Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypertension Concept Map
Uploaded by
gfhbgfhgfOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypertension Concept Map
Uploaded by
gfhbgfhgfCopyright:
Available Formats
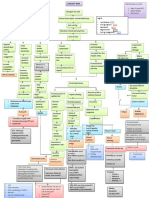
Concept Map
Risk Factors:
-Age
-Obesity
-Diet
-Lifestyle
-Stress
-Family History
-Diabetes Mellitus
Hypertension
(High blood pressure)
Means
Complications:
-Heart attack or stroke
-Aneurysm
-Heart failure
-Kidney Disease
-Vision loss
-Metabolic Syndrome
-Low cognitive thinking
Signs and Symptoms:
**Most of the time, there are no
symptoms
-Dyspnea
-Nosebleed
-Fatigue
-Confusion
-Headache
-Nape Pain
-Above normal BP
N &V
-Severe headache
- Dizziness
-Vision changes
Hypertension means high
pressure (tension) in the
arteries. Arteries are vessels
that carry blood from the
pumping heart to all the
tissues and organs of the
body.
Diagnostics:
-Blood pressure measurements
Normal Blood pressure (120/80mmhg)
Pre hypertension (120/80 -139/89mmhg)
Stage 1 hypertension (140/90-159/99)
Stage 2 hypertension(>160/100)
-High cholesterol level
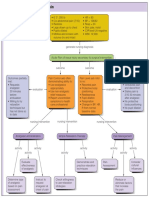
Prevention:
Eat a heart healthy diet, including
potassium and fiber.
Drink plenty of water.
Exercise regularly for at least 30
minutes of aerobic exercise a day.
If you smoke, quit.
Limit how much alcohol you drink to 1
drink a day for women, and 2 a day for
men.
Limit the amount of sodium (salt) you
eat -- aim for less than 1,500 mg per
day.
Reduce stress. Try to avoid things that
cause you stress, and try meditation or
yoga to de-stress.
Stay at a healthy body weight.
Acuyong, Yogananda G.
Alzona, Kimberly
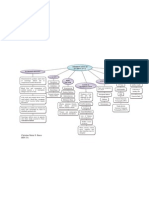
Nursing Diagnosis:
Nursing Diagnosis #1
- Acute pain: headache
related to increased
cerebral vascular
pressure.
Nursing Diagnosis #2
- Knowledge deficit
related to lack of
information about the
disease process and
self-care
Nursing Diagnosis #3
- Decreased Cardiac
Output related to
Increased vascular
resistance,
vasoconstriction
Medications:
Thiazide diuretics
angiotensin-converting
enzyme (ACE)
inhibitors
angiotensin II receptor
blockers (ARBs)
Calcium channel
blockers
Renin inhibitors
Alpha blockers
Beta Blockers
Alpha-Beta blockers
Central-acting agents.
Risk and implication:
Some of the medications can lower
your heart rate, some thin out the
blood. Risk of stroke is common with
many of the medications used to
treat HTN. Vasodilators work on
muscles in the walls of your arteries
and prevent them from narrowing. All
medications should be taken exactly
as prescribed by the doctor and
before taking any OTCs be sure to
consult with your primary care
provider.
