Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparativo b31.1 - b31.8
Uploaded by
wpsssamsungOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparativo b31.1 - b31.8
Uploaded by
wpsssamsungCopyright:
Available Formats
This is a LIVE STUDY document and will be changed without notice.
The content may contain errors and omissions.
ASME B31.1 (2008)
ASME B31.3 (2008)
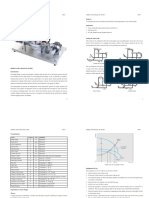
Power piping: typically found in electric power generating stations, in heating
and cooling systems
Process piping: typically found in petroleum refineries, chemical,
pharmaceutical, textile and paper plants
Gas transportation and dist
predominantly gas
Applicable: boiler external piping from first joint up to and including first block
valve for boilers where:
Exclusions:
Exclusions:
steam or vapor is generated over 100 kPa
high temperature water over 1103 kPa and/or temperatures of 120
nontoxic and not damaging to human tissues
Celsius
Excluding: fatigue due to pressure cycling
piping systems pressure above 0 and less 105 kPa nonflammable,
power boilers covered in BPV code and external piping covered in
tubes, tube headers, crossovers and manifolds of fired heaters
pressure vessels, heat exchangers, pumps
Including: fatigue due pressure cycling and thermal cycling
metal temperature
Celsius (450 F)
B31.1
pressure vessels,
piping beyond cus
piping in refineries
vent piping to subs
wellhead assembl
proprietary items s
liquid petroleum tr
dioxide and liquefi
Allowable stress:
as per tables in Appendix A
Allowable stress:
as per Table A-1 and A-2
as per table Appen
841.116A
shear to remain below 80%, bearing to remain below 160% of
allowable stress
Allowable stress
shear to remain below 80%, bearing to remain below 160% of
allowable stress
basis are same as ASME section II Part D Appendix 1 except for
cast iron and ductile iron
basis for bolting, cast iron, other material
flanges due to leakage below 75%
allowable stress of unlisted material (not conforming 323.1.2) can
not be used
Materials: material of unknown specification shall not be used for pressure
containing components
Materials: material of unknown specification shall not be used for pressure
containing components
Materials: material only as pe
ASME B31.1 (2008)
Quality factor E: depending type of weld, radiography and material
ASME B31.3 (2008)
Quality factor E: depending type of weld, radiography and material
Quality factor E
Factor y: factor depending Ferritic, Austenitic, Nickel and design temperature
Factor W: weld strength reduction factor
Factor W: weld strength reduction factor
Factor f: stress range factor
Factor F: design factor
Factor T: temperature deratin
values for temperature, Table
Pipe under internal pressure (104.1.2 and 104.1.4 (in creep)):
P = internal design pressure
D0 = outside diameter of pipe
SE = maximum allowable stress, including quality factor
tm = minimum required thickness
y = coefficient table 104.1.2A
A = additional thickness to compensate threading, provide additional strength,
corrosion allowance
Pipe under internal pressure (304.1.2):
Pipe under internal pressure
P = internal design pressure
P = internal design pressure
D = outside diameter of pipe
D = nominal outside diameter
S = stress value for material
S = specified minimum yield s
E = quality factor
E = longitudinal joint factor, tab
t = pressure design thickness
t = wall thickness
y = coefficient, also from table 304.1.1
F = design factor from table 84
W = Weld strength reduction factor
T = Temperature derating fact
Bend under internal pressure (304.2.1):
Bend under internal pressur
W = Weld strength reduction factor when in creep range, is 1 outside creep
range (table 102.4.7)
Bend under internal pressure (102.4.5):
For cold bends
according table in paragraph 8
ASME B31.1 (2008)
ASME B31.3 (2008)
Hot bends are to be designed
internal pressure rating shall n
seamless pipe and the intrado
pipe under internal pressure where I for intrados is:
pipe under internal pressure where I for intrados is:
where the t the wall thickness
and I for the extrados is:
and at sidewall I = 1.0,
R = radius of pipe bend
Elbows under internal pressure (102.4.5):
and I for the extrados is:
and at sidewall I = 1.0,
R = radius of pipe bend
Elbows under internal pressure (304.2.1):
Elbows under internal press
Elbows manufactured according standards listed in Table 126.1 are suitable for Elbows manufactured according standards listed in Table 326.1 are suitable for No specific design rules are lis
use at the pressure-temperature ratings specified by such standards.
use at the pressure-temperature ratings specified by such standards.
