Professional Documents
Culture Documents
N
Uploaded by
Istiak Ahmed PrinceOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
N
Uploaded by
Istiak Ahmed PrinceCopyright:
Available Formats
Non Traditional Machining
INTRODUCTION TO NTM
Types of Manufacturing Processes:
Manufacturing processes can be broadly divided into two groups
Primary manufacturing processes
Secondary manufacturing processes.
The Primary manufacturing process provides basic shape and size to the material as per
designers requirement. For example: Casting, forming, powder metallurgy processes
provide the basic shape and size.
The Secondary manufacturing processes provide the final shape and size with tighter control
on dimension, surface characteristics etc. Most of Material removal processes are mainly the
secondary manufacturing processes.
Material removal processes can be further divided into mainly two groups
Conventional Machining Processes
Non-Traditional Manufacturing Processes
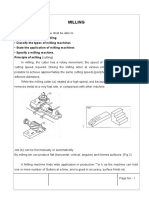
Examples of conventional machining processes are turning, boring, milling, shaping,
broaching, slotting, grinding etc.
Examples of non conventional ( or also called non traditional or unconventional)are Abrasive
Jet Machining (AJM), Ultrasonic Machining (USM), Water Jet and Abrasive Water Jet
Machining (WJM and AWJM), Electro-discharge Machining (EDM) ,Electro chemical
machining.
Characteristics
Processes
of
Conventional
Conventional machining processes mostly
remove material in form of chips by
applying forces on work material with a
cutting tool which is harder than the work
material. Such
forces induce plastic
deformation within the workpiece leading to
shear deformation along the shear plane.
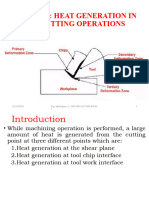
Figure 1.0 shows chip formation by shear
deformation in conventional machining.
Major
characteristics
of
conventional
machining are:
Generally chips are macroscopic and are formed by shear deformation
Material removal takes place due to application of cutting forces energy
domain can be classified as mechanical
Cutting tool must be harder than work piece at room temperature as well as
under machining conditions
There is a direct physical contact between tool and work
Material removal rate of the traditional processes is limited by the mechanical
properties of the work material.
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Non Traditional Machining
Characteristics of Non Conventional Processes
Non Traditional Machining (NTM) Processes are characterized as follows:
Material removal may occur with chip formation or even no chip formation may
take place. For example in AJM, chips are of microscopic size and in case of
Electrochemical machining material removal occurs due to electrochemical
dissolution at atomic level
In NTM, there may not be a physical tool present. For example in laser jet
machining, machining is carried out by laser beam. However in Electrochemical
Machining there is a physical tool that is very much required for machining
In NTM, the tool need not be harder than the work piece material. For example,
in EDM, copper is used as the tool material to machine hardened steels.
Mostly NTM processes do not necessarily use mechanical energy to provide
material removal. They use different energy domains to provide machining. For
example, in USM, AJM, WJM mechanical energy is used to machine material,
whereas in ECM electrochemical dissolution constitutes material removal.
Need for development of Non Conventional Processes
The strength of steel alloys has increased five folds due to continuous R and D effort. In
aero-space requirement of High strength at elevated temperature with light weight led to
development and use of hard titanium alloys, nimonic alloys, and other HSTR alloys. The
ultimate tensile strength has been improved by as much as 20 times. Development of
cutting tools which has hardness of 80 to 85 HRC which cannot be machined economically in
conventional methods led to development of non traditional machining methods.
1.Technologically advanced industries like aerospace, nuclear power, ,wafer
fabrication, automobiles has ever increasing use of High strength temperature resistant
(HSTR) alloys (having high strength to weight ratio) and other difficult to machine materials
like titanium, SST,nimonics, ceramics and semiconductors. It is no longer possible to use
conventional process to machine these alloys.
2.Production and processing parts of complicated shapes (in HSTR and other hard
to machine alloys) is difficult , time consuming an uneconomical by conventional methods of
machining
3.Innovative geometric design of products and components made of new exotic
materials with desired tolerance , surface finish cannot be produced economically by
conventional machining.
4.The following examples are provided where NTM processes are preferred over the
conventional machining process:
Intricate shaped blind hole e.g. square hole of 15 mmx15 mm with a depth
of 30 mm with a tolerance of 100 microns
Difficult to machine material e.g. Inconel, Ti-alloys or carbides, Ceramics,
composites , HSTR alloys, satellites etc.,
Low Stress Grinding Electrochemical Grinding is preferred as compared to
conventional grinding
Deep hole with small hole diameter e.g. 1.5 mm hole with l/d = 20
Machining of composites
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Non Traditional Machining
Differences between Conventional and Non conventional machining
processes.
