Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Daftar Pustaka
Uploaded by
Nurizaldo GinusOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Daftar Pustaka
Uploaded by
Nurizaldo GinusCopyright:
Available Formats
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
1.
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB,
Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES. 2013. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics
2013 Update: A Report from The American Heart Association. Circulation.
127: e6-e245. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 22 April 2014.
2.
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. 2013. Riset Kesehatan Dasar: Riskesdas
2013. Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan. Jakarta.
3.
Roberts CK, Vaziri ND, Wang XQ, Barnad JR. 2000. Enhanced NO
Inactivation and Hypertension Induced by A Fat, Refined-Carbohydrate
Diet. Hypertension. 36(3): 423-429. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 23 April
2014.
4.
Gimbrone MA Jr, Topper JN, Nagel T, Anderson KR, and Garcia-Cardena
G.
2000.
Endothelial
Dysfunction,
Hemodynamic
Forces,
and
Atherogenesis. Annals of The New york Academy of Sciences. 902: 230240. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 23 April 2014.
5.
Blann AD, Woywodt A, Bertolini F. 2005. Circulating Endothelial Cells.
Biomarker of Vascular Disease. Thromb Haemost. 93(2): 228-35.
Abstract. Diakses tanggal 27 Juli 2013.
6.
Joshi UH, Ganatra TH, Bhalodiya PN, Desai TR, Tirgar PR. 2012.
Comparative Review on Harmless Herbs with Allopathic Remedies As
Anti-Hypertensive. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and
Chemical Sciences. 3(2): 673-678. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 22 April 2014.
7.
Rong-hua L, Shi-sheng C, Gang R, FengS, Hui-lian H. 2013. Phenolic
Compounds from Roots of Imperata cylindrica var. Major. Chinese Herbal
Medicines. 5(3): 240-243. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 13 Februari 2014.
8.
Mak-Mensah EE, Komlaga G and Terlabi EO. 2010. Antihypertensive
Action of Ethanolic Extract of Imperata cylindrica Leaves in Animal
Models. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research. 4(14): 1486-1491.
Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 13 Februari 2014.
9.
Kaur N, Awadh AI, Ali RB, Sadikun A, Zubaid M, and Zaini M. 2012.
Cardio-Vascular Activity of Gynura procumbens Merr. Leaf Extract.
International journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 3(5):
1401-1405. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 13 Februari 2014.
10.
Kim MJ, Lee HJ, Wiryowidagdo S, and Kim HK. 2006. Antihypertensive
Effects of Gynura procumbens Extract in Spontaneusly Hypertensive Rats.
Journal of Medicinal Food. 9(4): 587-590. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 13
Februari 2014.
11.
Ismail A, Mohamed M, Sulaiman SA, and Ahmad WAN. 2013. Autonomic
Nervous System Mediates the Hypotensive Effects of Aqueous and Residual
Methanolic Extracts of Syzygium polyanthum (Wight) Walp. var.
Polyanthum
Leaves
in
Anaesthetized
Rats.
Evidence-Based
Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013: 1-16. Fulltext. Diakses
tanggal 13 Februari 2014.
12.
Dorland,
W.A.N.
2002.
Kamus
Kedokteran
Dorland.
29th
ed.
Jakarta:EGC, hal: 1051, 2147.
13.
Mansjoer, Arif dkk. 2001. Kapita Selekta Kedokteran Jilid I: Nefrologi
dan Hipertensi. Jakarta: Media Aesculapius FKUI.
14.
Kaplan, Norman. 1998. Measurement of Blood Pressure and Primary
Hypertension: Pathogenesis in Clinical Hypertension: Seventh Edition.
Baltimore, Maryland USA: Williams & Wilkins. 28-46.
15.
Kumar V, Cotran RS, dan Robbins SL. 2007. Buku Ajar Patologi
Robbins, Edisi 7, Volume 2. Diterjemahkan oleh Brahm U. Pendit. Editor
Bahasa Indonesia oleh Hartanto H, Darmaniah N, dan Wulandari N. Jakarta:
EGC. Halaman 366.
16.
Albert B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, and Walter P. 2002.
Molecular
Biology
of
the
Cell,
4th
Edition.
(Online),
(httphttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26848, diakses tanggal 11
Juni 2014).
17.
Godbole AS, Lu X, Guo X, and Kassab GS. 2009. NADPH Oxidase has a
Directional Response to Shear Stress. American Journal of Physiology
Heart Circulatory Physiology. 296: H152-H158. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal
11 Juni 2014.
18.
