Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 01
Uploaded by
AarizMalikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 01
Uploaded by
AarizMalikCopyright:
Available Formats
LAB MANUAL: & POWER GENERATION (EE-312)
EXPERIMENT # 01
EXPERIMENT NO.01
POWER PLANTS
Familiarization with Power Techniques
BACKGROUND THEORY:
A power plant, powerhouse or generating plant is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. At
the center of nearly all power stations is a generator, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power
into electrical power by creating relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor. The energy source
harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. There are many types of power plants some of them are given
below:
Thermal Power Plants
Hydel Power Plants
Nuclear Power Plants
Solar Power Plants
Wind Power Plants
Tidal Power Plants
Biogas Power Plants
Thermoelectric Power Plants
Magneto Hydro Electric Power Plants
Process detail each of the power plant is given in below section.
THERMAL POWER PLANTS:
Thermal power plants use water as working fluid. The way energy from fuel gets transformed into
electricity forms by the working of a power plant. In a thermal power plant a steam turbine is rotated
with help of high pressure and high temperature steam and this rotation is transferred to a generator
to produce electricity.
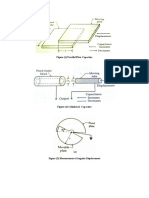
Figure 1-1: Power Produced in Thermal Power Plant by Rotating Steam Turbine
ENERGY ABSORPTION FROM STEAM:
When turbine blades get rotated by high pressure high temperature steam, the steam loses its energy.
This in turn will result in a low pressure and low temperature steam at the outlet of the turbine. Here
steam is expanded till saturation point is reached. Since there is no heat addition or removal from the
steam, ideally entropy of the steam remains same. This change is depicted in the following p-v and
T-s diagrams. If we can bring this low pressure, low temperature steam back to its original state, then
we can produce electricity continuously.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, WAH ENGINEERING COLLEGE, WAH CANTT
Page 1
LAB MANUAL: & POWER GENERATION (EE-312)
EXPERIMENT # 01
Figure 1-2: Pressure and Temperature Drop From Steam When Turbine absorbs Energy
USE OF CONDENSER:
Compressing a fluid which is in gaseous state requires a huge amount of energy, so before
compressing the fluid it should be converted into liquid state. A condenser is used for this purpose,
which rejects heat to the surrounding and converts steam into liquid. Ideally there will not be any
pressure change during this heat rejection process, since the fluid is free to expand in a condenser.
Changes in fluid are shown in the p-v and T-s diagram below.
Figure 1-3: Use of Condenser in order to Transform Vapour into liquid state
COMPRESSOR:
At exit of the condenser fluid is in liquid state, so it is easy for a compressor to raise its pressure.
During this process the volume and temperature (2-30C rise) of fluid hardly changes, since it is in
liquid state. Now the fluid has regained its original pressure.
Figure 1-4: Compressor Pumps the Fluid to its Original Pressure
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, WAH ENGINEERING COLLEGE, WAH CANTT
Page 2
LAB MANUAL: & POWER GENERATION (EE-312)
EXPERIMENT # 01
HEAT ADDITION IN BOILER & RANKINE CYCLE:
Here external heat is added to the fluid in order to bring fluid back to its original temperature. This
heat is added through a heat exchanger called a boiler. Here the pressure of the fluid remains the
same, since it is free to expand in heat exchanger tubes. Temperature rises and liquid gets
transformed to vapor and regains its original temperature. This completes the thermodynamic cycle
of a thermal power plant, called Rankine Cycle. This cycle can be repeated and continuous power
production is possible.
Figure 1-5: Heat addition to Boiler
CONDENSER HEAT REJECTION:
In order to reject heat from the condenser a colder liquid should make contact with it. In a
thermal power plant continuous supply of cold liquid is produced with the help of a cooling
tower. Cold fluid from the cooling tower absorbs heat from a condenser and gets heated, this
heat is rejected to the atmosphere via natural convection with the help of a cooling tower.
BOILER FURNACE FOR HEAT ADDITION:
Heat is added to the boiler with help of a boiler furnace. Here fuel reacts with air and
produces heat. In a thermal power plant, the fuel can be either coal or nuclear. When coal is
used as a fuel it produces a lot of pollutants which have to be removed before ejecting to the
surroundings. This is done using a series of steps, the most important of them is an electro
static precipitator (ESP) which removes ash particles from the exhaust. Now much cleaner
exhaust is ejected into the atmosphere via a stack.
