Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set 2 Completed
Uploaded by
Abhishek SuranaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set 2 Completed
Uploaded by
Abhishek SuranaCopyright:
Available Formats
ECON 213
PROBLEM SET 2
Name: _____________________
Problem Set 2 is to be completed by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Monday of Module/Week 4.
1. The following table presents data for wages in the market for internet security
professionals.
(HINT: in the labor market the roles are reversed. Those who want to hire labor are the
demanders. The workers enter the work force providing labor to the market place so they
are the suppliers.)
Wage
Quantity Demanded
Quantity Supplied
$50,000
20,000
14,000
$60,000
18,000
18,000
$70,000
16,000
22,000
$80,000
14,000
26,000
$90,000
12,000
30,000
What is the equilibrium wage? ___ ___$60,000________
Now, consider this scenario: Due to an increase in the internet security threats, the
government wants to apply a price control in this market to encourage more people to
become internet security professionals. Assume that a wage control is set at $75,000. Will
this increase the number of people entering this labor market? Why or why not? Will this
increase the number of people hired? Why or why not?
Yes, because people want to make more money.
No, because businesses will not hire as many people when they have to pay more for their
labor.
Page 1 of 2
ECON 213
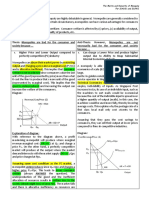
2. Assume you are a policymaker in Washington DC. Lobbyists for the preschoolers of
America have put pressure on their representatives to cap prices on graham crackers.
You have been assigned a position on a new committee to study the impact of a price
ceiling on graham crackers.
Your job is to:
a.) Illustrate using a fully labeled supply and demand graph (label all the axes and
any lines you put in your graph) what such an artificial price looks like. On
attached document.
b.) Explain what the results of such a move are for the graham cracker market. In
other words, will there be a SHORTAGE, a SURPLUS, or neither created? Why?
There will be a shortage because consumer demand will be so high that
producers will not be able to produce the amount demanded due to a limited
amount of resources.
3. Pollution is considered by most a negative externality. Some economists would like to
see the costs of these burdens incorporated into the price of goods that we buy. For
instance, since coal fire power plants increase emissions that could potentially lead to
climate change, these economists believe that the price we pay for electricity is not
adequately high enough. Draw a completely labeled graph and illustrate on the graph
how much higher electricity prices would be if the full costs of electricity production
were taken into account. You do not need to provide actual numbers; rather, show on
the price axis where the price would be before the externality is considered and the
price after the externality is included. What problems might exist in determining this
new, externality based, price?
(Graph is on attached document)
Problems would be figuring out if people would still purchase the same amount of
electricity after externalities because a lot people have no other options; they have
no other electricity provider of means of acquiring electricity. Also, does the
externailities create external cost or external benefire for consumers and producers?
4. In the old days lighthouses were built along the coast to prevent ships from running
aground on rocks in unfamiliar ports. By shining a beam of light over a port and
guiding ships away from rocks, these vital buildings reduced the risk for ship captains
and were generally considered to be extremely valuable resources. Curiously,
lighthouses were almost always run and maintained by local governments. Explain in
economic terms why private firms would not run a lighthouse.