Miao H, Yuan S, Wang Y, Tsygankov A, and Chien S. 2002. Role of Cbl in
Shear-Activation of PI 3-Kinase and JNK in Endothelial Cells. Biochemical
and Biophysical Research Communications. 292: 892-899. Abstract.
Diakses tanggal 12 Juni 2014.
19.
Tzima E, Irani-Tehrani M, Kiosses WB, Dejana E, Schultz DA, Engelhardt
B, Cao G, DeLisser H, and Schwartz MA. 2005. A Mechanosensory
Complex that Mediates the Endothelial Cell Response to Fluid Shear Stress.
Nature. 437: 426-431. Abstract. Diakses tanggal 12 Juni 2014.
20.
Fisslthaler B, Dimmeler S, Hermann C, Busse R, and Fleming I. 2000.
Phosphorylation and Activation of the Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase by
Fluid Shear Stress. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 168: 81-88. Abstract.
Diakses tanggal 12 Juni 2014.
21.
Kohnen SL, Mouithys-Mickalad AA, Deby-Dupont GP, Deby CMT, Lamy
ML, and Noels AF. 2001 Oxidation of Tetrahydrobiopterin by peroxynitrite
or oxoferryl Species Occurs by a Radical Pathway. Free Rad. Res. 35: 709721. Abstract. Diakses tanggal 12 Juni 2014.
22.
Boss CJ, Lip GYH, and Blann AD. 2006. Circulating Endothelial Cells in
Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
48: 1538-1547. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 27 Juli 2013.
23.
Goon PKY, Lip GYH, Boss CJ, Stonelake PS, and Blann AD. 2006.
Circulating Endothelial Cells, Endothelial Progenitor Cells, and Endothelial
Microparticles in Cancer. Neoplasia. 8: 79-88. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 26
Juli 2013.
24.
Woywodt A, Bahlmann FH, de Groot K, Haller H, and Haubitz M. 2002.
Circulating Endothelial Cells: Life, Death, Detachment and Repair of the
Endothelial Cell Layer. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 17: 1728-1730. Fulltext.
Diakses tanggal 26 Juli 2013.
25.
Don BR and Lo JC. 2007. Endocrine Hypertension. In: Gardner DG,
Shoback D (Ed). Greenspans Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 6 th Ed.
New York: International Edition Mc Graw Hill. P 396-420.
26.
Vinson GP. 2011. The Mislabelling of Deoxycorticosterone: Making Sense
of Corticosteroid Structure and Function. Journal of Endocrinology. 211:
3-16. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 5 Januari 2014.
27.
Iyer A, Chan V and Brown L. 2010. The DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Rat as a
Model of Cardiovascular Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress. Current
Cardiology Review. 6: 291-297. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 30 Oktober
2013.
28.
Arianti, Rini. 2012. Aktivitas Hepatoprotektor Dan Toksisitas Akut
Ekstrak Akar Alang-Alang (Imperata cylindrica). Skripsi. Departemen
Biokimia Fakultas Matematika Dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam Institut
Pertanian Bogor.
29.
Park JH. 2004. Medicinal Plants of Korea. Seoul: Shinil Publishing Co.
30.
Khaerunnisa ST. 2009. Pemanfaatan Senyawa Bioaktif dari Akar AlangAlang (Imperata cylindrica) sebagai Bahan Antioksidan. Skripsi.
Surabaya : Departemen Kimia, Fakultas Ilmu dan Teknologi, Universitas
Airlangga
31.
Parvathy NG, Padma R, Renjith V, Rahate KP, and Saranya TS.
Phytochemical Screening and Antihelmintic Activity of Methanolic Extract
of Imperata cylindrica. IJPPS. 4:232-234. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 22
April 2014.
32.
Turgut Coan D, et al. 2013. Impact of tannic acid on blood pressure,
oxidative stress and urinary parameters in L-NNA-induced hypertensive
rat).
33.
Robak J, Gryglewski RJ. 1988. Flavonoids are Scavengers of Superoxide
Anions. Biochem Pharmacol. 837-841.
34.
Hariyatmi. 2004. Kemampuan Vitamin E Sebagai Antioksidan
Terhadap Radikal Bebas Pada Lanjut Usia. Jurnal Penelitian. UMS.
35.
Kumalaningsih, Sri. 2007. Antioksidan Sumber dan Manfaatnya.
(Online),
(http://antioxidantcentre.com/index.php/Antioksidan/3.-
Antioksidan-Sumber-Manfaatnya, diakses tanggal 9 April 2014).
36.
Akowuah GA, Sadikun A, Mariam A. 2001. Structural Analysis of
Quercetin and Rutin from Gynura Procumbens. J Tropical Med Plants. 2
(2): 193-199
37.
