Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Graphics - 25 Questions Bank: Scale
Uploaded by
Warren RiveraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Graphics - 25 Questions Bank: Scale
Uploaded by
Warren RiveraCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Graphics - 25 Questions Bank
(a) Draw Isometric Projection using Isometric
Scale
(b) Draw Isometric View for following views.
(a)Draw the Isometric View from following.
(a)Draw Isometric Scale to Draw a line of 90 mm
(b)List the name of methods to draw Hyperbola and Ellipse.
(c) Differentiate between Aligned and Unidirectional Method of Dimensioning.
(d)Differentiate between Isometric Projection and Isometric Views to draw a sphere.
(a) Draw the following Isometric Views.
A pentagonal pyramid is having its base ABCDE and the apex O. the length of the axis is 80 mm and
the edge of base is 30 mm. the pyramid is resting on the HP with the edge CD on it. Draw the
projections when the axis of the pyramid is inclined at 30 to the HP and the plan of the axis of the
pyramid makes 45 with the VP.
A hexagonal prism with face width 30 mm and height 70 mm has its edge of base in the VP and
inclined at 60 to the HP. The base is inclined to the VP at 30 Draw the FV of the prism.
A cone having the diameter of base 80 mm and the height 90 mm is resting with its base on the HP it is
cut by AIP (Cutting plane) inclined at 450 to the HP. The cutting plane passes through the midpoint of
the axis of the cone. Draw the elevation, sectional plan and the true shape of the section.
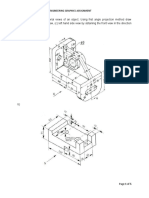
(a) Pictorial view of a machine component is
shown in Fig.
Draw: (1) F.V. From X (2) T.V. and (3) RHSV
from Y
(b) Draw the Isometric Views.
(b) Draw the F.V. and Sectional R.H.S.V.
A cylinder having the diameter of base 40 mm and the height 70 mm is resting with its base on the HP
it is cut by AIP (Cutting plane) inclined at 45 0 to the HP. The cutting plane passes through the midpoint
of the axis of the cylinder. Draw the elevation, sectional plan and the true shape of the section.
10
A tetrahedron of 70 mm long edges is lying on HP on one of its faces; with an edge of that face
perpendicular to the VP it is cut by a section plane perpendicular to both the reference plane in such a
way that the true shape of section in an isosceles triangle of 45 mm height. Draw elevation. Plan and
side view when smaller acute piece of the object is assumed to be removed.
11
Define Representative Fraction. Construct a plain scale of R.F. = 1:50 to show meters and decimeter
and long enough up to 8 meter. Indicate 6.7 m distance on scale.
12
A square pyramid, side of base 50 mm and height 64 mm, is freely suspended from one of the corners
of base. Draw its projections when vertical plane containing axis makes an angle of 45 o with the V.P.
13
The length of the Khandala tunnel on the Mumbai-Pune expressway is 330m. On the road map, it is
shown by a 16.5 cm long line. Construct a scale to show meter and to measure up to 400m. Show the
length of a 307 meter long on the expressway.
14
A throw of ball from boundary of a cricket ground reaches the wicket keepers gloves following the
parabolic path. Maximum height achieved by the ball above the ground is 31 meters. Assume the point
of throw and point of catching position 1 meter above the ground. Radial distance of boundary from
wicket keeper is 75 meters. Construct the path of ball.
15
Construct an ellipse when the distance of the directrix is equal to 50 mm and eccentricity is 2/3.
16
A cone, base 75 mm diameter and axis 80 mm long is resting on its base on the H.P. It is cut by a
section plane perpendicular to the V.P., inclined at 45 to the H.P. and cutting the axis at a 35 mm from
the apex. Draw front view, sectional top view and true shape of the section.
17
A circular plate of 60 mm diameter is resting on HP on a point A of its circumference. The plane is
inclined at 30 to the HP. The diameter AB of the plane makes an angle of 45 with the VP Draw the
projection of the circular plane.
18
A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls along the circumference of another circle of 150 mm diameter from
outside. Draw the path of a point P on the circumference of the rolling circle for one complete
revolution and name the curve.
