Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW Packet 2 - The Study of Life (KEY) PDF
Uploaded by
David StainesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW Packet 2 - The Study of Life (KEY) PDF
Uploaded by
David StainesCopyright:
Available Formats
8
z
V'
])arc
Name
Class
Cll"-[!ll':l'
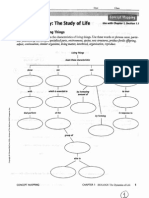
Biology: The Study of life
USf! with Chapter 1, Section 1.1
;;0
~
Characteristics of living Things
-<
Complete the concept map 0 11 the characteristics of living things. Use these words or phrases once: partic
ular fimaifJ11s, grow, stimuli. specialized pa'1s, environment, species, new .<trU.ctures, produce fertile offip'ing.
odjurt. continuation. simi"'r organisms, livinii matter, interbreed, orgonizntion, reproduce.
.
to
Living Things
CJ
~
share these characteristics
;2
- ,-
(1)
can
can
show
r;'
'"
o.....
organization
r-'
with
which ;s essential to
specialized
parts
continuation
IIIst perform
of the
to their
environment
in response to
by forming
particular
functions
can
new structures
group of
similar
organisms
able to
s::
"'1J
"'1J
CONCEPT MAPPING
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY The Oyn.mic, of Life
G)
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw- Hill , a divi~ion of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
.....
..&
U)
co
z
VI
Clas,>
Darc
N<1fllC
~
~
Cll"-l,ll::l'
Biology: The Study of life
;xl
A
m
Get the Big Picture
to
Find the section titles and the red and blue headings in Chapter 1 of your textbook. Use the
section titles to filJ in the rectangles in the idea map below. Use the red headings to fill in the
ovals. Some of the rectangles and ovals have been filled in for you.
-<
(5
l'
oC)
~
;1
(l)
tj
'3
The science
of biology
3ri'
'"
o....,
0:::"::
l'
Science and society
Each statement below goes with one of the headings in the ovals above. Write the letter of each
heading on the line in front of the statement it goes with.
All living thing', even hUlTlalls, need one another for survival.
All organiSITlS have structure and share traits with other organisms.
All organisms respond to stimuli and make adjustments to environmental conditions.
The microscope and the gas chromatograph are some of the tools biologists use in
their studies.
-I
Scientists always report measurements in S1.
Z
-I
Society as a whole must take responsibility for the ethical use of scientific discoveries.
oZ
m
VI
-I
CONTENT MASTERY
CHAPTER 1
R[OLOCY The Dynamics of Life
;xl
-<
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-HilI,
(I
division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Copynf,!"hl (;!cncoelMcC;rav.r-Hill,;j divj<;ion orThe i\kC;raw-Hill
Cnl1lp,lll i l.: ~ ,
Inc.
:;0
f);nc
Name
C la!'s
."
:;0
(ll ~l!t"l'
~
m
Z
-l
z
I:)
Ion
Section 1.2 The Methods of Biology
In your textbook, read about obJeroing and hypothesizing.
Answer the following questions.
the (ommon steps that scientists use to gather
information to solve problems
1. What is meant by scientific ""thod,)
-l
C
I:)
-<
The Study of Life, continued
2. What is a hypothesis'
a testable explanation for a q~estion or problem
Cl
3. How is a hypothesis te sted )
I:)
A hypothesis is tested by (ondu(ting an experiment.
In your textbook, read aboUl experimenting.
For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B.
Column B
Column A
d
4. A procedure that tests a hypothesis by collecting
a. dependent variable
infonnation lmder conrrolled conditions
5. In an experiment, the group in which all conditions
are kept the same
6. In an experiment, the group in which all conditions
are kept the same except for the one being tested
Ion
:!
m
:;0
8. The condition being observed or measured in
an experiment
-<
t::!:)
ot-<
~
.
(')
'"o
......
experimental results
experiment(s)
hypothesis
laws
theory
valid
verify
When (9)
experimental results
verify
other scientists may try to (11)
(12)
experiment(s)
by data from several scientists, it
scientific journals
are reported in (10)
the results by repeating the
. Usually when a(n) (13)
L' cor"idered (14)
hypothesis
valid
that is supported by many observations and experiments becomes a
Some well-established facts of nature, such as gravity, are recognized
-4
....