Rosidah, Yam MF, Sadikun A, Asmawi MZ. 2008. Antioxidant potential of
Gynura procumbens. Pharm Biol. 46: 616-625.
38.
Bhansali BB, Vyas S, Goyal R. 1987. Cardiac Effects of Quercetin on
Isolated Rabbit and Frog Heart Preparation. Indian Journal of
Pharmacology. 19: 100-107.
39.
Kaur N, Awadh AI, Ali RB, Sadikun A, Abdul Sattar MZ, Asmawi MZ.
2012. Cardiovascular Activity of Gynura procumbens merr. Leaf Extracts.
Int J Pharm Sci Res. 3: 1401-1405
40.
Kim MJ, Lee HJ, Sumali, and Kim HK. 2012. Antihypertensive Effects of
Gynura procumbens Extract in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J Med
Food. 9 (4), 587-590.
41.
Dalimartha, Setiawan. 2000. Salam (Syzygium polyanthum [Wight.]
Walp.). Atlas Tumbuhan Obat Indonesia. Jakarta: Trubus Agriwidya.
pp.161-165.
42.
Katzer,
G.
2000.
Gernot
Katzers
Spice
Dictionary.
(Online),
(http://www.ang.kfunigranz.ac.at/katzer/engrs/genericframe.html, diakses 1
Desember 2013).
43.
Lee Wei HAR dan Ismail IS. 2012. Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolics
and Total Flavonoids of Syzygium polyanthum (Wight) Walp Leaves. Int. J.
Med. Arom. 2: 219-228. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 13 Februari 2014.
44.
Ismail A, Mohamed M, Sulaiman SA, and Wan Ahmad WAN. 2013.
Autonomic Nervous System Mediates the Hypotensive Effects of Aqueous
and Residual Methanolic Extracts of Syzygium polyanthum (Wight) Walp.
var. polyanthum Leaves in Anaesthetized Rats. Hindawi Publishing
Corporation. 2013: 1-16. Fulltext. Diakses tanggal 13 Februari 2014.
You might also like
- CPG - Acute Pulmonary OedemaDocument4 pagesCPG - Acute Pulmonary OedemaFadhel Jimmy AnugerahNo ratings yet
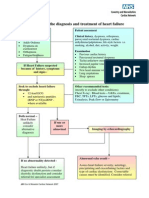
- 2 - Algorithm For The Diagnosis and Treatmentofheart FailureDocument1 page2 - Algorithm For The Diagnosis and Treatmentofheart FailureNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Ehw128 Addenda PDFDocument17 pagesEhw128 Addenda PDFHayat Hamzah DawiNo ratings yet
- Algoritma BradycardiaDocument1 pageAlgoritma BradycardiaFiya SahrulNo ratings yet
- CD RHD 12 03 08Document2 pagesCD RHD 12 03 08Chairunnisya NisyaNo ratings yet
- Achmad Deddy Fatoni Portfolio Side View 2010Document1 pageAchmad Deddy Fatoni Portfolio Side View 2010Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- KEPUSTAKAANDocument2 pagesKEPUSTAKAANNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- ATLS ProtocoloDocument21 pagesATLS Protocoloedgarjavier65100% (2)
- Pasien Centre CareDocument3 pagesPasien Centre CareNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Role of Cat-Scratch Disease in Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument7 pagesRole of Cat-Scratch Disease in Cervical LymphadenopathyNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Epidemiology of Vertigo, Migraine and Vestibular Migraine. Journal of Neurology. 236 (3) : 333-8Document1 pageDaftar Pustaka: Epidemiology of Vertigo, Migraine and Vestibular Migraine. Journal of Neurology. 236 (3) : 333-8Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Achmad Deddy Fatoni Portfolio Side View 2010Document1 pageAchmad Deddy Fatoni Portfolio Side View 2010Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- XCPT LIGHT-PC 14-02-11 15.41.36Document6 pagesXCPT LIGHT-PC 14-02-11 15.41.36Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- 1 - Algorithm For The Diagnosis of Heart FailureDocument1 page1 - Algorithm For The Diagnosis of Heart FailureNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Sodium NitriteDocument5 pagesSodium NitriteNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Homonymous Visual Field Defects Perimetric Findings and Corresponding Neuro-Imaging ResultsDocument6 pagesHomonymous Visual Field Defects Perimetric Findings and Corresponding Neuro-Imaging ResultsNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Homonymous Visual Field Defects Perimetric Findings and Corresponding Neuro-Imaging ResultsDocument6 pagesHomonymous Visual Field Defects Perimetric Findings and Corresponding Neuro-Imaging ResultsNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Sodium NitriteDocument5 pagesSodium NitriteNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease 6Document2 pagesAcute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease 6Jasmin K. BrarNo ratings yet