19
A room is 7 m long, 5 m wide and 4 high. A chandelier hangs at the centre of the ceiling and 1.5 m
below it. A thin straight wire connects the chandelier to a nail in one of the corner edges of the room.
The nail is 1 m above the floor. Draw the projection and find TL of the wire.
20
A pentagonal pyramid of base 20 mm and height 50 mm has its triangular face in the VP with a shorter
side inclined to the HP at 300. Draw its projections.
21
A line CD has its end C is 15mm above H.P. and 10 mm in front of V.P. The end D is 60 mm above H.P.
The distance between the end projectors is 50 mm. The line is inclined to H.P. by 25. Draw the
projections and find its inclination with V.P. and true length of line CD and draw also traces.
22
A tetrahedron of 50 mm long edges is lying on HP on one of its faces with one of its edges
perpendicular to VP so that the true shape of its section is an isosceles triangle of base 40 mm and
altitude 28 mm. Find the inclination of the section plane with HP. Draw the front view, sectional top
view and the true shape of the section.
23
A tetrahedron, edge of base 30 mm, is held on H.P on one of its base corner points such that the slant
edge containing the base corner is inclined at 60o to H.P. and the base edge opposite the corner point
inclined at 45 to the V.P. Draw its projections.
24
Draw an involute of a line of 10 mm for 5 turns.
25
Draw an involute of a circular arc which subtends an angle of 90 o at the centre of the circle of diameter
120 mm.
You might also like
- 02 Parallel-Lines-Angles Practice With AnswersDocument5 pages02 Parallel-Lines-Angles Practice With AnswersvkumarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder - ReferenceDocument95 pagesHydraulic Cylinder - ReferenceWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- SM6 Catalog2006 enDocument92 pagesSM6 Catalog2006 enwilliam huaytaNo ratings yet
- Ed Example ProblemsDocument11 pagesEd Example ProblemsME GECNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 1-Phy443Document9 pagesLab Report Exp 1-Phy443firdaus100% (2)
- Digital Pipeline Leak Detection: Remote MonitoringDocument3 pagesDigital Pipeline Leak Detection: Remote MonitoringSARFRAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Chlorella Repeated Batch Growth Algaemist Panel PBR Day-Night Cycle - 1 - MinDocument110 pagesChlorella Repeated Batch Growth Algaemist Panel PBR Day-Night Cycle - 1 - MinAntonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- EG Unit 1Document7 pagesEG Unit 1Jayakrishna KandasamyNo ratings yet
- ED Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesED Important QuestionsNitin NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- Egd Lab ManualDocument11 pagesEgd Lab ManualPatel AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Qus PaperDocument6 pagesQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanNo ratings yet
- 9a03101c Engineering DrawingDocument7 pages9a03101c Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For MidDocument2 pagesImportant Questions For MidBalaji BaluNo ratings yet
- Drawing AssignmentDocument6 pagesDrawing AssignmentJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)A.R. Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5Document7 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5florenceprasadNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007No ratings yet
- E.G Q.B. Solutions - Part BDocument28 pagesE.G Q.B. Solutions - Part BTeegavarapu Sriram hrithikNo ratings yet
- Ex-Students Assignment ED, Deadline 08 JANDocument2 pagesEx-Students Assignment ED, Deadline 08 JANKunal BangNo ratings yet
- Anna University QuestionsDocument20 pagesAnna University QuestionsMurugan PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Graphics - Question BankimamuddeenNo ratings yet
- 9a03101b Engineering DrawingDocument5 pages9a03101b Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Eg QPDocument5 pagesEg QPSurulivelrajantNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDocument6 pagesEngineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- GE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankDocument11 pagesGE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankNatarajan AgoramNo ratings yet
- Anna University Question Bank For Engineering GraphicsDocument11 pagesAnna University Question Bank For Engineering GraphicsRajkumarNo ratings yet
- Engg. Drawing QuestionsDocument9 pagesEngg. Drawing QuestionsdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- CURVEDocument8 pagesCURVEjuber_nriNo ratings yet
