Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Viruses
Uploaded by
Chris_Barber09Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Viruses
Uploaded by
Chris_Barber09Copyright:
Available Formats
MCAT Biology Core Concept Cheat Sheet
10: Viruses
Key Terms
Virus Genetics & Pathogenesis
Capsid: Protein shell enclosing the nucleic acid.
Nucleocapsid: Composed of the nucleic acid and its
surrounding proteins, forming the core of the virus.
Envelope: Glycoproteins embedded in bi-layer lipids
surrounding the nucleocapsid (not all viruses have this
layer).
Virion: A complete infectious viral particle.
Viroid: An infectious particle made of naked RNA molecules,
no protein.
Prion: An infectious particle made of protein molecules, no
nucleic acids; can be inherited.
Lytic Cycle: A virus infection cycle that results in virus
multiplication and lysis of the host cell.
Lysogenic cycle: Bacteriophage DNA can be integrated into
a host genome and replicated with host DNA; no cell lysis
occurs.
Latent infection: Virus DNA is incorporated into host cell
(usually higher organisms) and replicates with the host DNA.
Infection results with no symptoms for a period of time.
Transformation: The modification of the genotype of a cell
by introduction of DNA from another source.
Transduction: Transformation mediated by latent infection
the viral DNA becomes part of the host genome.
Cell transformation: The process during which a normal
cell becomes cancerous.
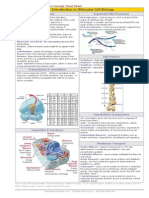
Viral Structure and Classification
Lytic cycle
Vs
Latent cycle
Host
phage
Cell lysis &
virion release
Assembly
Lytic induction
Virus
Host integration
Viral genetics:
High mutation rate for RNA virus due to absence of proofreading mechanism in genome replication.
Viral gene recombination due to simultaneous infection of
different viruses.
Two basic structures:
Rod (helical) shape
Isomeric shape
Viral pathogenesis:
Implantation of virus at the portal of entry
Local replication
Spread to target organs (disease sites)
Spread to sites or shedding virus into environment
Classification based on the genome:
DNA virus
dsDNA
ssDNA
RNA virus
dsRNA
ssRNA(+)
ssRNA(-)
retrovirus
Three factors:
Accessibility of virus to tissue
Cell susceptibility to virus multiplication
Virus susceptibility to host defenses
Cellular pathogenesis
Direct cell damage or cell death
Indirect cell damage such as inflammation
Bacteriophage
Virus Multiplication
Based on the genome, virus multiplication requires:
Head
DNA
Proteins
1. replication of viral genome & synthesis of viral structure
proteins.
2. utilizes host cell transcriptional and translational
machinery.
Neck
Collar
Core
attachment
release
Tail
Sheath
Pins
Fibers
uncoating
virus
assembly
replication
How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related to this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then write it out on a
blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exam.
RapidLearningCenter.com
Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- BIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandBIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology MasterDocument6 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Masterdealt100% (5)
- Muscular SystemDocument1 pageMuscular SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- ProteinsDocument1 pageProteinsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Human Physiology IntroductionDocument1 pageHuman Physiology IntroductionChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Cell Biology IntroductionDocument1 pageCell Biology IntroductionChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument1 pageChemical Basis of LifeChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument1 pagePeripheral Nervous SystemChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System Cheat Sheet - Key Terms & DivisionsDocument1 pageAutonomic Nervous System Cheat Sheet - Key Terms & DivisionsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- 01: Introduction To Evolutionary Thought: Key Evolution TermsDocument1 page01: Introduction To Evolutionary Thought: Key Evolution TermsBlaine Rogalski100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- High School Biology Core ConceptsDocument7 pagesHigh School Biology Core ConceptsChris_Barber0986% (7)
- Urinary SystemDocument1 pageUrinary SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis and MeiosisChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Hormone regulation and the hypothalamus-pituitary axisDocument16 pagesHormone regulation and the hypothalamus-pituitary axisCal GoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentDocument40 pagesBiotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentnescafeforeverNo ratings yet
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDocument8 pagesMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezNo ratings yet
- MCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFDocument16 pagesMCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- AP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide ANSWERSDocument4 pagesAP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide ANSWERSRam LouNo ratings yet
- Selective Attention and Problem Solving TechniquesDocument28 pagesSelective Attention and Problem Solving TechniquesMahdeeHaqueSyed100% (2)
- 03 Adaptive Immune SystemDocument14 pages03 Adaptive Immune SystemEnea NastriNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes PDFDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Notes PDFChris_Barber0950% (6)
