Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SDLC Models: Linear Approach
Uploaded by
vsrajeshvsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SDLC Models: Linear Approach
Uploaded by
vsrajeshvsCopyright:
Available Formats
1
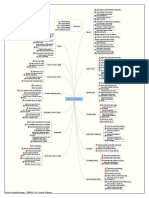
SDLC Models
ProcessModelsprovidesaspecificroadmapforsoftwareengineeringwork.Thepurposeoftheprocess
modelistotrytoreducethechaospresentindevelopingnewsoftwareproducts.
SystemDevelopmentLifecycle(SDLC)isaframeworkdescribingaprocessforforsoftware
development.
1. LinearLifecycle
2. Evolutionarylifecycle
Linearapproachdescribesasequenceoftasksthatarecompletedinorder,onlymovingtothenextstep
oncethepreviousstepiscomplete.
Evolutionaryapproach
evolves
thesolutionthrough
progressiveversions
,eachmorecompletethanthe
last&oftenusesaprototypingapproachtodevelopment.
SystemDevelopmentLifecycleVsSystemLifecycle
InSDLC,oncetheimplementationoccurs,theprojectisconsideredcomplete.
Linear Approach
LinearapproachfollowstheSDLCstagesinadefinedorder.Eachstepmustbecompleted,understood
andagreedbeforethenextstepcanbestarted.
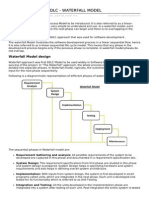
Waterfall
VModel
Incremental
Strengths
Weakness
Breaksdowntheproblemintodistinctstageseach Dependsgreatlyoneachstagebeingdone
withaclearpurpose.
properly.
Everythingisagreedinadvanceofbeingused,
Itishardorimpossibletobackandchangeitlater.
withnoneedtorevisitlater.
Providestructuretocomplexsystems,making
Forcomplexproblems,thetimerequiredtobe
distributedoroutsourceddevelopmenteasierto
throughateachstageleadstolongtimescales.
manage.
Haveaverydetailedspecification&design.
Difficulttoaccommodatechanges.
Lockingdowneachstageinadvancefornext
Customerorbusinessvalueisnotavailableuntil
makesiteasiertocontrolcost&scopecreep.
theend.
Simple&intuitiveforsmallerproblems.
Iftheprojectisstoppedearly,thereislittleof
businessvaluetoshowforthecost.
Waterfall or Classic Lifecycle
KeystrengthsofWaterfallmodelare
Simpletounderstandandeasytouse.
Goodfordevelopingsystemswheretherequirementsandlikelysolutionarewellunderstood
andunlikelytochange.
Rigour&controlaroundeachstagemakeiteasierforprojectmanagement.
Themajorweaknessofthismodelare
Realprojectsrarelyfollowsequentialflow.
Canbecostlytomanagechange,especiallyifchangesareidentifiedlaterinthecycle.
Workingsoftwarenotdelivereduntilthefinalstage.
Poorestimationcanseverelyimpactthecost&schedule.
Customercollaborationislimitedtorequirements&acceptancetesting.Forlongprojects,this
canleadtoalackofcustomerbuyin,particularlywherestakeholderschange.
V Model
Introducedasanextensiontowaterfallmodeltodealwiththeproblemwherebytimeallocatedfor
testingcouldoftengetsqueezedduringawaterfalliftimeandmoneystartedtorunout.
Thelefthandsideshows
projectdefinition
&righthandsideshows
verification&validation
.The
dottedlinesconnectingleft&righthandsideshowstherelationshipsbetweeneachstageofdefinition
withitsassociatedstageoftesting.
KeystrengthsareVmodelare
Additionalfocusontestingleadstoahighqualityproduct.
Idealforsystemswithcomplexorhighqualityattributes.(safetycritical,verylarge,integration
heavyetc.)
MajorweaknessofVmodelare
Heavytesting&integrationcostthatcanbeunnecessarilyexpensiveforsimplersystems.
