Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EEE313 A New Method For Reducing Magnetic Radial Force in Switched Reluctance Motor
Uploaded by
sathishOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EEE313 A New Method For Reducing Magnetic Radial Force in Switched Reluctance Motor
Uploaded by
sathishCopyright:
Available Formats
A NEW METHOD FOR REDUCING MAGNETIC RADIAL FORCE
IN SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR
K. Vijayakumar1*, R. Karthikeyan,2 S. Kannan3, S. Rajkumar4 and G.K. Sathishkumar5
1*
Assistant professor, Department of electrical & electronics engineering, Mailam Engineering
College, Mailam and k_vijaymec@yahoo.com.
2
Assistant professor, Department of electrical & electronics engineering, Shri Venkateswara
College of Engineering, Sriperumpudoor, Chennai and vijipreethi@rediffmail.com.
3
Final year student, Department of electrical & electronics engineering, Mailam Engineering
College, Mailam.
4
Lecturer, Manakula vinayar Institute of Technology, Madagadipet, pondicherry.
5
Design Engineer ITC Infotech, Bangalore.
Abstract--This paper investigates the influence of
II. SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR
rotor with feeble-magnetic portions (groove or hole
in a rotor) on electromagnetic radial force
characteristics of 6/4 switched reluctance (SR)
motor. Three different configurations viz (i)
Conventional rotor (ii) rotor with circular hole and
(iii) rotor with triangular hole SR motor have been
studied using finite element analysis tool ANSYS
10.0 to obtain their force and torque
characteristics. The study reveals that the rotor
with hole provision has lesser radial force level
which makes it a viable alternative in high speed
applications.
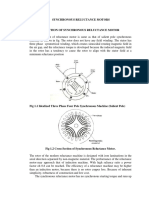
Fig. 1. The 2D CAD model of a 6/4 SRM.
Index Terms--Finite Element Analysis (FEA),
Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM), Torque ripple, A switched reluctance motor is an electrical
Radial force.
machine in which the torque is developed by the
tendency of the rotor to occupy a position so as
I. INTRODUCTION to minimize the reluctance of the magnetic path
The proliferation of power electronics of the excited stator phase winding. The SRM is
technology with advances in material technology a doubly salient but singly excited machine
has led to the development of special machines wherein the stator carries the winding while the
for myriad applications in recent times. One of rotor is simply made of stacked silicon steel
the such special machines, the Switched laminations. This lends to a simpler geometry for
Reluctance Motor (SRM) [1] is gaining SRM as evidenced from the two dimensional
recognition in the electric drives market due to (2D) CAD model of a 6/4 switched reluctance
its simple and rugged construction, low expected motor shown in Fig. 1.
manufacturing costs, fault tolerance capability,
high efficiency and high torque to inertia ratio.
Despite many advantages, the SRM has some III. THE 2D NUMERICAL FINITE ELEMENT
drawbacks. It requires an electronic control and ANALYSIS
shaft position sensor, a huge capacitor is needed The time stepped FEA is the most accurate
in the dc link and the double salient structure method available to obtain the magnetic
causes acoustic noise and torque ripple. This characteristics such as torque and force
paper presents the analysis of magnetic radial calculation in an electromagnetic device. In this
force and torque characteristics of a 6/4-switched paper a two-dimensional FEA has been carried
reluctance motor. The investigation is focused on out on the three configurations using FEA
the influence of groove or hole formed in a package ANSYS 10.0. [3].
projected pole of the rotor on the radial magnetic
of a 6/4 switched reluctance motor. The studied configurations of conventional
rotor SR motor, rotor with circular hole SR
motor and rotor with triangular hole switched
reluctance motor shown in Fig. 2, 3 and 4.
rotor in generally circumferential directions
quickly increases as the rotor rotates during a
cycle of the electric current distribution, and then
abruptly terminates at the time of switching the
current distribution. This on-off cycle of
magnetic attractive force causes the rotor and the
stator to considerably vibrate in generally
circumferential directions [4]-[5].
