Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors - EEP
Uploaded by
a_mohid17Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors - EEP
Uploaded by
a_mohid17Copyright:
Available Formats
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For
Motors
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors // Photo by TECO Middle East (TME)
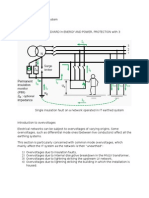
Scope Of Motor Testing
It should be noted that the scope of motor testing depends upon the motor type and size, this being
indicated on the inspection forms.
Motor vibration shall be measured in a tri-axial direction, i.e.:
Point x axis side of bearing housing at shaft height
Point y axis top of bearing housing
Point z axis axial of bearing housing at shaft height
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
1/7
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
The measurements shall be carried out with an instrument conforming to ISO 2954 (10-1000
Hz frequency range). With the motor at normal operating temperature, the vibration velocity shall not
exceed 2.8 mm/s RMS, or 4 mm/s PEAK, in any direction.
For bearings fitted with proximity probes, the unfiltered peak-to-peak value of vibration (including shaft
run-out) at any load between no load and full load, shall not exceed the following values:
50 m for two-pole motors
60 m for four-pole motors
75 m for six-pole or higher motors
Motor bearing (photo by CCLW INTERNATIONAL)
Bearing temperature rise limits following a heat run of 3.5 4 hours are as follows:
Rolling bearings:
Outer ring measurement max. 90 C
Temperature rise from ambient max. 50 C
Sleeve bearings:
Oil temperature max. 90 C
Bearing temperature rise by RTD max. 50 C
Lub. oil temperature rise from ambient max. 30 C (for forced lub. oil systems).
When commissioning or re-commissioning motors, precautions shall be taken to avoid excessive
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
2/7
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
vibration caused by the phenomenon known as soft foot; i.e. feet which do not have solid flat contact
with the base prior to the tightening of the holding-down bolts.
This may be measured and rectified during installation or detected during running by the loosening of
each holding-down bolt in turn while measuring motor vibration.
Motor Soft Foot Condition
Soft feet are those which do not have solid flat contact with the base prior to the tightening of the
holding-down bolts; one or more feet may be soft as shown in Figures 1 to 3.
The profile of the foot contact area may be as shown in Figures 4 to 6.
The profile of the foot contact area (Figures 1, 2 and 3)
Figure 1 - Machine resting on 3 feet, foot 4 is raised or soft
Figure 2 - Machine resting on diagonal formed by feet 3 and 4, feet 1 and 4 are soft
Figure 3 - Bottoms of all 4 feet are not parallel with base, feet 3 and 4 are soft
Profile of 'soft foot' contact area
NOTE: Re-machining of rotor feet is required in Figures 4 and 5; temporary use of wedge-shaped
shims may be acceptable (maintenance).
Advertisement
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
3/7
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
Forms
Form 14 Inspection of electric motor Cage-induction type (incl. control unit)
Inspection of electric motor cage-induction type (including control unit)
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
4/7
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
Form 4 Inspection of Switching Units HV Switchgear
Inspection of Switching Units - HV Switchgear
Form 11 Inspection Of Outgoing Unit LV Switchboard
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
5/7
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
Inspection Of Outgoing Unit - LV Switchboard
Reference: Field Commissioning and Maintenance Of Electrical Installations and Equipment Manual
Recommended EE articles
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
6/7
12/1/13
Testing and Commissioning Procedure For Motors | EEP
Edvard - Electrical engineer, programmer and founder of EEP. Highly specialized for
design of LV high power busbar trunking (<6300A) in power substations, buildings and
industry fascilities. Designing of LV/MV switchgears. Professional in AutoCAD
programming and web-design. Developer of awsome electrical design software
ePlusMenuCAD. Present on Google+.
Become EEP's Contributor and introduce yourself to 70k+ of our readers all across the web.
2013 EEP - Electrical Engineering Portal. All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy | 40 queries in 0.668
seconds.