Earlystagestakelongertocompleteastherearetestartefactstocomplete.
AnextendedVmodelwaslaterintroducedtoincludethefeasibility&benefitsrealizationstage.
Incremental
Theincrementalisstillalinearapproachinsomuchasthefirst3stagesoftheSDLCareconductedin
sequence,eachbeingcompletedbeforethenextisstarted.
Withthisprocess,somepartsofthesystemgetdeliveredbeforeotherparts.Thisenableshighpriority
requirementstobedeliveredfirst.
Incrementscanalsobedeliveredinparallel,asthecoredesignis
complete
.
Keystrengthsofincrementalmodelare
Deliversworkingsoftwaretousersearly.
Easiertomanagerisks
becauseriskypiecescanbeidentifiedandhandledinearlyincrements.
Easiertotest&debugsmallerincrements.
Incrementscanbebuiltinparallel,reducingoveralltimetomarket.
Majorweaknessofthismodelare
Hardtomanageparalleldeliveries.
Stilldifficulttomanagechanges,asrequirementsareagreedbeforeincrementsaredecided.
Overallcostcanbehigherduetoadditionaloverheadsofparallelimplementationand
additionalregressiontesting.
Thecorearchitectureneedstobestable.
Evolutionary Models
Twofundamentallifecyclescomesunderevolutionarymodelsare
Iterative
Spiral
Iterative
Iterativedevelopmentisalifecyclewherebytheoverallprojectiscomposedofseveralsmall
timeboxeddevelopments,callediterations,whichtakesplaceinsequence.
Eachiterationisaselfcontainedminiprojectcomposedofactivitiessuchasanalysis,design,
development&test.Requirementsareelicitedduringeachiterationandthendevelopedtoproducea
workingsystemthatdeliverssomevaluetothecustomer.
Attheendofeachiteration,alldevelopmentacrosstheteamsisintegratedandtestedintoaniteration
release,thatmaynotbereleasedexternally.
Typically,therewillbeminimumof3iterations
1. Investigate
Mainlyusedtoinvestigatethingssuchasrisksaroundthetechnologyorrisks
arounduserfunctionality.Oncethisiterationiscompleted,therewillbemoreunderstanding
aboutwhatisrequiredtodelivertheexternalorfirstrelease.
2. Refine
Duringthisiterationtherequirementsarefullydetailedanddesignedandthesystemis
developedtomeetthebusinessgoal.Therearesometimesmultiplerefinementiterations.
3. Consolidate
Thefinaliterationensuresthatthecodeanddesigndevelopedisstabilisedand
fullyintegratedwithanyotheriterationssothattheoverallbusinessgoalisachievedinthe
externalrelease.
KeystrengthsofIterativemodelare
Requirementsevolvethrougheachiteration.
Changeiseasiertomanage.
Costcanbecontrollable.
Encouragecollaborationwithcustomers.
Themainweaknessofthisapproachare
Projectmanagementisdifficultduetomultipleiterations&iterationteams.
Withoutcarefulmanagement,evolvingrequirementscanresultinscopecreep.
Ifpoorlymanaged,canstillappearlikeasingle,finalrelease.
Overallcostscanbehigherduetotheadditionalintegrationandtests.
Spiral
Thespiralmodel,likeiterativeapproach,doesnotneedrequirementstobedefinedinadvance.This
approachstartswithaconceptandrepeatedlyrevisitsthefourmainphasesofdevelopmentuntila
suitableworkingproductiscomplete.
(Iterative+Prototype)
Determineobjectives
Inthefirststage,thedevteamandbusinessownersidentifythe
objectivesforthedevelopmentandagreeprioritizationofrequirements.Throughoutthe
project,thisunderstandingisconstantlyreviewedandrevisited.
Identify&resolverisks
Atthisstage,thedevelopersexploretechnicalpossibilitiestomeet
thebusinessgoal&assessanyrisksthatthetechnologymaybring.Anearlyprototypeisakey
enablerhereandwillbeproduced.