In a switched reluctance motor, the projected
poles of a rotor have feeble-magnetic portions
each having a shape that extends radially inward
Fig. 2. The 2D CAD model of a 6/4 conventional SRM. approximately in the rotational direction from a
position relative close to a radially outer end of
the projected pole and to an end of the projected
pole facing in a counter-rotational direction, that
is, a direction opposite to the rotational direction,
or a shaped that has a side extending radially
inward approximately in the rotational direction
from a position relatively close to a radially outer
end and an counter-rotational direction-facing
end of the projected pole and that extends
radially inward approximately in the counter-
rotational direction. The feeble-magnetic
portions are weaker in magnetism than the
material of the rotor and reduce the magnetic
attraction force occurring at the time of
Fig. 3. The 2D CAD model of a 6/4 SR motor with circular switching of coil energization, thereby reducing
hole formed in a projected rotor. noises while ensuring generation of a desired
amount of torque.
Thus, the switched reluctance motor of the
invention reduces the magnetic attractive force
between the stator pole portions and the rotor
pole protrusions in the radial direction at the time
of switching the current distribution to the coils,
compared with the conventional SR motor [2]-
[3]. The invention also avoids a large amount of
torque reduction.
The torque and radial force characteristics of
three rotor configurations as shown in Fig. 5 and
6.
Fig. 4. The 2D CAD model of a 6/4 SR motor with triangular
hole formed in a projected rotor. TORQUE PROFILES OF THREE ROTOR
CONFIGURATIONS
IV. RADIAL FORCE OF SWITCHED- 150
RELUCTANCE MOTOR
TORQUE (in N-mm)
100
CIRCULAR HOLED
50 ROTOR
The switched reluctance motor is a doubly 0
TRIANGULAR
HOLED ROTOR
salient construction, with salient poles on both -50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 10
CONVENTIONAL
0
the stator and the rotor. Phase windings are -100
ROTOR
wound on the stator poles, each coil being -150
wound around a single pole or tooth. The SR ROTOR POSITION (in DEGREES)
motors generate torque by utilizing magnetic
attractive force that acts between the rotor and
the stator when the coils are magnetized. Fig. 5. Torque angle characteristics of three rotor
However, conventional SR motors normally configurations.
suffer vibration problems. The magnetic
attractive force acting between the stator and the
ROTOR POSITION Vs MAGNETIC RADIAL FORCE
VI. REFERENCES
MAGNETICE RADIAL FORCE
700 [1] R. Arumugam, D. A. Lowther, R. Krishnan and J.
600
CONVENTIONAL F. Lindsay, “Magnetic field analysis of a
500 ROTOR SRM
switched reluctance motor using a two
(in N-mm)
400 CIRCULAR HOLED
300 ROTOR SRM dimensional finite element model,” IEEE Trans.
200 TRIANGULAR Magn., vol. MAG-21, no. 5, pp. 1883-1885, Sep.
HOLED SRM
100 1985.
0 [2] R. Rabinovici, “Torque ripple, vibrations, and
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 10
0 acoustic noise in switched reluctance motors”,
ROTOR POSITION (in DEGREES) HAIT Journal of Science and Engineering B,
Volume 2, Issues 5-6, pp. 776-786, July 2005.
[3] “switched reluctance motor with reduced radial
Fig. 6. Magnetic radial force characteristics of three rotor
force”, United States Patent, Dec. 1998.
configurations.
The analysis of the torque and radial force [4] C.Y.Wu, C.Pollock, “Analysis and reduction of
characteristics of three rotor configurations acoustic noise and vibration in the switched
reluctance drive”, IEEE Trans. on Industry
indicates that there is indeed a reduction in Applications, Vol.31, No.1, January/February,
torque ripple and magnetic attraction force 1995, pp.91~98.
between the stator pole and rotor pole portions in [5] S. Colby, F.Mottier, T.J.E.Miller, “Vibration
the radial direction when compared with the modes and acoustic noise in a 4-phase switched
conventional configuration. reluctance motor”, Conference Record of the
1995 IEEE Industrial Application Society, 30th
V. CONCLUSION IAS Annual Meeting, Vol.1, Orlando, USA, Oct.
8-12, 1995, pp.441~447.
