Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review Curse PowerPoint
Uploaded by
BluebloodboyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review Curse PowerPoint
Uploaded by
BluebloodboyCopyright:
Available Formats
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.
Medical-Surgical Nursing
Certification Review
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
CMSRN Exam
Given four times a year
Spring (usually May)
Fall (usually October)
AMSN Annual Convention
(usually September)
Nursing 200x Symposium in the
Spring
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
AMSN Nursing Practice Roles
Helping Role 17% (32-36)
Teaching/coaching role 17% (32-36)
Diagnostic and Patient Monitoring Role
25% (38-42)
Administering and Monitoring
Therapeutic Intervention 25% (58-62)
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
AMSN Nursing Practice Roles
Effective Management of Rapidly
Changing Situations 10% (18-22)
Monitoring/Ensuring Quality Health
Care Practice 3% (4-7)
Organizational and Work-Role
Competencies 3% (4-7)
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Distribution Patient Problem
GI 19% (36-40)
Pulmonary 19% (36-40)
Cardiovascular 15% (28-32)
Diabetes/Other endocrine 15% (28-32)
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Distribution Patient Problem
Renal/GU-12%(22-29)
Musculoskeletal/Neuro 11%
(20-24)
Hematological / Immune /
Integumentary 9% (16-20)
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Preparing for the Test
Medsurg Nursing Certification
Board Requirements CMSRN
credential
Minimum of 3,000 hours in Medsurg
nursing as a staff nurse, clinical nurse
specialist, clinical educator, faculty,
manager, or supervisor.
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Practice in medical-surgical nursing
for at least two full years of the past
five years
Registered Nurse
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Preparing for the Test
Contacting Medical- Surgical
Nursing Certification Board
MSNCB Home Office
East Holly Avenue, Box 56, Pitman, NJ
08071-0056
Phone: 856-256-2323 or Toll free 866877-2676
Fax: 856-589-7463 (fax)
E-mail: msncb@ajj.com
http://www.medsurgnurse.org
9
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Publications to review
Scope and Standards for MedicalSurgical Nursing Practice
ANA Code for Nurses
Human Rights Guidelines for Nurses in
Clinical and other Research
10
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Preparing for the Test
AMSN Core Curriculum for MedicalSurgical Nursing
Medical Surgical Nursing Review
Questions
Review Course
Examination Prep Guide
Your nursing experience
11
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Test Taking Tips
Read questions all the way through
Eliminate obvious wrong answers
Take moment to relax occasionally
Have good reason to change answers
12
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Stress Reduction
Review prior to exam, but dont cram
especially the night before (raises
stress levels making it more difficult)
Take time during the exam to take deep
breaths and relax.
You will have 4 hours to take the exam
which has 200 questions plenty of
time!
13
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A patient begins to experience a severe GI
bleed. The plan of care to meet the
patients fluid needs should include, as a
priority, planning for which of the following?
A. Provision for skin care
B. Monitoring vital signs frequently
C. Decreasing PH of gastric fluids
D. Rapid infusion of IV blood and fluids
14
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
To prevent complications on the third day
after an uncomplicated acute MI, the nurse
would implement which action?
A. Monitor the patients ability to perform
activities of daily living without shortness
of breath
B. Accompany the patient ambulating for a
short distance at least each shift
C. Apply anti-embolic hose to the legs
D. Give the patient a nitroglycerin sublingual
to prevent chest pain before all out of bed
activities
15
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A patient is having a seizure activity. What
should the nurse do during this activity?
A. Insert an oropharyngeal airway
B. Promote safety of body systems
C. Protect the patients head on a pillow
D. Observe the length and after effects of the
seizure
16
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A patient in acute renal failure developed
acute pulmonary edema. Which of the
following interventions would be
inappropriate to include in the patients
care?