(Does this mean or allow that
uniform thickness?
Elbows not according above standards or for which design formulas and not
given in the code shall be based on calculations consistent with the design
criteria of this code. These calculations shall be substantiated by one or more
of the means stated in A B C or D of 104.7.2 (Does this mean or allow that an
elbow can be calculated according a bend with uniform thickness? Refer
B31.3)
Elbows not according above standards or for which design formulas and not
given in the code shall be based on calculations consistent with the design
criteria of this code. These calculations shall be substantiated by one or more
of the means stated in A B C or D of 304.7.2, or the elbow can be calculated
according the Bend calculation, refer 304.2.2.
Miter bends under internal pressure (104.3.3):
Miter bends under internal pressure (304.2.3):
Miter bends under internal p
1. When theta =< 22.5 deg than max. allowable pressure shall be the lesser of
1. If system hoop stress > 40%
ASME B31.1 (2008)
1. Only straight pipe calculations required if:
ASME B31.3 (2008)
(t = T - c):
are not permitted. Deflections
considered as miters.
2. If 10% < hoop stress < 40%
exceed 12.5 deg.
2. Pressure shall be limited to 70 kPa if:
and
3. If hoop stress < 10% SMYS
4. If hoop stress > 10% SMYS
less than one pipe diameter
or
and thickness is not less than required for straight pipe
3. Pressure shall be limited to 700 kPa if:
2. When theta > 22.5 deg than max. allowable pressure shall calculated as (t =
T - c):
and
and thickness is not less than required for straight pipe
For all miter bends the R1 shall not be less than:
4. For pressure over 700 kPa: proof test, FEA, etc required with a defined
minimum for closely spaced and widely spaced miter bend
with A:
(T-c) =< 13 mm A = 25
13 < (T-c) =< 22 mm A = 2(T-c)
(T-c) > 22 mm A = 2(T-c)/3 + 30
Reducer under internal pressure (104.6):
Reducer under internal pressure (304.6.1(b)):
Reducer under internal pres
1. Flanged reducer according Table 126.1 are considered suitable at the
specified pressure temperature ratings.
1. Reducers according Table 326.1 shall be considered suitable for use at
established pressure-temperature ratings or corresponding straight pipe with
87.5% of nominal wall thickness.
1. Steel butt welded fittings sh
Practice and shall have pressu
pipe of the same of equivalent
2. Concentric reducers not listed in Table 326.1 may be designed according
closures as per ASME VIII div.1
2. Other pressure containing c
philosophy of this code substa
2. Where butt welding reducers are made to a nominal pipe thickness, the
reducers shall be considered suitable for use with pipe of the same nominal
thickness.
ASME B31.1 (2008)
3. Components not covered by the standards listed in Table 126.1 shall be
based on calculation consistent with this code. Calculations are to be
substantiated by one of:
- extensive, successful service experience
ASME B31.3 (2008)
3. Eccentric reducers not listed in Table 326.1 are qualified as unlisted
components and shall be designed and documented substantiated by one of:
ASME B31.8 (2007)
- extensive, successful service experience
- experimental analysis
- extensive, successful service experience
- proof test
- experimental analysis
- experimental analysis
- engineering calculations
- proof test
- proof test
- detailed stress analysis, such as finite element analysis
- detailed stress analysis, such as finite element analysis
3. Closure heads such as flat, ellipsoidal, spherical or conical heads are allowed
for use under this code. Such items may be designed in accordance with ASME
VIII div.1 (UG32).