In this paper an in-depth study of groove or
hole formed in a projected pole of the rotor on
the radial magnetic force characteristics of a 6/4
switched reluctance motor with three
configurations viz (i) conventional rotor SR
motor (ii) rotor with circular hole SR motor and
(iii) rotor with triangular hole SR motor has been
conducted. The studied results shows that a
gradual decrease in the magnetic radial force of
rotor with hole configurations. Study has lead to
the rotor with hole provision has better magnetic
radial force characteristic.
You might also like
- of SRMDocument22 pagesof SRMGopoji Dayanand71% (7)
- Special Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorDocument51 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- VIT University SRM ChapterDocument27 pagesVIT University SRM ChapterRAJA MNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ControlDocument10 pagesDC Motor ControlIbrahim KhleifatNo ratings yet
- 3.switched Reluctance MotorDocument15 pages3.switched Reluctance MotorAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-Stepper MotorDocument29 pagesUNIT-2-Stepper MotorArivoli SundaramurthyNo ratings yet
- SRM Using Arduino PDFDocument9 pagesSRM Using Arduino PDFChristian AztecaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Switch Reluctance Motor Characteristics 3.1 Switched Reluctance MotorDocument9 pagesChapter-3 Switch Reluctance Motor Characteristics 3.1 Switched Reluctance MotorSree GaneshNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Reduction of Time Harmonic Rotor Loss in Solid-Rotor Synchronous Reluctance DriveDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Reduction of Time Harmonic Rotor Loss in Solid-Rotor Synchronous Reluctance DrivemitsuiNo ratings yet
- ROTOR StrikingDocument3 pagesROTOR StrikingDearRed FrankNo ratings yet
- Reluctance MotorDocument14 pagesReluctance MotorTeenaNo ratings yet
- Rotary and Linear Switched Reluctance MotorsDocument12 pagesRotary and Linear Switched Reluctance Motorskarthikeyan249100% (2)
- Servo Control Basics: Understanding Motion Control FundamentalsDocument24 pagesServo Control Basics: Understanding Motion Control FundamentalssybaritzNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument5 pagesBasic ConceptsRodrigo BobNo ratings yet
- Switched Reluctance Motor Construction and Working PrincipleDocument10 pagesSwitched Reluctance Motor Construction and Working PrincipleHAMID SULIAMANNo ratings yet
- Switched Reluctance Motor PDFDocument79 pagesSwitched Reluctance Motor PDFHAMID SULIAMANNo ratings yet
- Effect of Rotor Profiles On The Torque of A Switched ReluctaDocument6 pagesEffect of Rotor Profiles On The Torque of A Switched Reluctaapi-19827661No ratings yet
- Brushless DC Motor: Apurva Sanjay Mahajan, Yugandhara Sanjay Mahajan, Sneha Vijay WadjeDocument5 pagesBrushless DC Motor: Apurva Sanjay Mahajan, Yugandhara Sanjay Mahajan, Sneha Vijay WadjeShyamkantVasekarNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Axial Magnetic Centering Forces On Sleeve Bearing Induction MotorsDocument9 pagesThe Influence of Axial Magnetic Centering Forces On Sleeve Bearing Induction MotorsDavid Antonio Córdova LatorreNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Control of BLDC MotorDocument39 pagesModelling and Control of BLDC Motoritstutan_749916692No ratings yet
- Free Energy GenerationDocument3 pagesFree Energy Generationjohn peterNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 7 Load Test of A Three Phase Induction MotorDocument22 pagesExperiment # 7 Load Test of A Three Phase Induction MotorKumar shantanu BasakNo ratings yet
- Eletrical Machines-Iii Lecture Notes Unit-IDocument19 pagesEletrical Machines-Iii Lecture Notes Unit-IDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- Dhiviyansh - Electric MotorsDocument19 pagesDhiviyansh - Electric MotorsDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- EE402 SEM Module 1 PMDC&BLDCDocument41 pagesEE402 SEM Module 1 PMDC&BLDCJohn JNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SDocument112 pagesChapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SLim Kai XuanNo ratings yet