A. Administration of oxygen at 3 L/min per
nasal cannula
B. Administration of morphine and
Furosemide (Lasix)
C. Place the patient in high Fowlers position
D. Replace fluids with normal saline
17
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Fluids and Electrolytes
18
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Fluid
Intracellular
Body water
Extracellular
Body water
19
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Electrolytes
Same electrolytes in
intracellular space as
in extracellular space
Always measure
extracellular space
20
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Sodium
Necessary for protein synthesis
Fluid volume in extracellular spaces
21
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hyponatremia
Dilutional most common
Excessive fluid intake
Edema, confusion
Treatment decrease fluid intake
True
Fluid and sodium loss
Dry tissue
Treatment replace both sodium and
water
22
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hypernatremia
Most common, fluid loss without loss
of sodium
Dry tissue
Treatment replace fluids
Increased sodium with diet rare could
occur with full strength high protein
tube feeding
23
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Potassium
Irritant at neuromuscular junction
Increased muscular irritability
24
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hyperkalemia
Causes cell wall destruction,
increased intake, renal failure
Symptoms irritable muscles
Treatment Kayexalate, calcium
gluconate, insulin
25
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hypokalemia
Increased loss of potassium
or increased fluid
Muscle
flaccidity
Treatment potassium supplements
IV
Oral
26
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Calcium
Sedative at the neuro level
Necessary for coagulation
27
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hypercalcemia
Increased intake, hyperparathyroidism
Symptoms
Sedation
Treatment
Decrease calcium intake
28
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hypocalcemia
Decreased calcium intake, increased
phosphate levels, renal disease
Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
Chvosteks
Trousseaus
Laryngospasm
29
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Phosphate
Informal inverse relationship with
calcium
Symptoms may be opposite of
calcium (hypophosphatemia looks like
hypercalcemia, etc)
30
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Magnesium
Hypermagnesemia
Usually poor renal excretion
Muscular depression
Hypomagnesemia
Hyperactive
deep tendon reflexes
31
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Serum Osmolality
2(Na) + BUN/5 + glucose/20 = 275-295
mOsm/l
Quick and dirty 2(Na)
Higher the number, dryer the patient
32
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
IV Fluids
Hypertonic = above 295 mOsm/L
Isotonic = 275 295 mOsm/L
D5LR, D5NS
NS, LR
Hypotonic = below 275 mOsm/L
NS
33
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A patient experiencing a sodium imbalance
must be assessed for which of the following
symptoms?
A. Changes in level of consciousness
B. Irritability of skeletal muscles
C. Depression of deep tendon reflexes
D. Evidence of acid-base imbalances
34
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A patient who is severely dehydrated would
most likely be treated initially with which of the
following IV solutions?
A. Hypertonic
B. Isotonic
C. Hypotonic
D. Colloidal
35
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Which of the following assessment data are
consistent with hypovolemia?
A. Increased pulse and a swollen tongue
B. Neck vein distention and dry skin
C. Weight loss and thirst
D. Increased blood pressure and a fever
36
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Which of the following sets of signs and
symptoms would be exhibited by a patient with
a serum potassium of 6.8 mEq/L?
A. Bradycardia and constipation
B. Confusion and muscle cramps
C. Paralytic ileus and paresthesias
D. Diarrhea and spastic paralysis
37
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
38
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Immune System
Leukocytes
A. Granulocytes
1. Neutrophils first line of
defense against bacteria
2. Eosinophils phagocytize
antigen-antibody complexes
3. Basophils- contain
histamine and heparin
39
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Immune System
B. Nongranulocytes
1) Monocytes phagocytize
bacteria
2) Lymphocytes provide
immunity against foreign
invaders including transplants
C. Immune Response
1) Humoral B lymphocytes,
memory
2) Cellular T lymphocytes,
foreign invaders
40
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Compromised
Immune System
Steroids
suppression of system
Chemotherapy
41
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Acquired Immune
Deficiency Syndrome
In 2009
33.3 million people worldwide living
with AIDS
2.6 million new infections this year
Women and those 15-24 accounted for
50% of infections
Project that by 2012 100 million people
will be infected
42
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Transmission of AIDS
Blood
Semen
Vaginal fluids
Breast milk
Transplacental ?