- 9a03101e Engineering DrawingDocument4 pages9a03101e Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- GE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5Document7 pagesGE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5meckup123No ratings yet
- SET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Document8 pagesSET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Joel WallerNo ratings yet
- EnggqpDocument4 pagesEnggqpRambabuDaraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledSuyog ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Ge8152 GC A & B QuestionsDocument5 pagesGe8152 GC A & B QuestionsBalaChandarNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument3 pagesProblemRajesh JunghareNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankflorenceprasadNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 1Document10 pagesDrawing 2 Book-Ch 1Yasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Egd Manual-2023-24Document16 pagesEgd Manual-2023-24devambanugariya2803No ratings yet
- 9a03101a Engineering DrawingDocument7 pages9a03101a Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Projections of LineDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank: Projections of LineDevil GameNo ratings yet
- Eg Que BankDocument10 pagesEg Que BankAmey ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics AssignmentDocument5 pagesEngineering Graphics AssignmentVegeta899 vegetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document13 pagesUnit 5gansumaaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet CAEGDocument1 pageProblem Sheet CAEGPrabal JainNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics QB PDFDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics QB PDFKarthi SanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics Question BankSriram JNo ratings yet
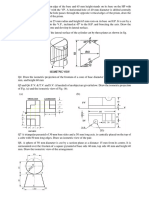
- Figure Shows The Pictorial Views of An Object. Using First Angle Projection Method DrawDocument5 pagesFigure Shows The Pictorial Views of An Object. Using First Angle Projection Method DrawmarysudhakarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Tutorial Question Bank - 0Document6 pagesEngineering Drawing Tutorial Question Bank - 0amsubra8874No ratings yet
- EG Question BankDocument11 pagesEG Question Bankganeshnaikoti143No ratings yet
- R7100107 Engineering GraphicsDocument3 pagesR7100107 Engineering GraphicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Plate For EgDocument4 pagesQuestion Plate For EgNagaraj Muniyandi0% (1)
- 2nd Sem EG-Questions 7 SheetsDocument7 pages2nd Sem EG-Questions 7 Sheetssunny045No ratings yet
- Model Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantDocument1 pageModel Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantculvertsNo ratings yet
- Anna University GE2111 Engineering Graphics Dec 2011 Question PaperDocument4 pagesAnna University GE2111 Engineering Graphics Dec 2011 Question PaperPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- 110013-Engineering Graphics Jun09Document3 pages110013-Engineering Graphics Jun09niketpatel3121No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument14 pagesAssignmentAdel AwadNo ratings yet
- Questions of Projection of PlanesDocument2 pagesQuestions of Projection of PlanesSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Engineering GraphicsDocument1 pageAssignment-Engineering GraphicsGoodmobo 123No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- Eg Question Bank - 2013Document18 pagesEg Question Bank - 2013kgmaheswaranNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-VDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Vramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Development of Surfaces - Isometric Projection-2 - 231124 - 133807Document1 pageDevelopment of Surfaces - Isometric Projection-2 - 231124 - 133807waahbetemojkardi123No ratings yet
- UNIT 06 Development of Lateral Surfaces Question BankDocument2 pagesUNIT 06 Development of Lateral Surfaces Question BanksirfentertertainmenthaiNo ratings yet
- Revision of Tariff in Students Special and Roam Free Plans Under Prepaid Mobile ServicesDocument1 pageRevision of Tariff in Students Special and Roam Free Plans Under Prepaid Mobile ServicesWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Toyota Kanban System PDFDocument10 pagesToyota Kanban System PDFAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Development of Kanban System at Local Manufacturing Company in Malaysia - Case StudyDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Kanban System at Local Manufacturing Company in Malaysia - Case StudyAarthy ChandranNo ratings yet