Lighthouses would be considered public property and the total cost of the government
running them would be cheaper than if a private firm ran the lighthouse.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Electricity Marginal Cost Pricing: Applications in Eliciting Demand ResponsesFrom EverandElectricity Marginal Cost Pricing: Applications in Eliciting Demand ResponsesNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Introduction To Micro-Economics Level: Ma / MSCDocument14 pagesCourse Name: Introduction To Micro-Economics Level: Ma / MSCMuhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Demand-Side View of Electricity Markets: Daniel S. Kirschen, Senior Member, IEEEDocument8 pagesDemand-Side View of Electricity Markets: Daniel S. Kirschen, Senior Member, IEEESteven Voltage HumenaNo ratings yet
- Business economic analysis tutorial questionsDocument11 pagesBusiness economic analysis tutorial questionsammon mabukuNo ratings yet
- Thesis Electricity MarketDocument4 pagesThesis Electricity MarketJackie Taylor100% (2)
- Power Shortage 3Document7 pagesPower Shortage 3Demisachew Tena100% (1)
- HW cH.7Document3 pagesHW cH.7Darin PromthedNo ratings yet
- Consumer views on solar energy productsDocument29 pagesConsumer views on solar energy productsAmit GusainNo ratings yet
- Q 1: Read The Following Text and Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument5 pagesQ 1: Read The Following Text and Then Answer The Questions That Followداود عزNo ratings yet
- The Value of Net MeteringDocument6 pagesThe Value of Net MeteringAbhishek LingwalNo ratings yet
- ECO3110 Assignment1 Sep 20112012Document7 pagesECO3110 Assignment1 Sep 20112012Razif RoketmanNo ratings yet
- 26 Economies and Diseconomies of ScaleDocument5 pages26 Economies and Diseconomies of ScaleAvikshita JoarderNo ratings yet
- Watt's#32 PowerpoliticsDocument2 pagesWatt's#32 PowerpoliticsJoDueckNo ratings yet
- 2020 SPRING Final Exam Environmental Economics and Policy 101 Economics 125Document8 pages2020 SPRING Final Exam Environmental Economics and Policy 101 Economics 125JL HuangNo ratings yet
- 2001 August - Steve Thomas - The Electricity Wholesale Market in The UK 1990-2001Document18 pages2001 August - Steve Thomas - The Electricity Wholesale Market in The UK 1990-2001Susanne Namer-WaldenstromNo ratings yet
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms for Reducing Greenhouse Gas EmissionsDocument3 pagesCarbon Pricing Mechanisms for Reducing Greenhouse Gas EmissionsNaman AroraNo ratings yet
- The Strong Economics of Wind EnergyDocument4 pagesThe Strong Economics of Wind EnergyMahad AbdiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Balancing Energy MarketDocument39 pagesAnalysis of The Balancing Energy MarketRobertMcCulloughNo ratings yet
- EC 307 Summer Flexi Tutorial 1 - SolutionsDocument6 pagesEC 307 Summer Flexi Tutorial 1 - SolutionsR and R wweNo ratings yet
- ECO603m: Price discrimination and efficiencyDocument4 pagesECO603m: Price discrimination and efficiencyNeale CacNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Designing and Evaluating Realistic Blockchain-Based Local Energy MarketsDocument17 pagesA Framework For Designing and Evaluating Realistic Blockchain-Based Local Energy Marketsamira dhorbaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Predictions For The Electric 2014Document19 pages10 Predictions For The Electric 2014lancenglotNo ratings yet
- Rising Utility Construction CostsDocument37 pagesRising Utility Construction Coststline1999No ratings yet
- The True Economics Behind Energy ProjectsDocument4 pagesThe True Economics Behind Energy ProjectsrajuanthatiNo ratings yet
- Chat Transcript January 26, 2010Document7 pagesChat Transcript January 26, 2010careysonNo ratings yet
- Homework 1B - G6Document4 pagesHomework 1B - G6CHUA JO ENNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Solutions 8Document5 pagesTutorial Solutions 8da3rXNo ratings yet
- Insta Grid SummaryDocument23 pagesInsta Grid SummaryShawn Paul Boike100% (2)
- Combinatorial Markets For Efficient Energy ManagementDocument7 pagesCombinatorial Markets For Efficient Energy Managementapi-3697505No ratings yet
- 158313695Document55 pages158313695Amer AlmansoryNo ratings yet
- Econ 101 A Final PracticeDocument5 pagesEcon 101 A Final PracticeateiskaNo ratings yet
