Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Base Plate Verification Example
Uploaded by
Karthikeyan VediOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Base Plate Verification Example
Uploaded by
Karthikeyan VediCopyright:
Available Formats
8.
2.
Determine required plate thickness:
Note: Since the Mpl is expressed in units of kip-in./in.,
the plate thickness expressions can be formatted without the plate width (B) as such:
tu req =
Verification Example
LRFD
ASD
AISC Design Guide 1, 2nd Edition
4 MPlate
Base
4 M a crit
u crit and Anchor Rod Design
Fy
411.1 kip-in.
0.9036 ksi
= 1.17 in.
=
9.
ta req =
LRFD
ASD
e = 720 kip-in./90 kips = 8.00 in.
e = 480 kip-in./60 kips = 8.00 in.
Then, e > ekern; therefore, anchor rods are required to
resist the tensile force. The anchor rods are assumed to
be 1.5 from the plate edge.
Fy
4 7.68 kip-in.1.67
36 ksi
= 1.19 in.
=
Assume a 14-in. 14-in. base plate. The effective eccentricity is
3.
Determine the length of bearing.
LRFD
ASD
3.06 ksi 14 in.12.5 in. 2.04 ksi 14 in.12.5 in.
f =
2
2
= 178 kips
= 268 kips
f=
Use plate size:
N = 19 in.
B = 19 in.
thus,
t = 14 in.
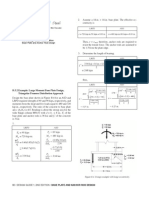
B.5.2 Example: Large Moment Base Plate Design,
Triangular Pressure Distribution Approach
Design the base plate shown in Figure B.4 for an ASD and
LRFD required strength of 60 and 90 kips, respectively, and
moments from the dead and live loads equal to 480 and 720
kip-in., respectively. The ratio of the concrete to base plate
area (A2/A1) is 4.0. Bending is about the strong axis for the
wide ange column W831 with d = bf = 8 in.; Fy of the
base plate and anchor rods is 36 ksi and fc of the concrete
is 3 ksi.
LRFD
ASD
3.0614
2682 4
6
268
(905.5) + 720
A=
3.0614
2.0414
1782 4
6
178
(605.5) + 480
A=
2.0414
= 5.27 in.
= 5.27 in.
1.
LRFD
Pu = 90 kips
M u = 720 kip-in.
Pp
A1
= 0.60(0.85)(3.0)(2)
ASD
Pa = 60 kips
M a = 480 kip-in.
Pp
A1
0.60(1.7)((3.0)
Pp
A1
= 3.06 ksi
Pp
A1
(0.85)(3.0)(2)
2.50
(1.7)(3.0)
2.50
= 2.04 ksi
Figure B.4. Design example with large eccentricity.
60 / DESIGN GUIDE 1, 2ND EDITION / BASE PLATE AND ANCHOR ROD DESIGN
4.
Anchor rods are placed at a 12-in. edge distance. The
required moment strength, Mu pl or Ma pl, for a 1-in. strip
of plate due to the tension in the anchor rods is
Determine the required tensile strength of the anchor
rod.
LRFD
ASD
2.04 ksi 5.27 in.14 in.
3.06 ksi 5.27 in.14 in.
60 kips
90 kips Ta =
2
2
= 15.2 kips
= 22.8 kips
Trod = Ta / 2 = 7.660 kips
= Tu / 2 = 11.4 kips
LRFD
Tu =
Trod
5.
22.8 kips(3.2 in. 1.5 in.)
2(3.2 in. 1.5 in.)
= 11.4 in.-kips/in.
M u pl =
ASD
M a pl
15.2 kips(3.2 in. 1.5 in.)
=
2(3.2 in. 1.5 in.)
= 7.60 in.-kips/in.
Determine the required plate thickness.