- Human Genetics: From DNA to ProteinsDocument28 pagesHuman Genetics: From DNA to ProteinsjasNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Cell Function and InheritanceDocument7 pagesGenetic Control of Cell Function and InheritanceSADAVEJO100% (1)
- College PhysicsDocument6 pagesCollege PhysicsDelixae Phoinix100% (1)
- Molecular BiologyDocument54 pagesMolecular BiologyAnonymous GhQ1eIyxunNo ratings yet
- Alan's Bio NotesDocument19 pagesAlan's Bio Notesluongc4100% (1)
- Amino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAmino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIU100% (1)
- MCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesDocument4 pagesMCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesNicole Ann LimNo ratings yet
- Microbiology MasterDocument13 pagesMicrobiology MasterDelixae Phoinix100% (6)
- ImmunologyDocument1 pageImmunologyChris_Barber0986% (7)
- DNA Structure and Replication ExplainedDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and Replication ExplainedJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Cell Exam Practice Multiple ChoiceDocument46 pagesCell Exam Practice Multiple ChoiceVulneraSanentur67% (3)
- Examkrackers General Chemistry NotesDocument16 pagesExamkrackers General Chemistry NotesddNo ratings yet
- Sensory Perception and Cognitive ProcessesDocument158 pagesSensory Perception and Cognitive ProcessesmedmedNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Notes 1 PDFDocument23 pagesMolecular Biology Notes 1 PDFChris_Barber09100% (3)
- Cell Organelles ReviewDocument5 pagesCell Organelles ReviewvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Cell CommunicationDocument45 pagesCell CommunicationWilson HindartoNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet (Bio) 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet (Bio) 1Kelvin KohNo ratings yet
- Intermediate FilamentsDocument4 pagesIntermediate FilamentsSai SridharNo ratings yet
- DAT Bootcamp Biology Notes PDFDocument123 pagesDAT Bootcamp Biology Notes PDFgefNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Structure and Function of Proteins and Their Constituent Amino AcidsDocument31 pagesAmino Acids: Structure and Function of Proteins and Their Constituent Amino AcidsNate Vojtik100% (4)
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument56 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJaime Soriano100% (1)
- Final Exam Study Guide TipsDocument22 pagesFinal Exam Study Guide Tipsrazgriz1211No ratings yet
- MC Chapter 48 TestDocument14 pagesMC Chapter 48 Testbori0905100% (2)
- MCAT Biology Complete OutlinesDocument34 pagesMCAT Biology Complete OutlinesJacob Mikhail90% (10)
- Cell Biology Exam 1 ReaDocument7 pagesCell Biology Exam 1 ReaCsa At Uh100% (3)
- Biology Staar Eoc Review Study GuideDocument67 pagesBiology Staar Eoc Review Study Guideapi-233187566100% (1)
- Chemistry Lecture 1 - Atoms, Molecules, and Quantum MechanicsDocument3 pagesChemistry Lecture 1 - Atoms, Molecules, and Quantum MechanicsChethranNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Multiple Choice ReviewDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Multiple Choice ReviewYasi0% (1)
- MCAT ReviewDocument114 pagesMCAT Reviewjustinwendel100% (4)
- Biology Midterm Study GuideDocument7 pagesBiology Midterm Study Guideapi-313911292No ratings yet
- MCAT Lab TechniquesDocument17 pagesMCAT Lab TechniquesJim Smith100% (1)
- AAMC Content Outline - Psych and SociologyDocument51 pagesAAMC Content Outline - Psych and SociologyShalini VijayNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument42 pagesBiology NotesNate VojtikNo ratings yet
- CH 5 - Virology 1Document60 pagesCH 5 - Virology 1Tariku TadesaNo ratings yet
- Virus characteristics and replication mechanismsDocument28 pagesVirus characteristics and replication mechanismsMeilana Sapta D67% (3)
- 4.Mdp Pengantar VirologiiDocument27 pages4.Mdp Pengantar VirologiiAhmad AgielNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Viruses and Viral Pathogenesis 1Document37 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Viruses and Viral Pathogenesis 1Gabriella CrooksNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System NotesDocument3 pagesReproductive System NotesChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Document5 pagesBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Notes CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Document4 pagesNucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- MCAT O-Chem NotesDocument1 pageMCAT O-Chem NotesChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Digestive System PDFDocument3 pagesDigestive System PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- BSC 2010: Explore Macromolecules and Their FunctionsDocument11 pagesBSC 2010: Explore Macromolecules and Their FunctionsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Heart Notes PDFDocument2 pagesHeart Notes PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Cardiovasculary System PDFDocument5 pagesCardiovasculary System PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Notes RNA and DNADocument23 pagesNotes RNA and DNAChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Rate Law GraphsDocument2 pagesRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Leaving GroupsDocument1 pageLeaving GroupsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Notes CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Aromatic