Transmitted even when asymptomatic
43
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Pathophysiology
Retrovirus, part of the Lentivirius family
Infects CD4 lymphocytes
Carries genetic information on RNA into
the cells DNA
CD4 cells, necessary to immune function,
decrease in numbers in acute phase
44
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
CD 4 Classification of AIDS
> 500 CD4 cells /micro L
Category I:
Category II: 200-400 CD4 cells/ micro L
Category III:
< 200 CD4 cells/ micro L
45
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Clinical Classification of AIDS
Clinical Category A= asymptomatic or
have persistent generalized
lymphadenopathy or symptoms of primary
HIV infection
Clinical category B= symptoms of immune
deficiency not serious enough to be AIDS
defining
Clinical Category C= AIDS-defining illness
46
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Treatment of AIDS
Prevention
Optimal treatment includes combination of
at least 3 drugs, often referred to as
HAART
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
Fusion inhibitors
47
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hematologic System
Erythrocytes: 120 day life span
Requires erythropoietin from kidneys
(80%) and liver (20%)
Thrombocytes: 7.5 day life span, 1/3
sequestered in spleen. Increased blood
platelet level following splenectomy
a. Clotting cascade
Extrinsic
Intrinsic
Enzymes
48
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
White blood cells
Neutrophils- first line of defense against
bacteria
Immature
cells are Bands
Eosinophils- break down antigen/antibody
complex
Basophils- work to keep blood flowing
through micro-vascular system
Monocytes-effective bacterial macrophage
49
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Lymphocytes:
T-lymphocytes-react against foreign or
abnormal cells
B-lymphocytes- becomes antibodies when
exposed to something seen as a long term
threat
50
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Assessment
History
Objective information
Physical
assessment
Diagnostic studies
51
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hematologic concerns
Anemia
Blood loss, Hemolytic
Sickle cell
Iron deficiency
Pernicious
Disseminated Intravascular coagulation
Hodgkins
52
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Sam Andrew had just been diagnosed with
pernicious anemia following his gastric
resection. He asked how long he will need to
take the vitaminnB12. You tell him hell need to
continue:
A. Until his anemia is corrected
B. For the rest of his life
C. It depends on his physicians assessment of
him
D. Its different in everyone
53
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A.
B.
C.
D.
Which of the following laboratory results
would be considered the most indicative of
DIC?
High platelet count
Elevated blood glucose
Increased bleeding times
Presence of fibrin degradation products
(FDP)
54
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Cardiovascular system
55
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Anatomy and Physiology
A. Heart: atria, ventricles, valves,
coronary circulation, cardiac,
conduction system
B. Cardiac Cycle: Systole, diastole
C. Peripheral vascular system:
Veins, arteries, arterioles, venioles,
capillaries
56
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
57
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
58
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
59
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
CO=HR
SV
Stroke
volume
Preload
Afterload
Contractility
Heart Rate
Impact of the ANS
60
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Assessment:
Nursing History
Past medical
Diet
Medication
Pain
Edema
Other
61
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Chest Pain
Description?
Location?
Does it radiate?
What causes it?
What causes it worse?
What makes it better?
62
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Physical Assessment
Inspection
Edema, skin assessment, hair
growth
Palpation
Peripheral pulses, PMI
63
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Heart sounds
Normal
S1
S2
Abnormal
S3 lub DUB dub
S4 lub dub DUB
Murmurs
Friction rub
64
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Diagnostic studies
Cardiac enzymes & proteins
Troponins
CPK-MB, myoglobin, troponins
LDH
Doppler ultrasound
ECHO:TEE
Thallium imaging
Pericardial fluid analysis
65
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Diagnostic procedures
Electrocardiogram
Electrophysiology
Echocardiography
Stress test
Doppler Ultrasound
Cardiac Catheterization
66
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS)
Sudden Death
Stable Angina
Coronary
Arterial
Thrombosis
Non-ST-Elevation
MI
STElevation MI
Sudden Death
67
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
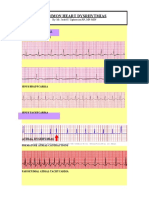
ECG Changes Consistent with
ACS
68
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Anti- ischemic Options
Nitrates
Dilate blood vessels; relaxes and expands
artery, increasing blood flow
Morphine
Pain relief, Dilate blood vessels; relaxes and
expands artery, including blood flow
Beta blockers
ACE inhibitors
Calcium blockers
Slows pumping action of the heart, reduce
oxygen requirements
Dilate blood vessels, prevent fluid retention, and
ease the workload of the heart
Dilate blood vessels and reduce vascular
smooth-muscle contraction
69
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Antiplatelets and Antithrombin Agents
Salicylates: Aspirin
ADP-receptor inhibitors: Clopidogrel
Glycoprotein(GP) Iib-IIIa receptor antagonists
Heparin-unfractionated heparin (UFH)
Low- Molecular weight heparins (LMWH) with
UA/NSTEMI indications
Enoxaparin
Dalteparin
Direct- acting Antithrombins
Bivalirudin
Argatrobran
Lepirudin
70
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
CV Conditions
CHF
Diuretics,
ACE Inhibitors, Digitalis, Beta
Blockers
BNP- Brain Naturetic Peptide
Hypertension
Highest Risk: African American males in
southeast United States
Weight loss- diet management; exercise,
Diuretics, Ace inhibitors, Beta blockers,
Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers
71
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
CV conditions
Chronic Peripheral Circulatory Disease
Arterial(
PAD-peripheral arterial disease):
Thrombolytics, antiplatelet aggregates,
revascularization-stents, arterioplasty,
bypass grafting
Venous )PVD-peripheral venous disease):
elevation, wound prevention- assessmentmanagement, antiplatelet aggregates
DVT: Heparin, LMWH, warfarin, labs:
PT/PTT/INR, D-dimer: SVC filter
72
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Which of the following complications would
likely to happen in a client receiving both a
calcium channel blocker and Lanoxin?
