Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology Complete Drug Table
Uploaded by
ninja-2001Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Complete Drug Table
Uploaded by
ninja-2001Copyright:
Available Formats
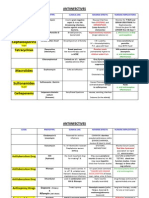
Drug
Name
Heparin
and
Low
Molecular
Weight
Heparins
Oral
Anti-
coagulant
Drug Classes
Fibrino-
lytics
Desai
Anticoagulants
Antiplatelet
Drugs
Aspirin
Clopidogrel/
Ticlopidine
Eptifibatide/
Abciximab/
Tirofiban
Acts as a catalyst and activates ATIII to rapidly inhibit
clotting factors IIa (thrombin) and Xa.
LMWH
Too small to bind/inactivate thrombin (IIa). But can
bind to ATIII and inactivate factor Xa.
Warfarin
Competitive inhibitor of Vit. K epoxide reductase, which
activates factors II, VII, IX, and X.
Streptokinase
Binds to plasminogen and converts it to active plasmin.
Systemic plasmin formation.
t-PA
Activates fibrin bound plasminogen. Theoretically acts
at site of clot formation.
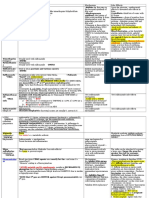
Drug Classes
Antiobesity
-lactams
Cell Wall
Crosses placenta teratogenic.
Dissolve clots after myocardial infarction,
deep vein thrombosis, massive pulmonary
emboli.
Bleeding, allergic reactions, hypotension,
fever.
Safest ad only hypocholesterolemic drug
recommended in children.
Carbapenems
Vancomycin
Given with statins leads to myopathy.
Given with statins leads to myopathy.
Flushing, dyspepsia, hepatotoxicity, and
avoid in pregnancy.
Not used in patients with
hypertriglyceridemia. Interfere absorption
of fat soluble vitamins. Bloating and
dyspepsia.
Reduce LDL with diet (10%) or drugs (20-
60%). Generally safe.
Major CV risk factor.
Prevent absorption of dietary fats by 30%.
Bloating, oily spotting, and fecal urgency.
Prevent absorption of Vit. A, D, E, K.
Allergic reactions and GI upset. Dont use
during pregnancy.
Nephrotoxicity. Dont use during
pregnancy.
Tetra-
cyclines
Maximal activity against rapidly dividing
bacteria. Treat infections caused by gram-
positive organisms.
See PCN. 4th gen. crosses BBB to treat
meningitis. 3rd gen. enters CSF.
See PCN.
See PCN. Strong activity against gram-
negative.
Active against gram-positive.
Topical use for gram-positive and certain
gram-negative.
Tetracyclines
Bind to 30S ribosomes to prevent aminoacyl-tRNA
attachment. Enter gram-positive by energy-dependent
process.
Rickettsial diseases: Rocky Mountain spotted
fever, typhus. Plague. Low dose: acne.
Bind to developing teeth and bone. Dont
use during pregnancy.
Macro-
lides
Inhibit synthesis of bacterial cell wall.. No -lactam
nucleus.
Hepatotoxicity and myopathy. Dont use
during pregnancy or breast feeding.
Erythromycin
Block peptide bond formation. Block translocation of
ribosome.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Streptococcal
upper respiratory tract infection. Legionella.
Dont use during pregnancy.
Amino-
glycosides
Bacitracin
Cleared unchanged by kidney avoid in
renal failure. Safety in pregnancy not
evaluated.
Prevent DVT or PE. Prevent
thromboembolism
Binds negatively charged bile acids. Liver must
synthesize new bile acids using cholesterol. Increase in
LDL receptors removes cholesterol from plasma.
Cephalosporins
Hemorrhage.
Heparin-induced
thrombocytopenia.
Streptomycin/
Gentamicin/
Neomycin
Cause misreading of mRNA so that wrong amino acid is
added. Bind to 16S rRNA prevent release of growing
protein.
Combine with penicillin for synergy.
Ineffective against anaerobic bacteria/fungi.
Toxicity is dose-related. Dont use during
pregnancy.
Chloram-
phenicols
Protein Synthesis
Increased bleeding.
Venous thrombosis and pulmonary
embolism. Anticoagulation during pregnancy
(doesnt cross placenta).
Prevent venous thromboembolism. Treat
venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism,
and unstable angina.
Resins
Monobactams
Chloramphenicol
Bacteriostatic. Prevent aminoacyl-tRNA binding to
mRNA codon. Block peptide bond formation.
Widely used in low income countries.
Effective against wide variety of organisms.
Rare but serious aplastic anemia. Dont use
during pregnancy.
Combination of both block 2 consecutive
steps: bactericidal.
Dont use during pregnancy.
Hypersensitivity, Stevens-Johnson
syndrome.
Urinary tract infection.
Carcinogenicity and mutagenicity. GI
effects. Hypersensitivity.
Inhibit DNA topoisomerase. Bind to enzyme-DNA
complex blocks DNA synthesis.
Second-line drug for tuberculosis.
GI effects, CNS agitations, and damage to
growing cartilage.
Bactericidal cationic detergents with both lipophilic and
lipophobic groups disrupt cell membranes.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter
baumannii.
Nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity.
Inhibition of mycobacterial DNA-dependent RNA
polymerase.
First-line drugs for tuberculosis.
Orange discoloration in secretions. GI
upset, hepatotoxicity, hypersensitivity,
rash.
Hepatotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy,
CNS effects.
Folate
Antagonists
Nitrofurans
Nucleic
Acid
Modification
During or after coronary artery procedures
like angioplasty.
Best agent to increase HDL, by reducing their
clearance in liver.
Penicillins (PCN)
Fluoro-
quinolones
Cytoplasmic
Membrane
Anti-
tuberculosis
Severe neutropenia, hemorrhage.
Increases lipoprotein lipase activity removes
chylomicrons and VLDL triglycerides from blood.
Orlistat
Antibacterial
Gastrointestinal bleeding.
Niacin
Prevents absorption of dietary cholesterol from
intestines.
Inhibit pancreatic and intestinal lipases. Inhibit
breakdown of dietary fat.
Inhibit synthesis of bacterial cell walls. Bacteriostatic.
Cephalosporins: only few enter CSF in sufficient
concentration.
Carbapenems: Highly resistant to beta-lactamases.
Monobactams: beta-lactam ring is alone.
Adverse Effects
Used in combination with aspirin for
synergistic activity.
Most effective for hyperlipidemia, except
when LDL receptor dysfunctional.
Least used. Treat severe
hypertriglyceridemia.
Ezetimibe
Other
Antibacterial
Therapeutic
Use
Prophylaxis
for
MI.
Post
MI.
Prophylaxis
for
TIA
or
post
TIA.
Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme that catalyzes
cholesterol biosynthesis.
Activates nuclear transcription factor receptor, PPAR-,
to cause metabolic changes.
Fibrates
Sawacki
Block GpIIb-IIIa receptor for fibrinogen on platelets and
prevent platelet aggregation.
Heparin
Statins
Glyco-
peptides
Mechanism
Irreversibly
inhibits
platelet
COX
and
prevents
formation
of
thromboxane
from
arachidonic
acid.
Contraindicated
in
pregnancy
and
childbirth.
Block
platelet
purinergic
P2Y
receptors
for
ADP
increase
cAMP.