Development&test
Reviewingtheprototypesenablesthedevteamtoassesshowwellthe
requirementsandriskswereaddressedandlookatimprovements.Designsarethendeveloped
foranotherprototype,whichisagreed,developed&tested.Afterafewiterations,thiswill
producetheoperationalprototype.
Planthenextiteration
Duringthisstage,theworkingsystemisreleasedintothelive
operationalenv.Thismaybejustanincrementalreleaseandthereforefurtherreleaseswillbe
plannedanddevelopedthroughsubsequentiterationsandreleasesuntilthecompletesystemis
developedandthebusinessobjectivesarefullymet.
Keystrengthsare
1. Risksareaddressedearly.
2. Requirementsevolve,soadditionalfunctionalitiescanbeaddedlater.
3. Collaborationwithuseristhroughout,socustomerbuyinisgood.
4. Aworkingsystemisdevelopedearlyinthedevlifecycle.
Mainweaknessofspiralmodelare
Highchanceofscopecreep.
Overallcostscanbehighduetothemanyimplementationsofworkingsoftwareintothe
operationalenv.
Asthefocusisonaworkingsystem,documentationofthesystemcanbecomedeprioritized,
makingthesystemhardertomaintainpostprojectdelivery.
Agile Methodology
Keyconceptsofagilemanifestoare
1. Individuals&interactionsoverprocess&tools.
2. Workingsoftwareratherthaninproducingcomprehensivedocs.
3. Customercollaborationratherthancontractnegotiation.
4. Respondingtochangesratherthancreatingaplanandthenfollowingit.
Theoverallobjectiveofagiledevistosatisfythecustomerbyearlyandcontinuousdeliveryof
valuablesoftware.
Agileisidealinsmall,highlycollaborativeteams.However,theyaremuchhardertoworkwellwhere
theenvischallenged.
Largerteams,especiallywheretheyaregeographicallydistributed.
Complexsystems.
Audit,regulatory&safetycriticalrequirementsthatexpecthigherqualityassurance.
Projectswithstrictcontractualcommitments.
Complexuserenvorwhereenduserisnotavailable.
Inthesesituations,Agileapproachescanstillbringconsiderablebenefits,buttheadditionalriskthat
theyalsobringmustbemitigatedinsomeotherway.
Therearemanymethodsthatimplementthetenetsoftheagilemanifesto.
1. Extremeprogramming
2. Scrum
3. Adaptivesoftwaredevelopment(ASD)
Prototype
Itisaneffectiveparadigmforsoftwareengineering.Thismodelconsistsof
1. Listentocustomer.
2. Build/Revisemockup.
3. Customertestdrivesmockup.
Theprocedureisrepeateduntilalltherequirementsofthesystemareidentifiedandacomplexsystem
canbedesignedforthesystem.
Systemprototyping
(Evolutionary)producesafullfeaturedworkingmodeloftheinfosystem,
whichisreadyfortheimplementationphaseoftheSDLC.
Designprototyping
(Throwaway)systemanalystsalsouseprototypingtoverifyuser
requirementsafterwhichtheprototypeisdiscardedandimplementationcontinues.
Prototypingoffermanybenefitslike
1.
Users&systemdeveloperscanavoidmisunderstandings.
2.
Systemdeveloperscancreateaccuratespecificationsforthefinishedsystembasedonthe
prototype.
3.
Managerscanevaluateaworkingmodelmoreeffectivelythanapaperspecification.
4.
Systemanalystscanuseaprototypetodeveloptestingandtrainingprocedures.
5.
Prototypingreducestheriskandpotentialfinancialexposurethatoccurwhenafinishedsystem
failstosupportbusinessneeds.
Potentialproblemswithprototypingare
Therapidpaceofdevelopmentcancreatequalityproblems,whicharenotdiscovereduntilthe
finishedsystemisoperational.
Othersystemrequirementssuchasreliability,maintainabilityetccannotbetestedadequately
usingaprototype.