- GMI AC Motor GuideDocument54 pagesGMI AC Motor GuideSmai HondoNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Reluctance Motors ExplainedDocument11 pagesSynchronous Reluctance Motors ExplainedVidhya M PNo ratings yet
- Dual Side Double Acting Water Pumping System Using Scotch Yoke MechanismDocument16 pagesDual Side Double Acting Water Pumping System Using Scotch Yoke MechanismGera workuNo ratings yet
- 1 - Switched Reluctance MotorDocument5 pages1 - Switched Reluctance MotorHARSHIT TOMARNo ratings yet
- DC Motors: Types, Design and ApplicationsDocument45 pagesDC Motors: Types, Design and Applicationstristan jeff bautistaNo ratings yet
- Scope For Designing High Torque Switched Reluctance Motor With Low RipplesDocument12 pagesScope For Designing High Torque Switched Reluctance Motor With Low RipplesEl Manaa BarhoumiNo ratings yet
- A Micro Corona Motor: Sanghoon Lee, Daejong Kim, Michael D. Bryant, Frederick F. LingDocument7 pagesA Micro Corona Motor: Sanghoon Lee, Daejong Kim, Michael D. Bryant, Frederick F. LingSebe DenesNo ratings yet
- MECHATRONICS IN ROBOTICS: ELECTRICAL DRIVESDocument34 pagesMECHATRONICS IN ROBOTICS: ELECTRICAL DRIVESDeepa Ragav RNo ratings yet
- Advantages Ac Motor Then DC MotorDocument17 pagesAdvantages Ac Motor Then DC Motorbobot80No ratings yet
- What is the function of commutator in DC motorDocument4 pagesWhat is the function of commutator in DC motorSovanNo ratings yet
- LN08Document9 pagesLN08ruzgaryilmazz5No ratings yet
- motorDocument19 pagesmotorRabi khanNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument21 pagesStepper MotorYaseen AlrawahiNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors: Ibrahim SENGOR, Abdullah POLAT and Lale T. ERGENEDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors: Ibrahim SENGOR, Abdullah POLAT and Lale T. ERGENESandesh BhakthaNo ratings yet
- EC Motors & Fan Applications: What Is An Ec Motor?Document5 pagesEC Motors & Fan Applications: What Is An Ec Motor?Arjun ReddyNo ratings yet
- Construction and control of PM, VR and hybrid stepper motorsDocument5 pagesConstruction and control of PM, VR and hybrid stepper motorsSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- EE313 Class10Document9 pagesEE313 Class10Zahid MarwatNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorsDocument9 pagesStepper MotorsAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- EE2403 Special Electrical Machines BackupDocument143 pagesEE2403 Special Electrical Machines BackupragupaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Alternating Current Motors: Electrical MachineDocument28 pagesChapter 7: Alternating Current Motors: Electrical MachineThe zeroNo ratings yet
- Switched Reluctance MachineDocument19 pagesSwitched Reluctance Machineapi-26587237100% (2)
- Iare Acm Lecture NotesDocument126 pagesIare Acm Lecture NotesAriel Ombajen MentawanNo ratings yet
- PMSM Vs Induction MotorDocument4 pagesPMSM Vs Induction MotorGarry GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Wevj 05 00546 PDFDocument4 pagesWevj 05 00546 PDFHenryHutabaratNo ratings yet
- Unit I Synchronous Reluctance MotorsDocument10 pagesUnit I Synchronous Reluctance MotorsLaxmikant BagaleNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Application of Spherical Magnetic Bearing in Magnetically Suspended Control and Sensitive GyroDocument11 pagesResearch Article: Application of Spherical Magnetic Bearing in Magnetically Suspended Control and Sensitive GyroM.ShNo ratings yet
- Thesis Switched Reluctance MotorDocument6 pagesThesis Switched Reluctance Motormelissalusternorman100% (2)