Sulfamethoxazole
(sulfonamides)
Trimethoprim
Nitrofurantoin
Ciprofloxacin/
Norfloxacin
(2nd),
Levofloxacin
(3rd),
Gatifloxacin/
Moxifloxacin
(4th)
Colistin
(Polymyxin
E)
Polymyxin
B
Rifamycin
Rifampin
INH
Isoniazid
Structural analog of para-aminobenzoic acid
completely inhibits dihydropteroate synthase.
Reversible inhibition of dihydrofolate reductase.
At concentrations reached in urine, nitrofurantoin is
bactericidal. Reduce form is highly reactive.
Enter via passive diffusion, activated by bacterial
catalase, and attack multiple targets. Inhibition of
mycolic acid synthesis.
Cell Wall
Caspofungin
Cell Membrane
Polyenes
Amphotericin B
Rash, headache, dizziness, nausea.
Antifungal.
May induce or intensify subacute
cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
Binds to tubulin, interfering with microtubule function,
thus inhibiting mitosis.
Ringworm infections of skin and nails.
Diarrhea, GI sensitivity, CNS effects.
Pyrimidine
analog
Athletes foot, ringworm, candidiasis.
Nucleic
Division
High fever, renal toxicity, anemia.
Nucleic
Acid
Synth.
Most widely used.
Griseofulvin
Flucytosine
(1) Converted to fluorouracil that interacts with RNA
biosynthesis disrupt protein syntheis.
(2) Inhibition of fungal DNA synthesis.
The only available antimetabolite drug with
antifungal activity.
Hypersensitivity. Dont use in pregnancy.
Oseltamivir/
Zanamivir
Inhibit neuraminidases of both influenza A and B viruses
prevent release of new virions.
Avian flu. Effective and safe for prophylaxis
and after exposure to influenza A and B.
Oseltamivir: GI discomfort and nausea.
Zanamivir: avoid if patient has respiratory
disease/asthma.
Amantadine/
Rimantadine
Block the viral membrane matrix protein M2, important
for viral uncoating.
Influenza A only. Active against some strains
of avian flu.
Recent substantial increase in resistance.
RNA
Inhibitor
Interferon
Induction of host cell enzymes that inhibit viral RNA
translation, degradation of RNA, and stimulate immune
system.
Hepatic viral infections: hepatitis B and C.
Flu-like symptoms, bone marrow
suppression, neurotoxicity, autoimmune
disorders.
DNA
Polymerase
Inhibitor
Acyclovir
Competitive inhibition of dGTP for viral DNA. Bind viral
DNA template, causing termination. Trap DNA
polymerase.
HSV1, HSV2, and VZV. Most common to treat
genital herpes infections.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
CCR5
Inhibitor
Maraviroc
CCR5 antagonist to inhibit entry.
Restricted to adults with CCR5-tropic HIV-1.
None as of yet. Long term unknown.
Used in combination therapy to treat HIV-1.
Injection site reactions, peripheral
neuropathy.
HIV.
Anemia, neutropenia, hepatotoxicity,
cardiomyopathy, myopathy.
DNA
Neuramin-
idase
Inhibitors
Viral
Uncoating
Inhibitors
Antithymocyte
globulins
Binds to gp41 and prevents conformational changes
that occur when HIV fuses with host.
Analogs of native nucleosides/nucleotides. Incorporated
by viral reverse transcriptase terminate viral DNA
elongation.
Highly selective, noncompetitive inhibitors of HIV-1
reverse transcriptase.
Inhibit HIV-1 integrase activity, preventing viral DNA
integrating with cellular DNA.
Selective, reversible inhibitors of HIV aspartyl protease,
and block viral maturation. Synergetic with NRTIs and
NNRTIs.
Most widely used. Regression of lymphoid tissue by
interfering with cell cycle. Inhibit leukocyte function,
antibody formation, and inflammatory mediators.
Preferentially suppress cell-mediated immune reactions.
Binds to cyclophilin to inhibit calcineurin. NFAT remains
inactive and cannot enter to promote cytokine synthesis.
More potent and allows lower dose of glucocorticoid.
Binds to different immunophilin: FKBP-12.
Also binds FKBP-12 to form complex with mTOR
block progression of activated T cells.
Structurally related to folate. Inhibits dihydrofolate
reductase, thus stopping production of tetrahydrofolic
acid. Decrease biosynthesis of adenine, guanine,
thymidine, depressed DNA/RNA/protein synthesis
cell death.
Depletion of T cells impaired T-cell responses.
Humoral antibody mechanism remains active.
Muromonab-CD3
Murine mAbs for the depletion of human T cells.
Pheno-
thiazines
Chlorpromazine
DA, -adrenergic, muscarinic, and histamine
antagonists.
Butyro-
phenones
Haloperidol
Blocks D1 and D2 dopamine receptors only.
Clozapine
D1, D2, 5-HT2 antagonists.
Fusion
Inhibitor
Retroviruses
Antiviral Therapy
Immunosuppressive Drugs
NRTI
NNRTIs
Schizophrenia
and
Neuroleptics
Enfuvirtide
Zidovudine
(AZT)/
Lamivudine
Nevirapine/
Delavirdine
Integrase
Inhibitor
Raltegravir
Protease
Inhibitor
Saquinavir
Gluco-
corticoids
Prednisone/
Prednisolone
Cyclosporine
Cytokine
Inhibitors
Tacrolimus
Sirolimus
Cytotoxic
Drugs
Second
Generation
Methotrexate
Risperidone
Olanzapine
Mood Disorders and Mood Stabilizers
Central Nervous System Pharmacology
Hypersensitivity, hepatic effects.
Grisovin
Antibodies
and
Biologic
Agents
Richardson
Itraconazole/
Fluconazole
Bind to ergosterol in cell membrane, form channels that
allow K+ and Mg2+ to leak out.
Inhibit synthesis of ergosterol by blocking 14-
demethylase.
Inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis via inhibition of Squalene
epoxidase.
Aspergillus, Candida.
Terbinafine
Liu
Immunoregulatory
Agents
Azoles
Inhibit synthesis of (1,3)-D-Glucan, component of
fungal cell wall.
Allyamines
RNA Viruses
Antifungal
Sawacki cont.
Echino-
candins
MAO
inhibitors
Non-
selective
Reuptake
inhibitors
Irreversible. Non-selectively binds to both MOA-A and
MOA-B.
Moclobemide
Reversible. Competitively binds to MOA-A.
Imipramine
Amitriptyline
Inhibit both NA and serotonin reuptake: broad
spectrum. Also block muscarinic and 1 receptors.
Venlafaxine
New drug. No affinity for neurotransmitter receptors.
Paroxetine
Inhibit only serotonin uptake.
Rash can be severe, fatal hepatotoxicity.
Many drug interactions.
Resistance occurs in patients not taking
other fully active drugs.
HIV.
GI intolerance. Disturbances in glucose and
lipid metabolism. Buffalo hump.
Organ and tissue transplantation.
Inflammatory diseases. Prednisone: treat
autoimmune diseases.
Suppress pituitary-adrenal axis. Increase
risk of serious infections. Peptic ulcers.
Inhibit cytokines: Interleukins (ILs),
Interferons (IFNs), Tumor necrosis factors
(TNFs), Transforming growth factors (TGFs),
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs), and
chemokines.
Many AEs are dose-dependent.
Nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, greater risk
of infection, lymphoma.
Other AEs: hypertension, hyperkalemia,
tremor, hirsutism, glucose intolerance,
gum hyperplasia.
Doses much lower than those needed for
cancer chemotherapy.
Ulcers, low white blood count, nausea,
abdominal pain.