(Is ASME VIII div.1 UG32 acceptable?)
(Is ASME VIII div.1 UG32 acceptable?)
Stubon under internal pressure (104.3.1(D)):
Stubon under internal pressure (304.3.3):
Stubon under internal pressure (831.4 and app. F):
Required reinforcement area is
Required reinforcement area is
Required reinforcement area is (Fig. F-5):
= angle between branch and run
= angle between branch and run
with
A is additional thickness for corrosion and
tolerances, tmh from straight pipe calculation (104.1.2)
reinforcement by header
excess header, with
reinforcement by branch with
header excess area, with
attached reinforcement, weld area and other area
Assessment:
Area A2 and A3 to be multiplied by the ratio of allowable working stress,
maximum multiplication factor is
1.0 (para. 831.4(f))
ASME B31.1 (2008)
ASME B31.3 (2008)
branch excess
ASME B31.8 (2007)
attached reinforcement, weld area and other area
Assessment:
tr is reinforcement pad thickness
Area A2, A3 and A4 to be multiplied by the ratio of allowable working stress,
maximum multiplication factor is 1.0 (para. 304.3.3(f3))
weld area
If
area reinforcement ring
then
assess
area saddle on right angle connections
If
then
assess
Assessment:
Area A2,A3, A4 and A5 to be multiplied by the ratio of allowable working
stress, maximum multiplication factor is 1.0 (para. 104.3.1(D.2.3))
Tee (extruded outlet) under internal pressure (104.3.1(G)):
Tee (extruded outlet) under internal pressure (304.3.4):
Tee (extruded outlet) under internal pressure (831.4 ref. App. F):
Required reinforcement area is
Required reinforcement area is
Required reinforcement area is
K = 1.0 when
K = 1.0 when
K = 1.0 when d/D > 0.60
K = 0.6+(2d)/(3D) when 0.15 < d/D <= 0.60
K=
K = 0.7 when
when
K=
K = 0.7 when
when
K = 0.7 when d/D <= 0.15
reinforcement by header
ASME B31.1 (2008)
ASME B31.3 (2008)
reinforcement by header
ASME B31.8 (2007)
reinforcement by header
reinforcement by branch with
reinforcement by branch with
reinforcement by branch with
excess branch area
excess branch area
Assessment:
excess branch area
Assessment:
Assessment:
If
then assess
If
then assess
Weldolet (branch) under internal pressure (104.3.1(D)):
Weldolet (branch) under internal pressure (304.3.3):
Weldolet (branch) under internal pressure (831.4 ref. App. F):
Required reinforcement area is
Required reinforcement area is
Required reinforcement area is (Fig. F-5):
reinforcement by header, with
reinforcement by header, with
reinforcement by header
reinforcement by branch with
attached reinforcement, weld area and other area
reinforcement by branch with
reinforcement by branch with
Assessment:
Area A2 and A3 to be multiplied by the ratio of allowable working stress,
maximum multiplication factor is 1.0 (para. 831.4(f))
ASME B31.1 (2008)
with
ASME B31.3 (2008)
ASME B31.8 (2007)
with
= thickness pad or height of 60 deg angle fitting with in reinforcement
material
= thickness pad or a height of 0
= area provided by deposited weld metal and attached reinforcement
= area provided by deposited weld metal
Assessment:
excess weldolet area in reinforcement zone
Area A2, A3 and A4 to be multiplied by the ratio of allowable working stress,
maximum multiplication factor is 1.0 (para. 304.3.3(f3))
Assessment:
Area A2,A3, A4 and A5 to be multiplied by the ratio of allowable working
stress, maximum multiplication factor is 1.0 (para. 104.3.1(D.2.3))
Cap under internal pressure (104.4.1(B)):
Cap under internal pressure (304.4.1(b)):
Cap under internal pressure (831.372 and 831.373):
Can be calculated with ASME VIII div.1 UG-32 app.1-4
Can be calculated with ASME VIII div.1 UG-32 app.1-4
L = radius dish
L = radius dish
r = radius knuckle
r = radius knuckle
Can be calculated with ASME VIII div.1 UG-32 app.1-4
L = radius dish
r = radius knuckle
or
or
or
Flat closure under internal pressure (104.4.1(b)):
Flat closure under internal pressure (304.4.1(b)):
Flat closure under internal pressure (831.373):
Can be calculated with ASME VIII div.1 UG 34
Can be calculated with ASME VIII div.1 UG 34
Can be calculated with ASME VIII div.1 UG 34
ASME B31.1 (2008)
ASME B31.3 (2008)
ASME B31.8 (2007)
Flange under internal pressure (104.5.1(B)):
Flange under internal pressure (304.5.1(b)):
Flange under internal pressure (831.2):
Can be calculated according ASME VIII div.1 app. 2 using B31.3 allowable
stresses and temperature limits with:
Can be calculated according ASME VIII div.1 app. 2 using B31.3 allowable
stresses and temperature limits with:
Allowed to use:
ASME B16 series as listed in Appendix A such as B16.5.
