Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set Waves and Wave Properties
Uploaded by
Yohana Glorya TobingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set Waves and Wave Properties
Uploaded by
Yohana Glorya TobingCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:________________________________________________Date:____________________
Unit 10
Waves and Wave Properties
Problem Set 10
Part One: General Wave Concepts
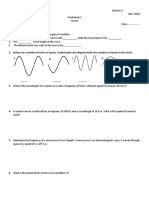
1. For the graph below, identify the crest, trough, wavelength and amplitude.
2. How are mechanical waves (such as sound waves) these different from electromagnetic waves (such
as light waves)?
3. How do transverse and longitudinal waves differ?
4. Identify which wave on diagram to the right is longitudinal
and which is transverse.
5. Are sound waves longitudinal or transverse waves? Are light waves longitudinal or transverse
waves?
6. As a result of a distance explosion, an observer first sees the explosion, then hears the it. What
accounts for this time lag? (why do you see it before you hear it?)
7. If the explosion had taken place in outerspace, how would what the observer sees and hears be
different?
8. As a wave passes by a duck floating on a lake, the duck bobs up and down but remains in essentially
one place. Explain why the duck is not carried along by the wave motion.
9. What is the difference between constructive interference and destructive interference?
10. Using the superposition principle, draw the resultant waves for each of the examples below.
11. Which picture below demonstrates two waves interfering constructively?
12. Which wave below is the resultant wave created by the other two?
13. Look at the standing wave shown here. How many nodes does this wave have? How many
antinodes?
Question #13
Question #11
Question #12
Part Two: Sound Wave Concepts
14. Two tuning forks with frequencies of 256 Hz and 512 Hz are struck. Which of the sound will move
faster through the air?
15. What is the only way to change the speed of which sound travels?
16. Look at the list below: Choose which of the follow factors change when a sound gets louder.
17. Look at the list below: Choose which changes when a pitch gets higher.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
Intensity
Speed of the sound wave
Frequency
Decibel level
Wavelength
Amplitude
Name:________________________________________________Date:____________________
Part Three: Electromagnetic Wave Concepts
18. Identify which type of wave (which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum) is used in each of the
devices.
a.
b.
c.
d.
19.
20.
21.
22.
A microwave oven, radar
A television set, GPS
A single-lens camera
Cancer treatments
How fast do X-rays travel in a vacuum? Microwaves? Visible light?
Which band of the electromagnetic spectrum has the lowest frequency?
Which band of the electromagnetic spectrum has the shortest wavelength?
Why do astronomers observing distant galaxies talk about looking backward in time?
Part Four: The Doppler Effect Concepts
23. If a star is moving away from Earth, will it be red shifted or blue shifted?
24. If a star is moving toward the Earth, will it be red shifted or blue shifted?
25. The diagram below depicts the Doppler Effect as it relates to sound. In this diagram, which
listener (A or B) hears a higher pitch (a higher frequency wave)?
Part Five: Problem Solving
26. A piano emits frequencies that range from a low of about 28Hz to a high of about 4200Hz. Find the
wavelength of each in air attained by this instrument when the speed of sound is air is 340m/s.
27. Yellow light travels through a certain glass block at a speed of 1.97x10 8m/s. The wavelength of the
light in this particular type of glass is 3.81x10-7m (381nm). What is the frequency of the yellow light
in the glass block?
28. What is the wavelength of a middle C-note if its frequency is 262 Hz?
29. Gamma-ray bursters are objects in the universe that emit pulses of gamma rays with high energies.
The frequency of the most energetic bursts has been measured at around 3.0x10 21 Hz. What is the
wavelength of these gamma rays?
30. The smallest insects that a bat can detect are approximately the size of one wavelength of the sound
the bat makes. What is the minimum frequency of sound waves required for the bat to detect an
insect that is 0.57cm long? (Assume the speed of sound is 340m/s).
31. The red light emitted by a He-Ne laser has a wavelength of 633 nm in air and travels at 3.00x10 8m/s.
Find the frequency of the laser light.
32. The portion of the visible spectrum that appears brightest to the human eye is around 560nm in
wavelength, which corresponds to yellow-green. What is the frequency of 560nm light?