Acute renal transplant rejection.
Autoimmune disorders and renal, cardiac,
and hepatic transplant patients.
DA antagonists reduce positive, but not
negative, symptoms of schizophrenia.
Antihistamine, antiemetic.
Neuroleptic, antiemetic.
Halt schizophrenia. Effective on both positive
and negative symptoms.
Tranylcypromine
Fluvoxamine
Combination therapy for experienced adults
with highly resistant HIV-1 strains.
D2, 5-HT2 antagonists.
Fluoxetine
Serotonin
Reuptake
inhibitors
HIV-1 only. Lack affinity for HIV-2.
Increase levels of serotonin, NA, and DA
neurons in brain. Increase absorption of
dietary tyramine from gut into bloodstream.
Increase levels of serotonin and NA in brain
without changes in tyramine in blood.
Half life of 17 hours. Antidepressant.
Half life of 38 hours. Antidepressant.
Half life of 7 hours. Antidepressant. Treats
generalized anxiety disorder.
Half life of 3 days. Active metabolite extends
half life to over 7 days. Antidepressant. Treat
OCD.
Half life of 15 hours. Lack active metabolites.
Antidepressant. Treats GAD, OCD, and
anxiety disorders.
Half life of 24 hours. Lack active metabolites.
Antidepressant. Treats GAD, OCD, and
anxiety disorders.
Cytokine release syndrome: fatigue, fever,
chills, myalgia, headaches, nausea.
EPS, pituitary, CTZ, tardive dyskinesia,
postural hypotension, PSNS, memory,
sedation, itching, etc.
EPS, hyperprolactinemia, tardive
dyskinesia.
Little to no EPS. Bone marrow suppression
agranulocytosis and death. Weekly blood
tests required.
Little or no EPS, nor other side effects.
Very few side effects: weight gain,
dizziness, dry mouth.
Wine-cheese reactions: increased heart
rate, throbbing, and possible hypertensive
crisis.
No wine-cheese reaction.
Impaired memory, postural hypotension.
Nausea, somnolence, dry mouth.
Inhibits cytochrome P450, causing
potentially fatal drug interactions with
narcotics, -blockers, etc.
Less serious P450 related drug
interactions than fluoxetine.
Mood Disorders and Mood Stabilizers cont.
Desipramine
Noradren-
aline
Reuptake
inhibitors
Non-
selective
Release
enhancer
Maprotiline
Anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer. Treat
epilepsy and bipolar disorder.
Anxiolytic, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, muscle
relaxant. Status epilepticus or prolonged
seizures.
Hynotic. Treat: jet lag, shift work,
bereavement.
Short half life withdrawal. Does not
produce normal sleep.
Clonazepam
Ethosuximide
Increase GABA levels but also block Na+ and Ca2+
channels, and increase K+ conductance.
Increase GABA inhibition, down-regulate
benzodiazepine receptors. Up-regulate downstream NA,
5-HT, etc.
Ideal sleeping pill: short half-life, drug eliminated by
morning. Rapid onset, sleep induction within an hour or
less. Little effect on brain activity during sleep.
Block Na+ channels but also potentiate postsynaptic
effects of GABA.
Increase GABA levels.
Block Ca2+ channels.
Sedation,
ataxia.
Ataxia,
sedation,
dizziness,
headaches,
tremors.
Nausea,
vomiting,
gastric
pain,
heartburn.
Rare
hepatotoxicity.
Overdose
not
lethal,
but
does
potentiate
lethal
actions
of
other
compounds
like
alcohols
or
narcotics.
Tolerance.
Gabapentin
Increase GABA levels.
Lamotrigine
Block Na+ channels.
Phenobarbital
Opens Cl- channels.
Epilepsy and Anti-Convulsants
Anxiety
and
Anxiolytics
Diazepam
Triazolam
Stimulants and Sympathomimetics
Central Nervous System Pharmacology cont.
Caffeine
Cocaine
Analgesics
Main action is to block Na+ channels but other things as
well.
Increase GABA levels but also block Na+ and Ca2+
channels, and increase K+ conductance.
Blocks receptors for adenosine, an inhibitory
neurotransmitter. Inhibits phosphodiesterase, leading to
increased cAMP and activates NA, DA, and other
pathways where cAMP is a second messenger.
Blocks reuptake of NA and DA.
Amphetamine
Stimulates
the
release
and
blocks
reuptake
of
NA,
DA,
and
5-HT.
Inhibits
MAO.
Direct
agonist
at
NA
receptors.
Methylphenidate
Morphine
Codeine
Meperidine
Synthetic mu agonist. Good oral absorption.
Naloxone
Blocks all EOP receptors. Poor oral absorption.
Blocks all EOP receptors. Good oral absorption, but first
pass metabolism.
Naltrexone
Aspirin/
Ibuprofen
Rofecoxib
Acetaminophen
Stimulant Recreational Drugs
Nicotine
Caffeine
Cocaine
Ephedrine
Amphetamine
Methylphenidate
Depressant
Recreational
Drugs
Predominant constituent of opium. Agonist at mu
receptors. Oral administration is poorly absorbed.
Also constituent of opium. Less potent than morphine at
mu receptors. Good oral absorption.
Synthetic mu agonist. Less respiratory depression than
morphine. Moderate oral absorption.
Methadone
Celecoxib
Drug Abuse
Richardson cont.
Valproic acid
Selective
Inhibitors
of
COX
II
Antipyretic
Agent
Polydipsia, tremor, nausea, GI upset.
Antidepressant. Treat epilepsy.
Phenytoin
Endorphin
Antagonists
Non-
selective
Inhibitors
of
COX
I/II
Bipolar
disorder.
Anticonvulsant,
mood
stabilizer.
Treat
epilepsy
and
bipolar
disorder.
Anticonvulsant,
anxiolytic.
Increase GABA levels.
Carbamazepine
Synthetic
Endorphin
Agonists
Generally mild side effects.
Gabapentin
Valproic
acid
Natural
Endorphin
Agonists
Half life of 30 hours. Antidepressant.
Dry mouth, sedation, constipation,
increased appetite.
Clonazepam
Carbamazepine
Benzo-
diazepine
Anxiolytic
Benzo-
diazepine
Hypnotic
Cardiac arrhythmia, genotoxicity, breast
cancer.
Dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, dry mouth.
Increase both noradrenaline and serotonin release.
Blocks presynaptic auto-receptors that inhibit release of
NA and serotonin. Blocks several postsynaptic serotonin
receptors.
Reduce neuronal inositol second messenger system.
Block Na+ channels but also potentiate postsynaptic
effects of GABA.
Increase GABA levels.
Mirtazapine
Lithium
Mood
Stabilizing
Agents
Selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors.
Nortriptyline
Half life of 38 hours. Active metabolite of
imipramine. Antidepressant.
Half life of 36 hours. Antidepressant.
Half life of 55 hours. Active metabolite of
amitriptyline. Antidepressant. Also treats
nocturnal enuresis.
Opioids
Ethanol
Marijuana
Barbiturates
Benzodiazepines
Irreversibly inhibit COX I/II reduce formation of
prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
Selective COX II inhibitors reduces various mediators
of inflammatory process, but no effect on GI mucosal
defenses or platelet aggregation.
Weak inhibition of PG formation in peripheral tissues.
Lacks anti-inflammatory actions.
Prototype nicotinic agonist.
Blocks receptors for adenosine, an inhibitory
neurotransmitter. Inhibits phosphodiesterase, leading to
increased cAMP and activates NA, DA, and other
pathways where cAMP is a second messenger.
Anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer. Treat
epilepsy and bipolar disorder.
Anticonvulsant, anxiolytic.
Anticonvulsant.
Antidepressant. Anticonvulsant. Treat
epilepsy.
Anticonvulsant. Treat epilepsy and bipolar
disorder.
Most widely used anticonvulsant worldwide.
Anticonvulsant. Treat epilepsy.
Anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer. Treat
epilepsy and bipolar disorder.
Half life of 5 hours.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic.
Half life of 40 minutes.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic. Local
anesthetic.
Half life of 20 hours.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic. Treat
narcolepsy and increase impulse control.
Half life of 2 hours.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic. Treat
narcolepsy, ADHD, and increase impulse
control.
Potent analgesic.
Analgesic. Good cough suppressant.
Fast acting analgesic.
Good analgesic profile, chronic pain
syndrome. Used in addiction treatment
programs.
Used in opioid overdose.
Used in addiction treatment for
narcotics/opoids. Reduce alcohol cravings.
Analgesic. Relieve arthritis, fever. Reset
thermoregulatory mechanism in
hypothalamus.
Arthritis, acute pain, menstrual symptoms.
Arthritis, acute pain, menstrual symptoms.
Withdrawn from market.
Analgesic and anti-pyretic actions. Less GI
distress than aspirin.
Stimulant.
Half life of 5 hours.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic.
Half life of 40 minutes.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic. Local
anesthetic.
Stimulant, appetite suppressant,
-adrenergic agonist.
concentration aid.
Half life of 20 hours.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic. Treat
narcolepsy and increase impulse control.
Stimulates the release and blocks reuptake of NA, DA,
Half life of 2 hours.
and 5-HT. Inhibits MAO. Direct agonist at NA receptors.
Stimulant/sympathomimetic. Treat
narcolepsy, ADHD, and increase impulse
control.
Refer to section Endorphin Agonists.
Refer to section Endorphin Agonists.
Suppresses neuronal excitability in concentration-
Moderate ethanol consumption has health
dependent manner.
benefits, perhaps due to antioxidant action.
Active ingredient: THC. Cannabinoid receptors found in cortex, hippocampus, and other areas of brain.
Stimulation decreases formation of cAMP reduce activity of NA, DA, glutamate and other pathways.
Refer to phenobarbital.
Refer to phenobarbital.
Refer to section Anxiety and Anxiolytics.
Refer to section Anxiety and Anxiolytics.
Blocks reuptake of NA and DA.
Dizziness, ataxia, diplopia.
Dizziness, ataxia, diplopia.
Sedation, ataxia.
GI upset, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness.
Ataxia, sedation, dizziness, headaches,
tremors.
Sedation, dizziness, headache, nausea,
rash.
Sedation, hypnosis, drug interactions.
Overdose is fatal.
Nystagmus, ataxia, sedation, gingival
hyperplasia, hirsutism.
Nausea, vomiting, gastric pain, heartburn.
Rare hepatotoxicity.
High doses activate DA reward pathways
abuse potential. Insomnia. Appetite and
growth suppression by NA. Drug holidays
when therapeutic action not needed.
Tolerance, addiction.
Tolerance, addiction. Contraindicated in
those with CV problems.
Nervousness, insomnia, drowsiness.
Tolerance, addiction, withdrawal.
Constipation.
Itching, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, dry
mouth.
May induce psychosis in the elderly.
Nausea, vomiting, sedation.
Itching, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, dry
mouth.
Nausea, nervousness, restlessness,
trembling, vomiting
Aspirin: overdose produces lethargy,
hyperventilation (fatal acidosis in
children). Inhibiting COX I: GI
irritation/ulceration, reduced coagulation.
Sulfonamide moiety may cause allergic
reactions. Teratogenic.
Reduces PGI2 but not TBX-A2 increased
platelet stickiness and reduced
vasodilation.
In many OTC products easily overdose
liver damage.
Addiction. Withdrawal.
High doses activate DA reward pathways
abuse potential. Insomnia. Appetite and
growth suppression by NA. Drug holidays
when therapeutic action not needed.
Tolerance, addiction.
Tachycardia, flushing, nausea.
Tolerance, addiction. Contraindicated in
those with CV problems.
Nervousness, insomnia, drowsiness.
Refer to section Endorphin Agonists.
N/A
N/A
Refer to phenobarbital.
Refer to section Anxiety and Anxiolytics.
Hallucinogenic Recreational Drugs
Drug Abuse cont.
CNS Pharmacology cont.
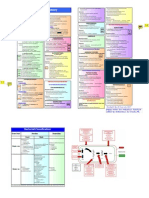
Endocrine
Richardson cont.
Oxytocics
Tocolytics
Oxytocics and Tocolytics
Gonadal Hormones, OCP, and Inhibitors of Gonodal Function
TMA, MDA, MDMA
N/A
Phencyclidine
Dose dependent. Unsteady gait, slurred
speech, bloodshot eyes, etc.
Selective
Estrogen
Receptor
Modulator
Clomiphene
Partial agonist blocking estrogen-mediated inhibition of
FSH/LH release from anterior pituitary.
Promote increased FSH/LH, thus promoting
ovulation and fertility.
Hot flashes, abdominal discomfort, visual
blurring.
Dopamine
D2
Agonists
Bromocriptine/
Cabergoline
Bind to D2 receptors on pituitary lactotrophs and
decrease production and release of PRL. Mimics the role
of dopamine.
Hyperprolactinemia,
galactorrhea
amenorrhea,
loss
of
menstrual
cycle,
infertile
males,
Parkinsonism,
acromegaly.
Nausea, orthostatic hypotension,
headaches, vomiting.
Synthetic
Vasopressin
replace-
ment
DDAVP
Selective V2 agonist and 4000x more potent that AVP
and longer acting. No V1 mediated adverse effects of
vasoconstriction or hepatic glycogenolysis.
Neurogenic diabetes insipidus. Hemophilia A.
Von Willebrands disease.
Headaches, facial flushing, nausea,
hyponatremia, seizures.
At term: induction of labor. Preterm:
augment incomplete abortion. Postpartum:
control hemorrhage, milk letdown.
H2O intoxication, hyponatremia.
Postpartum hemorrhage and uterine atony.
Nausea, vomiting, vasoconstriction, angina.
Ergot
Alkaloids
Oxytocin
Ergonovine/
Ergometrine
Released from posterior pituitary dilates cervix,
contracts myometrium and myoepithelial cells in
breasts. Positive feedback.
Stimulates both pregnant and non-pregnant uterus by
activating 1 receptors in myometrium.
Prosta-
glandins
PGF2/PGE2
Ripening and dilation of cervix. Increase uterine
contractions.
Steroid
Mifepristone
(RU486)
Potent progesterone antagonist, glucocorticoid
antagonist.
Terbutaline
Force Ca2+ out of myometrial cells.
Nifedipine
Inhibits Ca2+ influx via L-type channels in non-vascular
muscle cells.
2
Selective
Agonist
Ca2+
Channel
Blocker
NSAIDs
Other
Contra-
ceptives
Indomethacin
Atosiban
Leuprolide
acetate/
Abarelix
Progesterone
Mini
pill
Norplant
Diethylstilbestrol
Postcoital
Pill
and
Aborti-
faceint
Selective
Estrogen
Receptor
Modulators
Progest-
erone
Antagonist
Androgens
Antiandrogens
Methotrexate
Fulvestrant
Tamoxifen
Clomiphene
Raloxifene
Decrease production of prostaglandins by COX
inhibition.