Sl
No.
1
Conventional Process
Non Conventional Process
The cutting tool and work piece are
always in physical contact with
relative motion with each other,
which results in friction and tool
wear.
There is no physical contact between
the tool and work piece, In some non
traditional process tool wear exists.
Material removal rate is limited by
mechanical properties of work
material.
NTM can machine difficult to cut and
hard
to
cut
materials
like
titanium,ceramics,nimonics,
SST,composites,semiconducting
materials
Relative motion between the tool
and work is typically rotary or
reciprocating. Thus the shape of
work is limited to circular or flat
shapes. In spite of CNC systems,
production of 3D surfaces is still a
difficult task.
Machining of small cavities , slits ,
blind holes or through holes are
difficult
Many NTM are capable of producing
complex 3D shapes and cavities
Use relative simple and inexpensive
machinery and readily available
cutting tools
Capital cost and maintenance cost is
low
Traditional
processes
are
well
established and physics of process
is well understood
Conventional process mostly uses
mechanical energy
7.
Machining of small cavities, slits and
Production of non-circular, micro sized,
large aspect ratio, shall entry angle
holes are easy using NTM
Non traditional processes requires
expensive tools and equipment as well
as skilled labour, which increase the
production cost significantly
Capital cost and maintenance cost is
high
Mechanics of Material removal of Some
of NTM process are still under research
Most NTM uses energy in direct form
For example : laser, Electron beam in
its direct forms are used in LBM and
EBM respectively.
Surface finish and tolerances are
limited by machining inaccuracies
High surface finish(up to 0.1 micron)
and tolerances (25 Microns)can be
achieved
10
High metal removal rate.
Low material removal rate.
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Non Traditional Machining
Definition:
A machining process is called non-traditional if its material removal mechanism is
basically different than those in the traditional processes, i.e. a different form of
energy (other than the excessive forces exercised by a tool, which is in physical
contact with the work piece) is applied to remove the excess material from the work
surface, or to separate the workpiece into smaller parts.
Applications
Some of the applications of NTM are given below:
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Non Traditional Machining
Classification of Non Traditional processes:
Advanced machining process can be classified according to the fundamental energy
employed.
Classification of Advanced Machining Techniques.
Mechanical
Processes
AJM
USM
WJM
AWJM
AFM
MAF
Electro Chemical
Process
ECM
ECG
EJD
Electro Thermal
Process
EDM
LJM
EBM
PAM
Chemical
Process
CHM
PCM
ABREVIATIONS USED:
1. AJM
- Abrasive Jet Machining
2. USM - Ultrasonic Machining
3. WJM - Water Jet Machining
4. AWJM - Abrasive Water Jet Machining
5. ECM - Electro Chemical Machining
6. ECG - Electro Chemical Grinding
7. EJD
- Electro Jet Drilling
8. EDM - Electro Discharge Machining
9. LJM
- Laser Jet Machining
10. EBM - Electron beam Machining
11. PAM - Plasma Arc Machining
12. CHM - Chemical Milling
13. PCM - Photo Chemical Milling
History of Non Traditional processes:
Although, the non conventional machining processes have created a revolution in the
field of machining technology by the development of idea of various processes were
initiated as early as in nineteen- twenties in USSR.
1920
The initiation was first made by Gussev towards the end of 1920 in
USSR. He suggested a method of machining by combination of
Chemical and mechanical means. His work is basis for all Electro
Chemical processes known today.
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Non Traditional Machining
1941
Burgess, American Scientist had demonstrated the possibility of
ECM process by drawing a sharp contrast between the mechanical
and electrolyte methods in metal removal
1942
The idea of Ultrasonic machining was invented by Balamuth at the
He invented at the time of investigation of dispersion of solids in
Liquids with the help of a vibrating magne-tostrictive nickel tube
However, the origination of the process was made by Rosenberg
1943
DM was developed by B R Lazarenko and N I Lazarenko in USSR.
They first developed the idea of spark erosion machining. In the
early nineteen-sixties, the idea of Ultrasonic machining began to
to develop widely in USSR and basis of this development was laid
on extensive investigation that took place in the mechanism of
ultrasonic machining and in the design of Magneto-strictive
transducers, converters and wave guides.
1950
The basis of laser machining was established by the process which
Which were developed by Basov, Prokhorov and Fabrikanth in
USSR in 1950.