You might also like
- Concept Map HypertensionDocument1 pageConcept Map Hypertensiongeorge pearson0% (1)
- Concept Map COPDDocument2 pagesConcept Map COPDJilian McGugan88% (40)
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumonianursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of DMDocument2 pagesConcept Map of DMLeslie Marie Rendon100% (9)
- Concept Map Acute PainDocument1 pageConcept Map Acute PaincryblrNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Concept MapDocument1 pageCongestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Concept MapAndrew Godwin100% (5)
- Cholecystitis Concept MapDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (7)
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocument11 pagesPneumonia Concept Mapiz11100% (3)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- COPD Concept MapDocument2 pagesCOPD Concept MapJilian McGugan100% (9)
- Urosepsis-Sepsis - (KeithRN-Unfolding THIGPEN PDFDocument11 pagesUrosepsis-Sepsis - (KeithRN-Unfolding THIGPEN PDFOLga A. Thigpen100% (4)
- Nursing Concept Map ExampleDocument1 pageNursing Concept Map Exampledrowning_sux1491100% (1)
- Concept Map Liver CirrhosisssDocument2 pagesConcept Map Liver CirrhosisssAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah92% (12)
- Cholecystitis Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Nursing Care PlanMDCITY83% (6)
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDocument26 pagesFluid & Electrolytesanjana bhatia100% (1)
- Chronic Renal Failure: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageChronic Renal Failure: PathophysiologyCindy Mae Dela Torre100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Disease Concept MapDocument5 pagesCardiovascular Disease Concept MapRye Anch100% (1)
- Acute PainDocument1 pageAcute Painnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary DisordersDocument11 pagesRenal and Urinary DisordersChristian Espanilla100% (4)
- Concept Map StrokeDocument1 pageConcept Map StrokeMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Med Surg CardsDocument54 pagesMed Surg CardsIanne Merh100% (3)
- STUDENT-Eating - Disorder-F&E-UNFOLDING ReasoningDocument14 pagesSTUDENT-Eating - Disorder-F&E-UNFOLDING ReasoningPeggy100% (12)
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocument1 pageNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- Mabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument15 pagesMabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMabesNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular Disease NursingDocument13 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease NursingCatlyn Chatpman100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapChristine Marie Barce Martinez100% (2)
- Cellulitis Concept MapDocument3 pagesCellulitis Concept MapBien EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Week 6Document11 pagesMed Surg Week 6Eunice Cortés100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanGem Ma100% (7)
- Nursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideDocument9 pagesNursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument58 pagesNursing DiagnosisPrecious Santayana100% (3)
- Drug Card AspirinDocument3 pagesDrug Card Aspirincelosia23100% (10)
- 313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsDocument8 pages313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsChrissy Mendoza100% (2)
- ARDS Concept MapDocument1 pageARDS Concept Mapadro100% (2)
- Careplan Concept MapDocument1 pageCareplan Concept MapAmanda Simpson100% (3)
- Health Management of The Patient With Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pageHealth Management of The Patient With Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Sev Kuzmenko0% (1)
- Nursing StudentDocument1 pageNursing StudentShane LambertNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical: Nervous SystemDocument90 pagesMedical Surgical: Nervous SystemCatherine G. Borras100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingdmsapostolNo ratings yet
- Care Plan For Bowel ResectionDocument4 pagesCare Plan For Bowel Resectionviki840488% (8)
- Cellulitis Care PlanDocument6 pagesCellulitis Care PlanNaya Kayala0% (1)
- NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorDocument8 pagesNUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorAmber EssmanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Concept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument1 pageConcept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseWayne Calderon75% (4)
- Narrative ChartingDocument2 pagesNarrative Chartingearl_llamas0% (2)
- Concept Map Pleural EffusionDocument1 pageConcept Map Pleural Effusionapi-341263362No ratings yet
- Concept Map of Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesConcept Map of Myocardial InfarctionMingConol100% (4)
- Lloyd Bennett DocumentationDocument2 pagesLloyd Bennett Documentationnikdolly100% (7)
- NSG 330 NCLEX Kaplan Med Surg 2 Final Exam Predictor TestDocument18 pagesNSG 330 NCLEX Kaplan Med Surg 2 Final Exam Predictor TestabbieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument53 pagesNursing Care Planztvill88% (26)
- Shadow Health Cognition SubjectiveDocument7 pagesShadow Health Cognition Subjectiveqwivy.comNo ratings yet
- Nursing Plan of Care Concept Map - Immobility - Hip FractureDocument2 pagesNursing Plan of Care Concept Map - Immobility - Hip Fracturedarhuynh67% (6)
- ATI FinalPharmacologyDocument7 pagesATI FinalPharmacologyClaudia Manning100% (17)
- Renal and Urinary Concept MapsDocument8 pagesRenal and Urinary Concept Mapsnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is A Disease of Vascular Regulation Resulting From Malfunction ofDocument4 pagesHypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is A Disease of Vascular Regulation Resulting From Malfunction ofkewpietheresaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Medlineplus TopicsDocument31 pagesHypertension: Medlineplus TopicsMcNover Catlin OsamNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: High Blood PressureDocument6 pagesHypertension: High Blood PressureAnne BattulayanNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Written ReportDocument5 pagesHypertension Written ReportKate Felongco CambelNo ratings yet