Inhibitor of hormones oxytocin and vasopressin.
Desensitizes and down-regulates Gn-RH receptors on
pituitary.
Uterus: endometrial secretory mucus during luteal
phase. Cervix: thick, viscous mucous plug. Negative
nitrogen balance and increased basal body temperature.
Contains only low-progesterone and no estrogen. See
above.
Parenteral progesterone. Single injection in special
implant containing progestin.
High dose of EE2 for 3-5 days along with an anti-emetic.
Cytotoxic agent for placenta. Stimulate uteral
contractions, leading to expulsion.
Steroid. Pure competitive antagonist, a derivative of
estradiol.
Non-steroidal. Partial agonist, blocks estrogen receptors
in breast.
Non-steroidal. Blocks estrogen-induced inhibition of
FSH/LH release ovulation.
Non-steroidal. Mimics estrogen effect on bone and
decreases parathormone induced bone resorption.
Mifepristone
(RU486)
Steroid. Competitive antagonist of progesterone
terminate pregnancy during first 53 days.
17-testosterone
Stimulate and control androgenic development.
Stanozol
Selective anabolic steroid with less androgenic activity.
Leuprolide
acetate
Synthesis inhibitor. Desensitize receptors to reduce
FSH/LH release.
Synthesis inhibitor. Steroid that inhibits conversion of
testosterone to DHT by inhibiting 5 reductase.
Antiandrogen. Non-steroid competes with DHT for
androgen receptors, blocking testosterone action.
Antiandrogen. Steroid that is most potent blocker of
DHT receptor.
Synthesis inhibitor: steroid that inhibits 17
hydroxylase. Antiandrogen: blocks DHT receptors in
hair follicles.
Finasteride
Flutamide
Cyproterone
Spironolactone
Reduce
Gastric
Acid
Secretion
Tolerance develops to hallucinogenic
action. Cross tolerance develops to drugs
sharing same mechanism of action, but not
across mechanisms.
Produces altered body image detachment
of mind from body. Induces state very
similar to psychosis. Angel dust.
Steroid
Hormone
Antiulcer Agents
Peyote
cactus.
Magic
mushrooms.
Various plants, jimson weed, locoweed.
Gn-RH
Antagonists
Androgens and Antiandrogens
LSD.
Increase
neural
activity
in
NA,
DA,
and
5-HT
pathways.
Dissociative anesthetic agent. Agonist at the pcp
receptor, which modulates the NMDA glutamate
receptor.
Ideal Drug
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Lysergic
acid
diethylamide
Mescaline
Psilocybine
Amphetamine
analogs
Atropine/
Scopolamine/
Benztropine
Reduce activity in ACh pathways.
Nona-
peptide
Gopal
Uterine contractility, migraines, peripheral
vasoconstriction. Morning glory seeds.
Ergotamines
Induction of labor. Combine with
Mifepristone to terminate pregnancy in first
trimester.
Cushing syndrome. Abortion during first 2
months.
Selective to uterus, orally effective, less toxic
on fetus.
Nausea, vomiting, uterine pain.
No long-term studies as of yet.
Tachycardia, hypotension, pulmonary
edema, hyperglycemia.
Delay premature labor.
Headache, constipation, tachycardia,
hypotension.
Dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia.
GI irritation, nephritic syndromes.
Premature labor.
Still under review.
Prostatic cancer. Endometriosis.
Flushing, headache, hot flashes.
Leuprolide: initial flare
Given as combined oral contraceptive pill or
progesterone-only pill.
For patients suffering estrogen side effects.
Implantation under skin can last up to 5
years.
Pregnancy termination.
Early management of estrogen-dependent
breast carcinoma (when Tamoxifen fails).
Early stages of estrogen-dependent breast
carcinoma.
Secondary amenorrhea, anovulatory
menstrual cycles.
Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
Decreased HDL, increased LDL,
thrombophlebitis. Acne, hirsutism, weight
gain.
Irregular menstrual bleeding, spotting,
headache.
Menstrual irregularities may lead to
anxiety.
Nausea, vomiting.
Nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue. Highly
teratogenic.
None listed.
Endometrial carcinoma. Enhance deep
vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism.
Hot flushes, alopecia, headaches, multiple
pregnancy, ovarian hyperstimulation.
Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary
embolism.
Cushings syndrome, endometriosis.
No long-term studies as of yet.
Hypogonadism, osteoporosis, trauma, post
operative convalescence, intractable anemia.
Acne, prostatic hyperplasia and
hypertrophy. Behavioral changes,
cholestatic jaundice.
Prostate cancer.
Initial flare.
Prostate cancer, hirsutism.
Impotence, gynecomastia. Teratogenic.
Prostate cancer. Flutamide combined with
leuprolide gives no initial flare.
Hirsutism. Decreased libido and aggression
in male sex offenders.
Hepatotoxic.
Gynecomastia.
Hepatotoxic.
Hirsutism, primary hyperaldosteronism.
Antihypertensive, K sparing diuretic.
Gynecomastia.
H2
Receptor
Blocker
Cimetidine
Inhibits 90% of acid secretion.
Gastric/duodenal ulcers. Zollinger-Ellison
syndrome.
Confusion, somnolence, headache,
dizziness. Skin rashes, myalgia, itching.
Gynecomastia, impotence. Inhibits
CYP450.
Proton
Pump
Inhibitor
Omeprazole
Irreversible inhibitor of H+ K+ ATPase proton pump
block 98% of acid secretion.
Ulceration. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. No
need to combine H2 blocker with PPI unless
in ZES.
Headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain,
nausea, dizziness.
NaHCO3
Al(OH)2
Ca(CO)3
Mg(OH)2
Acid neutralization.
Immediate pain relief, but short duration of
effect rebound gastric acid secretion.
Sucralfate
Stimulates PGE1 production, adsorbs pepsin, gives a
protective gel coating.
Ulcers.
Misoprostol
Mimics PGE1, enhances production of mucus and HCO3.
Bismuth chelate
Increases mucous and prostaglandin production.
Neutralize
Acids
Enhance
Mucosal
Defense
Very effective in drug-induced peptic ulcers
by NSAIDs/corticosteroids.
Eradicates H. pylori.
Systemic alkalosis, fluid retention.
Constipation, hypophosphatemia.
Hypercalcemia, nephrolithiasis.
Diarrhea, hypermagnesemia.
Constipation, dry mouth. Decreases
bioavailability of other drugs.
Diarrhea. Contraindicated in pregnancy.
Prokinetic Agents
Antiemetics
Domperidone
Non-
antiemetics
Antiemetics
Anti-
migraine
Antiemetics and Antimigraine
Dopamine
Antagonists
5-HT3
Selective
Antagonists
Cannab-
inoids
Cortico-
steroids
Substance
P
Antagonists
Triptans
Ultra
Rapid
Acting
Interm.
Acting
Dimenhydrinate
Long Acting
Block inhibitory presynaptic D2 receptor increase
ACh.
Activates presynaptic 5-HT4 receptors increase ACh.
Increases cholinergic transmission in gastroduodenal
region.
Activate neural and smooth muscle motilin receptors.
Increase ACh release.
Block H1 receptors and prevent peripheral stimulation
of emetic center.
Scopolamine
Block peripheral stimulation of emetic center.
Lorazepam/
Alprazolam
Prevent central cortical induced vomiting. Enhance
effectiveness of antiemetic regimens.
