Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHY 215 Conservation of Energy
Uploaded by
JayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY 215 Conservation of Energy
Uploaded by
JayCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY215
Experiment for the Law of
Conservation of Energy
Objective: To study the law of conservation of energy as it is
applied to a free body diagram.
Theory:
When it is said that something is conserved, it is meant that
the quantity is a constant and does not change with time. It is a
somewhat surprising aspect of nature that when a body is in
motion, its position is changing with time,, its velocity is changing
with time, yet certain characteristics of that motion still remain
constant. One if these quantities served leads us to the law of
conservation of energy. In any closed system the total energy of
the system remains a constant. This is the law of conservation of
energy. There may be a transfer of energy from on form to
another, but the total energy remands the same. Observing a
body in free fall the body starts from restate the top, its velocity
zero, and thus its kinetic energy is zero. The total energy of the
body at the top is therefore all potential energy. Hence we use the
formula
E0=P E0 =mg h0
For the purpose of this experiment we want to plot the potential
energy, kinetic energy, and the total energy of the falling photo
gate as a function of height. In order to do so we must use the
following equations including the one up above. The total energy
at a point
Etotal=PE+ KE
So,
1
Etotal=mgh+ m v 2
2
Etotal=E 0=E f
Or
This would tell you,
1
Efinal =K E f = m v2f
2
Doing so will give us a graphical representation of all the energy
in terms of height.
Procedure: Items Used: meter stick, scale, photo gate, data
studio, Excel, Multiple picket fences taped together.
I.
II.
III.
First get your items set up properly
Tape your photo gates together
Connect your computer to data studio
IV.
Take a few practice runs of dropping your picket fences
through the photo gate
V.
Record your data and put it into Excel
VI. Measure the picket fence this is your starting height.
VII. Each point of the fence is 5cm apart so subtract 5 from
the total height until it hits zero or very close to it.
VIII. Calculate Potential, Kinetic, and Total energy at each
point.
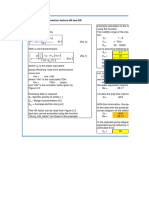
Data:
For the particular experiment the mass of the picket fence
was 129.20g the initial height was 71cm and the final height was
of course zero.
For example of initial energy:
E0=P E0 =mg h0
.129 kg 9.81
m
.71 m=.90 J
s2
For example of final energy:
1
Efinal =K E f = m v2f
2
1
m
.129 kg 3.73 =.90 J
2
s
Conclusion:
It is known that the final energy is equal to the initial energy.
From what is shown. The data gathered in this experiment was
used to calculate the kinetic, potential, and total energy at each
data point on the picket fence. The values that were calculated for
each energy at each data point support the theory that total
energy is equal to initial and final energy this can be shown
because the initial energy was .90 J
the final energy was .90 J
and the average total energy was .88 J . There is only 2.2% error
between the two. There could have been possible errors in the
data which might have been caused by the fence being drop
improperly. There could also be a chance that the picket fence hit
something while it was in free fall which would cause incomplete
data.
You might also like
- E201: Work, Energy and Power POLICIOUS, Mark Angelo FDocument5 pagesE201: Work, Energy and Power POLICIOUS, Mark Angelo FMark Angelo PoliciosNo ratings yet
- 6 Work and Energy 1Document14 pages6 Work and Energy 1John Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Winsem2018-19 Mee1003 TH Mb218 Vl2018195002924 Reference Material I TD Ppt1Document34 pagesWinsem2018-19 Mee1003 TH Mb218 Vl2018195002924 Reference Material I TD Ppt1Krishna LankaNo ratings yet
- Collision Lab - Air Track: Caleb BoampongDocument2 pagesCollision Lab - Air Track: Caleb Boampongapi-320251737No ratings yet
- Lab 126 Darshan PatelDocument7 pagesLab 126 Darshan PatelDarshan Patel0% (2)
- Lab 14Document2 pagesLab 145377773No ratings yet
- Experiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Page - 1Document6 pagesExperiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Page - 1Clemente Abines IIINo ratings yet
- Basic Science 3rd TermDocument15 pagesBasic Science 3rd TermIfekunmiNo ratings yet
- Mehek Gupta - PHYS 223-04 Lab 6Document6 pagesMehek Gupta - PHYS 223-04 Lab 6Ishani TarkarNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument36 pagesEnergyyuxing lieNo ratings yet
- PHY11L Experiment 1Document7 pagesPHY11L Experiment 1Rhon AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 39: Kinetic Energy & Potential EnergyDocument7 pagesLesson 39: Kinetic Energy & Potential EnergyHarryNo ratings yet