1950
Electro chemical Grinding has practically been developed in about
1950.
1960
The concept of whirling jet machining was innovated.
Many of these new techniques of machining have been developed in last few decades
to meet the challenges put forwarded by rapid development of hard to machine and
high strength temperature resistant (HSTR) alloys. It is anticipated that in near
future , these new technologies will find an ever increasing application in all branches
of mechanical engineering industry.
SELECTION OF PROCESS:
The correct selection of the non-traditional machining methods
must be based on the following aspects.
i)
Physical parameters of the process
ii)
Shape to be machined
iii)
Process capability
iv)
Economics of the processes
Physical parameter of the process:
The physical parameters of the different NTM are given in the Table 1.0 which
indicates that PAM and ECM require high power for fast machining. EBM and LBM
require high voltages and require careful handling of equipment. EDM and USM
require medium power . EBM can be used in vacuum and PAM uses oxygen and
hydrogen gas.
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
Non Traditional Machining
Table 1.0 Physical parameter of the process:
Parameters
Potential
(Volts)
Current
(amps)
Power
(kW)
Gap
(mm)
Medium
USM
AJM
NON TRADITIONAL PROCESS
CHM
ECM
EDM
EBM
LBM
PAM
220
220
10-30
100300
150 kV
4.5
kV
100
12
10000
50
0.001
500
2.4
0.22
100
2.70
0.15
50
0.25
0.75
0.20
0.025
100
150
7.5
Abrasives
In water
Abrasive
In gas
Liquid
chemical
Electrolyte
Dielectric
oil
Vacuum
Air
Argon
H2/O2
SHAPES CUTTING CAPABLITY
The different shapes can be machined by NTM. EBM and LBM are used for micro
drilling and cutting. USM and EDM are useful for cavity sinking and standard hole
drilling. ECM is useful for fine hole drilling and contour machining. PAM can be used
for cutting and AJM is useful for shallow pocketing
PROCESS CAPABILITY
The process capability of NTM is given in Table 2.0 EDM which achieves higher
accuracy has the lowest specific power requirement. ECM can machine faster and has
a low thermal surface damage depth. USM and AJM have very material removal rates
combined with high tool wear and are used non metal cutting. LBM and EBM are, due
to their high penetration depth can be used for micro drilling, sheet cutting and
welding. CHM is used for manufacture of PCM and other shallow components.
Jagadeesha T, Assistant Professor , MED, National Institute of Technology, Calicut
You might also like
- Non Traditional Machining Techniques - NotesDocument63 pagesNon Traditional Machining Techniques - Notesjayabalaji_7759100% (1)
- Metrology MODULE 2Document11 pagesMetrology MODULE 2buntyNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFDocument80 pagesUnit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - V01Document8 pagesUnit IV - V01hainerajaramanNo ratings yet
- Nontraditional Machining and Thermal Cutting Processes - Chapter 26Document67 pagesNontraditional Machining and Thermal Cutting Processes - Chapter 26xharpreetxNo ratings yet
- CH 21Document45 pagesCH 21Anonymous p0mg44xNo ratings yet
- 15ME202 Manufacturing Technology: Unit - 5 Machine ToolsDocument68 pages15ME202 Manufacturing Technology: Unit - 5 Machine ToolsMouriya0% (1)
- Automatic Sukuma Wiki Cutting MachineDocument10 pagesAutomatic Sukuma Wiki Cutting MachineAmos Mwangi100% (1)
- Vibration Assisted EDMDocument13 pagesVibration Assisted EDMSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Edm Wire Cut LabDocument6 pagesEdm Wire Cut LabJieMan BahRom100% (1)
- Milling Machine LectureDocument46 pagesMilling Machine LectureAnnieMalik100% (1)
- Hot MachiningDocument144 pagesHot MachiningsureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Hot MachiningDocument5 pagesHot Machiningpavi32No ratings yet
- Hybrid Machining: Made By:-Hiragar Yashkumar Dalpatbhai Guidede By:-Alok SirDocument28 pagesHybrid Machining: Made By:-Hiragar Yashkumar Dalpatbhai Guidede By:-Alok SirYash Hiragar100% (1)
- Module IV-Milling MachineDocument26 pagesModule IV-Milling MachineNalluriRavindra100% (2)
- Manganese 12 14%Document3 pagesManganese 12 14%Sreedhar Rakesh VellankiNo ratings yet
- Compound Tool For Press Tool WasherDocument6 pagesCompound Tool For Press Tool WasherDhaneshNo ratings yet
- Milling: Prepared By: Dinbandhu Singh 1Document23 pagesMilling: Prepared By: Dinbandhu Singh 1Dino SinghNo ratings yet
- How To Choose Cutting DataDocument31 pagesHow To Choose Cutting DataJose JacksonNo ratings yet