- Single Phase Induction Motor and Stepper MotorDocument11 pagesSingle Phase Induction Motor and Stepper MotorManthan deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Electrical Motors Flashcards - QuizletDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Electrical Motors Flashcards - QuizletAli UzairNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MachinesDocument18 pagesSynchronous MachinesDaffa SudianaNo ratings yet
- Construction of AlternatorDocument4 pagesConstruction of AlternatorMeet SatheyNo ratings yet
- Effect of Radial Magnetic Forces in Permanent Magnetic Motors With Rotor EccentricityDocument3 pagesEffect of Radial Magnetic Forces in Permanent Magnetic Motors With Rotor EccentricitylNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Basics and OperationDocument44 pagesStepper Motor Basics and OperationHansean WidjajaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Spectra and Molecular Structure: Physical Chemistry: A Series of MonographsFrom EverandRotational Spectra and Molecular Structure: Physical Chemistry: A Series of MonographsNo ratings yet
- Multi Phase InductionDocument11 pagesMulti Phase InductionsathishNo ratings yet
- Valliammai Engineering College Question Bank on Electrical Drives and ControlDocument13 pagesValliammai Engineering College Question Bank on Electrical Drives and Controlsathish0% (1)
- EE6351-Electrical Drives and ControlDocument10 pagesEE6351-Electrical Drives and ControlsathishNo ratings yet
- Art of LivingDocument155 pagesArt of Livingsathish50% (2)
- Realization of An Asynchronous Six-Phase Induction Motor Drive Test-RigDocument5 pagesRealization of An Asynchronous Six-Phase Induction Motor Drive Test-Rigsathish100% (1)
- BEEE CIAT TEST Design of Transformers and Induction MotorsDocument4 pagesBEEE CIAT TEST Design of Transformers and Induction MotorssathishNo ratings yet
- Unit1 EditedDocument32 pagesUnit1 EditedsathishNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument2 pagesArticlesathishNo ratings yet
- Lic Two Marks EditedDocument43 pagesLic Two Marks EditedsathishNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover LettersathishNo ratings yet
- Ijesit201405 31Document12 pagesIjesit201405 31sathishNo ratings yet
- PowSysEnggDocument38 pagesPowSysEnggvinodlifeNo ratings yet
- Thermal Model Induction MotorDocument17 pagesThermal Model Induction MotorTaylor100% (1)
- Emergency PowerDocument51 pagesEmergency PowersathishNo ratings yet
- Anna University PG Regulations 2013Document16 pagesAnna University PG Regulations 2013tskmeNo ratings yet
- Early Warning SystemDocument12 pagesEarly Warning SystemsathishNo ratings yet
- List of Deemed Universities: SR - No. WebsiteDocument6 pagesList of Deemed Universities: SR - No. WebsitesathishNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of A Hybrid Solar-Dish Brayton Engine: Sara Ghaem SigarchianDocument78 pagesModeling and Analysis of A Hybrid Solar-Dish Brayton Engine: Sara Ghaem SigarchiansathishNo ratings yet
- HVDC IN Future Transmission System: Reasons For Ac Generation and TransmissionsDocument6 pagesHVDC IN Future Transmission System: Reasons For Ac Generation and TransmissionssathishNo ratings yet
- Practical Induction 01Document5 pagesPractical Induction 01sathishNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBsathishNo ratings yet
- A Review of Induction Motors Signature Analysis As A Medium For Faults DetectionDocument10 pagesA Review of Induction Motors Signature Analysis As A Medium For Faults DetectiongasdeswerNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBsathishNo ratings yet
- Trends of Power Electronics On Renewable Energy SystemDocument8 pagesTrends of Power Electronics On Renewable Energy SystemsathishNo ratings yet
- Induction HeatingDocument9 pagesInduction HeatingsathishNo ratings yet
- Modelling BLDC Motor Drive Using Sensored and Sensorless ControlDocument10 pagesModelling BLDC Motor Drive Using Sensored and Sensorless ControlvishiwizardNo ratings yet