Notes 2 PDFDocument6 pagesAromatic Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Carbs: Nature's Most Abundant MoleculesDocument24 pagesCarbs: Nature's Most Abundant MoleculesGulus CfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionDocument2 pagesChapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Extra Chirality ProblemsDocument21 pagesExtra Chirality ProblemsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Amino Acid NotesDocument15 pagesAmino Acid NotesChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Physics Rules 5Document10 pagesPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- Physics Rules 1Document2 pagesPhysics Rules 1Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Physics Rules 4Document6 pagesPhysics Rules 4Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- MCAT Physics Equation SheetDocument6 pagesMCAT Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Regents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsDocument3 pagesRegents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Physics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Equation SheetChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- AAMC 11 Essay 1Document6 pagesAAMC 11 Essay 1Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Physics Rules 2Document4 pagesPhysics Rules 2Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Review: Essential Equations and ConceptsDocument9 pagesAP Physics 1 Review: Essential Equations and ConceptsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- 107 Rules in PhysicsDocument2 pages107 Rules in PhysicsChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- AAMC 11 Essay 2Document5 pagesAAMC 11 Essay 2Chris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Complete VaccinationDocument2 pagesComplete VaccinationNgoo NwosuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Management in The Critically Ill: Jean-Louis VincentDocument6 pagesFluid Management in The Critically Ill: Jean-Louis VincentFlorentina NadisaNo ratings yet
- Eo No. 013 - 2018 Reorganization of BhertDocument2 pagesEo No. 013 - 2018 Reorganization of BhertAnne Kimberly Peñalba BabaanNo ratings yet
- Google CardboardDocument3 pagesGoogle CardboardMartínJiménezNo ratings yet
- 11 - Comfort, Rest and Sleep Copy 6Document28 pages11 - Comfort, Rest and Sleep Copy 6Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nres1dm-Chapter I and IIDocument35 pagesNres1dm-Chapter I and IImlmmandapNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent Paternity LeaveDocument2 pagesLetter of Intent Paternity LeaveFloryen Daprosa100% (1)
- AgraLi The Low Chloride Liquid Fertilizer For Sensitive Crops enDocument2 pagesAgraLi The Low Chloride Liquid Fertilizer For Sensitive Crops enASHNo ratings yet
- Biology 3rd ESO Full DossierDocument54 pagesBiology 3rd ESO Full DossierNinaNo ratings yet
- Table : Number of Population, Hospitals and Beds in All Over JordanDocument8 pagesTable : Number of Population, Hospitals and Beds in All Over JordanjNo ratings yet
- DSM 5Document35 pagesDSM 5Hemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Risk for Infection AssessmentDocument7 pagesRisk for Infection AssessmentLouis RoderosNo ratings yet
- Everett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookDocument46 pagesEverett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookJessica OlsonNo ratings yet
- Pta ResumeDocument2 pagesPta Resumeapi-669470996No ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals For Ratio of Two Poisson Rates Using The Method of Variance Estimates RecoveryDocument23 pagesConfidence Intervals For Ratio of Two Poisson Rates Using The Method of Variance Estimates RecoveryJaneNo ratings yet
- GastroparesisDocument10 pagesGastroparesisapi-437831510No ratings yet
- Week 4-Physical Fitness TestDocument38 pagesWeek 4-Physical Fitness TestCatherine Sagario OliquinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Local Government's Historical BackgroundDocument16 pagesLesson 1 Local Government's Historical BackgroundLorienelNo ratings yet
- Symbols On PackegingDocument3 pagesSymbols On PackegingsakibarsNo ratings yet
- Being A Medical DoctorDocument14 pagesBeing A Medical DoctorMichael Bill GihonNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent and Release, Waiver, and Quitclaim: Know All Men by These PresentsDocument2 pagesInformed Consent and Release, Waiver, and Quitclaim: Know All Men by These PresentsRobee Camille Desabelle-SumatraNo ratings yet
- Care of A Child With Cardiovascular DysfunctionDocument71 pagesCare of A Child With Cardiovascular DysfunctionMorgan Mitchell100% (1)
- SC 2Document2 pagesSC 2Ryan DelaCourt0% (3)
- UNIT-I (A) - Hospital and It's OrganizationDocument25 pagesUNIT-I (A) - Hospital and It's Organizationrajeshwari ninaweNo ratings yet
- Intro To Wastewater Collection and PumpingDocument84 pagesIntro To Wastewater Collection and PumpingMoh'd KhadNo ratings yet
- Assessed Conference Presentations ScheduleDocument2 pagesAssessed Conference Presentations ScheduleAna Maria Uribe AguirreNo ratings yet
- KPI - Foruth EditionDocument30 pagesKPI - Foruth EditionAnonymous qUra8Vr0SNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Schools Safety Monitoring ChecklistDocument5 pagesComprehensive Schools Safety Monitoring ChecklistKriss Paran100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 2Document5 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 2SANJEEV KUMARNo ratings yet