The moment for this determination is to be taken at the
critical plate width. This is determined by assuming that
the load spreads at 45 to a location 0.95d of the column. The width is then taken as twice the distance from
the bolt to the critical section for each bolt, provided
that the critical section does not intersect the edge of the
plate.
The critical section, as shown in Figure B.5, is at 14
0.95(8)/2 = 3.2 in.
The required moment strength, Mu pl or Ma pl, for a 1-in.
strip of plate, determined from the bearing stress distribution in Figure B.4, is
LRFD
The required plate thickness is:
LRFD
tp =
4(12.5 in.-kips)
= 1.24 in.
0.9036 ksi
ASD
tp =
4(8.33 in.-kips)(1.67)
= 1.24
36 ksi
Use a 14 14 1-in. base plate.
ASD
2
M u pl =
The required moment strength due to the bearing stress
distribution is critical.
1.20 ksi (3.2 in.)
2
2 (3.06 ksi 1.20 ksi) (3.2 in.) 2
+ 3
2
= 12.5 in-kips/in.
M a pl =
0.80 ksi (3.2 in.)
2
2 ( 2.04 ksi 0.80 ksi) (3.2 in.) 2
3
+
2
= 8.33 in-kips/in.
Figure B.5. Critical plate width for anchor bolt (tension side).
DESIGN GUIDE 1, 2ND EDITION / BASE PLATE AND ANCHOR ROD DESIGN / 61
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
GEOMETRY
Column Section .................
W8X31
Width
Length
Column ..........
8.0
8.0
Plate ..............
14.0
14.0
Concrete Wp1 14.0 Lp1 14.0
Support
Wp2 14.0 Lp2 14.0
Rod Offset .....
5.5
5.5
Thickness of Grout ............
1.5
in
in
in
in
in
in
OK
OK
OK
OK
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
SERVICE LOADS (ASD)
Vertical Load P ................
60.0
Bending Moment M .........
40.0
Horizontal Load V ............
0.0
Design Eccentricity e .......
8.0
Design Eccentricity Is > L/2
MATERIALS
Plate Steel Strength Fy ....
36.0
Pier Concrete Strength f'c
3.0
kip
k-ft
kip
in
ksi
ksi
AXIALLY LOADED PLATES
Cantilever Model
Bearing Stress fp .............
0.31
Critical Section @ Long m
3.20
Critical Section @ Short n
3.80
Plate Thickness tp ..........
0.64
ksi
in
in
in
OK
Thornton Model
Bearing Strength Fp/ .....
2.04
Critical Section @ Int n' .
0.81
Design Moment @ Plate ...
0.10
Plate Thickness tp ............
0.14
ksi
in
k-in/in
in
BASE PLATES WITH MOMENT
Blodgett Method
Max. Bearing Stress fp ...... 1.64
Bearing @ Critical Section
0.88
Moment @ Critical Section
7.11
Moment due to Rod Tension 4.86
Design Moment @ Plate .... 7.11
Plate Thickness tp ............. 1.15
ksi
OK
ksi
k-in/in
k-in/in
k-in/in
in
DeWolf Method
Max. Bearing Stress fp ...... 2.04
Bearing @ Critical Section
0.80
Moment @ Critical Section
8.34
Moment due to Rod Tension 3.86
Design Moment @ Plate .... 8.34
Plate Thickness tp ............. 1.24
ksi
OK
ksi
k-in/in
k-in/in
k-in/in
in
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
ANCHORAGE DESIGN
Rod Material Specification .........
F1554-36
(4) Rods , fya = 36.0 ksi, futa = 58.0 ksi
Anchor Rod Size ..
1" diam. x 16.0 in emb.
Concrete Is Cracked at Service Load Level
Tension Analysis (kip)
Total Tension Force N ..........
15.4 kip
Tension Force per Rod Ni ....