33. What is the frequency of a sound wave produced by a flute playing C-note if the wavelength is 21m?
34. What is the frequency of highly energetic ultraviolet radiation that has a wavelength of 125nm?
35. What is the wavelength of a radar signal that has a frequency of 33 GHz?
36. What is the wavelength for an FM radio signal if the number on the dial reads 99.5MHz?
You might also like
- 300-430-ENWLSI Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks PDFDocument3 pages300-430-ENWLSI Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks PDFEdu100% (1)
- Test 3 Test Bank Physics 2Document70 pagesTest 3 Test Bank Physics 2Matheus Groberio100% (2)
- Drag of Conical Nose at Supersonic Speeds (Arthur Saw, EURECA 2013)Document2 pagesDrag of Conical Nose at Supersonic Speeds (Arthur Saw, EURECA 2013)Arthur Saw Sher-QenNo ratings yet
- Ib Physics ch12 PDFDocument2 pagesIb Physics ch12 PDFHansal Pravin KachharaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Investigation - Youngs Double Slit ExpDocument4 pagesSimulation Investigation - Youngs Double Slit ExppixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Standing Waves WorksheetDocument2 pagesStanding Waves WorksheetAdib HassanNo ratings yet
- Wavelength Frequency and Enegy Problems KEY PDFDocument2 pagesWavelength Frequency and Enegy Problems KEY PDFmijaggiNo ratings yet
- IM KR180A E 4thDocument80 pagesIM KR180A E 4thbatizap batizapNo ratings yet
- 33003788K01000 PDFDocument472 pages33003788K01000 PDFAji SukumaNo ratings yet
- Answer KEY of Nature of Light Online TestDocument12 pagesAnswer KEY of Nature of Light Online TestKhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument19 pagesChapter 32 - Electromagnetic WavesKarla PereraNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation TablesDocument6 pagesPhysics Equation TablesSangram NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Universal Gravitation Practice QuizDocument4 pagesUniversal Gravitation Practice QuizSrnt YyoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - WavesDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 - WavesMary BakhoumNo ratings yet
- Multiple Range MCQs On Introductory StatisticsDocument26 pagesMultiple Range MCQs On Introductory StatisticsKennyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Laser-MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Laser-MCQMAHAJAN and SON'SNo ratings yet
- PC Chapter 38Document80 pagesPC Chapter 38ultimu100% (1)
- Kami Export - Samuel C - Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument3 pagesKami Export - Samuel C - Electromagnetic Spectrumtom100% (1)
- Model Test I Kinematics MCQDocument10 pagesModel Test I Kinematics MCQKarlie NguyenNo ratings yet
- A2 Particle Physics Worksheet PDF MS - Part 2Document18 pagesA2 Particle Physics Worksheet PDF MS - Part 2TahirNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of Atoms: Multiple Choice Questions 1Document18 pagesQuantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of Atoms: Multiple Choice Questions 1Khawla MustafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)Document24 pagesChapter 9 Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)KarissaNo ratings yet
- Gp2 Worksheet 3 MidDocument6 pagesGp2 Worksheet 3 MidDuane Laude Pon-anNo ratings yet
- 01 Ray Optics MMDocument71 pages01 Ray Optics MMMission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- Sextant by MR - CharisDocument4 pagesSextant by MR - CharisCharis Israel AnchaNo ratings yet
- Central Force Motion NotesDocument4 pagesCentral Force Motion NotesJinshad Uppukoden100% (1)
- 3 ElectronicConfigurationsDocument5 pages3 ElectronicConfigurationsMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Document9 pagesExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- MCQ From Sound & WaveDocument3 pagesMCQ From Sound & WaveRaktimNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 WavesDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 WavesMary Bakhoum0% (1)
- GP2 - Module 2Document20 pagesGP2 - Module 2Jinja DelNo ratings yet
- Basic Motion - KeyDocument7 pagesBasic Motion - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Electrostatic Force WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 4 - Electrostatic Force WorksheetAnonymous jDrrLjra100% (1)
- Physics: (Mock Test-1) 1Document6 pagesPhysics: (Mock Test-1) 1ManishKumarNo ratings yet
- RelativityDocument42 pagesRelativityKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Ray Optics and Wave OpticsDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Ray Optics and Wave OpticsManoj Naik P100% (3)
- Electrostatics Questions Energy and Work With AnswersDocument14 pagesElectrostatics Questions Energy and Work With Answersmicheal_cksNo ratings yet
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 2 Practical Applications and Effects of EM WavesDocument42 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 2 Practical Applications and Effects of EM WavesRex Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Gravitation WorksheetDocument13 pagesGravitation Worksheetkaushik247No ratings yet
- Law of Reflection and RefractionDocument21 pagesLaw of Reflection and RefractionDarious PenillaNo ratings yet
- Waves Review Chapter 17nameDocument2 pagesWaves Review Chapter 17nametownsenr94No ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circuit Builder: Rebecca Rodriguez 5/7/2021Document4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit Builder: Rebecca Rodriguez 5/7/2021Rebecca RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFDocument6 pagesProblem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFclainNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit II Phy110Document27 pagesMCQ Unit II Phy110Ansh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Drift VelocityDocument5 pagesDrift Velocitye1f123No ratings yet