REINFORCEMENT AND STUDY GUIDE
"
theory
as (16)
CHAPTER 1
is supported
. Over time, a hypothesis
(15)
t:
(t'
U)
VJ:.L~~J
e. control group
scientific journals
11>
~"
Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
oC)
;1
c. independent variable
d. experiment
7 . The condition that is changed by the experimenter
7"
m
b. experimental group
laws
BIOLOGY The Dyn,mics of Life
Copyright Gl c ncoeJj\.fcGra w-Hjll, a
divi~ i o n
of The M(:G raw-H ili Co mpani es, In c.
(")
o
Z
-I
m
Z
-I
Date
N ame
U ,:f[)l\ol'
D ate
Cll"'lll"l'
1 I Biology: The Study of Life, continued
}>
Biology: The Study of Life,
Class
continued
Section 1.2 The Methods of Biology
Section 1.3 The Nature of Biology
Vl
-I
m
~9mc:
C lass
Review the Vocabulary
Study the Reading
adaptation (ad ap TAY shun)
data
energy
evolution (ev uh LEW shun)
homeostasis (hoh me 0
STAY sus)
organism
response
species (SPEE sheez)
Read the paragrapbs in the box and answer the question that follows.
A biologist named Katharine Payne visited the elephants at a zoo. She felt the air
around her throbbing like the rumbling of thunder. When she felt the air throb. she
noticed that the skin on the foreheads of the elephants moved.
Also. the elephants seemed to communicate without making any noise. They did not
make a sound. but they would start and stop moving at the same time . Payne knew that
some animals. such as whales. made sounds too low for humans to hear. She thought.
" Maybe elephants. like whales. use low sounds to communicate with each other."
control
development
ethics
growth
independent variable
reproduction
scientific methods
technology (tek NAHL uh jee)
The Chapter 1 vocabulary words are listed above. Review the definitions of these words. Then
draw a lin.e to match each word in the box with its definition.
An observation is something you see or notice. A fact is something you know.
Fill in the first box with something Payne observed the elephants doing. Fill in the second box
with something sbe observed about the air around ber. Fill in the last box with a fact sbe knew.
The elephants moved and stopped at the
same time.
Observation:
theory
biology
dependent variable
environment
experiment
hypothesis (hi PAHTH us sus)
organization
safety symbol
stimulus
}>
a. biology
1. What you do to test a hypothesis
2. Making of offspring
b. ethiCS
c. reproduction
d. homeostasis
e. experiment
4. Study of living things
5. Living things maintaining body functions
3. Moral principles and values held by humans
Vl
:!
m
Payne could not hear any sounds. She felt
the air throbbing.
Observation:
:;0
Use the words in the box to fill in the blanks in the sentences that follow. You will not use all
the words.
-<
Fact:
t:I:I
.....
ot"""'
o
GJ
~
Some animals make sounds too low for humans
to hear.
6.
Hypothesis: Maybe elephant' u,e low-pitched ,ound, to communicate
response
organism
organization
control
stimulus
adaptation
technology
evolution
A(n)
organism
has all four traits of life.
7. A(n)
stimulus
causes living things to respond .
with each other.
;i
8. Scientific research for society's needs or problems is called
technology
('I)
~.,
;:;3 .
en
o
.....,
t"""'
.......
~
In descriptive research, scientists report observations in the form of observational data such as written
descriptions.
In quantitative research, scientists report observations in the form of numerical data such as counts and
measurements .
9. A(n)
10.
control
Evolution
in an experiment is used as a standard for comparison.
is che change in a species Over time .