A.
B.
C.
D.
A change in the blood pressure
A decrease in the pulse rate
An increase in respiratory rate
Presence of a systolic murmur
73
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
You are caring for a patient post MI, who
suddenly develops bradycardia and
hypotension. What is the likely cause?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Anxiety reaction
Cardiogenic shock
Medication overdose
Pulmonary edema
74
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Mr. Jones, just returning from a coronary
angiogram, develops bradycardia and a
narrowing pulse pressure. What is the
most likely cause?
A. Cardiac tamponade
B. Positional hypotension
C. Myocardial infarction
D. Anaphylactic shock
75
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Which of the following antihypertensive
should be avoided in a person with
diabetes?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Calcium channel blockers
Beta Blockers
ACE inhibitors
Nitrates
76
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Cancer
Uncontrolled growth of cells Due
to alteration in cells genes
Immune system fails to destroy
Etiologic factors
Chemicals
Radiation
Viruses
Host-related
factors (tobacco use etc)
77
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Cancer Prevention
Age
Sex
Geographical
location
Racial or ethnic
origin
Familial tendency
Environmental
Lifestyle
Tobacco use
Diet
Alcohol
Occupational risks
Biological risks
Iatrogenic risks
Psychosocial
78
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Cancer screening and early
Detection
Early detection-attempt to diagnose at
a curable stage
Secondary prevention- to identify and treat
before disease is symptomatic thus halting
the disease
Health promotion requires consumer
involvement
79
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Therapeutic modalities
Surgery- for staging and treatment
Radiation-Side effects at site of radiation
Biologic therapy-alter host responses to
malignant cells
Chemotherapy- use of chemical agents
80
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Sue Lynn, a 50 year old diagnosed with an
autoimmune disorder, asks what that
means. You tell her:
1.
2.
3.
4.
The bodys ability to fight off infections has been
lost
She is experiencing an increase in one white
cell line
Her immune system is attacking her own body
cells
It is a short lived event which will make her
susceptible to bruising
81
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Which of the following sets of signs and
symptoms would be exhibited by a patient
with a serum potassium of 6.8 MEq/l?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Bradycardia and constipation
Confusion and muscle cramps
Paralytic ileus and paresthesia
Diarrhea and GI spasms
82
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A patient on your unit has been diagnosed
with AIDS. He expresses concerns for
your safety during his am care. You would
state:
1. lets talk about what we can call body
substance isolation
2. Youre not bleeding so theres no risk
3. Its just part of my job, so I dont think
about it.
4. It is scary, but you deserve my care
83
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Gastrointestinal system
84
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
History and subjective assessment
Past history of GI disorders, Surgery, allergy,
lactose intolerance
Pain: location and r/t eating (full or empty
stomach)
Condition of teeth, tongue, oral mucosa
Dysphagia, belching, indigestion/heart burn,
nausea, vomiting
Weight loss, anorexia
Bowel movement frequency: Diarrhea,
constipation, laxative or enema use, presence of
dark stools or frank blood
85
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Objective Assessment
Inspection: Weight, spider angioma
on trunk, visible peristalsis, distention,
jaundice, icterus, ecchymosis or
petechiae
2. Auscultation: Bowel sounds
3. Palpation: Distention, as, cites,
hepatomegaly (firm ridge below the rib
cage.
