFDocument8 pagesPreliminary Wing Design Parameter Selection Rev 3 PDFvirgilioNo ratings yet
- HW 2 SolDocument5 pagesHW 2 SoltechutechuNo ratings yet
- Surveying 2 Final ExamDocument3 pagesSurveying 2 Final ExamRodin James GabrilloNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifiers: Ranjith Office Level 4 - Building 193 - EEE BuildingDocument19 pagesPower Amplifiers: Ranjith Office Level 4 - Building 193 - EEE BuildingArambya Ankit KallurayaNo ratings yet
- UMTS TutorialDocument84 pagesUMTS Tutorialnale_2100% (1)
- Router Board Performance TestsDocument2 pagesRouter Board Performance TestsedkaviNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory of The AtomDocument18 pagesQuantum Theory of The AtomSpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- For And: Viterbi Decoding Satellite Space CommunicationDocument14 pagesFor And: Viterbi Decoding Satellite Space CommunicationRosi Marleny Machuca rojasNo ratings yet
- Condensatoare MLCC-1837944Document130 pagesCondensatoare MLCC-1837944gigiNo ratings yet
- Java LabDocument67 pagesJava Labشیخ صاحبNo ratings yet
- Elementary Data Organisation-1Document15 pagesElementary Data Organisation-1zidhi bachaNo ratings yet
- CS 515 Data Warehousing and Data MiningDocument5 pagesCS 515 Data Warehousing and Data MiningRahumal SherinNo ratings yet
- Communication Engineering 2 MarksDocument38 pagesCommunication Engineering 2 MarksNandhini100% (2)
- On The Coupling of Mechanics With Bioelectricity and Its Role in MorphogenesisDocument12 pagesOn The Coupling of Mechanics With Bioelectricity and Its Role in MorphogenesisVishvendraNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Radiology: Bachtiar MurtalaDocument75 pagesBasic Principles of Radiology: Bachtiar MurtalaMargaretha SonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Components of CADCAMCAE SystemsDocument35 pagesChapter 02 - Components of CADCAMCAE SystemsKeVal PaTelNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.A.VEX SimpleMachineInvestigationDocument14 pages1.1.1.A.VEX SimpleMachineInvestigationDivya Sureshkannan100% (2)
- Day 4 and 5 - Deductive Reasoning and Two Column Proofs AnswersDocument4 pagesDay 4 and 5 - Deductive Reasoning and Two Column Proofs Answersapi-253195113No ratings yet
- Comp 1 2022 1 Ho ActivityDocument5 pagesComp 1 2022 1 Ho ActivityGintoki SakataNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications-Notes PDFDocument110 pagesAnalog Communications-Notes PDFjyothimunjam100% (1)
- Testing & Maintenance of Rotating Machines Type Tests, Routine Tests & Special Tests of 1 & 3 Phase Induction MotorsDocument12 pagesTesting & Maintenance of Rotating Machines Type Tests, Routine Tests & Special Tests of 1 & 3 Phase Induction MotorsPKNo ratings yet