1. The observations made by Payne would be classified as what rype of research'
descriptive research
CONTENT MASTERY
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY: The Orn. mi", of Li fe
CHAPTER 1 JIIOLOGY The J)yn.nucs of Life
CONTENT MASTERY
You might also like
- Osmosis Gizmo - ExploreLearningDocument1 pageOsmosis Gizmo - ExploreLearningDanielle Bockmann0% (1)
- PRESTON HOLT - Cells Investigation LEXILE 610Document6 pagesPRESTON HOLT - Cells Investigation LEXILE 610Brian HoltNo ratings yet
- Bio Botany 11thDocument301 pagesBio Botany 11thPradeep Chandar100% (3)
- Characteristics of Living Things Worksheet Answers Key PDFDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things Worksheet Answers Key PDFJasmine PennieNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection Simulation - BasicDocument2 pagesNatural Selection Simulation - BasicImeeNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Debate Project PacketDocument6 pagesNuclear Power Debate Project Packetapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Chapter Outline: ELL Tructure and UnctionDocument5 pagesChapter Outline: ELL Tructure and Unctionrommel benamir100% (1)
- Comparing Plant and Animal Cells LabDocument5 pagesComparing Plant and Animal Cells LabkerwynnNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Physics Force and PressureDocument25 pagesClass 8 Science Physics Force and PressureSMKNo ratings yet
- Arun PPT - PPTX ..HUMAN REPRODUCTION FOR HSC Board Maharashtra State..Document65 pagesArun PPT - PPTX ..HUMAN REPRODUCTION FOR HSC Board Maharashtra State..arunmishra1986100% (1)
- Cell Structure Function Worksheet With HintsDocument7 pagesCell Structure Function Worksheet With Hintsapi-249772989No ratings yet
- Biology Unit PlanDocument10 pagesBiology Unit Planapi-246097943No ratings yet
- Resource 60786Document7 pagesResource 60786MariaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Chapter 30 Discussion AnswersDocument3 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 30 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (6)
- IB Bio Internet SitesDocument11 pagesIB Bio Internet SitesYammy LoNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Science 9Document9 pagesBiology Unit Science 9api-373530490No ratings yet
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDocument10 pagesCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riNo ratings yet
- Human Body 11 Organ Systems FoldableDocument4 pagesHuman Body 11 Organ Systems Foldablenaeleti1899No ratings yet
- Biome Research ProjectDocument3 pagesBiome Research Projectapi-472648158No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids WorksheetDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids WorksheetNatalie PembertonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 23Document12 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 23shkjsdhfskjd60% (5)
- Energy in The Cell LabDocument3 pagesEnergy in The Cell LabDoctorzo71% (7)
- Disease of The Nervous System AssignmentDocument3 pagesDisease of The Nervous System Assignmentapi-290895709100% (1)
- Grade 8 Mcas Review Question SetDocument13 pagesGrade 8 Mcas Review Question Setapi-294483847No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Guided NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 8 Guided NotesflyingmsNo ratings yet
- Middle School ChemistryDocument691 pagesMiddle School ChemistryChristian Homeschool-HubNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Active Reading GuideDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Active Reading GuideLâm TặcNo ratings yet
- Cladograms ActivityDocument6 pagesCladograms ActivityziribiriNo ratings yet
- Topics Biology Course SummaryDocument79 pagesTopics Biology Course SummaryMicaela Davis100% (1)
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Pre-AP Biology Class Schedule and SyllabusDocument12 pagesPre-AP Biology Class Schedule and SyllabusNoah LoyaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Daily Lesson Plans PDFDocument24 pagesAP Biology Daily Lesson Plans PDFJayCesarNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution SBI3UDocument13 pagesGenetics and Evolution SBI3UoboglerNo ratings yet
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Evolution AERON DEL SOCORRODocument9 pagesEvidence of Evolution AERON DEL SOCORROJezysaint Ruth Del SocorroNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science - Unit C Light and Optics - Unit Assessment PlanDocument14 pagesGrade 8 Science - Unit C Light and Optics - Unit Assessment Planapi-463860120No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology Genetics TestDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Biology Genetics TestValerieNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Life Is CellularDocument5 pages7.1 Life Is Cellularalex rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science Curriculum Map Final DraftDocument5 pages7th Grade Science Curriculum Map Final Draftapi-455790872No ratings yet