7.7 kip
Anchor Reinf: Use 2 Bars #5 per Rod
Failure Mode
Nn N / Nn/
Steel Strength Nsa
2.00
35.1
0.44
Rebars Strength Nrg
2.00
74.4
0.41
Conc. Breakout Ncbg
2.00
N.A.
N.A.
Pullout Strength Npn
2.00
36.0
0.43
Side Blowout Nsbg
2.00
N.A.
N.A.
N / Nn/ Tension Design Ratio ....
0.44 OK
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
SUMMARY OF RESULTS
Design Moment @ Plate ...
8.3 k-in/in
Plate Thickness tp ............
1.24 in
Max. Bearing Stress fp .....
2.04 ksi
Bearing Strength Fp/ ......
2.04 ksi
fp / Fp/ Design Ratio ..............
1.00 OK
DESIGN IS DUCTILE
Shear Analysis (kip)
Shear Taken by Anchor Rods only
Total Shear Force V ...........
0.0 kip
Shear Force per Rod Vi ......
0.0 kip
All Anchor Rods Are Effective
No Reinforcing Bars Provided
Failure Mode
Vn V / Vn/
Steel Strength Vsa
2.31
16.9
0.00
Rebars Strength Vrg
2.31
N.A.
N.A.
Conc. Breakout Vcbg
2.14
11.9
0.00
Conc. Pryout Vcpg
2.14
52.8
0.00
V / Vn/ Shear Design Ratio ......
0.00 OK
Tension-Shear Interaction
Combined Stress Ratio ...........
0.25
OK
DESIGN CODES
Steel design .............
AISC 360-10 (14th Ed.)
Base plate design ....
AISC Design Series # 1
Anchorage design ...
ACI 318-11 Appendix D
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
Tension Breakout
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
Shear Breakout
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
Column Section .................
Width
Length
Column ..........
in
Plate ..............
in
OK
Wp1
Lp1
in
OK
Wp2
Lp2
in
OK
Rod Offset .....
in
OK
Thickness of Grout ............
in
Concrete
Support
Bearing stress
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
Vertical Load P ................
kip
Bending Moment M .........
k-ft
Horizontal Load V ............
kip
Design Eccentricity e .......
8.0
in
Design Eccentricity Is > L/2
Plate Steel Strength Fy ....
ksi
Pier Concrete Strength f'c
ksi
60.0 / (14.0 * 14.0) = 0.3 ksi
Bearing strength
= 0.85 * 3.0 *
= 5.1 ksi
Under-strength factor = 2.50
Bearing strength ratio =
ACI 9.3.2.4
=
0.3
2.0 / 2.50
= 0.15
< 1.0 OK
Critical section m =
0.5 * (14.0 - 0.95 *8.0) = 3.2 in
Critical section n =
0.5 * (14.0 - 0.80 *8.0) = 3.8 in
[
+
=
Controlling section
ACI 10.14.1
4 * 8.0 * 8.0
(8.0 + 8.0)
] * 0.15 = 0.15
AISC-DG#1 3.1.2
AISC-DG#1 3.1.2
= 0.40
= 2.0 in
Max (3.2, 3.8, 0.40 * 2.0) = 3.8 in
Plate moment
0.3 * 3.8 / 2 = 2.2 k-in/in
Plate thickness
= 3.8 *
= 0.64 in
AISC-DG#1 3.1.2
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
Eccentricity
40.0 * 12 / 60.0 = 8.0 in
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
> L / 6 = 14.0 / 6 = 2.3in
Bearing length
Y = 1.5 * (14.0 / 2 + 5.5) - 0.5 *
Max bearing stress
]-
= 5.3 in
AISC-DG#1 B.4.2
2.0 ksi
Tension
2.0 * 5.3 * 14.0 / 2 - 60.0 = 15.4 kip
Bearing at critical section
2.0 * (1 - 3.2 / 5.3) = 0.8 ksi
Moment due to bearing
AISC-DG#1 B.4.2
AISC-DG#1 3.1.2
Mb = 0.8 * 3.2 / 2 + (2.0 - 0.8) * 3.2 / 3 = 8.3 k-in/in
Moment due to tension
Mt = 7.7 * [3.2 - (14.0 / 2 - 5.5)] / [2 * (3.2 - (14.0 / 2 - 5.5))] = 3.9 k-in/in