86
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Diagnostic Studies
Lab tests: Electrolytes, LFTs, fecal
studies, analysis of gastric secretions
2. Radiography: Barium swallow,
barium enema, ultrasound, ERCP,
endoscopy, arteriography,
colonoscopy, nuclear medicine
imaging, CT scan
87
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Liver Disease
Cirrhosis- Hardening of the liver
Medical
treatment-paracentesis, Transjugular
intra-hepatic Porto-systemic shunting (TIPS),
organ transplant
Nursing interventions: Monitor for bleeding,
albumin, B vitamin levels, serum ammonia;
treat alcoholism (refer to rehab); teach
avoidance of hepatotoxic substances and use
of OTC meds; control ammonia related
encephalopathy-neomycin, lactulose, reduced
protein intake
88
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Esophageal varices
Medical treatment- Banding, sclerosing,
esophageal balloon tamponade,
transfusion of RBCs and clotting factors
(FFP)
Nursing interventions: monitor VS, S&S of
bleeding, PT, PTT, platelets, refer to
treatment for alcoholism
89
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Viral Hepatitis
Transmission
A-
Fecal-oral, contaminated food
B and C-Blood and body fluid
Medical treatment
Hepatitis
A- supportive treatment, antdiarrhea and anti ememitics
Hepatitis B gamma globulin, prevention with
hepatitis vaccine
90
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Hepatitis C initial infection is rarely treated
due to flu-like symptoms. Chronic state is
treated with antiviral therapy(ribavirin,
interferon injections) treatment similar to
cirrhosis when fibrosis develops
Nursing interventions
Teach hand washing and safe food handling,
safe sex, and recommend hepatitis A and
B vaccines
Monitor LFTs
Provide symptom management
91
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease
Medical
treatment- corticosteroids, azulvidine,
surgery( Colectomy/Colostomy or ileostomy)
Nursing Interventions: monitor for S&S of
bleeding, test stools for occult blood, ostomy
care including diet teaching and address body
image
92
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Irritable bowel syndrome
Conventional medical treatment-imodium for
diarrhea; tegaserod maleate (Zelnorm) for
constipation; Alosetron hydrochloride ( Lotronex)
for diarrhea if conventional therapy is not
effective
Nursing intervention: Teach avoidance of the
individuals triggers- large meals, wheat, rye,
barley, chocolate, milk products, alcohol, drinks
with caffeine; stress or emotional upsets. Teach
avoidance of overusing saline enemas and OTC
laxatives
93
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Bowel Disease
Obstruction
Medical treatment- NG tube, NPO, surgery
Nursing interventions: Monitor bowel
sounds, IV fluids, TPN, prepare for
diagnostic studies and surgery, treat N&V
94
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Colon Cancer
Medical Treatment- polypectomy, tumor
resection, colectomy/ostomy, chemo and
or radiation
Nursing Interventions: Bowel prep, ostomy
care, diet teaching, teach effects of chemo
and radiation
95
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Pancreatitis
Acute: NPO, fluids, possibly TPN.
Monitor glucose, acid balance, K, Ca,
Serum Co2, and amylase, lipase. Pain
management, I7O monitoring; be alert for
signs of hemorrhage, renal and respiratory
failure
Chronic: Pancreatic enzymes, teach low
fat diet, pain management
96
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Peptic Ulcer disease
Causes: Helicobter pylori has been found
to be the cause in most ulcers, 50% of the
population is colonized
NASAIDS are another significant factor for
gastric and duodenal ulcers in individuals
over 60
Corticosteroids cause erosion of gastric
mucosa
97
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Peptic Ulcer disease
Interventions:
Assess
VS for signs of blood loss, assess
emesis for coffee ground appearance, and
test stools for occult blood
During acute bleeding-NG tube, NPO, IV
fluids, Monitor Hgb & Hct, RBC transfusions
may be necessary
Teach patient bland diet and medication
regimen
98
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Peptic Ulcer disease
Antibiotics
Histamine 2 blockers
proton pump inhibitors
Barrier medications
99
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Peritonitis
Nursing assessment
Monitor VS, WBCs, assess pain level,
assess firmness of the abdomen(rebound
tenderness)
Treatment:
Antibiotics(
intraperitoneal in peritoneal
dialysis patient)
Pain management
Antiemetics PRN
100
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Mrs. Stone, 68, is on your unit with
ascites, as a complication of her liver
cancer. Her potassium level is elevated
and would most likely be related to:
A. Hypomagnesemia
B. Increased ammonia levels
C. Decreased albumin levels
D. Poor lymphatic system
101
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
A client with advanced cirrhosis is
admitted to your unit from the E.D.
