Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ssans End of Module Test
Uploaded by
samiul71Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ssans End of Module Test
Uploaded by
samiul71Copyright:
Available Formats
SS
END OF UNIT TEST
Answers to The Steel Story End of Unit Test
Q
Answer with marks
Marking suggestions
1(a)
X magnesium sulphide (1)
Y calcium oxide and/or magnesium oxide (1)
Z aluminium oxide (1)
Allow correct formulae
1(b) (i)
P4O10/P2O5/SiO2 (1)
Allow SO2
1(b) (ii)
Acidbase (1)
1(b) (iii)
It can be burnt as a fuel (1); it is toxic/harmful to life (1)
Allow causes smog
1(c)
Steel containing small amount of carbon (1)
flexible/can be moulded (1)
use: paper clip/car bodies/wire, etc (1)
Allow about 0.1% carbon
Answer with marks
2(a)
When the first pink tinge remains (1)
2(b) (i)
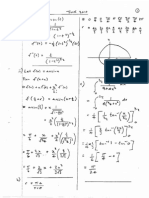
(12.9 0.025)/1000 (1); = 3.225 104 (1)
2(b) (ii)
Answer to (b)(i) 5 = 1.613 103 (1)
2(b) (iii)
Answer to (b)(ii) 10 56 (1) = 0.903 g (1) includes unit and 2/3 sf
Answer 100/1.00 = 90.3% (1) includes sf
2(c)
Quote (or imply) 2H+ + 2e H2 ; E ! = 0 (1)
When Fe/Fe2+ is connected to the above half-reaction in a cell,
electrons flow to the half-cell with the more positive potential
or since Fe/Fe2+ is more negative than H+/H2 (1);Fe is changed
(oxidised) to Fe2+ (1) but Fe2+ cannot be changed to Fe3+ by H+ (1)
2(d)
3d
ie (1) for good explanation of
direction for one case. Answers
just in terms of two potentials
printed can score max (2) if
explanation good
4s
Fe2+ [Ar]
Fe3+ [Ar]
Marking suggestions
(1) each
The Fe3+ has a half-filled set of 3d orbitals/only one electron in each
d orbital/minimum electron repulsion (1);
hence it is more energetically stable than Fe2+ (1)
2(e)
A (dark) green (1); precipitate (1)
Answer with marks
3(a)
Water (1); Air (oxygen) (1)
3(b)
Sn2+ + Fe Sn + Fe2+ (1)
3(c) (i)
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) 2Fe2+(aq) + 4OH(aq)
(1) for correct species
(1) for balancing
(1) for state symbols if at least first mark scored
3(c) (ii)
3.3 (1)
IRON
IRON
Pit in iron
Electron flow (1)
containing
electrolyte
3.1 (1)
150
A2 LEVEL
Marking suggestions
END OF UNIT TEST
High resistance voltmeter
V
Salt bridge
3(d) (i)
Platinum
Solution of
Fe2+(aq)
and Fe3+(aq)
SS
Ignore any connections to terminals
Accept unreative metal in place of
platinum
Tin
Solution of
Sn2+(aq)
(1) for left beaker; (1) for right beaker; (1) for salt bridge;
(1) for standard conditions: all solutions 1.0 mol dm3; stated
temperature usually 298 K; 1 atm pressure
3(d) (ii)
0.91 V (1)
Ignore sign
3(d) (iii)
Description (or diagram) of standard hydrogen electrode replacing
left-hand electrode:
hydrogen gas over platinum electrode (1)
standard conditions: 1 atm pressure, 1.0 mol dm3 H+ (1)
Maximum (1) if not made clear
that the hydrogen electrode replaces
the Fe3+/Fe2+ electrode
Answer with marks
Marking suggestions
4(a)
Catalyst (1)
4(b)
Colour is caused by movement of electrons within d sub-shells (1);
this cannot happen in Cu+ as d sub-shell is full (1)
4(c) (i)
1. NH3/H2O/en (1)
2. CN/edta4 (1)
4(c) (ii)
More than one point of attachment (or words to that effect) to
metal ion (1)
4(c) (iii)
It indicates the stability of the complex (1); the higher the value, the
more stable the complex compound compared to reactants (1)
4(c) (iv)
[Cu(CN)4(H2O)2]2 (1)
4(c) (v)
H2O
H3N
Cu2+
NH3
NH3
H3N
H2O
(1) for indication of octahedral structure
(1) for Cu2+
(1) for 4 ammonia and 2 water molecules (in any positions)
4(d) (i)
It absorbs in the red/orange (1)
4(d) (ii)
Make up a variety of Cu2+ concentrations and measure their
absorbance/transmittance in a colorimeter (1);
using a red/orange filter (1);
plot graph of absorbance/transmittance against concentration (1);
from which concentration of unknown can be read from its
absorbance/transmittance (1)
A2 LEVEL
151
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 04 Briony Holmes - TWI PDFDocument32 pages04 Briony Holmes - TWI PDFSupratim Biswas100% (2)
- Metal Joining and Cutting ProcessesDocument155 pagesMetal Joining and Cutting Processestuvu100% (4)
