Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Direct and Reported Speech: A Comprehensive Guide
Uploaded by
Ancuta S. AndreeaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Direct and Reported Speech: A Comprehensive Guide
Uploaded by
Ancuta S. AndreeaCopyright:
Available Formats
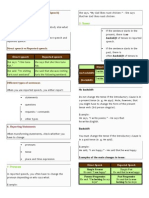
Direct Speech
Reported Speech
Simple Present
He said: "I am happy"
Simple Past
He said that he was happy
Present Progressive
He said: "I'm looking for my keys"
Past Progressive
He said that he was looking for his keys
Simple Past
He said: "I visited New York last year"
Past Perfect Simple
He said that he had visited New York the
previous year.
Present Perfect
He said: " I've lived here for a long time "
Past Perfect
He said that he had lived there for a long time
Past Perfect
Past Perfect
He said: "They had finished the work when I He said that they had finished the work when he
arrived"
had arrived"
Past Progressive
He said: "I was playing football when the
accident occurred"
Past Perfect Progressive
He said that he had been playing football when
the accident had occurred
Present Perfect Progressive
He said:"I have been playing football for
two hours."
Past Perfect Progressive
He said that he had been playing football for two
hours
Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I had been reading a newspaper
when the light went off"
Past Perfect Progressive
He said that he had been reading a newspaper
when the light had gone off
Future Simple (will+verb)
He said: "I will open the door."
Conditional (would+verb)
He said that he would open the door.
Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I would buy Mercedes if I were
rich"
Conditional (would+verb)
He said that he would buy Mercedes if he had
been rich"
The verbs could, should, would, might, must, needn't, ought to, used to do not
normally change.
Example:
He said, She might be right. He said that she might be right.
Place, demonstratives and time expressions
Place, demonstratives and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement
(i.e. the location and/or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes of place; demonstratives and time
expressions.
Direct Speech
Reported Speech
Time Expressions
today
that day
now
then
yesterday
the day before
days ago
days before
last week
the week before
next year
the following year
tomorrow
the next day / the following day
Place
here
there
Demonstratives
this
that
these
those
Reporting Questions
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
pronouns
place and time expressions
tenses (backshift)
Also note that you have to:
transform the question into an indirect question
use the question word (where, when, what, how) or if / whether
Types of questions
With question word (what,
why, where, how...)
Direct speech
Reported speech
"Why" dont you speak He asked me why I didnt
English?
speak English.
Without question word (yes or Do you speak
no questions)
English?
He asked me whether / if I
spoke English.
Reporting requests / commands
When transforming requests and commands, check whether you have to change:
pronouns
place and time expressions
Direct speech
Nancy,do the exercise.
Reported speech
He told Nancy to do the exercise.
"Nancy, give me your pen, please." He asked Nancy to give him her pen.
Tenses are not relevant for requests simply use to / not to + verb (infinitive without "to")
Example:
She said, Sit down." - She asked me to sit down.
She said, "don't be lazy" - She asked me not to be lazy
For affirmative use to + infinitive (without to)
For negative requests, use not to + infinitive (without to).
Other transformations
Expressions of advice with must, should and ought are usually reported using
advise / urge.
Example:
You must read this book.
He advised / urged me to read that book.
The expression lets is usually reported using suggest. In this case, there are
two possibilities for reported speech: gerund or statement with should.
Example:
Lets go to the cinema.=
1. He suggested going to the cinema.
2. He suggested that we should go to the cinema.
Main clauses connected with and/but
If two complete main clauses are connected with and or but, put that after the conjunction.
Example:
He said,I saw her but she didn't see me. He said that he had seen her but that she hadn't
seen him.
If the subject is dropped in the second main clause (the conjunction is followed by a verb), do
not use that.
Example:
She said,I am a nurse and work in a hospital. He said that she was a nurse and worked in
a hospital.