= design gauge pressure
= design gauge pressure
= bolt design stress at atmospheric temperature
= bolt design stress at atmospheric temperature
= bolt design stress at design temperature
= bolt design stress at design temperature
= product SE
= product SEW
Blind flange under internal pressure (104.5.2(B)):
Blind flange under internal pressure (304.5.2(b)):
Can be calculated according ASME VIII div.1 UG-34 with:
Can be calculated according ASME VIII div.1 UG-34 with:
= sum of allowances
= internal design gauge pressure
= product SE
= pressure design thickness as per ASME VIII div. 1 UG-34
Blanks (spade) under internal pressure (304.5.3(B)):
Also MSS SP-44.
For slip-on welding flanges reference is made to ASME VIII div.1 design.
Can ASME VIII div.1 be used for calculation?
Blind flange under internal pressure:
Can ASME VIII div.1 be used?
= sum of allowances
= internal design gauge pressure
= product SEW
= pressure design thickness as per ASME VIII div. 1 UG-34
Blanks (spade) under internal pressure (304.5.3(b)):
Blanks (spade) under internal pressure:
Can ASME VIII div.1 be used?
= sum of allowances
= sum of allowances
ASME B31.1 (2008)
= inside diameter of gasket
ASME B31.3 (2008)
= inside diameter of gasket
ASME B31.8 (2007)
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Valve DatasheetsDocument21 pagesValve DatasheetsArya Evan PerdanaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Training Module 6 - PID PresentationDocument54 pagesTraining Module 6 - PID PresentationSergio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Viscosity by Efflux TimeDocument3 pagesViscosity by Efflux TimeAmit Jharbade67% (3)
- Part II - PumpsDocument242 pagesPart II - PumpsaaaNo ratings yet
- Water Feature 1,2,3Document15 pagesWater Feature 1,2,3Anonymous 6HjnToW6No ratings yet
- Repair of Rails On Site by Welding XA00127720Document20 pagesRepair of Rails On Site by Welding XA00127720wpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- SAEeDocument40 pagesSAEeAnonymous 4IpmN7OnNo ratings yet
- Radial Turbine ThesisDocument94 pagesRadial Turbine Thesisdamjan0611No ratings yet
- 24UTP Railway GBDocument8 pages24UTP Railway GBwpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- Method Statement: Long Carbon EuropeDocument4 pagesMethod Statement: Long Carbon EuropewpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- Bohler Welding Germany 176Document1 pageBohler Welding Germany 176wpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- WPS TranslarailDocument2 pagesWPS TranslarailwpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- Custo SoldagemDocument16 pagesCusto SoldagemwpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- Welding NormsDocument14 pagesWelding NormsimupathanNo ratings yet
- Rules For The Classification of Ships, Pt. 26, 2009 PDFDocument79 pagesRules For The Classification of Ships, Pt. 26, 2009 PDFdang2172014No ratings yet
- EN 1090 White Paper17 119019 PDFDocument24 pagesEN 1090 White Paper17 119019 PDFZaza PokumbaNo ratings yet