- FP2 2010 June SolutionsDocument4 pagesFP2 2010 June Solutionssamiul71No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme For Topic 7: Exam-Style Topic TestDocument3 pagesMark Scheme For Topic 7: Exam-Style Topic Testsamiul71No ratings yet
- Maths A2 ProjectilesDocument1 pageMaths A2 Projectilessamiul71No ratings yet
- ES3 - Storylines Assignment 5Document1 pageES3 - Storylines Assignment 5samiul71No ratings yet
- As Support Pack Module 2 Developing FuelsDocument45 pagesAs Support Pack Module 2 Developing Fuelssamiul71No ratings yet
- As Support Pack Module 1 Elements of LifeDocument29 pagesAs Support Pack Module 1 Elements of Lifesamiul71No ratings yet
- Simb GlomalinDocument1 pageSimb GlomalinPatricia Lopes LealNo ratings yet
- Word Problem Concerning Gravimetric Factor QDocument2 pagesWord Problem Concerning Gravimetric Factor QDave Gato VestalNo ratings yet
- CHM 421: Analytical Chemistry: Title: Solubility of Ionic Salts in SeawaterDocument11 pagesCHM 421: Analytical Chemistry: Title: Solubility of Ionic Salts in Seawateriyla sallehNo ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap sc4b Homework2Document1 pageEdgcse Aap sc4b Homework2venusNo ratings yet
- What Is 30c8 SteelDocument3 pagesWhat Is 30c8 SteelSanjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Iron OreDocument9 pagesIron OreAnimesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- EML 2322L - Welding - MAE Design and Manufacturing LabDocument21 pagesEML 2322L - Welding - MAE Design and Manufacturing LabBhaiJan59No ratings yet
- Chemistry Extra Credit!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Document10 pagesChemistry Extra Credit!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!bestgirlaroundNo ratings yet
- I.S.en15510 2017 (Full Permission)Document33 pagesI.S.en15510 2017 (Full Permission)WalidNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet - Ni - CD - Polypropylene Containers - Filled - R1 PDFDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet - Ni - CD - Polypropylene Containers - Filled - R1 PDFFrancis TomyNo ratings yet
- D and H NewDocument37 pagesD and H NewBharat AhirNo ratings yet
- Test 2: State of Matter (Gas) and ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesTest 2: State of Matter (Gas) and ElectrochemistryDai Fei PohNo ratings yet
- Seminario 1Document5 pagesSeminario 1Javier FrancoNo ratings yet
- 01 - Hardening, Tempering, and Heat TreatmentDocument63 pages01 - Hardening, Tempering, and Heat TreatmentKhin Aung ShweNo ratings yet
- 1 ATI Stellram U INCIMA DimenzijeDocument8 pages1 ATI Stellram U INCIMA DimenzijeBosko LukavicNo ratings yet
- Cevi UniDocument6 pagesCevi UniGoran PatekNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument141 pagesFull ThesissreenuNo ratings yet
- DefeitoscDocument62 pagesDefeitosccalvaoNo ratings yet
- Las 1-10 (Che 029)Document6 pagesLas 1-10 (Che 029)Lyna FloridaNo ratings yet
- Astm E527 23Document4 pagesAstm E527 23Vishal UpadhyeNo ratings yet
- 14 Writing Reactions and BalancingDocument12 pages14 Writing Reactions and BalancingSHAMS QUAMARNo ratings yet
- THE Dissolving Mechanisms of Cadmium and Lead in Nitric AcidDocument5 pagesTHE Dissolving Mechanisms of Cadmium and Lead in Nitric AcidAbdul JaleelNo ratings yet
- HKCEE Chem Distribution Table 1990-2008Document4 pagesHKCEE Chem Distribution Table 1990-2008Michael Ng Yuey ZhunNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding 1Document18 pagesCovalent Bonding 1claudia gomesNo ratings yet
- SMK Bandar Bintulu Chemistry 962 Semester 1 2016: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument9 pagesSMK Bandar Bintulu Chemistry 962 Semester 1 2016: Answer All Questions in This Sectiontang ka ongNo ratings yet
- Lab 13 - Testing For Oxidising and Reducing AgentsDocument3 pagesLab 13 - Testing For Oxidising and Reducing AgentsFina ShoNo ratings yet
- Price Trend of Foundry Raw MaterialsDocument2 pagesPrice Trend of Foundry Raw MaterialsPradeep Kumar JenaNo ratings yet
- Mining of Precious Metals and Minerals - August 2018Document220 pagesMining of Precious Metals and Minerals - August 2018Marcus HowardNo ratings yet