- AMT-Forming (Compatibility Mode)Document15 pagesAMT-Forming (Compatibility Mode)Abdulhmeed MutalatNo ratings yet
- Dry Machining: Under The Guidance of Prof. S. R. PatilDocument19 pagesDry Machining: Under The Guidance of Prof. S. R. PatilChetan ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 - Shaper, Planer, Slotter, Grinding MachinesDocument70 pagesModule - 4 - Shaper, Planer, Slotter, Grinding MachinesIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- EDM Wire Cut ReportDocument12 pagesEDM Wire Cut ReportAidilNo ratings yet
- Workshop ManualDocument96 pagesWorkshop ManualDatta YallapuNo ratings yet
- JJ104 Workshop Technology Chapter6 Milling MachineDocument27 pagesJJ104 Workshop Technology Chapter6 Milling MachineAh Tiang100% (3)
- Plasma Arc MachiningDocument18 pagesPlasma Arc MachiningStephen WeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Heat Treatment of Iron and SteelsDocument24 pagesUnit 2: Heat Treatment of Iron and SteelsRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Hybrid Machining ProcessesDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Hybrid Machining ProcessesGAURAV KUMAR100% (1)
- MillingDocument54 pagesMillingVickyVenkataramanNo ratings yet
- General Purpose Machine Tools - SpalDocument33 pagesGeneral Purpose Machine Tools - SpalmecoolguysNo ratings yet
- Me6411 Manufacturing Technology-II Lab ManualDocument35 pagesMe6411 Manufacturing Technology-II Lab ManualdibyenindusNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet and Water Jet Machining Mp2Document50 pagesAbrasive Jet and Water Jet Machining Mp2Drew LadlowNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocument12 pagesAbrasive Jet MachiningTejas SuratiNo ratings yet
- Iv-Sem DTDMDocument14 pagesIv-Sem DTDMAryanNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Process Parameters in Wire-EDM of AL6063-T6 Alloy Using Taguchi DOEDocument12 pagesOptimization of Process Parameters in Wire-EDM of AL6063-T6 Alloy Using Taguchi DOEIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1AzizNo ratings yet
- 02 Dividing HeadDocument22 pages02 Dividing HeadMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Work HoldingDocument5 pagesWork HoldingKANDALA RAJASHEKAR REDDYNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 MMDocument74 pagesUnit-4 MMRama SamyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 04 Experiment Name: Study and Observation of Compression Test of A HelicalDocument5 pagesExperiment No: 04 Experiment Name: Study and Observation of Compression Test of A Helicalmd.Aktaruzzaman aktarNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes - II - Lecture Notes PDFDocument18 pagesManufacturing Processes - II - Lecture Notes PDFDharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- CARDBOARD Robotic Hydraulic ArmDocument12 pagesCARDBOARD Robotic Hydraulic ArmRAVI RanjanNo ratings yet
- ForgingDocument54 pagesForgingMaheshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Heat Generation in Metal Cutting OperationsDocument36 pagesLecture 5 Heat Generation in Metal Cutting Operationsnickokinyunyu11No ratings yet
- Automatic PVC Pipe Cutting MachineDocument9 pagesAutomatic PVC Pipe Cutting MachinemathstopperNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting Theory - ProblemDocument12 pagesMetal Cutting Theory - ProblemZohaib RafiqNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam PDFDocument96 pagesCad Cam PDFABHISHEKMISHRA100% (1)
- Sheet Metal WorkingDocument10 pagesSheet Metal WorkingBhupendhar HarshawardanNo ratings yet
- EDMDocument36 pagesEDMshifas 558No ratings yet
- Explosive WeldingDocument18 pagesExplosive WeldingShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Welding ProcessesDocument46 pagesWelding Processesbabitasharma100% (1)
- Electrical Discharge MachiningDocument16 pagesElectrical Discharge MachiningRizwan MrnNo ratings yet
- Die Sinking ReportDocument11 pagesDie Sinking Report15 thnNo ratings yet
- Non-Traditional MachiningDocument48 pagesNon-Traditional MachiningSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Report On Non-Traditional Machining ProcessDocument29 pagesReport On Non-Traditional Machining ProcessRahul JHANo ratings yet
- Non Traditional MachiningDocument71 pagesNon Traditional MachiningShamanth SHNo ratings yet
- Advanced Manufacturing TechniqueDocument80 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing TechniqueMURTHY RAJNo ratings yet
- 1st PDFDocument15 pages1st PDFKanchan MondalNo ratings yet