Inverycomplexsystems,theprototypebecomesunwieldyanddifficulttomanage.
RAD
RADreferstoadevlifecycledesignedtogivemuchfasterdevelopmentandhigherqualitysystems
thanthetraditionallifecycle.ItisdesignedtotakeadvantageofpowerfuldevsoftwarelikeCASE
tools,prototypingtools&codegenerators.ThekeyobjectivesofRADare
Highspeed
Highquality
Lowcost
Component Assembly
Thisistheprocesstobeusedwhenreuseisadevelopmentobjective.
Concurrent Development
How to Choose an Approach
Complexityoftheproblem.
Teamexperience.
Stabilityofrequirements.
Deliveryspeedandquality
Customerinvolvement
Uniqueness
Highregulatoryrequirements.
SystemInitiation
Feasibilityanalysis
SystemAnalysis
InDepthstudyofenduserinfoneedsthatproducesfunctionalrequirementsthatare
usedasthebasisfordesign.
OrganalysisOrgenvinwhichthesystemislocated.
Analysisofpresentsystems.
Logicalanalysis
10
Functionalrequirements.
SystemDesign
Designinvolvesfollowingsteps.
1. InputdesignDeterminingvariousinputsandtheformatsthatarerequiredtobeprocessedto
producethedesiredoutputs.
2. OutputdesignHowoutputisproducedandinwhatformat.
3. FiledesignMasterfiles(database)havetobedesignedtostoretheinput&outputasrequired.
4. ProcessdesignThecompleteprocessinglogic,navigationflows,errorconditionsandnon
functionalrequirementsaretobedesigned.
5. UIdesignNavigation,humancomputerinterface,usabilityetc.
Designinvolvestwothings.
PhysicaldesignThehardwarecomponentsthatconstitutethesystem.
LogicaldesignSoftware&datadesign.
Basedonthis,detaileddesigndocumentationisprepared.Insomeprojects,lowleveldesigndocuments
arealsoprepared.Thedesigndocumentsincludeflowcharts,recordlayouts,andreportlayouts,ER
diagramsasapplicable.
SystemImplementation
Acquisitionofhardware&software.
Softwaredevelopmentormodification.
Dataconversion
Testing
Endusertraining
ConversionDirect,Pilot,Parallel,Phased
SystemMaintenance
Correctivedefectfixing
Adaptiveenhancement
Perfectiveimproveperformance
Preventiveautomatedregression
You might also like
- Popular SDLC Models Followed in The Industry Lec 2Document30 pagesPopular SDLC Models Followed in The Industry Lec 2UCIZAMBO ITNo ratings yet
- SDLC ModelDocument11 pagesSDLC ModelTan LopezNo ratings yet
- System Development Life Cycle: It Fundamentals and Information Systems DesignDocument63 pagesSystem Development Life Cycle: It Fundamentals and Information Systems DesignsgsitsindorNo ratings yet
- Describe What Is SDLC. SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) - Refers To A Methodology With Clearly Defined Processes ForDocument3 pagesDescribe What Is SDLC. SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) - Refers To A Methodology With Clearly Defined Processes ForLyco BikoNo ratings yet
- CSC 709 AssignmentDocument16 pagesCSC 709 AssignmentTeQ BitsNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument8 pagesSDLCSruthi RajendranNo ratings yet
- Software Process ModelsDocument10 pagesSoftware Process ModelsTahreem MasoodNo ratings yet
- Software ModelsDocument21 pagesSoftware ModelssudanharshpreetkaurNo ratings yet
- Lec3 & 4 - System Development LifecycleDocument71 pagesLec3 & 4 - System Development LifecyclePriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Study-02Document51 pagesCase Study-02Madhura BoregowdaNo ratings yet
- Iterative Waterfall ModelDocument3 pagesIterative Waterfall ModelkokorororNo ratings yet
- Waterfall ModelDocument3 pagesWaterfall Modelparthu1710No ratings yet
- Synopsis of SDLCDocument2 pagesSynopsis of SDLCRaging AuntyNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: SubjectDocument7 pagesSoftware Engineering: SubjectDibyam DeyNo ratings yet
- Process ModelsDocument12 pagesProcess ModelsEMELIA THOMPSON-BROOKSNo ratings yet
- Area 3Document31 pagesArea 3mi920865No ratings yet
- SDLC - Waterfall ModelDocument5 pagesSDLC - Waterfall Modelpradeepkumar116803No ratings yet
