Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 Multisim DC PDF
Uploaded by
JeffreyBeridaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 Multisim DC PDF
Uploaded by
JeffreyBeridaCopyright:
Available Formats
MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
EE-2050
EE-2050 LABORATORY
EXPERIMENT 4 Week 5
Computer Circuit Simulation MULTISIM for DC Analysis
Goal To learn how to use a simulation program (Multisim) to analyze DC electric circuits. The same
simulation techniques also help in designing circuits.
Background In engineering, computer software is used extensively in the analysis and design of
electrical and electronic circuits. Computer simulations are one of the fundamental tools that allow you to
quickly and accurately determine how a circuit functions.
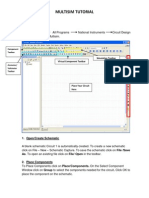
Procedure Run Multisim from:
Start / All Programs / National Instruments / Circuit Design Suite 10.x / Multisim
Youll first see the workspace, with the various toolbars. Note the blue buttons of the Virtual Toolbar near
the upper right. If its not enabled, then use View / Toolbars to enable it.
Virtual components differ from normal
ones in that they can be set to any
value, not just the commonlymanufactured values. Lets draw a
circuit with a DC voltage source
driving a two-resistor voltage divider.
In the Virtual Toolbar, click on Power
Source Components:
Click the DC Power Source icon and
then click the workspace to place it in
the drawing. Double-click it to
change its Voltage (V) value to 10
volts.
In the Virtual Toolbar, click on Basic Components:
Click on the Resistor and place one on the drawing. Do the same to
place a second one. To rotate the second one, right-click it and select rotate 90 clockwise. Change the
resistors to 2k and 3k as shown.
From the Power Source
Components window on the Virtual
Toolbar, choose Ground and place it
on the drawing. Now, wire the
components together by clicking the
first node, and then clicking the next
node.
Also, about two-thirds of the way
down the right-hand Instrument
Toolbar, click the Agilent Multimeter,
and then place it on the drawing.
Double-click the instrument icon to
see the photo. Connect the icon as
shown. Note how the terminals on
the icon are positioned as on the real
instrument.
MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
EE-2050
Turn on the Agilent Multimeter by clicking its Power button, and then press DC V to measure DC volts.
Finally, click the 0/1 simulation on/off switch at the far upper right of the screen:
to start the simulation. After a few seconds the Agilent Multimeter should read the
voltage (6 volts).
Stop the simulation and delete the Agilent Multimeter. Now, use a Measurement Probe:
which is in the Instrument Toolbar, near the bottom.
Run the simulation and note how the Measurement Probe
listbox shows the voltage and current:
Component abbreviations such as k (for kilo), u (for micro)
and m (for milli) can be used.
Try the multimeter, at the top of the Instrument Toolbar,
as a DC voltmeter (left), and also as a DC ammeter (right).
Note how the connection is broken to insert the ammeter
(DC is chosen using the ---- button):
In this experiment we dont need any controlled sources. But if we did, you could click on the Place
Source symbol at the upper left of the screen. This will show a complete set of components in the
Library. From that you can select a controlled source of any type. Note the diamond-shaped source, and
the rectangular sensor, both of which would need to be connected.
MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
EE-2050
Laboratory Assignment
For the circuit shown, analyze
the circuit three ways on
paper using KVL and KCL, by
building and measuring, and by
Multisim. Find the voltage
across and current through
every element.
Enter results in the table. Show calculations below:
Component
Vs
R1
R2
R3
Multisim Results
Voltage Current
Measured Results
Voltage Current
When finished, show the Multisim simulation to your professor.