- PremiumTechnicals-Nov26 15 GammonDocument2 pagesPremiumTechnicals-Nov26 15 GammonWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Javascript InterviewDocument5 pagesJavascript InterviewWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Stuck in A Range: Punter's CallDocument4 pagesStuck in A Range: Punter's CallWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
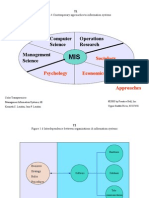
- Computer Science Operations Research Technical Approaches: Sociology Economics Psychology Behavioral ApproachesDocument101 pagesComputer Science Operations Research Technical Approaches: Sociology Economics Psychology Behavioral ApproachesWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Varshit Doshi: Mobile: +91 8866514555 Address: D-502, Sahaj Sapphire, Opp APMC MarketDocument2 pagesVarshit Doshi: Mobile: +91 8866514555 Address: D-502, Sahaj Sapphire, Opp APMC MarketWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Innovheads Design Studio: DT 09/12/15 Sr. No Size Inch SQ - Ft. Glass Work 1 2 3 4 5Document6 pagesInnovheads Design Studio: DT 09/12/15 Sr. No Size Inch SQ - Ft. Glass Work 1 2 3 4 5Warren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Managers and Their Information NeedsDocument34 pagesManagers and Their Information NeedsWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1-Carbon Fibre RainforcedDocument21 pages1-Carbon Fibre RainforcedWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Eneren Chillers & Heat Pumps Product Line - en - 2021Document2 pagesEneren Chillers & Heat Pumps Product Line - en - 2021Arun MuraliNo ratings yet
- GATE EE/ECCapacitorDocument9 pagesGATE EE/ECCapacitornarendra mauryaNo ratings yet
- Justus UK Kamine 2020 21Document112 pagesJustus UK Kamine 2020 21Paulo Cesar ArgôloNo ratings yet
- Topic 05 One Dimensional Kinematics NotesDocument28 pagesTopic 05 One Dimensional Kinematics NotesRukiezillaNo ratings yet
- DNR-DNRW DataSheet A05-0422Document4 pagesDNR-DNRW DataSheet A05-0422HAMDYNo ratings yet
- (PHYSB) TH02 KinematicsDocument23 pages(PHYSB) TH02 KinematicsJazz EsquejoNo ratings yet
- (Radition Poisoning) PPTDocument16 pages(Radition Poisoning) PPTDivithNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation in 2 Variables Class 9 CbseDocument9 pagesLinear Equation in 2 Variables Class 9 Cbseriya rajputNo ratings yet
- Calibration Requirements For Elemental Analysis of Petroleum Products and LubricantsDocument13 pagesCalibration Requirements For Elemental Analysis of Petroleum Products and LubricantsChulaka PitigalaNo ratings yet
- Ee6404 Measurements and InstrumentationDocument69 pagesEe6404 Measurements and InstrumentationAbiodun IloriNo ratings yet
- Ensayo para Tanque Criogenico PDFDocument9 pagesEnsayo para Tanque Criogenico PDFAlberto Acosta GongoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 and Chapter-4 Thermoelectric Effect and Chemical Effect of Current - SA Sir PDFDocument30 pagesChapter-3 and Chapter-4 Thermoelectric Effect and Chemical Effect of Current - SA Sir PDFKim MNo ratings yet
- Bhejni Hai 3Document69 pagesBhejni Hai 3sourabhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Chapter 12 Oxidation - ReductionDocument18 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Chapter 12 Oxidation - ReductionSairille ManejaNo ratings yet
- Sorcerous Origins: Radiation FreakDocument1 pageSorcerous Origins: Radiation FreakI love you Evans PeterNo ratings yet
- Nits AND Easurement: Hapter WODocument23 pagesNits AND Easurement: Hapter WOFelipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4che syakirNo ratings yet
- Subplate Mounting ISO 4401-05 P Max: Bar Max L/minDocument14 pagesSubplate Mounting ISO 4401-05 P Max: Bar Max L/minCarlos AugustoNo ratings yet
- 03 Rig InstrumentationDocument34 pages03 Rig InstrumentationArkhatTompakovNo ratings yet
- R6315 PDFDocument2 pagesR6315 PDFKasnowo DiponegoroNo ratings yet
- Hobart Handler 175 Wire Feed Problem OkDocument5 pagesHobart Handler 175 Wire Feed Problem OkSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- CEN 314-Lab 1: Introduction/Safety Alkalinity AcidityDocument8 pagesCEN 314-Lab 1: Introduction/Safety Alkalinity AcidityMuhammad Shaqeem RosdiNo ratings yet
- Dewatering Pump: Instruction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument5 pagesDewatering Pump: Instruction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualDeepNo ratings yet
- Me2203 PDFDocument31 pagesMe2203 PDFNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Property SheetDocument6 pagesProperty SheetsivaNo ratings yet