- Economic Capacity Withholding: Effects of Power Plant Operational Characteristics On Optimal Dispatch DecisionsDocument19 pagesEconomic Capacity Withholding: Effects of Power Plant Operational Characteristics On Optimal Dispatch DecisionsSushayan HunsasukNo ratings yet
- Quota Modeling in Hydrothermal Systems: M. M. Belsnes, A. Haugstad and B. Mo, SINTEF Energy Research, P. Markussen, ElsamDocument6 pagesQuota Modeling in Hydrothermal Systems: M. M. Belsnes, A. Haugstad and B. Mo, SINTEF Energy Research, P. Markussen, ElsamItalo ChiarellaNo ratings yet
- Least-Cost Planning Issues and Methods for Electric UtilitiesDocument9 pagesLeast-Cost Planning Issues and Methods for Electric UtilitieszhaobingNo ratings yet
- Course Notes For EE394V Restructured Electricity Markets: Locational Marginal PricingDocument62 pagesCourse Notes For EE394V Restructured Electricity Markets: Locational Marginal PricingLTE002No ratings yet
- Textbook Electricity Markets Elearning 2008 With Cover Eng FINAL PDFDocument68 pagesTextbook Electricity Markets Elearning 2008 With Cover Eng FINAL PDFAnis.MNo ratings yet
- Merits and Demerits of MPYDocument4 pagesMerits and Demerits of MPYCharlyne SeahNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1Document47 pagesSeminar 1Jonathan AndersenNo ratings yet
- Thesis Solar Power SystemDocument4 pagesThesis Solar Power Systemandreajimenezomaha100% (2)
- cmt2s Tutorial Week 2 SolutionsDocument5 pagescmt2s Tutorial Week 2 SolutionsBáchHợpNo ratings yet
- 801-2 CDocument15 pages801-2 CMuhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Market DesignDocument24 pagesElectricity Market DesignrtorrescoralNo ratings yet
- Chapter One SampleDocument7 pagesChapter One SampleChimzy IwumuneNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Grid DefectionDocument4 pagesThe Economics of Grid DefectionBernie C. MagtalasNo ratings yet
- The Effect of The Transmission Grid On Market Power: Steven StoftDocument32 pagesThe Effect of The Transmission Grid On Market Power: Steven StoftRicky MaloneNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument63 pages8 PDFHunter cNo ratings yet
- How Predictable Is Technological ProgressDocument29 pagesHow Predictable Is Technological ProgressAaron WuNo ratings yet
- Addisu M Research ProposalDocument16 pagesAddisu M Research ProposalAddisu MengeshaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension: Smart EnergyDocument4 pagesReading Comprehension: Smart EnergyK.35Kevin Elky TimothyNo ratings yet
- Abadie13 InvestmentEnergyAssetsUncertaintyDocument193 pagesAbadie13 InvestmentEnergyAssetsUncertaintynormanmvaNo ratings yet
- Using Heat Rates in Production Cost and Market ModelingDocument124 pagesUsing Heat Rates in Production Cost and Market Modelingnclarke6No ratings yet
- More Practice Problems CH 1-5 EconomicsDocument23 pagesMore Practice Problems CH 1-5 EconomicsAdam GillNo ratings yet
- Jacksoncarter ReasearchproposalDocument4 pagesJacksoncarter Reasearchproposalapi-310040346No ratings yet
- General Equilibrium Incidence of Energy TaxationDocument14 pagesGeneral Equilibrium Incidence of Energy Taxationnicolas rojasNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Distributed GenerationDocument40 pagesAn Introduction To Distributed GenerationNopadol PrasertkanchanaNo ratings yet
- The Energy Sectors Perfect Storm ZdnetDocument3 pagesThe Energy Sectors Perfect Storm Zdnetapi-263198911No ratings yet
- Complite Cost of CapitaDocument41 pagesComplite Cost of CapitaAmrit TejaniNo ratings yet
- On An "Energy Only" Electricity Market Design For Resource AdequacyDocument39 pagesOn An "Energy Only" Electricity Market Design For Resource AdequacyEsteban GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Diseño Del Mercado Eléctrico - Peter CramtonDocument24 pagesDiseño Del Mercado Eléctrico - Peter Cramtonjuan manuelNo ratings yet