Calculated Results
Voltage
Current
You might also like
- Lab - 2 Handout-ELEC 201Document11 pagesLab - 2 Handout-ELEC 201AmroKashtNo ratings yet
- Work Bench PDFDocument25 pagesWork Bench PDFJimi DbonoNo ratings yet
- MultiSim TutorialDocument25 pagesMultiSim TutorialskelleonNo ratings yet
- Electronic Workbench Multisim Tutorial (Basic)Document25 pagesElectronic Workbench Multisim Tutorial (Basic)ជើងកាង ភូមិNo ratings yet
- Multisim Tutorial: Basic Circuit SimulationDocument25 pagesMultisim Tutorial: Basic Circuit SimulationSilver WolvesNo ratings yet
- Multisim TutorialDocument9 pagesMultisim Tutorialapi-240822427No ratings yet
- Electroic Circuits Lab ReportDocument7 pagesElectroic Circuits Lab ReportYeabsiraNo ratings yet
- MtE-205 EPD LAB 03Document7 pagesMtE-205 EPD LAB 03Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- Starting Up with TINA TutorialDocument10 pagesStarting Up with TINA TutorialĐinh Bá ThànhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Drawing A 555 Timer CircuitDocument9 pagesTutorial 2 Drawing A 555 Timer CircuitCarlos OrtaNo ratings yet
- Multisim Tutorial: Component ToolbarDocument9 pagesMultisim Tutorial: Component ToolbarDeepikaNo ratings yet
- Multisim TutorialDocument9 pagesMultisim TutorialfreepizzaNo ratings yet
- LTspice Familiarization ActivityDocument5 pagesLTspice Familiarization ActivityHans PinonNo ratings yet
- E-Tap Software Simulation of Multi-Bus Power System Fault AnalysisDocument23 pagesE-Tap Software Simulation of Multi-Bus Power System Fault Analysisdeepesh chhetriNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Electricity Chapter 1 Multisim Laboratory: Introduction To Virtual vs. Real (Or Live) ComponentsDocument13 pagesElectronics and Electricity Chapter 1 Multisim Laboratory: Introduction To Virtual vs. Real (Or Live) ComponentsRubia IftikharNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Preparation of Electrical Circuits Simulations Using Multisim Electronics Workbench and Introduction To Lab Equipment'sDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 1 Preparation of Electrical Circuits Simulations Using Multisim Electronics Workbench and Introduction To Lab Equipment'sM. Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to NI MultiSIM Circuit Simulation SoftwareDocument36 pagesIntroduction to NI MultiSIM Circuit Simulation SoftwareDaniel Enrique Erazo MujicaNo ratings yet
- LTSpice TutorialDocument5 pagesLTSpice TutorialNanta FakihNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Simulating DC Circuits with MultisimDocument7 pagesIntroduction to Simulating DC Circuits with MultisimZwe Zan LynnNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document17 pagesLab Report 2aznia shireenNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Intro To Multisim - Revised - 07202009Document16 pagesLab 3 - Intro To Multisim - Revised - 07202009Vivian Hana NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18: Circuit Simulation in ProteusDocument7 pagesLecture 18: Circuit Simulation in ProteusHuzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- KFUPM EE201 Electric Circuits Lab Manual Simulation IntroductionDocument56 pagesKFUPM EE201 Electric Circuits Lab Manual Simulation Introductionsieged_rj3165No ratings yet
- Live Wire TutorialDocument6 pagesLive Wire TutorialMagfur RamdhaniNo ratings yet
- EE203 Lab ManualDocument48 pagesEE203 Lab Manualkannanchammy100% (1)
- 311 SPICE TutorialDocument9 pages311 SPICE TutorialBsomething1978No ratings yet
- R - H I T: Lab 1 Introduction To First Order Circuits Using Multisim, Matlab and Simulink ObjectiveDocument136 pagesR - H I T: Lab 1 Introduction To First Order Circuits Using Multisim, Matlab and Simulink ObjectiveGeorge BrownNo ratings yet
- Introduction to PSpice simulationDocument11 pagesIntroduction to PSpice simulationAseem GhimireNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electrical Circuit - Practical WorkbookDocument27 pagesFundamental of Electrical Circuit - Practical WorkbookBetel WondwossenNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With ADSDocument17 pagesGetting Started With ADSbayman66No ratings yet
- Lab 1 Exercise 1 Basic System Modelling and Data InputDocument7 pagesLab 1 Exercise 1 Basic System Modelling and Data InputScott SawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pspice PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Pspice PDFAseem GhimireNo ratings yet
- Vacation Training ELEC 1200 Working with NI Instruments MultisimDocument5 pagesVacation Training ELEC 1200 Working with NI Instruments Multisimjaya1816No ratings yet
- Simulating DC Circuits Using Pspice SoftwareDocument8 pagesSimulating DC Circuits Using Pspice SoftwareAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Multisim Extensions: ObjectiveDocument9 pagesMultisim Extensions: ObjectiveTara GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Drawing A Test Probe CircuitDocument10 pagesTutorial 3 Drawing A Test Probe CircuitFernando Valente100% (1)