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 2016Document5 pagesReported Speech 2016Alex PeraNo ratings yet
- Say What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.From EverandSay What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechJohn Alvin de LaraNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechDoris Ana-MariaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech in EnglishDocument6 pagesReported Speech in EnglishIoanaR2011No ratings yet
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocument10 pagesIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported Speechstanjack99No ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument12 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsOfelia MontielNo ratings yet
- 2-Tenses: Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument4 pages2-Tenses: Direct Speech Reported SpeechAbdelhadi Ait AllalNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting StatementsDocument6 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting Statementsriaadria100% (1)
- Reported Speech GuideDocument5 pagesReported Speech GuideKatita VieraNo ratings yet
- Grammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFDocument4 pagesGrammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Guide: How to Transform Direct Quotes Into Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesReported Speech Guide: How to Transform Direct Quotes Into Indirect SpeechZaniShiraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument5 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsSofia AngelovaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument4 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsZaniShira100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechLisseth Andrea Ledesma GarriazoNo ratings yet
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pages01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ChartDocument4 pagesReported Speech ChartAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGunjan GargNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechNoa PahlićNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ExplainedDocument14 pagesReported Speech ExplainedДильназ КожахметоваNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument9 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechYevit RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ProjectDocument21 pagesReported Speech ProjectS fu fu86% (7)
- Using Indirect SpeechDocument11 pagesUsing Indirect SpeechGeorge PoroNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonDocument5 pagesReported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonRishit ChandaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAdine RachmadinnaNo ratings yet
- Direct and indirect speech rulesDocument8 pagesDirect and indirect speech rulessarfarazNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech / Quoted SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect Speech / Quoted Speechpedro ordoezNo ratings yet
- Direct vs Indirect Speech RulesDocument7 pagesDirect vs Indirect Speech RulesSadhna TiwariNo ratings yet
- (GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)Document15 pages(GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)NamNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechHasib QureshiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument13 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDaiana Tufaro100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument11 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechsigiryaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Document3 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Pili Lema BlancoNo ratings yet
- Uses of The Perfect InfinitiveDocument24 pagesUses of The Perfect InfinitivemiraeNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExampleDocument6 pagesDirect Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExampleIvan AldinataNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechShenali NupehewaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech GuideDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech GuideArlyn AristoNo ratings yet
- Direct, Indirect, Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesDirect, Indirect, Reported SpeechKHALIDOO6No ratings yet
- Reported speech rulesDocument6 pagesReported speech rulesaravindrnairNo ratings yet
- NarrationDocument9 pagesNarrationArun SomanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDivya Rai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJohann Alwi Candyn'machineloverNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument14 pagesExercisesJoyCamilleReyesNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesReported SpeechMonica Adina BaneaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Short SummaryDocument2 pagesReported Speech Short Summaryfederica fissoreNo ratings yet
- For Example:: She Said, "Today's Lesson Is On Presentations." "Today's Lesson Is On Presentations", She SaidDocument14 pagesFor Example:: She Said, "Today's Lesson Is On Presentations." "Today's Lesson Is On Presentations", She SaidWallace SantosNo ratings yet