- Cells HW PacketDocument11 pagesCells HW PacketSandy Tana100% (2)
- Google 9th Grade Biology Book PDFDocument2 pagesGoogle 9th Grade Biology Book PDFGinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Coloring Worksheet WD Answer Key PDFDocument2 pagesCell Coloring Worksheet WD Answer Key PDFPatrick Jelo100% (1)
- Entire Lab Report Due Nov. XX - Equivalent To A Quiz GradeDocument5 pagesEntire Lab Report Due Nov. XX - Equivalent To A Quiz GradeJaga_Sahsiny_1No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Cells and Micro k5 CellDocument7 pagesUnit Plan Cells and Micro k5 Cellapi-371640211No ratings yet
- Modeling Mitosis Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesModeling Mitosis Lesson Planapi-302580039No ratings yet
- Dichotomous Key Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesDichotomous Key Lesson Planapi-241043893No ratings yet
- Osmosis Jones WorksheetDocument1 pageOsmosis Jones Worksheetapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Macromolecule ProjectDocument3 pagesMacromolecule Projectapi-240096234100% (2)
- Jessica Le - Virtual Microscope Lab WorksheetDocument5 pagesJessica Le - Virtual Microscope Lab Worksheetapi-523306558No ratings yet
- Study Guide Questions StudentDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Questions Studentapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Active Reading: Answer KeyDocument3 pagesActive Reading: Answer KeyJonas Montero100% (2)
- Animal Cell - Assessment1Document5 pagesAnimal Cell - Assessment1Dheeraj Rai50% (2)
- HW Packet 2 - The Study of Life PDFDocument4 pagesHW Packet 2 - The Study of Life PDFDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module #2-Events in The Cell TheoryDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module #2-Events in The Cell TheoryGi GiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary: 1 The Science of BiologyDocument3 pagesChapter Summary: 1 The Science of BiologyJoanne TolopiaNo ratings yet
- Deeper Life High School Biology NotesDocument78 pagesDeeper Life High School Biology NotesEmmanuel Eyo100% (4)
- Chapter 1: Exploring Life: Biology - The Study of LifeDocument27 pagesChapter 1: Exploring Life: Biology - The Study of LifeJustin RobenyNo ratings yet
- Review Notes on the Concept of Life and Origin of First Life FormsDocument8 pagesReview Notes on the Concept of Life and Origin of First Life FormsClaire Jhuzl CanoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biology Exploring LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Biology Exploring Lifemzunl25476No ratings yet
- Biology: The Science of Our Lives - : Back To TopDocument42 pagesBiology: The Science of Our Lives - : Back To TopwaryawandodiNo ratings yet
- HW Packet 2 - The Study of Life PDFDocument4 pagesHW Packet 2 - The Study of Life PDFDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- HW Packet 1 - The Study of LifeDocument5 pagesHW Packet 1 - The Study of LifeDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes - Biology The Study of Life PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Notes - Biology The Study of Life PDFDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Teacher Guide Offers Chapter 1 Biology AnswersDocument2 pagesTeacher Guide Offers Chapter 1 Biology AnswersDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Charles Law LabDocument4 pagesCharles Law LabDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- HW 4E - Electron ConfigurationsDocument2 pagesHW 4E - Electron ConfigurationsDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Determining Isotopes and Atomic Mass of Pennium (Pe) Using PenniesDocument2 pagesDetermining Isotopes and Atomic Mass of Pennium (Pe) Using PenniesDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- WS 3BDocument2 pagesWS 3BDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Hour Name 1. Describe The Experiment Conducted J.J. ThornsonDocument2 pagesHour Name 1. Describe The Experiment Conducted J.J. ThornsonDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet NEWDocument1 pageGas Laws Worksheet NEWDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ion Quiz 6ADocument1 pagePolyatomic Ion Quiz 6ADavid StainesNo ratings yet
- HW 3D - Radio Active IsotopesDocument2 pagesHW 3D - Radio Active IsotopesDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- HW 8D (2) - Combustion Reactions Worksheet, With KEY (11-12)Document3 pagesHW 8D (2) - Combustion Reactions Worksheet, With KEY (11-12)David StainesNo ratings yet