- EEE111_Multisim_ManualDocument14 pagesEEE111_Multisim_ManualSHADOW manNo ratings yet
- Multisim Lab Tutorial - 1 PhaseDocument7 pagesMultisim Lab Tutorial - 1 PhasetbmNo ratings yet
- LTspice TutorialDocument5 pagesLTspice Tutorialcofffeee21No ratings yet
- Lab2-CAD ToolsDocument9 pagesLab2-CAD ToolsBEN KAPANSANo ratings yet
- LabManual PSBook2006 Revised Sept2010Document53 pagesLabManual PSBook2006 Revised Sept2010boopelectraNo ratings yet
- ECE Lab Manual on Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument92 pagesECE Lab Manual on Electric Circuit AnalysisMuhammad EjazNo ratings yet
- Lab#2Document21 pagesLab#2Hamza HassanNo ratings yet
- Spice For Ece 3041/ece3042: Pspice Ad - LNKDocument7 pagesSpice For Ece 3041/ece3042: Pspice Ad - LNKRyan Alexander BahrNo ratings yet
- PSIM Simulation Software Guide for Electrical Power Circuit AnalysisDocument11 pagesPSIM Simulation Software Guide for Electrical Power Circuit AnalysisMilton Barrientos Ramos Of̲̲̅̅i̲̲̅̅c̲̲̅̅i̲̲̅̅a̲̲̅̅l̲̲̅̅'̲̲̅̅F̲̲̅̅b̲̲̅̅No ratings yet
- Electronic Workbench Tutorial: Copy As BitmapDocument18 pagesElectronic Workbench Tutorial: Copy As Bitmapmclade01No ratings yet
- EWB TutorialDocument18 pagesEWB TutorialXereal SuarezNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Circuits BasicsDocument3 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits BasicsJuan Carlos MartinezNo ratings yet
- Introduction to ORCAD/PSPICE Capture SimulationDocument24 pagesIntroduction to ORCAD/PSPICE Capture SimulationSanjay ParelkarNo ratings yet
- Digital LED Thermometer with Microcontroller AVR ATtiny13From EverandDigital LED Thermometer with Microcontroller AVR ATtiny13Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsFrom EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Abc of Power Modules: Functionality, Structure and Handling of a Power ModuleFrom EverandAbc of Power Modules: Functionality, Structure and Handling of a Power ModuleNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionFrom EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Electronics Explained: Fundamentals for Engineers, Technicians, and MakersFrom EverandElectronics Explained: Fundamentals for Engineers, Technicians, and MakersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- CSE ReviewerDocument51 pagesCSE ReviewerJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- MCQ in EST by Melvin C. Arceo of PERC DCDocument35 pagesMCQ in EST by Melvin C. Arceo of PERC DCLocrian IonianNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF Preparation For Engineering PDFDocument14 pagesCurrent Electricity Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF Preparation For Engineering PDFJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- Emerging Management PracticesDocument13 pagesEmerging Management PracticesShielle AzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document21 pagesChapter 15JeffreyBerida100% (1)
- Arens Auditing and Assurance Services 13eDocument9 pagesArens Auditing and Assurance Services 13eintanfidztiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document42 pagesChapter 19Karissa GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Emerging Management PracticesDocument13 pagesEmerging Management PracticesShielle AzonNo ratings yet
- IC IntroductionDocument16 pagesIC IntroductionjhpandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document42 pagesChapter 19Karissa GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic CircuitsDocument36 pagesCombinational Logic CircuitsNalabolu Eshwari EshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document35 pagesChapter 18Mariechi Binuya100% (1)
- Practical Teaching Ideas For Multisim 12Document300 pagesPractical Teaching Ideas For Multisim 12Julio DinisNo ratings yet
- TB Raiborn - Responsibility Accounting and Transfer Pricing in Decentralized OrganizationDocument44 pagesTB Raiborn - Responsibility Accounting and Transfer Pricing in Decentralized OrganizationMayla Lei Pablo100% (1)
- TB Raiborn - Implementing Quality ConceptsDocument22 pagesTB Raiborn - Implementing Quality ConceptsJoan Grachell TaguilasoNo ratings yet
- NDocument9 pagesNJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- TB-Raiborn - Capital Bud GettingDocument43 pagesTB-Raiborn - Capital Bud Gettingtophey100% (1)
- Chapter 12 RaibornDocument20 pagesChapter 12 RaibornSuzette Estipona100% (1)
- Basics of Satellite Communication 1Document42 pagesBasics of Satellite Communication 1rajeev1579100% (4)
- Introduction To Wireless Communication Radio CommunicationDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Wireless Communication Radio CommunicationJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- Integrated CircuitsDocument43 pagesIntegrated CircuitsJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Joint and by ProductDocument41 pagesChapter 11 - Joint and by ProductSheena Belleza Fernan89% (28)