- Software ProjectDocument18 pagesSoftware ProjectMd Fazlay Rabbi 191-15-12315No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument14 pagesUnit IksheikNo ratings yet
- Models of SDLC - PPT OriginalDocument51 pagesModels of SDLC - PPT Originals_coolbugNo ratings yet
- Waterfall Model - DesignDocument4 pagesWaterfall Model - DesignIT LAb 2No ratings yet
- SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) - NewDocument17 pagesSDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) - NewSayantanBaraiNo ratings yet
- Software Developement Life CycleDocument21 pagesSoftware Developement Life CycleJAI THAPANo ratings yet
- Definitions: Software Is More Than Just A Program Code. A Program Is An Executable Code, Which ServesDocument22 pagesDefinitions: Software Is More Than Just A Program Code. A Program Is An Executable Code, Which Servessusovan garaiNo ratings yet
- Ch00 (3) Perceptual Knowledge-1 NewDocument37 pagesCh00 (3) Perceptual Knowledge-1 NewRafia RafiNo ratings yet
- SDLC ModelsDocument5 pagesSDLC ModelsNobel Education Channel قناة نوبل التعليميةNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document9 pagesLecture 4Said Sabri KibwanaNo ratings yet
- University of Antique College of Computer StudiesDocument14 pagesUniversity of Antique College of Computer StudiesRuBie Sumanga EstimeraNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Fundamentals (Agile and Software Testing)Document13 pagesSoftware Engineering Fundamentals (Agile and Software Testing)Bairineni Sai AnudeepNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument22 pagesSoftware EngineeringSubrinaNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Lecture 1.1.4Document10 pagesSoftware Engineering Lecture 1.1.4Ashutosh mishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2monikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document31 pagesChapter 01gfdsa jklNo ratings yet
- Nitya A20405220131Document8 pagesNitya A20405220131Nitya KushwahNo ratings yet
- Dca7103 & Advanced Software EngineeringDocument9 pagesDca7103 & Advanced Software Engineeringarmaan rathoreNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument81 pagesSDLCمحمد احمدNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument20 pagesSoftware EngineeringSuresh PatroNo ratings yet
- Waterfall ModelDocument19 pagesWaterfall Modelilias ahmed100% (2)
- SDLCDocument27 pagesSDLCGeethma RamanayakaNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering ConceptsDocument4 pagesSoftware Engineering ConceptsSyed SafwanNo ratings yet
- Systems Development Life CycleDocument17 pagesSystems Development Life CycleMaxwell100% (4)
- Se QBDocument10 pagesSe QBshruti.exe03No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Software Process ModelDocument101 pagesChapter 3 Software Process Modelsukhmanaulakh54No ratings yet
- WaterfallDocument3 pagesWaterfallTeju MelapattuNo ratings yet
- Cs507 Water Fall vs. IncrementalDocument4 pagesCs507 Water Fall vs. Incrementalrabirabi75% (4)
- SDLC Waterfall ModelDocument3 pagesSDLC Waterfall ModelHasby RosyadiNo ratings yet
- R20 IT 4-1 - DevOps - UNIT - 1Document23 pagesR20 IT 4-1 - DevOps - UNIT - 1Bitra VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Maliha Rahim b-25781 Sir Asad Sajjad Software Engineering AssignmentDocument2 pagesMaliha Rahim b-25781 Sir Asad Sajjad Software Engineering AssignmentMaliha RahimNo ratings yet
- SDLC Lab2Document16 pagesSDLC Lab2Chauhan AkanshaNo ratings yet
- SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT Quiz 2Document22 pagesSOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT Quiz 2Abdul QadeerNo ratings yet
- SE Long AnswersDocument48 pagesSE Long AnswersRagnar LothbrokeNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument32 pagesSDLCgfdsa jklNo ratings yet