- 07 Paying For The Smart Grid 1 2Document25 pages07 Paying For The Smart Grid 1 2bvasconezNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument13 pagesBusiness PlanAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Precise Data Business Plan PDFDocument12 pagesPrecise Data Business Plan PDFAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Comparisonnetwork-Based Approach and A Gantt ChartDocument4 pagesComparisonnetwork-Based Approach and A Gantt ChartAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- FIN 341 - Quiz#3 - Based On Exercise#3 Due Date - To Be DeterminedDocument6 pagesFIN 341 - Quiz#3 - Based On Exercise#3 Due Date - To Be DeterminedAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- MaytagDocument2 pagesMaytagAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- $13,511.28 Highest Present Value Financial Theory Supports Choosing Option CDocument5 pages$13,511.28 Highest Present Value Financial Theory Supports Choosing Option CAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- FIN 341 - Quiz#6 - Based On - Exercise#6: Due Date - 3-03-15 - Tuesday-MidnightDocument5 pagesFIN 341 - Quiz#6 - Based On - Exercise#6: Due Date - 3-03-15 - Tuesday-MidnightAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Sheet1: Workings 2013 2012 Liquidity RatiosDocument1 pageSheet1: Workings 2013 2012 Liquidity RatiosAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Discussion 2Document2 pagesWeek 3 - Discussion 2Abhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- FIN 341 Payback Method Calculation ExamplesDocument3 pagesFIN 341 Payback Method Calculation ExamplesAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- DSF Report 24022015 VapDocument9 pagesDSF Report 24022015 VapAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- 326 Project 1 Spring15 Workbook. - DonexlsxDocument41 pages326 Project 1 Spring15 Workbook. - DonexlsxAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Ethics AssignmentDocument1 pageEthics AssignmentAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Fin 341 Quiz#5 Basedonexercise#5Document5 pagesFin 341 Quiz#5 Basedonexercise#5Abhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Finance DiscussionsDocument4 pagesFinance DiscussionsAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Health WK 4 - Wilson ResponseDocument2 pagesHealth WK 4 - Wilson ResponseAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Finance DiscussionsDocument4 pagesFinance DiscussionsAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- $13,511.28 Highest Present Value Financial Theory Supports Choosing Option CDocument5 pages$13,511.28 Highest Present Value Financial Theory Supports Choosing Option CAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Business MemoDocument1 pageBusiness MemoAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology WK 9 - Proff ResponseDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology WK 9 - Proff ResponseAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- CH 5 - 6 ProblemsDocument4 pagesCH 5 - 6 ProblemsAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9 SolutionDocument13 pagesExercise 9 Solutionsl00redNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Wk3-Baker ResponseDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Wk3-Baker ResponseAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Math 135Document2 pagesMath 135Abhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- AdlyDocument1 pageAdlyAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology WK 2-DQ-Challenging QuestionDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology WK 2-DQ-Challenging QuestionAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Annual Report Project (ARP)Document17 pagesAnnual Report Project (ARP)Abhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology - Wk2 AssignmentDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology - Wk2 AssignmentAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology WK 2-DQ-Challenging QuestionDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology WK 2-DQ-Challenging QuestionAbhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Config FICODocument72 pagesStep by Step Config FICOswetha devarakondaNo ratings yet
- 21 Tapping Into Global MarketsDocument21 pages21 Tapping Into Global Marketsjenicejoy100% (4)
- Final Year DocumentationDocument23 pagesFinal Year Documentation5C0 PENDLIMARRI REDDYSAI VARDHANNo ratings yet
- Background & Theory of Relationship Marketing: Compiled by DR Rosaline FernandezDocument26 pagesBackground & Theory of Relationship Marketing: Compiled by DR Rosaline FernandezOmar SanadNo ratings yet