Plate thickness
= 1.24 in
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
Rod Material Specification ...... F1554-36 , Use (4) Rods , fya = 36.0 ksi, futa = 58.0 ksi
Anchor Rod Size .... 1" diam. x 16.0 in emb. ,
Ase = 0.61 in , Abrg = 1.50 in
ACI D.5
Total tension force N = 15.4 kip ,
# of tension rods = 2 , Tension force per rod Ni = 7.7 kip
- Steel strength of anchors in tension
Steel strength
ACI D.5.1
0.606 * 58.0 = 35.1 kip
ACI Eq. (D-2)
Under-strength factor = 2.00
Steel strength ratio =
ACI D.4.3
=
7.7
= 0.44 < 1.0 OK
35.1 / 2.00
ACI D.4.1.1
- Concrete breakout strength of anchors in tension
ACI D.5.2
Anchor reinforcement: Use 2 bars #5 per rod
Bar strength
0.31 * 2 * 2 * 60 = 74.4 kip
Under-strength factor = 2.00
Bar strength ratio =
ACI D.5.2.9
=
15.4
= 0.41 < 1.0 OK
74.4 / 2.00
Effective embedment
ACI D.4.1.1
19.50 / 1.5 = 13.00 in
ACI D.5.2.3
Anchor group area
Anc = (19.5 + 8.5) * (8.5 + 11.0 + 8.5) = 784.0 in
Single anchor area
Single anchor strength
Eq. (D-5)
= 24
Eccentricity factor
= 61.6 kip
1.00 (No eccentric load)
Edge effects factor
Cracking factor
ACI D.5.2.1
9 * (13.0) = 1521.0 in
= 0.7 + 0.3
1.00
Eq. (D-6)
ACI D.5.2.4
8.5
= 0.83
1.5 * 13.0
(Cracked concrete at service load level)
ACI D.5.2.5
ACI D.5.2.6
Breakout strength
784.0
1.00 * 0.83 * 1.00 * 61.6 = 26.4 kip
1521.0
Eq. (D-4)
Under-strength factor = 2.00
ACI D.4.3
Breakout strength ratio =
15.4
= 1.17 > 1.0 NG
26.4 / 2.00
Bar strength ratio controls (0.41 < 1.17)
ACI D.5.2.9
- Concrete pullout strength of anchors in tension
Single anchor strength
Cracking factor
ACI D.5.3
8 * 1.50 * 3.0 = 36.0 kip
1.00
(Cracked concrete at service load level)
Pullout strength
1.00 * 36.0 = 36.0 kip
ACI Eq. (D-14)
ACI D.5.3.6
ACI Eq. (D-13)
Under-strength factor = 2.00
Pullout strength ratio =
ACI D.4.1.1
ACI D.4.3
=
7.7
= 0.43
36.0 / 2.00
< 1.0 OK
ACI D.4.1.1
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
- Concrete side-face blowout strength of anchors in tension
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
ACI D.5.4
Side-face blowout Nsbg = N.A. (Embed < 2.5 Ca , 16.0 < 2.5 * 8.5 = 21.3)
ACI D.5.4.1
Tension Design Ratio =
ACI D.4.1.1
= 0.44 < 1.0 OK
ACI D.5
Shear resisted by Anchor Rods only
Total shear force V = 0.0 kip ,
(anchor rods are welded to the base plate)
Shear per rod Vi = 0.0 kip , (all anchor rods are effective)
- Steel strength of anchor rods in shear
Steel strength
0.6 * 0.61 * 58.0 * 0.80 = 16.9 kip
Under-strength factor = 2.31
Steel strength ratio =
ACI D.6.1.2
ACI D.4.3
0.0
= 0.00
16.9 / 2.31
< 1.0 OK
- Concrete breakout strength of anchors in shear
ACI D.4.1.1
ACI D.5.2
No Reinforcing bars provided
Anchor group area
Avc = (1.5 * 8.00) * (8.50 + 11.00 + 8.50) = 336.0 in
Single anchor area
ACI D.6.2.1
4.5 * (8.00) = 288.0 in
Eq. (D-32)
Single anchor strength
Vb =
Vb = 11.2 kip
Eccentricity factor
1.00 (No eccentric load)
Edge effects factor
Cracking factor
= 0.7 + 0.3
1.00
Eq. (D-33)
ACI D.6.2.5
8.50
= 0.91
1.5 * 8.0
(Cracked concrete at service load level)