- Self Check 4-1 - Balancing Redox ReactionsDocument9 pagesSelf Check 4-1 - Balancing Redox ReactionsDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quiz A, B and C (With Keys) 2012-13Document16 pagesTake Home Quiz A, B and C (With Keys) 2012-13David StainesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 9 NotesDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- LAB 15A Evolution by Natural SelectionDocument8 pagesLAB 15A Evolution by Natural SelectionDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- New Lab Redox Titration - OxalateDocument1 pageNew Lab Redox Titration - OxalateDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Notes - Nuclear ChemistryDocument13 pagesChapter 19 Notes - Nuclear ChemistryDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Notes (Addendeum, From Chapter 11)Document5 pagesChapter 4 Notes (Addendeum, From Chapter 11)David StainesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HW Set (09-10)Document19 pagesChapter 4 HW Set (09-10)David StainesNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 1 - Matter and Measurements (09-10) - 1Document12 pagesNotes - Chapter 1 - Matter and Measurements (09-10) - 1David StainesNo ratings yet
- HW Chapter 6 - Thermochemistry (2012-13) KEYDocument162 pagesHW Chapter 6 - Thermochemistry (2012-13) KEYDavid StainesNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis Support Vector MachineDocument5 pagesMaster Thesis Support Vector Machinednqjxbz2100% (2)
- USE OF ENGLISH REPORTED SPEECHDocument5 pagesUSE OF ENGLISH REPORTED SPEECHHuyền Phạm Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Pancasila Character EducationDocument6 pagesPancasila Character EducationDaniel Prayoga D100% (1)
- Duolingo Homework PDF 22 MayDocument6 pagesDuolingo Homework PDF 22 MayPriya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Attestation Process ChecklistDocument2 pagesAttestation Process ChecklistConcepcion MpsNo ratings yet
- Support Vector ClassificationDocument8 pagesSupport Vector Classificationapi-285777244No ratings yet
- Social Work NotesDocument4 pagesSocial Work NoteszahidazizNo ratings yet
- Premiere Products Exercise Chapter 8 Complete SolutionDocument6 pagesPremiere Products Exercise Chapter 8 Complete SolutionMatthew BeckwithNo ratings yet
- Cognitve TheoryDocument8 pagesCognitve Theorymanu sethiNo ratings yet
- Explore Science's History and PhilosophyDocument6 pagesExplore Science's History and PhilosophyPhilip LaraNo ratings yet
- 5265 Brief-1 CameraDocument2 pages5265 Brief-1 CameraDanWagnerNo ratings yet
- Job DescriptionDocument32 pagesJob DescriptionGipsy CamargoNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Understanding EthicsDocument29 pagesChap 1 Understanding Ethicsphuonganhvu0310No ratings yet
- DLL Q4 G1 Math W1Document8 pagesDLL Q4 G1 Math W1Mary Jane Yoro MartinNo ratings yet
- Top Business Schools in South Asia and ComparisonDocument4 pagesTop Business Schools in South Asia and Comparisonraihans_dhk3378No ratings yet
- RankBook ProfileDocument5 pagesRankBook ProfilevandanaNo ratings yet
- Wordpress Thesis 182Document6 pagesWordpress Thesis 182PaperWritingServiceCheapCanada100% (2)
- Crucial Conversations - Kerry PattersonDocument13 pagesCrucial Conversations - Kerry PattersonVera S100% (1)
- Visualization Without VisionDocument21 pagesVisualization Without Vision11Dewi Meiliyan Ningrum dewimeiliyan.2020No ratings yet
- Experienced Music Teacher CVDocument4 pagesExperienced Music Teacher CVأصدقاء كريشندو للموسيقى والفنونNo ratings yet
- Sample Statement of Purpose Computer Engineering (SOP)Document1 pageSample Statement of Purpose Computer Engineering (SOP)theonlybbb86% (7)
- CV 11607816Document1 pageCV 11607816wolvarine 999No ratings yet
- Q1-M1 Ans (Eapp)Document9 pagesQ1-M1 Ans (Eapp)JD MartinNo ratings yet
- Final Dissertation Paper - Role of Open Spaces in LearningDocument8 pagesFinal Dissertation Paper - Role of Open Spaces in LearninghasnaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 2Document3 pagesĐỀ SỐ 2Nguyễn Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- 14JE000423-Rajat Kumar Jain - B.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering)Document2 pages14JE000423-Rajat Kumar Jain - B.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering)AshNo ratings yet
- Q1 Practical Research 2 - Module 1bDocument15 pagesQ1 Practical Research 2 - Module 1bRhea Mae MacabodbodNo ratings yet
- Today.: Technology For The Next DecadeDocument26 pagesToday.: Technology For The Next DecadeBschool caseNo ratings yet
- B.tech Apjktu (2019 Scheme)Document21 pagesB.tech Apjktu (2019 Scheme)Amarnath RajeshNo ratings yet
- Get the Most Out of Your Nutanix Cloud Platform TrainingDocument12 pagesGet the Most Out of Your Nutanix Cloud Platform TrainingJohramoNo ratings yet