Non-selective DA antagonist. Act at CTZ by inhibitng
dopaminergic transmission and decrease vomiting by
inhibitng peripheral vagal and sympathetic afferents.
Phenothiazines
Metoclopramide/
Domperidone
Ondansetron
(1st)
Palonesetron
(2nd)
Tetrahydro-
cannabinol
Dexamethasone
Increase gastric emptying. Relieve gastric
stasis. Prevent reflux esophagus, heart burn,
and regurgitation of gastric contents.
Decrease nausea, vomiting. Aid in
overcoming postvagotomy gastroparesis or
prior to small bowel intubation.
Motion sickness and inner dysfunctions
(Meniers disease and Labrynthitis).
Motion sickness.
Anxiety, anticipatory emesis (chemotherapy).
Not used anymore due to side effects.
D2 selective antagonists. Selective blockade of D2 CTZ
receptors.
Anticipatory emesis (chemotherapy).
Inhibit serotonin mediated responses by blocking 5-HT3
receptors involved in vomiting reflex. Most effective.
Not available.
Aprepitant
Control emesis when all other agents fail.
Feelings of well-being. Anticipatory emesis.
Control emesis in motion sickness from
mountaineering. Anticipatory emesis.
Combine with Dexamethasone and
Palonesetron for late cancer (CINV).
Selectively constrict collateral blood vessels.
Headaches, migraines.
Lispro
Analog of human insulin: B28Proline and B29Lysine are
switched to B28Lys-B29Pro.
Aspart
Analog of human insulin: B28Proline is replaced with
B28Aspartate.
Dissolve rapidly at site of administration and
enters 2x faster than regular very short
action. Immediate use before meals only.
Increasing dose only increases intensity, not
duration.
Used intravenously during emergencies.
Administered subcutaneously in ordinary
maintenance regimens.
Regular
crystalline
insulin
NPH
Glargine
Detemir
Sulfonyl-
ureas
Glyburide
Miglitinides
Repaglinide
Biguanides
Crystalline zinc insulin. Rapid onset and short action.
Used alone or mixed with intermediate- or long-acting
preparations.
Neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin. Protamine: protein
isolated from rainbow trout sperm in a zinc
suspension.
Used to provide basal insulin level. Injected morning
only, or morning and evening to provide maintenance
for 12-24 hours. Withdrawn from market.
Two additional arginine residues in B-chain and one
glycine in place of A21Aspargine.
Deletion of B30 threonine and the attachment of a 14-
carbon fatty acid chain to B29Lysine.
Inhibit K+ATP channels in -cell membrane. May
increase number of functional insulin receptors in
peripheral tissues or increase insulin sensitivity.
Crosses BBB. Hyperprolactinemia,
iatrogenic Parkinsonism.
Does not cross BBB. Hyperprolactinemia.
Torsades de pointes (long QT syndrome).
Watery diarrhea (although useful in
constipation).
Drowsiness, sedation, blurred vision, dry
mouth.
Dry mouth, drowsiness, blurred vision,
tachycardia.
Drowsiness.
Acute dystonic reaction, orthostatic
hypotension, extrapyramidal side effects,
blood dyscrasias.
Metoclopramide precipitates
extrapyramidal AEs (domperidone does
not).
None listed.
Sumatriptan/
Naratriptan
Lente
Subcutaneous injection, not suitable for
intravenous use. NPH preferred when mixing
with regular insulin, because lente can retard
onset of regular insulin.
Hallucination,
bulimia.
Osteoporosis,
Cushingoid
features,
hyperglycemia,
peptic
ulcers,
etc.
Not
available.
Mild
pain,
stinging/burning
sensation,
feeling
of
heaviness
or
pressure
in
the
head.
Contraindicated:
angina
and
peripheral
vascular
disease.
Hypoglycemia: tachycardia, confusion,
vertigo, diaphoresis, possible brain
damage. Treatment: prompt
administration of glucose or glucagon.
Insulin-induced immunologic
complication: formation of insulin
antibodies.
Subcutanous injection once or twice daily.
Basal insulin level may be supplemented
with injection of lispro or regular during the
day to meet required carbohydrate intake.
Hypoglycemic drug.
Drug-induced hypoglycemia, skin rash,
allergy.
Stimulate release of endogenous insulin by inhibiting
K+ATP channels in -cell membrane.
Hypoglycemic drug. Unlike sulfonylureas,
repaglinide has rapid onset and short action.
Taken before meals to control postprandial
glucose concentrations.
No effect on patients lacking -cells.
Metformin
Increase number/affinity of insulin receptors in
peripheral tissues. Reduce hepatic output. Stimulate
glucose uptake and glycolysis in skeletal muscle and
adipose tissue. Doesnt stimulate insulin release from -
cells.
First-line drug for T2DM, especially in
patients with obesity and/or hyperlipidemia.
Used alone or combine with sulfonylurea.
GI distress: nausea, diarrhea. Lactic
acidosis (rare) in patients with renal/liver
disease, alcoholism, etc.
Thiazolidin
ediones
Rosiglitazone/
Pioglitazone
Activate PPAR- in adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and
liver. Regulates transcription of genes encoding proteins
involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Increase
GLUT4 expression.
Used alone or combined with other
antidiabetic drugs.
Edema, mile anemia. Both increase risk of
heart failure. Rosig: increase risk of MI and
death.
-
glucosidase
Inhibitor
Acarbose
Inhibits -glucosidase, slows absorption of
carbohydrates, reduces postprandial hyperglycemia.
Used alone or combined with other
antidiabetic drugs. No effect on fasting blood
sugar.
Flatulence, diarrhea, cramping.
Synthetic
Levothyroxine
(T4)
Preferred. Long half-life (7 days), oral bioavailability
80%. Orally once a day.
Replace-
ment
Therapy
Liothyronine (T3)
Faster-acting, higher oral bioavailability (95%), but
shorter half-life (1 day). More expensive.
Treatment for all forms of hypothyroidism is
replacement therapy with either T4 or T3.
Excessive doses similar to effects of
hyperthyroidism. Contraindications with
oral anticoagulants, antidiabetic drugs,
female hormones.
Thioureas
Propylthiouracil/
Methimazole
Inhibit peroxidase-catalyzed steps (iodination &
coupling).
PTU: also inhibits conversion of T4 to T3 in peripheral
tissues.
Graves disease, to induce remission or
control symptoms prior to surgery or RAI
treatment. Requires 3-4 weeks for full effect.
Skin rash (common), severe immune
reactions (rare). Contraindicated with
pregnancy crosses placenta.
Iodide Salts
Lugols solution
Inhibit iodination of tyrosine & thyroid hormone
release. Decrease size and vascularity of hyperplastic
thyroid gland.
Short-term basis to treat thyroid storm.
Prepare for thyroid surgery. Inhibit release of
thyroid hormones following RAI therapy.
Skin rashes. Other hypersensitivity
reactions.
Iodinated
Radiocon-
trast
Media
Ipodate
Suppress conversion of T4 to T3 in liver, kidney, and
other peripheral tissues.
Very useful in rapidly reducing T3
concentrations in thyrotoxicosis.
Uncommon.
RAI
Therapy
Radioactive
iodine
(131I)
Ablation of thyroid tissue. RAI taken up and
concentrated in thyroid gland.
Most popular method. Emit particles that
destroy thyroid tissue without endangering
other tissues.
Should not be used in pregnant or nursing
women.
Parathyroid
Hormone
Acts on membrane G-protein coupled receptor to
increase cAMP in bone and renal tube. Net effect:
increase circulating Ca2+, decrease PO4-.