TOP
Powered by CsanyiGroup
Get
PDF
electrical-engineering-portal.com/testing-and-commissioning-procedure-for-motors
7/7
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 2 Most Common Contributing Factors in Insulation FailureDocument3 pages2 Most Common Contributing Factors in Insulation Failurea_mohid17No ratings yet
- Battery Testing, Test Methods and ProceduresDocument6 pagesBattery Testing, Test Methods and Proceduresa_mohid17No ratings yet
- Guide to Lowering Costs With Variable Speed PumpingDocument22 pagesGuide to Lowering Costs With Variable Speed PumpingGilberto Sanchez100% (1)
- Can I Parallel A DY1 and DY11 Transformer - Electric Power & Transmission & Distribution FAQ - Eng-TipsDocument1 pageCan I Parallel A DY1 and DY11 Transformer - Electric Power & Transmission & Distribution FAQ - Eng-Tipsa_mohid17No ratings yet
- PM Framework Project ManagementDocument58 pagesPM Framework Project Managementa_mohid17No ratings yet
- MRDP503 Project Planning and ImplementationDocument23 pagesMRDP503 Project Planning and Implementationa_mohid17No ratings yet
- Standard Commissioning Procedure For Variable Frequency Motor DrivesDocument6 pagesStandard Commissioning Procedure For Variable Frequency Motor DrivesOndi PuliNo ratings yet
- Construction Management and TurnerDocument23 pagesConstruction Management and Turnera_mohid17No ratings yet
- Huawei Honor Holly Price in India - Buy Huawei Honor Holly Black - White 16 GB Online - Huawei - FlipkartDocument10 pagesHuawei Honor Holly Price in India - Buy Huawei Honor Holly Black - White 16 GB Online - Huawei - Flipkarta_mohid17No ratings yet
- Introducing HVDCDocument8 pagesIntroducing HVDCa_mohid17No ratings yet
- Modern VFD Guide - Technical & Economic AspectsDocument2 pagesModern VFD Guide - Technical & Economic Aspectsa_mohid17No ratings yet
- OPP Project ReportDocument17 pagesOPP Project ReportSunnyVishalSharmaNo ratings yet
- Overvoltages in The IT SystemDocument6 pagesOvervoltages in The IT Systema_mohid17No ratings yet
- Customer Manual March2011Document29 pagesCustomer Manual March2011leen_badiger911No ratings yet
- Study of Equipment Prices in The Power SectorDocument121 pagesStudy of Equipment Prices in The Power Sector이주성100% (1)
- Personal Internet Banking FormDocument1 pagePersonal Internet Banking Forma_mohid17No ratings yet
- Saudi Petrochemical Industry Report SummaryDocument8 pagesSaudi Petrochemical Industry Report SummaryHossam Mohamed KandilNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument5 pagesSteam Power Planta_mohid17No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 01-Bra-Efs-100002-11-50 AC SafeDocument68 pages01-Bra-Efs-100002-11-50 AC Safea_mohid17No ratings yet
- Sbi Swift CodesDocument10 pagesSbi Swift Codesa_mohid17No ratings yet
- Lessons Learned in Startup and Commissioning of Simple Cycle and Combined Cycle Combustion Turbine PlantsDocument114 pagesLessons Learned in Startup and Commissioning of Simple Cycle and Combined Cycle Combustion Turbine PlantsTerry A. Waldrop50% (4)
- Kitabal Sawm Sahihmuslim 110731085007 Phpapp01Document66 pagesKitabal Sawm Sahihmuslim 110731085007 Phpapp01a_mohid17No ratings yet
- 01-Brb-Efs-100002-11-50 AC SafeDocument66 pages01-Brb-Efs-100002-11-50 AC Safea_mohid17No ratings yet
- Operation and Control of MSF Plant Seawater SystemsDocument71 pagesOperation and Control of MSF Plant Seawater Systemsa_mohid17No ratings yet
- 80-GE-MFB-001 (Rev A0) P&ID - Process Flow DiagramDocument1 page80-GE-MFB-001 (Rev A0) P&ID - Process Flow Diagrama_mohid17No ratings yet
- O365 Guide ForRollOut enDocument43 pagesO365 Guide ForRollOut ena_mohid17No ratings yet
- Book 2 Purification (Kitab Al Taharah)Document30 pagesBook 2 Purification (Kitab Al Taharah)Fahim Akthar UllalNo ratings yet
- Zakat (Alms Tax) : Compiled By: Ms. Iffat KhalidDocument27 pagesZakat (Alms Tax) : Compiled By: Ms. Iffat Khalida_mohid17No ratings yet
- Zakatvstaxes 140219133811 Phpapp02Document40 pagesZakatvstaxes 140219133811 Phpapp02a_mohid17No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- FrankensteinDocument24 pagesFrankensteinLisa WardNo ratings yet