Thickness factor
ACI D.6.2.6
ACI D.6.2.7
ACI D.6.2.8
Breakout strength
336.0
288.0
1.00 * 0.91 * 1.00 * 1.00 * 11.2 = 11.9 kip
Under-strength factor = 2.14
Breakout strength ratio =
Eq. (D-31)
ACI D.4.3
0.0
= 0.00 < 1.0 OK
11.9 / 2.14
Breakout strength ratio controls (0.00 < 0.00)
ACI D.4.1.1
ACI D.6.2.9
Project: Verification Example
Engineer: Javier Encinas, PE
Descrip: Base Plate Verification
STEEL BASE PLATE DESIGN
ASDIP Steel 3.2.5
Page # ___
7/20/2014
www.asdipsoft.com
- Concrete pryout strength of anchors in shear
Pryout strength
2.0 * 11.9 = 52.8 kip
ACI D.6.3.1
Under-strength factor = 2.14
ACI D.4.3
Pryout strength ratio =
Shear Design Ratio =
0.0
= 0.00
52.8 / 2.14
< 1.0 OK
= 0.00 < 1.0 OK
ACI D.4.1.1
ACI D.4.1.1
Combined Stress Ratio =
Combined Stress Ratio =
= 0.25
< 1.0 OK
ACI RD.7
Anchorage design is ductile
Steel design ...................
AISC 360-10 (14th Ed.)
Base plate design ..........
AISC Design Series # 1
Anchorage design .........
ACI 318-11 Appendix D
You might also like
- F - Deludge SystemDocument11 pagesF - Deludge Systemkelvin_totNo ratings yet
- Structural Requirements For EquipmentDocument11 pagesStructural Requirements For EquipmentJDGM01No ratings yet
- PILE FDN DESIGN For NMD TOWERDocument12 pagesPILE FDN DESIGN For NMD TOWERraj mNo ratings yet
- Hilti - Factored Loads in The Context of Anchor DesignDocument21 pagesHilti - Factored Loads in The Context of Anchor DesignPatrice AudetNo ratings yet
- LRFD AsdDocument9 pagesLRFD Asdshilpijain0504No ratings yet
- Shear Key or Shear Lug Design - US AISC SectionDocument4 pagesShear Key or Shear Lug Design - US AISC SectionJun AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Basic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorDocument1 pageBasic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorYaser ShabasyNo ratings yet
- GS. Load Types in STAAD - ProDocument2 pagesGS. Load Types in STAAD - ProFrancis CayananNo ratings yet
- Concrete Anchor Foundation Bolt Design Calculations With Example As Per ACI 318 Appendix D-Part4-Blow Out Strength in TensionDocument3 pagesConcrete Anchor Foundation Bolt Design Calculations With Example As Per ACI 318 Appendix D-Part4-Blow Out Strength in TensionVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- SP 1275 Rev 02 Spec and Criteria For Design of Civil Building Works Update 03 96Document200 pagesSP 1275 Rev 02 Spec and Criteria For Design of Civil Building Works Update 03 96santhosh kumar BudiNo ratings yet
- 10753-Ep 4-1-1Document37 pages10753-Ep 4-1-1FcosmeNo ratings yet
- 1090-Structural Design Basis For Brazil ProjectDocument7 pages1090-Structural Design Basis For Brazil Projectask.kulkarni KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - General Principles of Dynamic DesignDocument36 pages3.1 - General Principles of Dynamic DesignKevin OzNo ratings yet
- Appendix-2 Seismic "G" Load CalculationDocument2 pagesAppendix-2 Seismic "G" Load Calculationkemo10No ratings yet