- 5energy Textbook V 1-1.1Document35 pages5energy Textbook V 1-1.1Kaiden KinseyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Physical Laboratory Practices Year 2018Document50 pagesMechanical Physical Laboratory Practices Year 2018Miller PerezNo ratings yet
- Experiment Em-4: Conservation of Energy 1.0 Learning OutcomesDocument3 pagesExperiment Em-4: Conservation of Energy 1.0 Learning OutcomesHaziq HakimieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Work, Power and EnergyDocument6 pagesChapter 8-Work, Power and EnergyLesther James CastroNo ratings yet
- Newtons Second LawDocument7 pagesNewtons Second LawPrinces Katherine Vergara100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5 Work, Energy, and Energy ConservationDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 5 Work, Energy, and Energy ConservationRolando Jerome MagoNo ratings yet
- NRG Conservation of Energy - Maximize The Mechanical Energy of A Rollercoaster Lab Manual EnglishDocument7 pagesNRG Conservation of Energy - Maximize The Mechanical Energy of A Rollercoaster Lab Manual EnglishDISTOR, JOSH GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Summer Experiment 5 (Physics For Eng) .UpdatedDocument6 pagesSummer Experiment 5 (Physics For Eng) .Updatedjhayve stephen mark patrimonioNo ratings yet
- Laboratory #8: Student Horsepower: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLaboratory #8: Student Horsepower: Objectivealpha omegaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Potential and Kinetic EnergyDocument15 pagesModule 3 - Potential and Kinetic EnergyLaiza GranaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry CollegeDocument115 pagesThermochemistry CollegeBlanche Iris Estrel SiapnoNo ratings yet
- NewtonssecondlawDocument10 pagesNewtonssecondlawapi-276881836No ratings yet
- Ch06 SlidesDocument73 pagesCh06 SlidesbeelzeburtonNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 MEE1003 TH VL2020210103023 Reference Material I 31-Jul-2020 First Law of Thermodynamics - IIDocument52 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 MEE1003 TH VL2020210103023 Reference Material I 31-Jul-2020 First Law of Thermodynamics - IIRahul rajelliNo ratings yet
- Energy (Physics)Document90 pagesEnergy (Physics)Christina SterlingNo ratings yet
- Phy11l - E201Document4 pagesPhy11l - E201Idate PatrickNo ratings yet
- Sci 8 L4-EnergyDocument19 pagesSci 8 L4-EnergyTorres Jhon Chriz GabrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Work Energy and Power (Lecturer Only)Document52 pagesChapter 4 Work Energy and Power (Lecturer Only)Jerome FizzowNo ratings yet
- Verification of Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy Using Air TrackDocument6 pagesVerification of Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy Using Air Tracksenior highNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document5 pagesLab Report 2Joseph Bernard Cantre DalusongNo ratings yet
- Chem 101 Chapter 5: Üsküdar UniversityDocument85 pagesChem 101 Chapter 5: Üsküdar UniversityNora Zor-elNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Student NameDocument13 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics: Student NameShehbazShoukatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 "Work and Energy": Honors PhysicsDocument68 pagesChapter 5 "Work and Energy": Honors PhysicsNick Andrew Dequilla NiervaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Romar King D. Celebre, 2011104475, BS CEM-2Document5 pagesExperiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Romar King D. Celebre, 2011104475, BS CEM-2Romar King CelebreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Work and EnergyDocument68 pagesChapter 5 Work and EnergyDylan HNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document83 pagesChapter 06ken020439No ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document31 pagesGeneral Physics 1Ali aliraqiNo ratings yet
- Work, Power, Energy WorksheetDocument6 pagesWork, Power, Energy WorksheetDato Dato DatoNo ratings yet
- Tes 3 Practice Test-SolutionsDocument9 pagesTes 3 Practice Test-Solutionsdavidchoikekekek100% (1)
- Laboratory Report in LBYPH11Document4 pagesLaboratory Report in LBYPH11Bernard Jomari Blancada RazoteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: Cengel Florio 14FDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction: Cengel Florio 14Fs73a1thNo ratings yet
- Lec.3 TPDocument20 pagesLec.3 TPhamaNo ratings yet
- 09 Rotational Kinetic EnergyDocument4 pages09 Rotational Kinetic EnergylacbNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics - L-4 - JLD 3.0Document57 pagesChemical Thermodynamics - L-4 - JLD 3.0PpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Work Energy and PowerDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Work Energy and PowerGimarino Lahra MaeNo ratings yet