- ExportDocument18 pagesExportDolon MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Chich The ChickenDocument23 pagesChich The ChickenSil100% (4)
- Day 2 TaskDocument4 pagesDay 2 TaskYaathriganNo ratings yet
- MATH 8 QUARTER 3 WEEK 1 & 2 MODULEDocument10 pagesMATH 8 QUARTER 3 WEEK 1 & 2 MODULECandy CastroNo ratings yet
- My RepublicDocument4 pagesMy Republicazlan battaNo ratings yet
- No-Till For Micro Farms: The Deep-Mulch Method (Lean Micro Farm)Document20 pagesNo-Till For Micro Farms: The Deep-Mulch Method (Lean Micro Farm)Chelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- The Role of Historical Cultural Memory in Uzbek Documentary CinemaDocument5 pagesThe Role of Historical Cultural Memory in Uzbek Documentary CinemaResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Manage a micro business with BSB30315Document3 pagesManage a micro business with BSB30315Theo A W JacksonNo ratings yet
- Rostam's Seven LaboursDocument3 pagesRostam's Seven LaboursArifin SohagNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE COLOMBIA PALMIRA ENGLISH PROGRAMDocument1 pageUNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE COLOMBIA PALMIRA ENGLISH PROGRAMAlejandro PortoNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Hacker Conferences Attendees: Their Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Scores and Self-Reported Adulthood ExperiencesDocument25 pagesFemale and Male Hacker Conferences Attendees: Their Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Scores and Self-Reported Adulthood Experiencesanon_9874302No ratings yet
- Case Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinesDocument26 pagesCase Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument28 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA Biology Investigatory Projectvishali GNo ratings yet
- Design of Helical Antennas For 433 MHZ Radio Telemetry Ground Station and Uav (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)Document7 pagesDesign of Helical Antennas For 433 MHZ Radio Telemetry Ground Station and Uav (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)Tiara Nira SariNo ratings yet
- Cult of KUDocument31 pagesCult of KUEli GiudiceNo ratings yet
- CVR College of Engineering: UGC Autonomous InstitutionDocument2 pagesCVR College of Engineering: UGC Autonomous Institutionshankar1577No ratings yet
- Hireena Essay AnsDocument2 pagesHireena Essay AnsTasniiem ChandraaNo ratings yet
- Demo TeachingDocument22 pagesDemo TeachingCrissy Alison NonNo ratings yet
- CFC KIDS FOR CHRIST 2020 FINAL EXAMDocument13 pagesCFC KIDS FOR CHRIST 2020 FINAL EXAMKaisser John Pura AcuñaNo ratings yet
- On MCH and Maternal Health in BangladeshDocument46 pagesOn MCH and Maternal Health in BangladeshTanni ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Rules & Guidelines of Elliott WaveDocument12 pagesRules & Guidelines of Elliott WaveNd Reyes100% (2)
- Limit Switch 1LX7001-J AZBILDocument8 pagesLimit Switch 1LX7001-J AZBILHoàng Sơn PhạmNo ratings yet
- Percentage Practice Sheet - RBEDocument11 pagesPercentage Practice Sheet - RBEankitNo ratings yet
- Openstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFDocument197 pagesOpenstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFBinank PatelNo ratings yet
- Mapúa Welding Shop PracticeDocument7 pagesMapúa Welding Shop PracticeJay EmNo ratings yet
- CMC4 Controller Technical Support DocumentDocument148 pagesCMC4 Controller Technical Support DocumentZurab ChanturiaNo ratings yet
- EMA Guideline on Calculating Cleaning LimitsDocument4 pagesEMA Guideline on Calculating Cleaning LimitsshivanagiriNo ratings yet
- Synetek Controls Inc.: Ds1-S: Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesSynetek Controls Inc.: Ds1-S: Installation Instructionsdgd_electromecNo ratings yet
- Genigraphics Poster Template 36x48aDocument1 pageGenigraphics Poster Template 36x48aMenrie Elle ArabosNo ratings yet