- Wind Loads For High-Solidity Open-Frame StructuresDocument14 pagesWind Loads For High-Solidity Open-Frame StructuresEric Chien100% (1)
- PEC EN STN C 13619 17 Mar 2014Document169 pagesPEC EN STN C 13619 17 Mar 2014Raja RamNo ratings yet
- Imp Design GuideDocument32 pagesImp Design GuideRahulNo ratings yet
- Circular Footing (HUGO2)Document89 pagesCircular Footing (HUGO2)nelsonhugoNo ratings yet
- WeldDocument7 pagesWeldMuhammad Akbar Faereza NugrahaNo ratings yet
- AASHTO-2009 Highway Signs 159 PDFDocument1 pageAASHTO-2009 Highway Signs 159 PDFer_rahmansNo ratings yet
- Practical Design Stepped ColumnsDocument12 pagesPractical Design Stepped ColumnstaosyeNo ratings yet
- Seismic Coefficients Non Building StructuresDocument3 pagesSeismic Coefficients Non Building StructuresBunkun15No ratings yet
- 00calculation Sheet For MMII Compressor Shed1Document31 pages00calculation Sheet For MMII Compressor Shed1clarkgaguiNo ratings yet
- Calculations For Rectangular Storage TankDocument44 pagesCalculations For Rectangular Storage TankSiva ShankarNo ratings yet
- 420 Transformer FDN For Panjarpur-6.0mtr26.5.06Document21 pages420 Transformer FDN For Panjarpur-6.0mtr26.5.06Zulkifli BasriNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack 1803-Pr-01 Calculation For Pilings & Pile Caps: Megha Engineering & Infrastructure LTD Intecsa IndustrialDocument1 pagePipe Rack 1803-Pr-01 Calculation For Pilings & Pile Caps: Megha Engineering & Infrastructure LTD Intecsa IndustrialphanikrishnabNo ratings yet
- 1613.8 ASCE 7-10, Table 12.2-1 SesmicDocument4 pages1613.8 ASCE 7-10, Table 12.2-1 Sesmiclaila. areebNo ratings yet
- 01 Rpspl-Civil-Doc-Ct-01-31-01-20 PDFDocument75 pages01 Rpspl-Civil-Doc-Ct-01-31-01-20 PDFkapilNo ratings yet
- Day 2 S3 BNBC 2020Document75 pagesDay 2 S3 BNBC 2020November RainNo ratings yet
- BY Pooja Pingle: Structwel Designers & ConsultantsDocument23 pagesBY Pooja Pingle: Structwel Designers & ConsultantssachinapkarNo ratings yet
- Anchor Design HILTIDocument14 pagesAnchor Design HILTIRohit GadekarNo ratings yet
- QES PEVC-ENG262 - Checklist For Tower Foundation Design & DrawingDocument2 pagesQES PEVC-ENG262 - Checklist For Tower Foundation Design & DrawingRupesh KhandekarNo ratings yet
- USD T BeamDocument10 pagesUSD T BeammanowarNo ratings yet
- Design Base Plate For I Beam - Bottom BracketDocument1 pageDesign Base Plate For I Beam - Bottom BracketCon CanNo ratings yet
- Bentley Q&ADocument35 pagesBentley Q&AinnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Detailing BrochureDocument2 pagesReinforcement Detailing BrochureAbd Al-Gaffar BajouriNo ratings yet
- Section Modulus 012004Document2 pagesSection Modulus 012004dakidofdaboomNo ratings yet
- Calculation Note For Removeable Side - Rev ADocument28 pagesCalculation Note For Removeable Side - Rev AmaniaxpdfNo ratings yet
- Excel Sheet 2007Document20 pagesExcel Sheet 2007Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Chapter J Design of ConnectionsDocument16 pagesChapter J Design of Connectionsghosh73No ratings yet