- Single-Switch High Step-Up Converters With Built-In Transformer Voltage Multiplier CellDocument11 pagesSingle-Switch High Step-Up Converters With Built-In Transformer Voltage Multiplier CellsathishNo ratings yet
- Proposal Guidelinesproposal - Guidelines PDFDocument5 pagesProposal Guidelinesproposal - Guidelines PDFKilari UmeshNo ratings yet
- Solar CoolDocument10 pagesSolar CoolBhanu Shree GowdaNo ratings yet
- Work Shop Course Brochure-Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument2 pagesWork Shop Course Brochure-Hybrid Electric VehiclessathishNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermo-Mechanical PowerDocument2 pagesSolar Thermo-Mechanical PowerROBINSON PRADO VILLEGASNo ratings yet
- Beam Powered PropulsionDocument19 pagesBeam Powered PropulsionSai Sushma100% (1)
- BT-3 200 PDFDocument3 pagesBT-3 200 PDFaqil khanNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Rectifier Using A Sepic DC-DC Converter in Continuous Conduction Mode For Power Factor CorrectionDocument7 pagesThree-Phase Rectifier Using A Sepic DC-DC Converter in Continuous Conduction Mode For Power Factor CorrectionuakragunathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Women EnvironmentDocument27 pagesChapter 1.3 Women Environmentdonna mendozaNo ratings yet
- PedgkDocument32 pagesPedgkGokulakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Inputs To Piping DisciplineDocument2 pagesInputs To Piping DisciplineJACKMAAAANo ratings yet
- Actuators & Positioners Linear Pneumatic Actuators: Data SheetDocument10 pagesActuators & Positioners Linear Pneumatic Actuators: Data SheetTai Dang HuyNo ratings yet
- Aircraft DesignDocument159 pagesAircraft DesignVinod Kumar sNo ratings yet
- HV Generation and Testing 1.0 Slides PDFDocument43 pagesHV Generation and Testing 1.0 Slides PDFzuhairulNo ratings yet
- Steam Generator HDocument2 pagesSteam Generator HNoor NoorNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EssayDocument2 pagesClimate Change EssaySammNo ratings yet
- Lect01 (MT 353)Document14 pagesLect01 (MT 353)Afzal Khan sulemaniNo ratings yet
- Mesura Nirmal CatalogDocument48 pagesMesura Nirmal CatalogShivBharatNo ratings yet
- 巴拉圭DIGITAL ENG H2 Propuesta de InnovacionDocument57 pages巴拉圭DIGITAL ENG H2 Propuesta de InnovacionXA ShrexerNo ratings yet
- A2vk PDFDocument10 pagesA2vk PDFMohar SinghNo ratings yet
- COACHING SET 2 MergedDocument17 pagesCOACHING SET 2 Mergedjohn-john castañedaNo ratings yet
- Genesis TM900 TM1000 Prioir To Serial Hay90564029Document97 pagesGenesis TM900 TM1000 Prioir To Serial Hay90564029tepys9112100% (2)
- India-Iran Relations Progress Problems and ProspecDocument53 pagesIndia-Iran Relations Progress Problems and Prospecمريم جاسمNo ratings yet
- PAPER SIDIQ ICOS FixDocument7 pagesPAPER SIDIQ ICOS FixAtika AssalafiyahNo ratings yet
- Design Mech DryersDocument5 pagesDesign Mech DryersBrandon DouglasNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets Complete Version F2013Document58 pagesSummary Sheets Complete Version F2013Minjae LeeNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Cooling Water Systems: August 2011Document23 pagesOptimal Design of Cooling Water Systems: August 2011Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- JVC GR-AX260 ManualDocument48 pagesJVC GR-AX260 ManualTamara EganNo ratings yet
- Request For Information: 8 June 2020Document11 pagesRequest For Information: 8 June 2020Mhae PotNo ratings yet
- Laporan Harian OverhoulDocument234 pagesLaporan Harian OverhoulRosyadNo ratings yet
- Serdi 4.5Document4 pagesSerdi 4.5Yeam_90No ratings yet
- Caie As Level Geography 9696 Core Model Answers v1Document31 pagesCaie As Level Geography 9696 Core Model Answers v1kgethilwemakgotsoNo ratings yet
- Robin Engine EH650 EH650DA JapanDocument29 pagesRobin Engine EH650 EH650DA JapanyewlimNo ratings yet
- 2005 Dec - Approved Module For Stage Wise Training OfLoco Running StaffDocument91 pages2005 Dec - Approved Module For Stage Wise Training OfLoco Running StaffR Sathish KumarNo ratings yet