Which of the following orders should
you question?
A. Phenobarbital 100 mg HS
B. Neomycin sulfate 300 mg
Q6 x 4 doses
C. Low protein diet
D. Serum ammonia levels daily
102
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Jerry Thomas, 22, is being treated with
dexamethasone (Decadron) for an
acute head injury caused by a skiing
accident. He is also receiving ranitidine
(Zantac) because of dexamethasones
propensity to:
A. Increase peristalsis
B. Erode gastric mucosa
C. Decrease secretions
D. Irritate mucous membranes
103
SE5l, Medical-Surgical Review curse PowerPoint.pdf
Nutrition
Essential for adequate functioning of all
body systems
Calculating nutrition intake is based on kcalKilocalories
Carbohydrates 4 Kcal/gram
Protein
4 Kcal/gram
Fat
9 Kcal/gram
Enteral feeding is preferred over parenteral
feeding because it is important to maintaining a
functioning GI tract
104
You might also like
- SpellsDocument86 pagesSpellsGypsy580% (5)
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesFrom EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Professional Nursing Concepts CompetenciesDocument572 pagesProfessional Nursing Concepts CompetenciesM Ifadh Arifqy JNo ratings yet
- Linear Space-State Control Systems Solutions ManualDocument141 pagesLinear Space-State Control Systems Solutions ManualOrlando Aguilar100% (4)
- Ob Nursing BulletsDocument67 pagesOb Nursing Bulletsyunmi27100% (2)
- Drug Study Guide Calculation PDFDocument49 pagesDrug Study Guide Calculation PDFHarley Justiniani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Critical Nursing Care ExamDocument42 pagesCritical Nursing Care ExamRandy80% (5)
- Mastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyFrom EverandMastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Dysrhythmias ExamDocument4 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmias Exambobtaguba100% (3)
- ספר חישוב רוקחי- סופי-1Document30 pagesספר חישוב רוקחי- סופי-1Bluebloodboy100% (1)
- CardiacDocument10 pagesCardiacMarcus Reynolds100% (1)
- Capstone Final ExamDocument19 pagesCapstone Final ExamEileen Arboleda100% (3)
- 7saunders 8THDocument175 pages7saunders 8THnjNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacolocy Part 2Document176 pagesNursing Pharmacolocy Part 2TkNo ratings yet
- Cum in Mouth ScriptsDocument10 pagesCum in Mouth Scriptsdeudaerlvincent72No ratings yet
- Sim LabDocument4 pagesSim Laballycat2390% (10)
- Stuvia 1507039 Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing 10th Edition by Rector PDFDocument331 pagesStuvia 1507039 Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing 10th Edition by Rector PDFMuniraNo ratings yet
- Bersin PredictionsDocument55 pagesBersin PredictionsRahila Ismail Narejo100% (2)
- Ati PN Comprehensive Predictor Exam 2Document27 pagesAti PN Comprehensive Predictor Exam 24 u100% (1)
- Critical Care Nursing A Holistic Approach 10th Edition Morton Test Bank PDFDocument6 pagesCritical Care Nursing A Holistic Approach 10th Edition Morton Test Bank PDFa806088253No ratings yet
- Pharmacology and The Nursing Process 5th Edition Lilley Test BankDocument3 pagesPharmacology and The Nursing Process 5th Edition Lilley Test BankStuartCarrsNo ratings yet
- 90 Pharmacology and Parenteral Therapy NCLEXDocument30 pages90 Pharmacology and Parenteral Therapy NCLEXHope YanesNo ratings yet
- Cardio Exam Test BankDocument17 pagesCardio Exam Test BankPINKY CUARESMA0% (1)
- NURS 419 Community Health NotesDocument16 pagesNURS 419 Community Health NotesSarah AnneNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Otitis 2022Document20 pagesNecrotizing Otitis 2022asmashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Public HealthDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Public HealthKristelle Marie Enanoria Bardon50% (2)
- Med Surg Proctored Concept GuideDocument4 pagesMed Surg Proctored Concept GuideKiayaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Children Principles and Practice 4th Edition James Test BankDocument5 pagesNursing Care of Children Principles and Practice 4th Edition James Test BankCherokeeNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Exam: All Question and Answers: Click Here For AnswersDocument38 pagesMed Surg Exam: All Question and Answers: Click Here For Answershasan ahmdNo ratings yet