Substitute for PTH replacement.
Primary/secondary parahyperthyroidism.
Vitamin D3
Functions as a true hormone. Net effect: increase
circulating Ca2+ and PO4-. Bone formation may be
increased.
Osteomalacia (Rickets).
Overdose: hypercalcemia, toxicity.
Osteo-
porosis
Insulin
Preparations
Hyperthyroidism
Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Agents
Hypothy-
roidism
Four (roughly) Major Classes of
Oral Antidiabetic Agents
Insulin and Antidiabetic Drugs
Rapid
Acting
Wu
Cisapride
Erythromycin
Anti-
histamine
Anti-
cholinergic
Benzo-
diazepines
Drugs
Affecting
Bone
Drugs
in
Bone
Mineral
Homeostasis
Metoclopramide
Raloxifene/
Estrogen
Inhibition of PTH-stimulated bone resorption. Inhibit
secretion of IL-6 by osteoblasts decrease osteoclast
differentiation and activation.
Alendronate
Inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone-resorption. Used in
place or in addition to estrogen.
Calcitonin
Secreted by C (clear) cells of thyroid in response to
increased plasma Ca2+ levels. Inhibits activity of
osteoclasts.
Bisphosphonates
Inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone-resorption.
Plicamycin
Cytotoxic antibiotic as potent osteoclast inhibitor.
Abnormal
Mineralization
Drugs Affecting Bone cont.
Wu
cont.
Osteo-
porosis
cont.
Pagets
Disease
Prevent or delay bone loss in
postmenopausal women.
Postmenopausal or glucocorticoid-induced
osteoporosis. Prevent bone loss and decrease
fractures.
Decreases bone resorption without
disturbing mineralization. Protect during
periods of Ca2+ loss: pregnancy, lactation.
Treat Pagets disease of bone, hypercalcemia,
osteolytic bone lesions in cancer patients.
May decrease tumor burden on bone, bone
pain, and risk of fractures.
Hypercalcemia and bone resorption in
Pagets disease.
Hot flashes, leg cramps. Possible blood
clots.
Esophageal ulceration. Skin rash.
None listed.
Esophageal ulceration (oral
administration). Mild and transient
nausea, dyspepsia, constipation, diarrhea.
Hemorrhage, hepatic and renal damage,
and frequent nausea/vomiting.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pharmacology Chart 3Document2 pagesPharmacology Chart 3Omar ClorNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BDocument30 pagesDrug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BCess Lagera Ybanez0% (1)
- Pharmacology ChartDocument6 pagesPharmacology ChartPaula67% (3)
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument19 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsAl-nazer Azer Al100% (5)
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (16)
- MBBS Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesMBBS Pharmacology PDFAdeeb Aiman Rosli100% (6)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Pharma MnemonicsDocument12 pagesPharma MnemonicsUsman Ali Akbar100% (1)
- Pharmacology Charts PDFDocument88 pagesPharmacology Charts PDFMohamad Samir90% (10)
- The Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDocument16 pagesThe Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDianne Chua100% (7)
- Pharmacology List of DrugsDocument66 pagesPharmacology List of DrugsSohail Adnan100% (2)
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsOccamsRazor100% (1)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Pharm Drug ListDocument17 pagesPharm Drug Listanon_523534678No ratings yet
- Mnemonics For Antibiotics-2Document10 pagesMnemonics For Antibiotics-2totallyfakeusernameNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Quick ReviewDocument5 pagesAntibiotics Quick Reviewpranjl100% (5)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument32 pagesPharmacology Summaryminikatiting95% (22)
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocument3 pagesCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Key Drugs Mnemonics Study Tips 1 PDFDocument16 pagesKey Drugs Mnemonics Study Tips 1 PDFChrissy Layug100% (4)
- Drugs Cards 208Document11 pagesDrugs Cards 208SOOOS94100% (3)
- Pharm MnemonicsDocument33 pagesPharm MnemonicsThomson George75% (4)
- Drug Charts: Pharmacology OverviewDocument39 pagesDrug Charts: Pharmacology OverviewAsim Ishaq100% (5)
- Pharmacy MnenomicsDocument12 pagesPharmacy MnenomicsNaresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- Drugs PharmacologyDocument75 pagesDrugs Pharmacologyapi-25987870100% (16)
- Urinary Tract and Bladder DrugsDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract and Bladder Drugslhayes1234100% (2)
- Antibiotics Chart 2Document10 pagesAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNo ratings yet
- Drug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherDocument4 pagesDrug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- AB ClassesDocument4 pagesAB Classesrayooona88100% (2)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M IhtishamDocument32 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M Ihtishammuhammad ihtisham ul hassan100% (1)
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocument21 pagesRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics.Document16 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics.Shan Shani67% (3)
- Pharmacology - Antibiotics Flash CardsDocument20 pagesPharmacology - Antibiotics Flash CardsJamil100% (2)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16No ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside Toxicity and NephrotoxicityDocument47 pagesAminoglycoside Toxicity and NephrotoxicityAimee Gutierrez91% (55)
- Antibiotics Summary - Flattened PDFDocument3 pagesAntibiotics Summary - Flattened PDFmicheal1960100% (6)
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsCyrus100% (1)
- Drug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut HereDocument60 pagesDrug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut Heredlneisha61100% (13)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)From EverandNAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Top 300 Drugs Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- MULTISTATE PHARMACY JURISPRUDENCE EXAMINATION (MPJE): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMULTISTATE PHARMACY JURISPRUDENCE EXAMINATION (MPJE): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamFrom EverandPharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drugs I N Der Mato Lo GyDocument85 pagesDrugs I N Der Mato Lo GySilviuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Fast and Dirty Board ReviewDocument7 pagesPharmacology: Fast and Dirty Board ReviewRochelleth7278No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: PGI: Mikhail Jude L. OpayDocument45 pagesTuberculosis: PGI: Mikhail Jude L. OpayMikkoOpayNo ratings yet
- Anti-Tuberculosis DrugsDocument12 pagesAnti-Tuberculosis DrugsAkashNo ratings yet
- Newer Antibiotics: Guide: DR Saroja A ODocument51 pagesNewer Antibiotics: Guide: DR Saroja A OparahulNo ratings yet
- Antimycobacterial Drugs LectureDocument7 pagesAntimycobacterial Drugs Lectureنشط عقلكNo ratings yet
- MS Drug StudyDocument16 pagesMS Drug StudyNathaniel VelascoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document39 pagesUnit - 3ujjwalNo ratings yet