- CraneDocument44 pagesCraneEka KurobaNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument48 pagesCastingwpsssamsungNo ratings yet
- CraneDocument44 pagesCraneEka KurobaNo ratings yet
- SingerValve 106 PR UL Fire Valve Sheet Product PagesDocument2 pagesSingerValve 106 PR UL Fire Valve Sheet Product PagesAhlan kpNo ratings yet
- L8-Water Supply Pipe AppurtenancesDocument10 pagesL8-Water Supply Pipe AppurtenancesMidhun Chowdary100% (1)
- 8 20Q Basic Aerodynamics: 8.1 2 (3Q) Physics of The AtmosphereDocument27 pages8 20Q Basic Aerodynamics: 8.1 2 (3Q) Physics of The AtmosphereAkash Dey100% (1)
- CL351: Chemical Engineering Lab-II Semester 1, 2014-2015 IIT GandhinagarDocument7 pagesCL351: Chemical Engineering Lab-II Semester 1, 2014-2015 IIT GandhinagarPradeep DiwakarNo ratings yet
- US1851006 8566 Certified Test Curve 1Document5 pagesUS1851006 8566 Certified Test Curve 1Alvaro SernaNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub - 13 Deluge Valve HD Fire PDFDocument17 pagesIdoc - Pub - 13 Deluge Valve HD Fire PDFĐinh TrọngNo ratings yet
- Compressor Blow Down TankDocument4 pagesCompressor Blow Down Tankمحمد مجديNo ratings yet
- PUMP IN SERIES and PARRALEL FM51Document4 pagesPUMP IN SERIES and PARRALEL FM51Abenezer TasewNo ratings yet
- Agard TurbulenceDocument113 pagesAgard TurbulenceVivek KantiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To: Transport PhenomenaDocument11 pagesIntroduction To: Transport Phenomenadeepak patidarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Advanced Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageCourse Outline Advanced Fluid MechanicsTsegaye GetachewNo ratings yet
- ICH3800 Class 7: 1st Semester 2022Document92 pagesICH3800 Class 7: 1st Semester 2022catalinaNo ratings yet
- PPRC Rate List - 2019Document3 pagesPPRC Rate List - 2019naumandarNo ratings yet
- D1-160 LEWA Ecoflow-Metering-Pumps enDocument19 pagesD1-160 LEWA Ecoflow-Metering-Pumps encandra trisilawatiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Lecture Notes - 9Document13 pagesFluid Flow Lecture Notes - 9Lin Xian Xing100% (1)
- CHE 406, Spring 2020 (Lecture 5) Transport Phenomena (Chapter 2)Document26 pagesCHE 406, Spring 2020 (Lecture 5) Transport Phenomena (Chapter 2)Ahmad IjazNo ratings yet
- US2246038-Bomba Electrica 1 - Certified Test CurveDocument5 pagesUS2246038-Bomba Electrica 1 - Certified Test CurveFranklin Gustavo Zagaceta BautistaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics PDFDocument37 pagesHydraulics PDFaktk1234No ratings yet
- Fire Deluge Valve: 800 Series (Tubular Diaphragm Valve)Document2 pagesFire Deluge Valve: 800 Series (Tubular Diaphragm Valve)dmitosNo ratings yet
- RANQUE-HILSCH VORTEX TUBE-To StudentsDocument12 pagesRANQUE-HILSCH VORTEX TUBE-To StudentsMohamed MoatazNo ratings yet
- BEM NREL Phase VI PDFDocument218 pagesBEM NREL Phase VI PDFIjaz FazilNo ratings yet
- FM24 (A4) PDFDocument3 pagesFM24 (A4) PDFahmad pidotNo ratings yet
- Flow Coeffi Cients: Catalog # 77-1006ADocument8 pagesFlow Coeffi Cients: Catalog # 77-1006AFelipe Gamboa GálvezNo ratings yet