- NCLEXDocument7 pagesNCLEXmsdrewn30No ratings yet
- Basic Nursing 2nd Treas Test BankDocument16 pagesBasic Nursing 2nd Treas Test BankRamiqq100% (1)
- Critical Care Nursing: Learning from PracticeFrom EverandCritical Care Nursing: Learning from PracticeSuzanne BenchNo ratings yet
- Nursing Test Taking Strategy IDocument20 pagesNursing Test Taking Strategy Iicy431100% (1)
- Prioritization Delegation and Assignment PrinciplesDocument1 pagePrioritization Delegation and Assignment PrinciplesPaola Agustin0% (1)
- SIMCLEX Renal and Genitourinary DisordersDocument7 pagesSIMCLEX Renal and Genitourinary DisordersLLLJJJ100% (1)
- Latest Priorities in Critical Care Nursing 6th Edition Urden Test BankDocument11 pagesLatest Priorities in Critical Care Nursing 6th Edition Urden Test BankBaxterNo ratings yet
- MSDS PetrolDocument13 pagesMSDS PetrolazlanNo ratings yet
- Ob 2Document9 pagesOb 2Danica Chiara Motia100% (1)
- MOtivating Your Teenager PDFDocument66 pagesMOtivating Your Teenager PDFElleMichelle100% (1)
- Study Guide HESI CommunityDocument29 pagesStudy Guide HESI CommunityBeth Ann100% (1)
- Hurst Pathophysiology-Ch01 986x PDFDocument42 pagesHurst Pathophysiology-Ch01 986x PDFeng78ineNo ratings yet
- N 313 Pediatric Nursing Syllabus Fall 2011 Part 1Document12 pagesN 313 Pediatric Nursing Syllabus Fall 2011 Part 1bmccsnresourcesNo ratings yet
- Calcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Document552 pagesCalcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Débora BretasNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Questions With RationaleDocument2 pagesAcute Renal Failure Questions With RationaleAngelica Mae Adlawan Desalesa0% (2)
- Nursing Process QuestionsDocument12 pagesNursing Process QuestionsSritama Ghosh100% (1)
- Module 1 ExamDocument109 pagesModule 1 Examnursehelp12100% (2)
- Community Hesi Study GuideDocument17 pagesCommunity Hesi Study Guidewhereswaldo007yahooc100% (2)
- Question Number 1 of 40Document8 pagesQuestion Number 1 of 40ja100% (1)
- Test Bank For Wongs Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 8th Edition by HockenberryDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Wongs Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 8th Edition by Hockenberrya704676050No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing LectureDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Nursing LectureChristianArvinMañego100% (3)
- Test Bank Leading and Managing in Nursing 6th EditionDocument9 pagesTest Bank Leading and Managing in Nursing 6th EditionRichard1LauritsenNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument85 pagesCritical Care NursinganreilegardeNo ratings yet
- 50 Shades of Practice QuestionsDocument11 pages50 Shades of Practice QuestionsAmie Ray100% (1)
- HURST NCLEX Review Facts PDFDocument6 pagesHURST NCLEX Review Facts PDFMikeNo ratings yet
- CEN Guide 4: Guide For The Inclusion of Environmental Aspects in Product StandardsDocument18 pagesCEN Guide 4: Guide For The Inclusion of Environmental Aspects in Product StandardsLauren GarciaNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy Lippincott Manual of Nursing PracticeDocument20 pagesIV Therapy Lippincott Manual of Nursing PracticeHejia MagangcongNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument9 pagesMed SurgCharlie Gemarino LumasagNo ratings yet
- HEsi HintsDocument5 pagesHEsi HintsOMGStudy100% (2)
- Chapter 30Document26 pagesChapter 30Nurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- NLN Pharmacology Study GuideDocument65 pagesNLN Pharmacology Study GuideLauraysha McMillanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SYSTEM - Heart Dysrythmia IllustrationsDocument3 pagesCardiovascular SYSTEM - Heart Dysrythmia IllustrationsKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Community Health Study GuideDocument9 pagesCommunity Health Study GuideShae Thomas100% (3)