- Physical Quantities - (Standards and Units) - 2Document5 pagesPhysical Quantities - (Standards and Units) - 2gayathri gayuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsRavi Inder Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula List - As at 6 Jul 2011 (Normal)Document4 pagesPhysics Formula List - As at 6 Jul 2011 (Normal)Lim Kew Chong100% (1)
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument68 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentBiprodeep14No ratings yet
- Physics Questions Sem..Document14 pagesPhysics Questions Sem..VinitgaNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument11 pagesPhysics NotesSwaraj SamalNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics ExamDocument5 pagesModern Physics Examsattar28No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science QuizDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science QuizVanda RemaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Matter and Measurement: Chapter OneDocument57 pagesChemistry: Matter and Measurement: Chapter OneWarakorn AkarasareenonNo ratings yet
- 1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticeDocument12 pages1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticerbgrossNo ratings yet
- Definition of Wave-Particle DualityDocument4 pagesDefinition of Wave-Particle DualityHarshaAch0% (1)
- Characteristics of PopulationsDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of PopulationsAnn Marilette100% (2)
- The Schrödinger Equation in One DimensionDocument23 pagesThe Schrödinger Equation in One DimensionjunaidNo ratings yet
- The Key: Units of Reaction Rate Are Unit of Concentration Divided by The Unit of Time (Mol LDocument31 pagesThe Key: Units of Reaction Rate Are Unit of Concentration Divided by The Unit of Time (Mol LSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Karen May P. UrlandaDocument47 pagesKaren May P. UrlandaKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticDocument4 pagesElectromagneticDini Sukaseal100% (1)
- Assignment #1: Intro To Light: Information: The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument20 pagesAssignment #1: Intro To Light: Information: The Electromagnetic SpectrumBrianss AyangssNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum Simulation C12-2-1Document6 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum Simulation C12-2-1Marilyn Castro LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Specification For Construction of Concrete ReservoirsDocument18 pagesSpecification For Construction of Concrete ReservoirsKeysha ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Info - Iec61340-5-1 (Ed2 0 RLV) enDocument23 pagesInfo - Iec61340-5-1 (Ed2 0 RLV) enArhamNo ratings yet
- Scania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFDocument2 pagesScania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFMehmet ErenNo ratings yet
- LGP4247L-12LPB-3P Eay62608902 PLDF-L103B Psu SM PDFDocument74 pagesLGP4247L-12LPB-3P Eay62608902 PLDF-L103B Psu SM PDF00dark100% (1)
- Ericsson Essentials Health & Safety Plan Sample: Good For Smaller Projects and Bid QualificationsDocument18 pagesEricsson Essentials Health & Safety Plan Sample: Good For Smaller Projects and Bid QualificationsmohammedelrabeiNo ratings yet
- 201 Harga + Brosur (Alat Lab. Beton - Struktur 2014)Document14 pages201 Harga + Brosur (Alat Lab. Beton - Struktur 2014)Ridho Aidil FitrahNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of MOSFET Based Amplifier in Different ConfigurationsDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of MOSFET Based Amplifier in Different ConfigurationsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Vineeth - Curriculum VitaDocument8 pagesVineeth - Curriculum VitaVineeth NBNo ratings yet
- Singapore - GCCM Talk SlidesDocument115 pagesSingapore - GCCM Talk SlidesChimhuee ChuaNo ratings yet
- CostingDocument5 pagesCosting83pankajNo ratings yet
- AFTES Geological Tunnel RisksDocument46 pagesAFTES Geological Tunnel RisksmerinofalNo ratings yet
- Roof Manual p10Document1 pageRoof Manual p10AllistairNo ratings yet
- FP CLOCK - csproj.FileListAbsoluteDocument14 pagesFP CLOCK - csproj.FileListAbsolutePhi Huỳnh NgôNo ratings yet
- Falcon DEMCO Fire Alarm Bell (Weatherproof Type)Document1 pageFalcon DEMCO Fire Alarm Bell (Weatherproof Type)LaMinn PaingNo ratings yet
- Engine Test CellDocument44 pagesEngine Test Cellgrhvg_mct8224No ratings yet
- MSDS - Molecular Sieve 4ADocument4 pagesMSDS - Molecular Sieve 4AadeliaaaNo ratings yet
- Nutanix TN 2072 ESXi AHV Migration Version 2.2Document23 pagesNutanix TN 2072 ESXi AHV Migration Version 2.2Alejandro DariczNo ratings yet
- Vanguardia, Robert John T - Amte 125L - 1X - Aircraft Fuel Lines (Research)Document5 pagesVanguardia, Robert John T - Amte 125L - 1X - Aircraft Fuel Lines (Research)Robert VanguardiaNo ratings yet
- Cap Screws: Sae J429 Grade IdentificationDocument6 pagesCap Screws: Sae J429 Grade IdentificationHomer SilvaNo ratings yet
- CT v2.0 UnderstandingDocument36 pagesCT v2.0 UnderstandingAbel Chaiña GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Boiling MechanismDocument16 pagesBoiling MechanismherawanadifNo ratings yet
- Differential Current-Based Fault Protection With Adaptive Threshold For Multip (Le PV Based DC MicrogridDocument13 pagesDifferential Current-Based Fault Protection With Adaptive Threshold For Multip (Le PV Based DC MicrogridANURAAGNo ratings yet
- Pdca Cycle Problem SolvedDocument3 pagesPdca Cycle Problem Solvedjose luisNo ratings yet
- Seismic Strengthening of Reinforced Concrete Columns With Straight Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) AnchorsDocument15 pagesSeismic Strengthening of Reinforced Concrete Columns With Straight Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) AnchorsKevin Paul Arca RojasNo ratings yet
- Owatch VR Games Quotation - 2017!4!24Document3 pagesOwatch VR Games Quotation - 2017!4!24ali4957270No ratings yet
- Precast Capping Beam Formers DatasheetDocument2 pagesPrecast Capping Beam Formers Datasheetsantoshgpr100% (1)