- Testing NotesDocument18 pagesTesting NotesKuldeep AroraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionBonsa MesganawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionBonsa MesganawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Understand The Basic of Softwate Engineering Life CycleDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Understand The Basic of Softwate Engineering Life CycleFaizur FarihaNo ratings yet
- He Waterfall Model Was First Process Model To Be Introduced-Tutorials PointDocument8 pagesHe Waterfall Model Was First Process Model To Be Introduced-Tutorials Pointmadhu_devu9837No ratings yet
- Adaptive Community For The Continuity of Education and Student Services National Teachers CollegeDocument7 pagesAdaptive Community For The Continuity of Education and Student Services National Teachers CollegeJay GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life CycleDocument12 pagesSoftware Development Life CycleNobel Education Channel قناة نوبل التعليميةNo ratings yet
- The Tech Debt PlaybookDocument10 pagesThe Tech Debt PlaybookvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- SAFe Implementation RoadmapDocument5 pagesSAFe Implementation Roadmapvsrajeshvs50% (4)
- Facilitation Process Reference CardDocument1 pageFacilitation Process Reference CardvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Agile Fluency Project Ebook RTW 1Document37 pagesAgile Fluency Project Ebook RTW 1vsrajeshvs100% (1)
- How To Select Individuals For Agile Teams VFinalDocument13 pagesHow To Select Individuals For Agile Teams VFinalvsrajeshvs100% (1)
- 2018 Kanban Guide For Scrum TeamsDocument8 pages2018 Kanban Guide For Scrum TeamsvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Brainstorm Checklist 2018Document1 pageBrainstorm Checklist 2018vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- The 8 Stances of A Scrum Master Whitepaper v2Document36 pagesThe 8 Stances of A Scrum Master Whitepaper v2Valmir Maia Meneses JuniorNo ratings yet
- Cynefin Nov17Document2 pagesCynefin Nov17vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Postera4 Optimized PDFDocument2 pagesPostera4 Optimized PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum Community - Scrum AllianceDocument3 pagesScrum Community - Scrum AlliancevsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Kanbanworkbook SampleDocument23 pagesKanbanworkbook Samplevsrajeshvs100% (2)
- Scrum ChecklistDocument2 pagesScrum ChecklistcmihaiNo ratings yet
- Kanban ExampleDocument2 pagesKanban Examplemehul3685No ratings yet
- Scrum Checklist Prio1 PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist Prio1 PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- TheHandbookofAgileKeywords v1Document35 pagesTheHandbookofAgileKeywords v1vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum Checklist All PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist All PDFvsrajeshvs0% (1)
- Agile Version Control With Multiple Teams CheatsheetDocument1 pageAgile Version Control With Multiple Teams CheatsheetbmintegNo ratings yet
- Agile Version Control With Multiple Teams CheatsheetDocument1 pageAgile Version Control With Multiple Teams CheatsheetbmintegNo ratings yet
- Lean Study Tour 2009Document6 pagesLean Study Tour 2009vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- 01 ValuationDocument7 pages01 ValuationvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum Checklist All PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist All PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum in Large Companies Public Edition v1.1 PDFDocument4 pagesScrum in Large Companies Public Edition v1.1 PDFvsrajeshvs100% (1)
- 01 IntroductionDocument5 pages01 IntroductionvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- AidaDocument97 pagesAidaSanaNo ratings yet