- Equity Valuation Report - TESCODocument2 pagesEquity Valuation Report - TESCOFEPFinanceClub100% (1)
- Trading TermDocument3 pagesTrading Termanrea100% (1)
- Last Assignment by Sajjad Malik v2Document56 pagesLast Assignment by Sajjad Malik v2muzamilmf5No ratings yet
- MBA Distribution & Supply Chain Management Course PackDocument19 pagesMBA Distribution & Supply Chain Management Course PackakshayNo ratings yet
- smbp10 Studentppt08Document21 pagessmbp10 Studentppt08Miks EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Unit11-Unit16Document4 pagesVocabulary Unit11-Unit16Anna EgriNo ratings yet
- Canvas: Created By: Emad SaifDocument35 pagesCanvas: Created By: Emad SaifNurul HikmahNo ratings yet
- For Emerging Economies: Power LeaderDocument20 pagesFor Emerging Economies: Power LeadertarkdeepڪNo ratings yet
- PDF Book Read MeDocument3 pagesPDF Book Read MenevatiamlmNo ratings yet
- Sales Budgeting: Sales and Distribution ManagementDocument9 pagesSales Budgeting: Sales and Distribution ManagementBalramNo ratings yet
- CLF 2nd Grading Cycle 1Document10 pagesCLF 2nd Grading Cycle 1SEM06-G32-Velasco, Geryne D.No ratings yet
- DHL's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and ThreatsDocument2 pagesDHL's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and ThreatsDulanji Imethya YapaNo ratings yet
- JPIM GanjilDocument8 pagesJPIM GanjilNanda Juragan Sandal JepitNo ratings yet
- MKT STGDocument106 pagesMKT STGAmeya Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Mishkin FMI9ge PPT C04Document65 pagesMishkin FMI9ge PPT C04kbica21No ratings yet
- JPM - Insurance PrimerDocument104 pagesJPM - Insurance Primerbrettpeven50% (2)
- M-127244 Nea 361Document2 pagesM-127244 Nea 361Lonely NessNo ratings yet
- DerivDocument34 pagesDerivhim4ughz0% (1)
- PDF p2 Guerrero Ch15 CompressDocument27 pagesPDF p2 Guerrero Ch15 CompressWillisNo ratings yet
- Black Scholes Option Pricing Model For Selected StocksDocument12 pagesBlack Scholes Option Pricing Model For Selected StocksAyushmaan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Nirmal Bang Securities Pvt. LTD Company ProfileDocument7 pagesNirmal Bang Securities Pvt. LTD Company ProfileTeja Choudhary Medarametla100% (2)
- Perfromance Task 2nd Quarter UcspDocument18 pagesPerfromance Task 2nd Quarter Ucsppalmajulius365No ratings yet
- Prec. Wires (I)Document9 pagesPrec. Wires (I)AnilKumarNo ratings yet
- Plan Your Online Business StrategyDocument9 pagesPlan Your Online Business StrategyivyNo ratings yet
- 05 Activity 1 - ARG (Reinald Zach Ramos)Document2 pages05 Activity 1 - ARG (Reinald Zach Ramos)Dan DalandanNo ratings yet
- International School of Asia and The Pacific Management Advisory Services Institutional ReviewDocument27 pagesInternational School of Asia and The Pacific Management Advisory Services Institutional ReviewCharles BarcelaNo ratings yet
- Kleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldFrom EverandKleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (25)
- The Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldFrom EverandThe Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenFrom EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNo ratings yet
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereFrom EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsFrom EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomFrom EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNo ratings yet
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaFrom EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo ratings yet
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentFrom EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (92)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsFrom EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyFrom EverandThe Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistFrom EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- Kaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineFrom EverandKaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)
- Poor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyFrom EverandPoor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (263)
- How an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionFrom EverandHow an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (102)