- Cology PageDocument4 pagesCology PageAbdulhakim ZekeriyaNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic Drugs BY Kenneth Chisamanga PharmacistDocument41 pagesCytotoxic Drugs BY Kenneth Chisamanga PharmacistMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument33 pagesProtein Synthesis InhibitorssaifNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in PeadiatricsDocument14 pagesAntibiotics in PeadiatricsrisanaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: by Dr. Jihad AnadDocument89 pagesAntibiotics: by Dr. Jihad AnadJihad AnadNo ratings yet
- Behavioral QuizDocument56 pagesBehavioral Quizninja-2001No ratings yet
- Behavioral QuizDocument56 pagesBehavioral Quizninja-2001No ratings yet
- 07 Peroxi ERDocument32 pages07 Peroxi ERninja-2001No ratings yet
- 06 NucleusDocument26 pages06 Nucleusninja-2001No ratings yet
- Peroxisomes ERDocument4 pagesPeroxisomes ERninja-2001No ratings yet
- 04 Ph-IntroDocument31 pages04 Ph-IntroAnonymous t5TDwdNo ratings yet
- Cy To SkeletonDocument6 pagesCy To Skeletonninja-2001No ratings yet
- Quiz Behavioral ScienceDocument91 pagesQuiz Behavioral ScienceMedShare92% (12)
- Golgi DiseasesDocument1 pageGolgi Diseasesninja-2001No ratings yet
- 07 MitoDocument36 pages07 Mitoninja-2001No ratings yet
- Catalase Uses The H2O2 H2O2 + R'H2 - R' + 2H2ODocument2 pagesCatalase Uses The H2O2 H2O2 + R'H2 - R' + 2H2Oninja-2001No ratings yet
- 08 Vessicular TraffDocument84 pages08 Vessicular Traffninja-2001No ratings yet
- 03 Med BiochemistryDocument81 pages03 Med Biochemistryninja-2001No ratings yet
- 01 Med BiochemistryDocument51 pages01 Med Biochemistryninja-2001No ratings yet
- Istology: Lymphatic SystemDocument48 pagesIstology: Lymphatic Systemninja-2001No ratings yet
- 01 Med BiochemistryDocument51 pages01 Med Biochemistryninja-2001No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System-IIDocument39 pagesCardiovascular System-IIninja-2001No ratings yet
- 02 Med BiochemistryDocument41 pages02 Med Biochemistryninja-2001No ratings yet
- Week 7 PPTDocument90 pagesWeek 7 PPTKevinMathewNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises For EpidemiologyDocument8 pagesPractice Exercises For Epidemiologyninja-2001100% (2)
- Usmle Study Tip 4Document10 pagesUsmle Study Tip 4ninja-2001No ratings yet
- Quick Immunology ReviewDocument9 pagesQuick Immunology Reviewninja-2001No ratings yet
- Immunology High Yield For STEP 1Document13 pagesImmunology High Yield For STEP 1Lucykesh100% (6)
- Inflammation Phagocytosis Chemical MediatorsDocument53 pagesInflammation Phagocytosis Chemical Mediatorsninja-2001No ratings yet
- Behavioral Science Practice QuestionsDocument52 pagesBehavioral Science Practice QuestionsUsman KhanNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Infections-MicroDocument1 pageOpportunistic Infections-Microninja-2001No ratings yet
- 4 ImmunopathDocument136 pages4 Immunopathninja-2001No ratings yet
- Pathoma NotesDocument28 pagesPathoma NotesHarun Rashid100% (4)
- Opportunistic InfectionsDocument1 pageOpportunistic Infectionsninja-2001No ratings yet
- Opportunistic Infections-MicroDocument1 pageOpportunistic Infections-Microninja-2001No ratings yet
- 10-Ashique-2020-NaturalProductsBioprospecting-A Systemic Review On Topical MarketDocument21 pages10-Ashique-2020-NaturalProductsBioprospecting-A Systemic Review On Topical MarketGD & Hair ManagementNo ratings yet
- Positive Effect of Topical Ketoconazole, Minoxidil and Minoxidil With Tretinoin On Hair Growth in Male MiceDocument6 pagesPositive Effect of Topical Ketoconazole, Minoxidil and Minoxidil With Tretinoin On Hair Growth in Male MiceAyuNo ratings yet
- Estrogenization of ManDocument19 pagesEstrogenization of MangushensNo ratings yet
- Cefasabal Saw Palmetto and Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument9 pagesCefasabal Saw Palmetto and Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaJose Luis Marin CatacoraNo ratings yet
- Indian Herbs That Act As 5-Alpha Reductase InhibitorsDocument9 pagesIndian Herbs That Act As 5-Alpha Reductase InhibitorsMan ManNo ratings yet
- Laser Enhancement ProtocolsDocument25 pagesLaser Enhancement ProtocolsWolfManNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Endocrinology Review MCQS: Part - 4Document33 pagesPediatric Endocrinology Review MCQS: Part - 4Reem 10No ratings yet
- BPHDocument81 pagesBPHFlo Neri BerondoNo ratings yet
- 21 Natural Scientific Pathways Shown To Stimulate Hair Growth and Prevent Hair Loss 21 Natural ... (PDFDrive)Document36 pages21 Natural Scientific Pathways Shown To Stimulate Hair Growth and Prevent Hair Loss 21 Natural ... (PDFDrive)Mohamed KhaterNo ratings yet
- Male vs Female Sex DifferentiationDocument9 pagesMale vs Female Sex DifferentiationAKHIRUL SIREGARNo ratings yet
- ALOPECIADocument1 pageALOPECIAKAIGWA AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - UpToDateDocument9 pagesEpidemiology and Pathogenesis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - UpToDateFeer VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Case Report BPH Qorry WelendriDocument39 pagesCase Report BPH Qorry WelendriDindaNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Behavior: Jill E. Schneider, Jeremy M. Brozek, Erin Keen-RhinehartDocument16 pagesHormones and Behavior: Jill E. Schneider, Jeremy M. Brozek, Erin Keen-RhinehartKerin ArdyNo ratings yet
- Tocomin SupraBio - Hair Growth StudyDocument6 pagesTocomin SupraBio - Hair Growth StudyjassenNo ratings yet
- Guide For Good Prostate HealthDocument9 pagesGuide For Good Prostate HealthAlceir FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Topical Ketokonazol For Androgenetic Alopecia A Systematic ReviewDocument6 pages2020 - Topical Ketokonazol For Androgenetic Alopecia A Systematic ReviewnancyerlenNo ratings yet
- Androgenetic Alopecia: E. Sawaya, and JerryDocument15 pagesAndrogenetic Alopecia: E. Sawaya, and JerrylisnallNo ratings yet
- Keratinocytes Undergo A Differentiation Process, Starting From A Single Layer of Stem Cells at The Basis ofDocument14 pagesKeratinocytes Undergo A Differentiation Process, Starting From A Single Layer of Stem Cells at The Basis ofHarish KakraniNo ratings yet
- Beard BibleDocument27 pagesBeard BibleEtor LozanoNo ratings yet
- UTS - Chapter 2Document129 pagesUTS - Chapter 2Rhonel Alicum GaluteraNo ratings yet
- List of Human Hormones: Hormone ListingDocument7 pagesList of Human Hormones: Hormone ListingMohammed AslumNo ratings yet
- Male Hypogonadism: Approval Number: G.MKT - GM.MH.04.2018.0513Document19 pagesMale Hypogonadism: Approval Number: G.MKT - GM.MH.04.2018.0513Billi Siddiqui100% (1)
- Scally - Anabolic Steroids - A Question of Muscle PDFDocument253 pagesScally - Anabolic Steroids - A Question of Muscle PDFpavel100% (1)
- Meta Dbol CycleDocument4 pagesMeta Dbol CyclestuNo ratings yet
- Mark Horowitz LetterDocument2 pagesMark Horowitz LetterrktNo ratings yet
- 10.male Reproductive System 2 BlocksDocument220 pages10.male Reproductive System 2 BlocksANA CAROLINE ANDRADE DE MELONo ratings yet
- Transgender Women - Evaluation and Management - UpToDateDocument29 pagesTransgender Women - Evaluation and Management - UpToDateRicardo Alessandro Teixeira Gonsaga0% (1)
- Hiperandrogenismo ArtigoDocument11 pagesHiperandrogenismo ArtigoFernando RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Emerging Mechanisms of ResistanceDocument11 pagesEmerging Mechanisms of Resistancemilenerato2240No ratings yet