- Amp Notes Unit-1Document44 pagesAmp Notes Unit-1DJNo ratings yet
- The Three Main Forms of Energy Used in Non-Conventional Machining Processes Are As FollowsDocument3 pagesThe Three Main Forms of Energy Used in Non-Conventional Machining Processes Are As FollowsSeshi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical CellsAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility Plastic Material Chart For PA66, PEEK, PPS, PVDF and POMDocument9 pagesChemical Compatibility Plastic Material Chart For PA66, PEEK, PPS, PVDF and POMDeepak patilNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) PDFDocument4 pagesInspection and Test Plan (ITP) PDFSAIIN khodirNo ratings yet
- DSC OverviewDocument6 pagesDSC Overviewprabhat singhNo ratings yet
- Shaft Failure AnalaysisDocument36 pagesShaft Failure Analaysisbalaji100% (1)
- 12 - Nano & Biomaterials ReportDocument95 pages12 - Nano & Biomaterials ReportVenus Abigail Gutierrez100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Checklist As Per TEMADocument6 pagesHeat Exchanger Checklist As Per TEMAMONANo ratings yet
- Benchmarks PDFDocument1,761 pagesBenchmarks PDFSyed Imtiaz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Discussion Wash Water Systems - UOPDocument21 pagesDiscussion Wash Water Systems - UOPAvinaw100% (1)
- Din 8077-8078 & Iso 15874-2Document7 pagesDin 8077-8078 & Iso 15874-2Filip100% (4)
- MS 01 54Document6 pagesMS 01 54fagundds2No ratings yet
- Pile Foundations Solved ProblemsDocument27 pagesPile Foundations Solved ProblemsSujata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialDocument15 pagesBuilding Materialbirendra prasadNo ratings yet
- INSULWOOD - A Scalable High-Porosity Wood For SoundDocument13 pagesINSULWOOD - A Scalable High-Porosity Wood For Soundnahomy.castillo.aNo ratings yet
- IsoplatonDocument1 pageIsoplatonikahashimNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry by A. K. deDocument1 pageEnvironmental Chemistry by A. K. deRohan Ahmed28% (25)
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon CompoundDocument32 pagesWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon Compoundnur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- B.O.Q Wacher Room MelsiripuraDocument17 pagesB.O.Q Wacher Room MelsiripuraChinthakaNo ratings yet
- 03 120611e Kolliphor SLS Kolliphor SLS FineDocument6 pages03 120611e Kolliphor SLS Kolliphor SLS FineMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Development and Performance Characterization of An Advanced Solid Propellant Cast and Cure ProcessDocument6 pagesDevelopment and Performance Characterization of An Advanced Solid Propellant Cast and Cure Processeolson2No ratings yet
- 2024 RedoxDocument4 pages2024 Redoxjoshualiew06No ratings yet
- Submersible Wastewater Pumps With Single Vane Impeller 3" Discharge - 2" SolidsDocument2 pagesSubmersible Wastewater Pumps With Single Vane Impeller 3" Discharge - 2" SolidsAdemir JúniorNo ratings yet
- Numerical Investigation of Extended & Flushed Ultra-Large Capacity End-Plate ConnectionsDocument31 pagesNumerical Investigation of Extended & Flushed Ultra-Large Capacity End-Plate ConnectionsNora MostafaNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Biofuel ProductionDocument5 pagesThesis On Biofuel Productionaflpaftaofqtoa100% (2)
- Plastic Part and Mold Design Guide PlastDocument58 pagesPlastic Part and Mold Design Guide PlastTornadoAbdoNo ratings yet
- Molybond Dry FilmDocument2 pagesMolybond Dry FilmAlex LevinNo ratings yet
- Study of Interfacial Area in Rectification of Two-Component MixturesDocument7 pagesStudy of Interfacial Area in Rectification of Two-Component MixturesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Modified Mid Autumn 2020 ETE 413Document8 pagesModified Mid Autumn 2020 ETE 413Noba MurshedNo ratings yet
- Mechanical BookDocument93 pagesMechanical BookShiba Narayan SahuNo ratings yet
- Microchemical Tests ReagentsDocument4 pagesMicrochemical Tests ReagentsdlbookNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceFrom EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNo ratings yet
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationFrom EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignFrom EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo ratings yet
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)
- Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsFrom EverandWearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsEdward SazonovNo ratings yet