- TRT RazinDocument8 pagesTRT RazinNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Buku Modul Mahasiswa Skenario KetigaDocument7 pagesBuku Modul Mahasiswa Skenario KetigaNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- EULA0Document9 pagesEULA0Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Release NotesDocument8 pagesRelease NotesDias AnggarsrNo ratings yet
- XCPT TOSHIBA-PC 12-12-02 18.58.59Document5 pagesXCPT TOSHIBA-PC 12-12-02 18.58.59Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- XCPT TOSHIBA-PC 12-11-16 20.59.46Document5 pagesXCPT TOSHIBA-PC 12-11-16 20.59.46Nurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Kegiatan Aspirasi II Peserta PanitiaDocument8 pagesJadwal Kegiatan Aspirasi II Peserta PanitiaNurizaldo GinusNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2-Marks Question and Answer Unit-IDocument44 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing Technology 2-Marks Question and Answer Unit-IM.ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Exporters: Index by CountryDocument113 pagesExporters: Index by CountrySyam WadiNo ratings yet
- Jyothy Institute of TechnologyDocument4 pagesJyothy Institute of TechnologyBasavaraj hsNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactn McqsDocument12 pagesRedox Reactn McqsIlma GaurNo ratings yet
- Constant HeadDocument14 pagesConstant HeadfujiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SBA7 ReportDocument6 pagesChemistry SBA7 ReportSam ChanNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDocument19 pagesEcosystem and Its ComponentsSooraj KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Solutions of ElectrolytesDocument55 pagesSolutions of Electrolytesneha_dand1591100% (1)
- Profile Prince Decoware Furniture HandlesDocument54 pagesProfile Prince Decoware Furniture HandlesRushabh ShahNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Lab Exercise on Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumDocument21 pagesGroup 4 Lab Exercise on Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumEUNICE JOI SARCONNo ratings yet
- Selective MediaDocument10 pagesSelective Mediaprincess_likemist4No ratings yet
- Test For Cations, Anions and Gases (QA) NotesDocument10 pagesTest For Cations, Anions and Gases (QA) Noteschong56100% (2)
- Titrimetric Methods of AnalysisDocument28 pagesTitrimetric Methods of AnalysisPraveen Kumar Avvaru100% (2)
- Syntheses of Soap and DetergentDocument4 pagesSyntheses of Soap and DetergentChin Castro Zabat100% (2)
- ZeTo RulesDocument30 pagesZeTo RulesRamli Disa100% (5)
- Omeprazole: by Jennica Mae V. CuicoDocument7 pagesOmeprazole: by Jennica Mae V. Cuicoジェンニカ メイNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental ManagementDocument12 pagesJournal of Environmental ManagementAjeng FadillahNo ratings yet
- 1 Auxilliary Equipment - US PricingDocument132 pages1 Auxilliary Equipment - US PricingOscar EspitiaNo ratings yet
- 1010750-Steam Quality TestingDocument11 pages1010750-Steam Quality TestingHendra Hadriansyah100% (1)
- 02 Heubach No 00181 ZPA RZ Epoxy Dispersion WDocument2 pages02 Heubach No 00181 ZPA RZ Epoxy Dispersion WnanoNo ratings yet
- Spot WeldingDocument5 pagesSpot WeldingRao MaazNo ratings yet
- Zuellig Pharma Corporation: Item Name of Medicine Brand Name Principal Name Quantity Unit PriceDocument2 pagesZuellig Pharma Corporation: Item Name of Medicine Brand Name Principal Name Quantity Unit PriceJZik SibalNo ratings yet
- Expwb3ans eDocument67 pagesExpwb3ans eOlivia LinNo ratings yet
- Warna Daun Padi LCCDocument12 pagesWarna Daun Padi LCCM Hisyam NasrullohNo ratings yet
- Sspc-Ab 1Document5 pagesSspc-Ab 1Anton Thomas Punzalan100% (3)
- Packed bed axial thermal conductivityDocument7 pagesPacked bed axial thermal conductivityAdriano HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Mineral-rich Bilimbi fruit analysisDocument3 pagesMineral-rich Bilimbi fruit analysisveronica francisNo ratings yet
- Astm D1785-15Document11 pagesAstm D1785-15david franco0% (1)
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetZirve PolimerNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Bacteria and MollicutesDocument13 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Bacteria and MollicutesPrincess Mehra0% (1)