- Bosch Motorsport ECU MS 15 Sport Calibration GuideDocument107 pagesBosch Motorsport ECU MS 15 Sport Calibration GuideMauricio Navarro santanaNo ratings yet
- RAILWAY Geogrid DesignDocument11 pagesRAILWAY Geogrid DesignPetrucio José Dos Santos JuniorNo ratings yet
- Civil Layout DrawingsDocument2 pagesCivil Layout DrawingsAnonymous IwqK1NlNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110Document11 pagesSpreadsheets To BS 8110NitinShepurNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap Design 3 PilesDocument1 pagePile Cap Design 3 PilesdantevariasNo ratings yet
- Vessel Side Shell Check CalculationsDocument5 pagesVessel Side Shell Check CalculationsShahir MeledathNo ratings yet
- GB1516 Sac 240 CV RP 0004 - BDocument69 pagesGB1516 Sac 240 CV RP 0004 - BkkkkNo ratings yet
- BSPL 1242 Iot2 Me Cal 0004 Rev.a1Document70 pagesBSPL 1242 Iot2 Me Cal 0004 Rev.a1SachinNo ratings yet
- As Per RCC Design (B.C. Punmia) Page 184 Example 7.6 Design of Cantilever ChajjaDocument32 pagesAs Per RCC Design (B.C. Punmia) Page 184 Example 7.6 Design of Cantilever ChajjajaffnaNo ratings yet
- Skid Resistance For Paved Surfaces (Full Scale Tire)Document6 pagesSkid Resistance For Paved Surfaces (Full Scale Tire)Kongsak AkkharawongwhatthanaNo ratings yet
- Structures of Gas Station in Saint PetersburgDocument97 pagesStructures of Gas Station in Saint PetersburgassdaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Wind LoadDocument18 pagesSeminar Wind LoadKaustubh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Fillet Weld Strength Calculation Example For Welded Connection Subjected To BendingDocument6 pagesFillet Weld Strength Calculation Example For Welded Connection Subjected To BendingpipestressNo ratings yet
- Stepped Columns - A Simplified Design MethodDocument23 pagesStepped Columns - A Simplified Design MethodwrayroNo ratings yet
- ASDIP Steel - Base Plate Verification ExampleDocument4 pagesASDIP Steel - Base Plate Verification ExampleEdwin VizueteNo ratings yet
- One Way Slab DesignDocument16 pagesOne Way Slab DesignAssad Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Steel Beam DesignDocument26 pagesSteel Beam DesignWazini D. Izani100% (1)
- Pile Cap DesignDocument25 pagesPile Cap DesignGanesh Konar100% (5)
- XL InterpolatorsDocument6 pagesXL InterpolatorsKarthikeyan VediNo ratings yet
- Steel TableDocument288 pagesSteel TableKarthikeyan VediNo ratings yet
- 9013Document14 pages9013Sujoy RoyNo ratings yet
- One Layer Theory ChartsDocument9 pagesOne Layer Theory ChartsKarthikeyan VediNo ratings yet
- WP-3r0 Urban StreetsDocument37 pagesWP-3r0 Urban StreetsKarthikeyan VediNo ratings yet
- IS: 73 - 1992 Paving Bitumen - SpecificationDocument7 pagesIS: 73 - 1992 Paving Bitumen - SpecificationKarthikeyan Vedi83% (6)
- Tutorial Class 1 Questions 1Document2 pagesTutorial Class 1 Questions 1Bố Quỳnh ChiNo ratings yet
