Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aggregate
Uploaded by
isaacmureithiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aggregate
Uploaded by
isaacmureithiCopyright:
Available Formats
Aggregate
The aggregates used for ordinary concrete can be divided into two types by their sizes. The one whose
diameter is more than 4.75mm is called coarse aggregate, and the one whose diameter is less than
4.75mm is called fine aggregate. The fine aggregates used in ordinary concrete generally are the natural
sand which comes into being when the natural rock (excluding soft rock and weathered rock) has
experienced natural weathering, water transportation, sorting, and stacking and other kinds of natural
conditions; the machine-made sand (is made by grinding and sorting by machine, and the diameter of
the rock particles is less than 4.75mm, except the particles of soft rock and weathered rock.) through
de-dust treatment and the mixed sand (made by mixing machine-made sand and natural sand) are
collectively call manufactured sand. According to different sources, natural sand can be divided into
river sand, sea sand, mountain sand and desalted sea sand.
Mud and Clod Content
The mud content refers to the total amount of the dust, silt and clay whose diameters are smaller than
0.075mm in aggregates. The clod content refers to the content of particles whose diameters are more
than 1.18mm and become less than 0.60mm after being washed by water and pinched by hand in the
fine aggregates; or the content of the particles whose diameters are more than 4.75mm and become
less than 2.36mm after being washed by water and pinched by hand in coarse aggregates. The stone
dust content means the content of the particles with diameters less than 0.075mm. The mud particles in
aggregates are very fine that can adhere to the surface of aggregates, which will impact the bond force
between cement paste and Sand Stone Sand Stone. And clays will become the vulnerable parts in
concrete, which will have a big impact on the quality of concrete.
The harmful substances in aggregate mainly refer to sulfides, sulfate, organic matter, mica, chloride,
clay, light substances, and so on. Clay and light substances (coal and slag, etc.) will adhere to the surface
of aggregate, which impacts the cohesiveness between aggregate and cement and reduces the frostresistance and impermeability; sulfides, sulfate and organic matter will be corrosive to cement, which
will decreases the strength and durability of cement; chloride will corrode steel, which accelerates the
damage of reinforced concrete.
Gradation and Coarseness
The aggregate gradation refers to the collocation distribution of particles with different diameters. Good
gradation will not only reduce the amount of cement but also improve density, intensity and other
properties of concrete.
Water for Concrete
The basic quality requirements for the water used in concrete should: not contain any harmful
impurities impacting the normal setting and hardening of cement; not destroy the development of
strength and durability of concrete; not speed up steel corrosion; not cause brittle fracture of prestressed steel bars; and assure that the surface of concrete cannot be polluted.
You might also like
- Bridge MaterialsDocument10 pagesBridge MaterialsisaacmureithiNo ratings yet
- Road Unit Rate DerivationDocument18 pagesRoad Unit Rate Derivationisaacmureithi100% (1)
- ITEMDocument1 pageITEMisaacmureithiNo ratings yet
- Road Cross Section PDFDocument1 pageRoad Cross Section PDFisaacmureithiNo ratings yet
- ITEMDocument1 pageITEMisaacmureithiNo ratings yet
- Column Info SheetDocument5 pagesColumn Info SheetisaacmureithiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocument20 pagesLiquid Liquid ExtractionRavi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Alamat Perusahaan Perusahaan Di CilegonDocument19 pagesAlamat Perusahaan Perusahaan Di CilegonSri RahayuNo ratings yet
- Is 5556 1991Document10 pagesIs 5556 1991Narasimha DvlNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2023Document28 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2023Rohee TariqNo ratings yet
- SeparationDocument3 pagesSeparationeladeb eladebNo ratings yet
- Gating ManualDocument84 pagesGating Manualmr.nguyenk100% (4)
- Chemical Dechlorination of PCBs From Dielectric OilsDocument6 pagesChemical Dechlorination of PCBs From Dielectric Oilsgerodot2falconNo ratings yet
- Sewage and Waste WaterDocument4 pagesSewage and Waste WaterMuhammad DzikrulNo ratings yet
- Meehanite Worldwide Specification Handbook Ver09.07.2013 PDFDocument203 pagesMeehanite Worldwide Specification Handbook Ver09.07.2013 PDFUlises Quintana Carhuancho100% (1)
- Oxidations With Cerium Sulphate SolutionsDocument4 pagesOxidations With Cerium Sulphate Solutionsliz_hobbs79No ratings yet
- PAN Precursor Fabrication, Applications and Thermal Stabilization Process in Carbon Fiber Production - Experimental and Mathematical ModellingDocument39 pagesPAN Precursor Fabrication, Applications and Thermal Stabilization Process in Carbon Fiber Production - Experimental and Mathematical ModellingFlor GINo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopDocument30 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopJeannie UyNo ratings yet
- EDIP - Catalogue (1) BS EN 545 2010 MS1919Document6 pagesEDIP - Catalogue (1) BS EN 545 2010 MS1919Mohamad SyafiqNo ratings yet
- ModTech2015 Program Book of AbstractsDocument293 pagesModTech2015 Program Book of AbstractsBuluc GheorgheNo ratings yet
- TCXD 205-1998 Pile Foundation-Specifications For DesignDocument68 pagesTCXD 205-1998 Pile Foundation-Specifications For Designrpb10No ratings yet
- Ternary Phase Diagrams IntroductionDocument41 pagesTernary Phase Diagrams IntroductionGikiTopiNo ratings yet
- Natsteel BRCDocument8 pagesNatsteel BRClwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Feeder Canal Lining 29Document12 pagesFeeder Canal Lining 29ABAMELANo ratings yet
- Lime Neutralization Wastewater TreatmentDocument15 pagesLime Neutralization Wastewater TreatmentMehrdad AminkazemiNo ratings yet
- SSR 2022-23Document624 pagesSSR 2022-23Chikodi UGD78% (9)
- Transformer Oil DetailDocument8 pagesTransformer Oil DetailBaSant KohliNo ratings yet
- TUNNEL FORMWORK TECHNOLOGYDocument93 pagesTUNNEL FORMWORK TECHNOLOGYP.K.MallickNo ratings yet
- Shed BuildingDocument59 pagesShed BuildingdomesNo ratings yet
- Aluminum ChlorideDocument1 pageAluminum ChlorideK.m. Ehsan Morshed RanaNo ratings yet
- Aise Standard No 9Document17 pagesAise Standard No 9Sos de HoyosNo ratings yet
- Preformulation drug optimizationDocument49 pagesPreformulation drug optimizationShaimaa AlsamarraiNo ratings yet
- 4ch1 1cr Rms 20230302Document15 pages4ch1 1cr Rms 20230302LAITH ROBERT WADIE SWAIDANNo ratings yet
- Proposed Design Methods For Lateral Torsional Buckling of Unrestrained Steel Beams in FireDocument7 pagesProposed Design Methods For Lateral Torsional Buckling of Unrestrained Steel Beams in FireReaditReaditNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of A Deep Excavation Near A Shield TunnelDocument9 pagesNumerical Simulation of A Deep Excavation Near A Shield TunnelEfi GusfianaNo ratings yet
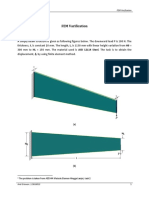
- FEM Varification: ProblemDocument11 pagesFEM Varification: Problemandi0610bNo ratings yet