- Chap10 Global BrandingDocument29 pagesChap10 Global BrandingvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- BC NotesDocument5 pagesBC NotesvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Verbal CommunicationDocument1 pageVerbal CommunicationvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- 02 ContractLaw 2Document12 pages02 ContractLaw 2vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- 02 ContractLaw 1Document10 pages02 ContractLaw 1vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Ai Norm V1 03Document5 pagesAi Norm V1 03Akhil SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Mockaroo - Random Data Generator and API Mocking Tool - JSON - CSV - SQL - ExcelDocument3 pagesMockaroo - Random Data Generator and API Mocking Tool - JSON - CSV - SQL - ExcelWilhelminaNo ratings yet
- How To Implement Angular Data Table With CRUD Using ASPDocument13 pagesHow To Implement Angular Data Table With CRUD Using ASPAnonymous IhmXvCHj3cNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document56 pagesModule 3dr.reshmabanuvvietNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 DM in SSASDocument37 pagesAssignment 3 DM in SSASsdNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Java Swing Vs Java FXDocument3 pagesDifference Between Java Swing Vs Java FXPhoenix Liebe JeffNo ratings yet
- Ansible NotesDocument18 pagesAnsible NotesRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Service Oriented ArchitectureDocument25 pagesService Oriented ArchitectureSurangma ParasharNo ratings yet
- Remote Method Invoacation - RMI PDFDocument15 pagesRemote Method Invoacation - RMI PDFthillaiNo ratings yet
- Lint Error Clarifications eFUSEDocument27 pagesLint Error Clarifications eFUSERathnambiga UnnikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Revit LT: Revit LT Make The Move To 3D BIMDocument1 pageRevit LT: Revit LT Make The Move To 3D BIMSasa KalanjNo ratings yet
- C Code by Shradha KhapraDocument34 pagesC Code by Shradha Khapraswainsatyaprakash316No ratings yet
- Revision SQLDocument5 pagesRevision SQLSarvesh MariappanNo ratings yet
- Ocs752 Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument10 pagesOcs752 Introduction To C ProgrammingJegatheeswari ic37721No ratings yet
- 74 - B.SC Syllabus..Document44 pages74 - B.SC Syllabus..Satish KumarNo ratings yet
- Online Notice Board: Project Report For Bachelor of Computer ApplicationDocument30 pagesOnline Notice Board: Project Report For Bachelor of Computer ApplicationAnUp KaSuLaNo ratings yet
- Lattice Diamond User Guide: January, 2017Document156 pagesLattice Diamond User Guide: January, 2017Petr BruzaNo ratings yet
- Web Based Claim Processing SystemDocument3 pagesWeb Based Claim Processing SystemhoceroNo ratings yet
- My Class Jukebox SlidesManiaDocument19 pagesMy Class Jukebox SlidesManiaVanessa JpmNo ratings yet
- CP Lab ManualDocument81 pagesCP Lab ManualVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Spark SQLDocument24 pagesSpark SQLJaswanth ChowdarysNo ratings yet
- ADBMS Chapter OneDocument21 pagesADBMS Chapter OneNaomi AmareNo ratings yet
- Guía de Pacbase - Juan Rodríguez ParraDocument38 pagesGuía de Pacbase - Juan Rodríguez ParraJuan Parra100% (1)
- SQLServerGeeks Magazine August 2021Document59 pagesSQLServerGeeks Magazine August 2021rexpanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Computers - FlashcardsDocument1 pageIntro To Computers - FlashcardsknightttttNo ratings yet
- Different Types of SoftwareDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Softwarefayyaz aliNo ratings yet
- (CVE-2023-25616) Code Injection Vulnerability in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (CMC) - SAP For MeDocument1 page(CVE-2023-25616) Code Injection Vulnerability in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (CMC) - SAP For MePhildarPhunsiNo ratings yet
- Programming Languages ReviewerDocument3 pagesProgramming Languages ReviewerDoms TVNo ratings yet
- Newgenlib Group Assignment ICM 663Document13 pagesNewgenlib Group Assignment ICM 663Alif HaiqalNo ratings yet
- CSPO Course Workbook 1.0Document27 pagesCSPO Course Workbook 1.0utinf07100% (1)