Figure 1-6: Main Accessories in Rankine Cycle
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, WAH ENGINEERING COLLEGE, WAH CANTT
Page 3
LAB MANUAL: & POWER GENERATION (EE-312)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, WAH ENGINEERING COLLEGE, WAH CANTT
EXPERIMENT # 01
Page 4
You might also like
- Most Commonly Used PhrasesDocument19 pagesMost Commonly Used PhrasesAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Carbon FiberDocument30 pagesCarbon FiberAarizMalik100% (1)
- LVDT MAnufacturerDocument12 pagesLVDT MAnufacturerAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Modification of Impedence MatrixDocument14 pagesModification of Impedence MatrixAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Figure (1) Parallel Plate CapacitorDocument4 pagesFigure (1) Parallel Plate CapacitorAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Characterization and Finite Element Modeling of Sandwich CompositeDocument12 pagesMechanical Characterization and Finite Element Modeling of Sandwich CompositeAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Most Commonly Used PhrasesDocument19 pagesMost Commonly Used PhrasesAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Construction Of Bi-Directional Meter for measuring Reverse PowerDocument16 pagesConstruction Of Bi-Directional Meter for measuring Reverse PowerAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Impede NceDocument3 pagesImpede NceAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- AM ManufacturingDocument78 pagesAM ManufacturingAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Design-for-Manufacture of NextGen Aerospace CompositesDocument13 pagesDesign-for-Manufacture of NextGen Aerospace CompositesAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- LECT 2 Writing A ProposalDocument32 pagesLECT 2 Writing A ProposalAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Generate Heat & Electricity Using Salinity-Gradient Solar PondsDocument5 pagesGenerate Heat & Electricity Using Salinity-Gradient Solar PondsAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrinic Instumentation & Measurement Techniques Chapter-4Document55 pagesModern Electrinic Instumentation & Measurement Techniques Chapter-4AarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis Formulation Using Y-Bus MatrixDocument56 pagesLoad Flow Analysis Formulation Using Y-Bus MatrixlaxmanNo ratings yet
- MOSFET VI Characteristics Lab ManualDocument4 pagesMOSFET VI Characteristics Lab ManualAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power TransmissionDocument19 pagesWireless Power TransmissionAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06: To Investigate The Operation 4 Stroke Diesel Engine For Power GenerationDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 06: To Investigate The Operation 4 Stroke Diesel Engine For Power GenerationAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- Types of CablesDocument3 pagesTypes of CablesAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- MT Slides Logistics (14 NovDocument24 pagesMT Slides Logistics (14 NovRyan Tw ChoumingNo ratings yet
- Angle Style, Pressure Relief Valves For Steam, Gas, and Liquid ServicesDocument14 pagesAngle Style, Pressure Relief Valves For Steam, Gas, and Liquid ServicesCHRISTIAN ZAVALANo ratings yet
- 1) Computer Concepts NotesDocument6 pages1) Computer Concepts NotesVenus Leilani Villanueva-Granado100% (2)
- Class XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementDocument29 pagesClass XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementLakshmi Puthiyedath71% (7)
- Operations Management 1St Edition Cachon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesOperations Management 1St Edition Cachon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwayne.martin885100% (11)
- This Study Resource Was: Titration Level 1Document4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Titration Level 1Camaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- Filter 7Document480 pagesFilter 7Pranjal TripathiNo ratings yet
- Installation and Setup Guide For The Cisco Active Directory Agent, Release 1.0Document62 pagesInstallation and Setup Guide For The Cisco Active Directory Agent, Release 1.0Madelaine Velasquez Blacutt100% (1)
- COSC 2307: Sub-QueriesDocument23 pagesCOSC 2307: Sub-QueriesBhavikDaveNo ratings yet
- Transformer X - R CalculationDocument2 pagesTransformer X - R CalculationTharindu WimalasekaraNo ratings yet
- Training Seminar ON GSM Held at BSNL: Presented By: Charli Bagga Kriti Rastogi (AEI-08)Document51 pagesTraining Seminar ON GSM Held at BSNL: Presented By: Charli Bagga Kriti Rastogi (AEI-08)Ankita BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Homework Lesson 6-10Document9 pagesHomework Lesson 6-10Valerie YenshawNo ratings yet
- PLC Introduction: Programmable Logic Controller BasicsDocument3 pagesPLC Introduction: Programmable Logic Controller Basicssreekanthtg007No ratings yet
- Wind Load Sheet by Abid SirDocument4 pagesWind Load Sheet by Abid SirMohammad KasimNo ratings yet
- Spe 58987 Propped Fracturing in Gas Carbonate Formations MexicoDocument12 pagesSpe 58987 Propped Fracturing in Gas Carbonate Formations MexicoJose Gregorio FariñasNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis method for quantifying anti-cancer drug CurcuminDocument6 pagesUV-Vis method for quantifying anti-cancer drug Curcuminwhy uNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi: Classification and PredictionDocument29 pagesUnit Vi: Classification and PredictionpalaniappanNo ratings yet
- Problems On Heat Transfer ConductionDocument3 pagesProblems On Heat Transfer ConductionGenerale, Rey marck C.No ratings yet
- Noc18 cs48 Assignment3Document4 pagesNoc18 cs48 Assignment3shweta100% (1)
- Convert Decimal To Binary Sunday ClassDocument14 pagesConvert Decimal To Binary Sunday ClassLaila HammadNo ratings yet
- AerialSolution - 280 - Brochure - LT - New Design - Final - LRDocument20 pagesAerialSolution - 280 - Brochure - LT - New Design - Final - LRRover DmsNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology For Cloud Storage - A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument33 pagesBlockchain Technology For Cloud Storage - A Systematic Literature ReviewNgocNo ratings yet
- Putzmeister Pump TrucksDocument17 pagesPutzmeister Pump Truckslwin_oo243575% (4)
- J Gen Physiol-1952-Hershey-39-56Document18 pagesJ Gen Physiol-1952-Hershey-39-56api-277839406No ratings yet
- Survey Whole Circle BearingDocument19 pagesSurvey Whole Circle BearingVin GaragiNo ratings yet
- Connection Design Steel Base Plate Bs5950 v2015 01Document4 pagesConnection Design Steel Base Plate Bs5950 v2015 01Anonymous j9PxwnoNo ratings yet
- Benzophenone/THF StillDocument3 pagesBenzophenone/THF Stillbloggsjoe1970No ratings yet
- 1956 - Colinese - Boiler Efficiencies in SugarDocument7 pages1956 - Colinese - Boiler Efficiencies in SugarPaul DurkinNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory 6Document30 pagesGraph Theory 6Zeeshan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Calcs HETPDocument50 pagesCalcs HETPChemEngGirl89No ratings yet