- Virtual English Lesson Report: Reported Speech, Exercises, and Life Project PresentationDocument6 pagesVirtual English Lesson Report: Reported Speech, Exercises, and Life Project PresentationYefer romañaNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Vs Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect Speech Vs Reported SpeechMiguel MontoyaNo ratings yet
- HS-001A L 4 Reported SpeechDocument39 pagesHS-001A L 4 Reported SpeechS KohliNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech RulesDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech RulesskitteringkiteNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech FinalDocument8 pagesDirect Speech FinalMahnoor AkhterNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechJackie RicoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechWaleed Marouf A. NueiratNo ratings yet
- Table For Change in Tense of Reported Speech For All TENSESDocument10 pagesTable For Change in Tense of Reported Speech For All TENSESnavi_khiNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - SummaryDocument2 pagesReported Speech - SummaryFreddy Murrugarra100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported SpeechLinda FatmasariNo ratings yet
- Cultura Org AdelinaDocument10 pagesCultura Org AdelinaAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Cultura Org AdelinaDocument10 pagesCultura Org AdelinaAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Speech Acts StsDocument6 pagesSpeech Acts StsAncuta S. Andreea100% (1)
- Decentralization Around The WorldDocument2 pagesDecentralization Around The WorldAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Speech Acts Applications StsDocument11 pagesSpeech Acts Applications StsAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported Speech: A Comprehensive GuideDocument3 pagesDirect and Reported Speech: A Comprehensive GuideAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Language PracticeDocument152 pagesAdvanced Language PracticeAncuta S. AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Destinos Grammar 1-26Document70 pagesDestinos Grammar 1-26jototl100% (1)
- Materi Pertemuan 9 - Compound SentenceDocument16 pagesMateri Pertemuan 9 - Compound Sentencetania hennaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4,5 PHRASES AND CLAUSESDocument41 pagesLecture 4,5 PHRASES AND CLAUSESjehoshua35No ratings yet
- TOEFL Skill 1 Subject and VerbDocument3 pagesTOEFL Skill 1 Subject and VerbBerliana FebriantyNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument5 pagesSubject Verb AgreementAlecia R. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Word and Its StructureDocument2 pagesWord and Its StructureSry Hardyanti Taufik71% (7)
- ParticipleDocument3 pagesParticipleMahendra PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Ingles 2024 IIIDocument48 pagesIngles 2024 IIIFrank GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Complete Sentences ReviewDocument8 pagesComplete Sentences ReviewPaulNo ratings yet
- Rules On Subject Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesRules On Subject Verb AgreementTasyo LCruz Jr.No ratings yet
- Online English Classes Interview TechniquesDocument20 pagesOnline English Classes Interview TechniquesJessicaK.CutipaNo ratings yet
- English Language Grade 8Document3 pagesEnglish Language Grade 8Danielle AkutagawaNo ratings yet
- PreposicionesDocument4 pagesPreposicioneskattya40No ratings yet
- Unit 3. Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesUnit 3. Passive VoiceEsri DewiNo ratings yet
- 100 Juegos y Actividades Ludicas para Enseñar InglesDocument14 pages100 Juegos y Actividades Ludicas para Enseñar InglesHOBSHURA55% (11)
- Spanish 2 - Preterite Conjugation RacesDocument2 pagesSpanish 2 - Preterite Conjugation RacesJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document4 pagesUnit 7Eli MicóNo ratings yet
- Bit by Bit 5Document318 pagesBit by Bit 5Miss MehwishNo ratings yet
- Conditional IfDocument31 pagesConditional IfMarciaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument5 pagesReported SpeechMANUEL RINCON GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Technical Writing 1 For Criminology StudentsDocument40 pagesTechnical Writing 1 For Criminology StudentsJesmar Lobo97% (38)
- Appendix I.-List of Irregular VerbsDocument7 pagesAppendix I.-List of Irregular VerbsMarisol Rojas RojasNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument29 pagesActive and Passive Voicegian93No ratings yet
- V2202 Part-IDocument53 pagesV2202 Part-Izainab jamidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Ambiguous and Unambiguous Grammar-1Document26 pagesLecture 3 Ambiguous and Unambiguous Grammar-1Snehal PoptaniNo ratings yet
- 13 Productive Lexical Processes in Present-Day English (Hickey)Document17 pages13 Productive Lexical Processes in Present-Day English (Hickey)Диана БлагоеваNo ratings yet
- Correcting Illogical SubordinationDocument2 pagesCorrecting Illogical SubordinationEnrico SanchezNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument218 pagesInglesAlejandra ArriagaNo ratings yet
- Daily Language Review 4 TH GradeDocument261 pagesDaily Language Review 4 TH Gradeaon poatNo ratings yet
- Biber (1992)Document35 pagesBiber (1992)skripsi1904No ratings yet