- 9C606C.64 To 65Document24 pages9C606C.64 To 65SHIRISHA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Reading Material CH 14 Other Artificial Lift MethodsDocument18 pagesReading Material CH 14 Other Artificial Lift MethodsSagar DadhichNo ratings yet
- Winter Internship Report (23/09/2016 - 31/01/2017)Document56 pagesWinter Internship Report (23/09/2016 - 31/01/2017)AyushNo ratings yet
- DRM Transmitter PresentationDocument22 pagesDRM Transmitter PresentationJuan Jose PerezNo ratings yet
- Technical Owner Manual Nfinity v6Document116 pagesTechnical Owner Manual Nfinity v6Tom MondjollianNo ratings yet
- Apple A9Document10 pagesApple A9Savithri NandadasaNo ratings yet
- Iso 9974-2Document4 pagesIso 9974-2willianNo ratings yet
- TIL 1881 Network Security TIL For Mark VI Controller Platform PDFDocument11 pagesTIL 1881 Network Security TIL For Mark VI Controller Platform PDFManuel L LombarderoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Feb-Mar 2017Document40 pagesCloud Computing - Feb-Mar 2017Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Sd-1-Parts-Book Manual Propietario SpreaderDocument30 pagesSd-1-Parts-Book Manual Propietario Spreadergabriel sanchezNo ratings yet
- Pre-Spud Checklist # 4Document2 pagesPre-Spud Checklist # 4Yougchu LuanNo ratings yet
- Battery Power Management For Portable Devices PDFDocument259 pagesBattery Power Management For Portable Devices PDFsarikaNo ratings yet
- Jun SMSDocument43 pagesJun SMSgallardo0121No ratings yet
- Experiment SCDocument5 pagesExperiment SCnitinmgNo ratings yet
- Wrights Mushroom ColumnDocument33 pagesWrights Mushroom ColumnKeithy GandhiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics (5th Edition) - Munson, OkiishiDocument818 pagesFundamentals of Fluid Mechanics (5th Edition) - Munson, OkiishiMohit Verma85% (20)
- Libeskind Daniel - Felix Nussbaum MuseumDocument6 pagesLibeskind Daniel - Felix Nussbaum MuseumMiroslav MalinovicNo ratings yet
- OTM Reports FTI Training ManualDocument78 pagesOTM Reports FTI Training ManualAquib Khan100% (2)
- Desmophen 1200 - en - 00134597 17947398 20766463Document3 pagesDesmophen 1200 - en - 00134597 17947398 20766463Sabri AeroChemNo ratings yet
- EM000039Rev1 PDFDocument1 pageEM000039Rev1 PDFGustavo RiveraNo ratings yet
- JAVA Stack Installation in ERPDocument2 pagesJAVA Stack Installation in ERPsai_balaji_8No ratings yet
- Misc Forrester SAP Competence CenterDocument16 pagesMisc Forrester SAP Competence CenterManuel ParradoNo ratings yet
- E Insurance ProjectDocument10 pagesE Insurance ProjectChukwuebuka Oluwajuwon GodswillNo ratings yet
- Porting Relations 2 StrokesDocument10 pagesPorting Relations 2 Strokespistonbreaker100% (8)
- FHV19 - Exhibitor Manual - 10 DECEMBER - Manual PDFDocument50 pagesFHV19 - Exhibitor Manual - 10 DECEMBER - Manual PDFHien Hien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Electrical 02Document10 pagesElectrical 02Hary Kriz33% (3)
- Chap 08Document63 pagesChap 08Sam KashNo ratings yet
- CambuzaDocument45 pagesCambuzaMia Marin Pâslaru100% (2)
- Final Upcat Mock ExamDocument24 pagesFinal Upcat Mock Examjbgonzales8No ratings yet