- This Study Resource Was: G R A D E S L A B - C O MDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: G R A D E S L A B - C O MHugsNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument5 pagesStudy Guide For Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMandi Goetz HarmonNo ratings yet
- Nclex-Pn Examination: Test Plan For The National Council Licensure Examination For Practical NursesDocument61 pagesNclex-Pn Examination: Test Plan For The National Council Licensure Examination For Practical NursesBeatrice Ioana Ciupală100% (1)
- Hesi Med Surg-6Document1 pageHesi Med Surg-6GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41: The Child With An Infectious Disease Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesChapter 41: The Child With An Infectious Disease Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Community Nursing HESI Study GuideDocument2 pagesCommunity Nursing HESI Study Guidebrittanyann1033% (3)
- 1 - תרופות החולה בביתDocument3 pages1 - תרופות החולה בביתBluebloodboyNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Complications From Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesManagement of Patients With Complications From Heart DiseaseBluebloodboyNo ratings yet
- 1 Perspectives of Pediatric NursingDocument57 pages1 Perspectives of Pediatric NursingBluebloodboyNo ratings yet
- WPhO (Singapore) - World Physics Olympiad (WPhO) - 2011Document20 pagesWPhO (Singapore) - World Physics Olympiad (WPhO) - 2011GXGGXG50% (2)
- Chapter 9 - PPT (New)Document43 pagesChapter 9 - PPT (New)Syarifah NourazlinNo ratings yet
- Distributing Business Partner Master Data From SAP CRMDocument28 pagesDistributing Business Partner Master Data From SAP CRMJarko RozemondNo ratings yet
- Operations Management (Scheduling) PDFDocument4 pagesOperations Management (Scheduling) PDFVijay Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- August Strindberg's ''A Dream Play'', inDocument11 pagesAugust Strindberg's ''A Dream Play'', inİlker NicholasNo ratings yet
- 4 Major Advantages of Japanese Education SystemDocument3 pages4 Major Advantages of Japanese Education SystemIsa HafizaNo ratings yet
- PSYC1111 Ogden Psychology of Health and IllnessDocument108 pagesPSYC1111 Ogden Psychology of Health and IllnessAleNo ratings yet
- A Study On Investors Perception Towards Sharemarket in Sharekhan LTDDocument9 pagesA Study On Investors Perception Towards Sharemarket in Sharekhan LTDEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- TOPIC I: Moral and Non-Moral ProblemsDocument6 pagesTOPIC I: Moral and Non-Moral ProblemsHaydee Christine SisonNo ratings yet
- MPCDocument193 pagesMPCpbaculimaNo ratings yet
- Echnical Ocational Ivelihood: Edia and Nformation IteracyDocument12 pagesEchnical Ocational Ivelihood: Edia and Nformation IteracyKrystelle Marie AnteroNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic Drugs: - Classification of SeizuresDocument31 pagesAnti-Epileptic Drugs: - Classification of SeizuresgopscharanNo ratings yet
- WaiverDocument1 pageWaiverWilliam GrundyNo ratings yet
- Saber Toothed CatDocument4 pagesSaber Toothed CatMarie WilkersonNo ratings yet
- Ottley Sandra 2009Document285 pagesOttley Sandra 2009Lucas Fariña AlheirosNo ratings yet
- Level 5 - LFH 6-10 SepDocument14 pagesLevel 5 - LFH 6-10 SepJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Rita Ora - Shine Ya LightDocument4 pagesRita Ora - Shine Ya LightkatparaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Intensive Health Education On Adherence To Treatment in Sputum Positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis PatientsDocument6 pagesEffect of Intensive Health Education On Adherence To Treatment in Sputum Positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis PatientspocutindahNo ratings yet
- Papadakos PHD 2013Document203 pagesPapadakos PHD 2013Panagiotis PapadakosNo ratings yet
- Capstone Report FormatDocument11 pagesCapstone Report FormatAnkush PalNo ratings yet
- A Lei Do Sucesso Napoleon Hill Download 2024 Full ChapterDocument23 pagesA Lei Do Sucesso Napoleon Hill Download 2024 Full Chapterdavid.brown752100% (12)
- Test Statistics Fact SheetDocument4 pagesTest Statistics Fact SheetIra CervoNo ratings yet