- Which of These Are Stores, Which Are Transfers?: Energy Store Energy TransferDocument8 pagesWhich of These Are Stores, Which Are Transfers?: Energy Store Energy TransferchrisNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document11 pagesModule 3Teofilo Matthew AriñoNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument9 pagesWork, Energy and PowerAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- John Andre Cagampang - GPHY1 - Q2 - Module8 - Wk8 ANSWERSDocument16 pagesJohn Andre Cagampang - GPHY1 - Q2 - Module8 - Wk8 ANSWERSAndrejohn CagampangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Work, Power and Energy Formal ReportDocument3 pagesExperiment 7: Work, Power and Energy Formal Reportroyce_navera3_1415926535897932No ratings yet
- Impulse - MomentumDocument5 pagesImpulse - MomentumMichael CaingletNo ratings yet
- Physics Ia First DraftDocument2 pagesPhysics Ia First DraftKingsley JuniorNo ratings yet
- Co777Document10 pagesCo777Rafi HossainNo ratings yet
- Work & EnergyDocument8 pagesWork & EnergyOrlee Villafañe JrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1Chris RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Casio Aq140w UputstvoDocument1 pageCasio Aq140w UputstvoalazovicNo ratings yet
- UTAR Convocation Checklist For Graduands Attending Convocation (March 2019) - 1Document5 pagesUTAR Convocation Checklist For Graduands Attending Convocation (March 2019) - 1JoyleeeeeNo ratings yet
- Economics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesEconomics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceigcsepapersNo ratings yet
- JD Data Analyst CapgeminiDocument2 pagesJD Data Analyst CapgeminiShivansh KansalNo ratings yet
- Case Studies Public LibraryDocument4 pagesCase Studies Public LibraryHimalya Kaim83% (6)
- Mike She Printed v1Document370 pagesMike She Printed v1Grigoras MihaiNo ratings yet
- PiraeusDocument9 pagesPiraeusBen JamesNo ratings yet
- Job Search & Interview Skills: or Some Real-World Advice That May Prove Useful To YouDocument97 pagesJob Search & Interview Skills: or Some Real-World Advice That May Prove Useful To YouShah NawazNo ratings yet
- Modern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesDocument10 pagesModern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesCristina AronNo ratings yet
- Belgian Overseas Chartering and Shipping NDocument2 pagesBelgian Overseas Chartering and Shipping NMXKatNo ratings yet
- Manual de Serviços QQ PDFDocument635 pagesManual de Serviços QQ PDFLéo Nunes100% (1)
- Allison at 500, at 1500 Series Parts Catalog: 2 1 See Section 10Document7 pagesAllison at 500, at 1500 Series Parts Catalog: 2 1 See Section 10amin chaabenNo ratings yet
- Cost Justifying HRIS InvestmentsDocument21 pagesCost Justifying HRIS InvestmentsNilesh MandlikNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci 10 12-09-2022Document3 pagesDLL Sci 10 12-09-2022Lovely Shiena Cain AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- Test Your Skills For Computer Basics: November 2013Document24 pagesTest Your Skills For Computer Basics: November 2013Charie C. OrbocNo ratings yet
- Indiabulls PILDocument64 pagesIndiabulls PILPGurus100% (1)
- MT7605B DSDocument7 pagesMT7605B DSVishal dtuNo ratings yet
- Iata 2008 - Annex ADocument11 pagesIata 2008 - Annex Agurungbhim100% (1)
- k90mcc6 PDFDocument381 pagesk90mcc6 PDFTammy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MEMORIAL ON BEHALF OF APPELLANTS DocsDocument29 pagesMEMORIAL ON BEHALF OF APPELLANTS DocsPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Ahi Evran Sunum enDocument26 pagesAhi Evran Sunum endenizakbayNo ratings yet
- ''Adhibeo'' in LatinDocument5 pages''Adhibeo'' in LatinThriw100% (1)
- 01 FundamentalsDocument20 pages01 FundamentalsTay KittithatNo ratings yet
- Is LNG Still Competitive With Other Liquid Fuels?: Proceedings, Ascope'97 ConferenceDocument18 pagesIs LNG Still Competitive With Other Liquid Fuels?: Proceedings, Ascope'97 Conferencemanolo8catalanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Climate Change in NigeriaDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Climate Change in Nigeriac5rn3sbr100% (1)
- New Micra BrochureDocument14 pagesNew Micra BrochureGlobalGroupOfDealersNo ratings yet
- CS8792 CNS Unit5Document17 pagesCS8792 CNS Unit5024CSE DHARSHINI.ANo ratings yet
- Warman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q PDocument2 pagesWarman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q Pyoel cueva arquinigoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PythonDocument10 pagesUnit 5 PythonVikas PareekNo ratings yet
- Operating Instruction PMD55Document218 pagesOperating Instruction PMD55Dilip ARNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxFrom EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)