- Chapter 34 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 34 PDFJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- Satellite CommunicationDocument66 pagesSatellite Communicationpawan100% (6)
- Microwave & Optical Communication Lab Manual - SRMDocument102 pagesMicrowave & Optical Communication Lab Manual - SRMwizardvenkat100% (6)
- MCQ in EST by Melvin C. Arceo of PERC DCDocument35 pagesMCQ in EST by Melvin C. Arceo of PERC DCLocrian IonianNo ratings yet
- Color Smith ChartDocument1 pageColor Smith ChartKẻ Lãng DuNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF Preparation For Engineering PDFDocument14 pagesCurrent Electricity Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF Preparation For Engineering PDFJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Labs Data With List of Experiments Final PDFDocument20 pages2012 - Labs Data With List of Experiments Final PDFJeffreyBeridaNo ratings yet
- Hilton Chapter 08 SolutionsDocument65 pagesHilton Chapter 08 SolutionsKaustubh Agnihotri75% (8)
- STR File Varun 3Document61 pagesSTR File Varun 3Varun mendirattaNo ratings yet
- RRR Media Kit April 2018Document12 pagesRRR Media Kit April 2018SilasNo ratings yet
- IJRP 2018 Issue 8 Final REVISED 2 PDFDocument25 pagesIJRP 2018 Issue 8 Final REVISED 2 PDFCarlos VegaNo ratings yet
- Defender 90 110 Workshop Manual 5 WiringDocument112 pagesDefender 90 110 Workshop Manual 5 WiringChris Woodhouse50% (2)
- Effectiveness of Using High Gas Pressure in A Blast Furnace As A Means of Intensifying The Smelting OperationDocument10 pagesEffectiveness of Using High Gas Pressure in A Blast Furnace As A Means of Intensifying The Smelting Operationchandan kumar100% (1)
- Calibration GuideDocument8 pagesCalibration Guideallwin.c4512iNo ratings yet
- Digital Burner Controller: Tbc2800 SeriesDocument4 pagesDigital Burner Controller: Tbc2800 SeriesSUDIP MONDALNo ratings yet
- Ips 350:400:450:500:600 07:05 PDFDocument124 pagesIps 350:400:450:500:600 07:05 PDFRandall PettersonNo ratings yet
- Big Band EraDocument248 pagesBig Band Erashiloh32575% (4)
- HV 2Document80 pagesHV 2Hafiz Mehroz KhanNo ratings yet
- Internal auditing multiple choice questionsDocument4 pagesInternal auditing multiple choice questionsSantos Gigantoca Jr.No ratings yet
- DOW™ HDPE 05962B: High Density Polyethylene ResinDocument3 pagesDOW™ HDPE 05962B: High Density Polyethylene ResinFredo NLNo ratings yet
- 4MB0 02R Que 20160609 PDFDocument32 pages4MB0 02R Que 20160609 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDiego S. FreitasNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Blooming GroveDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Blooming GroveHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Predictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBDocument36 pagesPredictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBVenkata Nelluri PmpNo ratings yet
- Questions 32 - 34: Sunny English MqaDocument9 pagesQuestions 32 - 34: Sunny English MqaHạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Helmholtz DecompositionDocument4 pagesHelmholtz DecompositionSebastián Felipe Mantilla SerranoNo ratings yet
- The Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsDocument28 pagesThe Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsAngela FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation SS2Document88 pagesDifferentiation SS2merezemenike272No ratings yet
- Benedict - Ethnic Stereotypes and Colonized Peoples at World's Fairs - Fair RepresentationsDocument16 pagesBenedict - Ethnic Stereotypes and Colonized Peoples at World's Fairs - Fair RepresentationsVeronica UribeNo ratings yet
- IntegrityDocument5 pagesIntegrityPritam Kumar100% (1)
- Tipolo WH Gantt ChartDocument15 pagesTipolo WH Gantt ChartMayeterisk RNo ratings yet
- 2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11Document90 pages2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11eko sulistyo75% (4)
- Optitex Com Products 2d and 3d Cad SoftwareDocument12 pagesOptitex Com Products 2d and 3d Cad SoftwareFaathir Reza AvicenaNo ratings yet
- Interview Question SalesforceDocument10 pagesInterview Question SalesforcesomNo ratings yet
- PanimulaDocument4 pagesPanimulaCharmayne DatorNo ratings yet
- 2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilDocument2 pages2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilSaugata HalderNo ratings yet
- Generate Ideas with TechniquesDocument19 pagesGenerate Ideas with TechniquesketulNo ratings yet
- Transistor Amplifier Operating ParametersDocument21 pagesTransistor Amplifier Operating ParametersReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet