Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economy - Overview
Uploaded by
Milaj YuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economy - Overview
Uploaded by
Milaj YuCopyright:
Available Formats
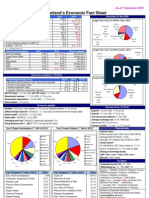
Economy - overview:
The economy has weathered global economic and financial downturns better than its regional peers due to minimal
exposure to troubled international securities , lower dependence on exports, relatively resilient domestic consumption,
large remittances from four- to five-million overseas Filipino workers , and a rapidly expanding business process
outsourcing industry. The current account balance had recorded consecutive surpluses since 2003; international reserves
are at record highs; the banking system is stable; and the stock market was Asia's second best-performer in 2012 . Efforts
to improve tax administration and expenditure management have helped ease the Philippines' tight fiscal situation and
reduce high debt levels. The Philippines has received several credit rating upgrades on its sovereign debt, and has had
little difficulty tapping domestic and international markets to finance its deficits. Economic growth in the Philippines
averaged 4.5% during the MACAPAGAL-ARROYO administration, but poverty worsened during her term. Growth has
accelerated under the AQUINO government, but with limited progress thus far in bringing down unemployment, which
hovers around 7%, and improving the qualit y of jobs. Underemployment is nearly 20% and more than 40% of the employed
are estimated to be working in the informal sector. The AQUINO administration has been working to boost the budgets for
education, health, cash transfers to the poor, and other social spending programs, and is relying on the private sector to
help fund major infrastructure projects under its Public-Private Partnership program. Long term challenges include
reforming governance and the judicial system, building infrastructure, improving regulatory predictability, and the ease of
doing business, attracting higher levels of local and foreign investments. The Philippine Constitution and the other laws
continue to restrict foreign ownership in important activities/sectors (such as land ownership and public utilities).
Gross domestic product is defined by OECD as "an aggregate measure of production equal to the sum of the gross values
added of all resident institutional units engaged in production.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$454.3 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3 2
$425.3 billion (2012 est.)
$398.2 billion (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$272.2 billion (2013 est.)
GDP - real growth rate:
6.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2 7
6.8% (2012 est.)
3.6% (2011 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$4,700 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1 6 5
$4,400 (2012 est.)
$4,200 (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
Gross national saving:
22.9% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6 3
21.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
23.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption: 72.6%
government consumption: 11.5%
investment in fixed capital: 20.2%
investment in inventories: -0.2%
exports of goods and services: 28.3%
imports of goods and services: -32.4%
(2013 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture: 11.2%
industry: 31.6%
services: 57.2% (2013 est.)
Agriculture - products:
sugarcane, coconuts, rice, corn, bananas, cassava (manioc, tapioca), pineapples, mangoes; pork, eggs, beef; fish
Industries:
electronics assembly, garments, footwear, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, wood products, food processing, petroleum
refining, fishing
Industrial production growth rate:
9% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1 9
Labor force:
41.33 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1 6
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture: 32%
industry: 15%
services: 53% (2012 est.)
Unemployment rate:
7.4% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8 1
7% (2012 est.)
Population below poverty line:
26.5% (2009 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 2.6%
highest 10%: 33.6% (2009 est.)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
44.8 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 4 2
46.6 (2003)
Budget:
revenues: $38.88 billion
expenditures: $43.89 billion (2013 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
14.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1 9 6
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-1.8% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8 1
Public debt:
50.2% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6 8
51.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
note: data cover debt issued by the national government, and excludes debt instruments issued by government entities
other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data exclude debt issued by social
security institutions, government-owned and controlled corporations, the Central Bank, and local government units
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
2.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
3.2% (2012 est.)
Central bank discount rate:
5.3% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6 3
5.6% (31 December 2011 est.)
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
5.8% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1 3 8
5.68% (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of narrow money:
$43.67 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5 0
$39.01 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of broad money:
$137.7 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4 9
$121.6 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of domestic credit:
$150.3 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4 7
$129.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares:
$266.3 billion (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 3 0
$198.4 billion (31 December 2011)
$202.2 billion (31 December 2010)
Current account balance:
$7.512 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2 5
$7.126 billion (2012 est.)
Exports:
$47.45 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5 8
$46.28 billion (2012 est.)
Exports - commodities:
semiconductors and electronic products, transport equipment, garments, copper products, petroleum products, coconut
oil, fruits
Exports - partners:
Japan 19%, US 14.2%, China 11.8%, Singapore 9.3%, Hong Kong 9.2%, South Korea 5.5%, Thailand 4.7% (2012)
Imports:
$63.91 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4 7
$61.49 billion (2012 est.)
Imports - commodities:
electronic products, mineral fuels, machinery and transport equipment, iron and steel, textile fabrics, grains, chemicals,
plastic
Imports - partners:
US 11.5%, China 10.8%, Japan 10.4%, South Korea 7.3%, Singapore 7.1%, Thailand 5.6%, Saudi Arabia 5.6%, Indonesia
4.4%, Malaysia 4% (2012)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$85.04 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2 6
$83.83 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Debt - external:
$72.81 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5 4
$NA (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:
$33.28 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6 1
$30.38 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:
$9.435 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5 4
$8.435 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Exchange rates:
Philippine pesos (PHP) per US dollar 42.69 (2013 est.)
42.229 (2012 est.)
45.11 (2010 est.)
47.68 (2009)
44.439 (2008)
You might also like
- Economy - OverviewDocument4 pagesEconomy - OverviewAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- Dwqdwqfwefewf: Economy - OverviewDocument4 pagesDwqdwqfwefewf: Economy - OverviewAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument7 pagesEconomicsDoodz DingleNo ratings yet
- PFP 2013 workplan and budget proposalDocument25 pagesPFP 2013 workplan and budget proposaloxade21No ratings yet
- Country Comparison To The World:: GDP (Purchasing Power Parity)Document2 pagesCountry Comparison To The World:: GDP (Purchasing Power Parity)api-278303182No ratings yet
- ER 2013-01-2012 Yearend ReportDocument12 pagesER 2013-01-2012 Yearend ReportLyn EscanoNo ratings yet
- Economy - OverviewDocument18 pagesEconomy - OverviewRendy MokogintaNo ratings yet
- Economic Environment: 1. Macroeconomic TrendsDocument13 pagesEconomic Environment: 1. Macroeconomic TrendsJonathan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Conventional Long FormDocument13 pagesConventional Long FormJugal DesaiNo ratings yet
- Philippines Country DataDocument7 pagesPhilippines Country DataArangkada PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economy Profile 2012: GDP, Exports, Imports and MoreDocument8 pagesPakistan Economy Profile 2012: GDP, Exports, Imports and MoreUmair GujjarNo ratings yet
- Business Startups: Comparing China and India's EconomiesDocument2 pagesBusiness Startups: Comparing China and India's EconomiesSivaraman P. S.No ratings yet
- Nigeria: A Dynamic and Diversifying EconomyDocument2 pagesNigeria: A Dynamic and Diversifying EconomyAdeniyi AleseNo ratings yet
- Country Statistical Profile: South Africa 2011-2012Document2 pagesCountry Statistical Profile: South Africa 2011-2012mttcgNo ratings yet
- Comparing the economies of France and UAEDocument16 pagesComparing the economies of France and UAEuowdubaiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Economic ConditionDocument5 pagesBangladesh Economic ConditionBilkisNo ratings yet
- Country Strategy 2011-2014 MoldovaDocument21 pagesCountry Strategy 2011-2014 MoldovaBeeHoofNo ratings yet
- Thailand's Economic Fact Sheet: As of April 2014Document5 pagesThailand's Economic Fact Sheet: As of April 2014Oon KooNo ratings yet
- Doing Deals in Peru 2012 PDFDocument88 pagesDoing Deals in Peru 2012 PDFalxmalagaNo ratings yet
- Economy of GeorgiaDocument22 pagesEconomy of GeorgiaAman DecoraterNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Economy: SWOT AnalysisDocument16 pagesBangladesh Economy: SWOT AnalysisMarshal Richard83% (6)
- Economy - OverviewDocument7 pagesEconomy - OverviewAmir RashidNo ratings yet
- Low Soo Peng Singapore BusinessDocument16 pagesLow Soo Peng Singapore BusinessLow Soo PengNo ratings yet
- What Is Econmy AnalysisDocument7 pagesWhat Is Econmy AnalysisFaisal HanifNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between The Economies of Pakistan and India: Submitted byDocument20 pagesComparison Between The Economies of Pakistan and India: Submitted byscholastictutoringNo ratings yet
- Measuring Economic Freedom in GhanaDocument2 pagesMeasuring Economic Freedom in GhanaMoinul HossainNo ratings yet
- Eco Factsheet 20131220 100445 235435 PDFDocument3 pagesEco Factsheet 20131220 100445 235435 PDFRaafat FarshidNo ratings yet
- Doing Busines in The PhillipinesDocument131 pagesDoing Busines in The PhillipinespapashuNo ratings yet
- KPMG Zimbabwe 2012Q2Document4 pagesKPMG Zimbabwe 2012Q2Arvind ChariNo ratings yet
- How Do We Measure Canada's Economic FreedomDocument2 pagesHow Do We Measure Canada's Economic FreedomjarnysNo ratings yet
- SingaporeDocument2 pagesSingaporeAdibsulNo ratings yet
- Regional GDP Growth Slows Further to 4.7% in 1Q12Document9 pagesRegional GDP Growth Slows Further to 4.7% in 1Q12enleeNo ratings yet
- Bank of Kigali Investor Presentation Q1 & 3M 2012Document43 pagesBank of Kigali Investor Presentation Q1 & 3M 2012Bank of Kigali100% (1)
- Economy::BANGLADESH: Source: CIA Fach SheetDocument5 pagesEconomy::BANGLADESH: Source: CIA Fach SheetFahad Hasan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth Development in SingaporeDocument36 pagesEconomic Growth Development in SingaporeNazir AnsariNo ratings yet
- Norway: Overall Performance Basic FactsDocument4 pagesNorway: Overall Performance Basic Factsbuturca sorinNo ratings yet
- A Macroeconomic Analysis of BangladeshDocument35 pagesA Macroeconomic Analysis of Bangladeshnazmul_85No ratings yet
- Economy of DenmarkDocument26 pagesEconomy of DenmarkAman DecoraterNo ratings yet
- GenpactLtd 8K 20130207Document15 pagesGenpactLtd 8K 20130207sssneha_rNo ratings yet
- Greece: Economic Freedom ScoreDocument2 pagesGreece: Economic Freedom ScoreYana Fitri Mawaddatan WarahmahNo ratings yet
- Parte 3 y 4Document2 pagesParte 3 y 4Maryori salvador gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Release 4Q12Document18 pagesRelease 4Q12Klabin_RINo ratings yet
- Eco Factsheet 2012-09-0Document2 pagesEco Factsheet 2012-09-0thailand2dayNo ratings yet
- Economy of NepalDocument10 pagesEconomy of NepalAman DecoraterNo ratings yet
- Earnings ReleaseDocument7 pagesEarnings ReleaseBVMF_RINo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument22 pagesChapter ThreewomenwingrssNo ratings yet
- S&P 500 2013: Global Sales Year in Review: ResearchDocument15 pagesS&P 500 2013: Global Sales Year in Review: Researchapi-70097803No ratings yet
- 2012 Ev-SerDocument11 pages2012 Ev-Sershantalnicole2No ratings yet
- Economic Overview of GreeceDocument5 pagesEconomic Overview of GreeceRavi PandyaNo ratings yet
- Argentina Chile Etc Ebook 2015dec04Document121 pagesArgentina Chile Etc Ebook 2015dec04ascar57No ratings yet
- India: South AsiaDocument6 pagesIndia: South Asiagrovermegha12No ratings yet
- Business Environment AustraliaDocument10 pagesBusiness Environment AustraliaSabeena MathayasNo ratings yet
- Egypt PEST AnalysisDocument12 pagesEgypt PEST AnalysisMohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- Economy of EgyptDocument42 pagesEconomy of EgyptAman DecoraterNo ratings yet
- Econ Club Extra Credit ProjectDocument4 pagesEcon Club Extra Credit ProjectSpencer GladdenNo ratings yet
- Country Analysis BrazilDocument31 pagesCountry Analysis Brazilsagar17100% (1)
- Our Network: Our Presence, in All Corners of Pakistan, Is More Than Just Being ThereDocument4 pagesOur Network: Our Presence, in All Corners of Pakistan, Is More Than Just Being ThereRulz MakerNo ratings yet
- Economy of ChadDocument6 pagesEconomy of ChadAman DecoraterNo ratings yet
- An Unconventional Introduction to Development Economics: A lively and user-friendly case studies method using hundreds of real-life macroeconomic scenarios from 52 countriesFrom EverandAn Unconventional Introduction to Development Economics: A lively and user-friendly case studies method using hundreds of real-life macroeconomic scenarios from 52 countriesNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Investment Pools & Funds Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandMiscellaneous Investment Pools & Funds Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Construct v-t and a-t graphs for bicycle position problemDocument3 pagesConstruct v-t and a-t graphs for bicycle position problemMilaj YuNo ratings yet
- Physics projectile motion and velocity word problemsDocument4 pagesPhysics projectile motion and velocity word problemsMilaj YuNo ratings yet
- Stress - ProblemsDocument13 pagesStress - ProblemsMilaj YuNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument37 pagesRisk ManagementMilaj YuNo ratings yet
- Computer NOTES: OUTPUT FORMATTINGDocument2 pagesComputer NOTES: OUTPUT FORMATTINGMilaj YuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document4 pagesLesson 3Milaj YuNo ratings yet
- TV Series Air TimeDocument1 pageTV Series Air TimeMilaj YuNo ratings yet
- 122 0704Document35 pages122 0704api-27548664No ratings yet
- CBS News Poll: Fiscal CliffDocument14 pagesCBS News Poll: Fiscal CliffCBS_News0% (1)
- 11th Five Year Plan Objectives and ChallengesDocument42 pages11th Five Year Plan Objectives and ChallengesJeet Pawar100% (1)
- Pre-Feasibility Study for Dermatology Hospital in Jordan's Dead SeaDocument52 pagesPre-Feasibility Study for Dermatology Hospital in Jordan's Dead SeaKlare MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Research Anvikshiki - EnglishDocument63 pagesIndian Journal of Research Anvikshiki - EnglishHimani MittalNo ratings yet
- International Macroeconomics: Slides For Chapter 7: Twin Deficits: Fiscal Deficits and Current Account ImbalancesDocument74 pagesInternational Macroeconomics: Slides For Chapter 7: Twin Deficits: Fiscal Deficits and Current Account ImbalancesM Kaderi KibriaNo ratings yet
- Board Development: Budgeting For Not-for-Profit OrganizationsDocument8 pagesBoard Development: Budgeting For Not-for-Profit Organizationsfaris nasserNo ratings yet
- (Article) What Drives Performance Budgeting To Perform - A Survey Examination in Taiwan (2013)Document15 pages(Article) What Drives Performance Budgeting To Perform - A Survey Examination in Taiwan (2013)AbusamraMousaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Approaches and Techniques in Budgeting The Philippine Budgeting by Niña SaltingDocument22 pagesChapter 11 Approaches and Techniques in Budgeting The Philippine Budgeting by Niña Saltingblddsrmfb4aNo ratings yet
- Macro 95 Ex 2Document17 pagesMacro 95 Ex 2Engr Fizza AkbarNo ratings yet
- (BS) Economics B.K Singh: SourcesDocument35 pages(BS) Economics B.K Singh: SourcesAyesha NaazNo ratings yet
- Asiabest Group International Inc. - 17A - 10may2022Document97 pagesAsiabest Group International Inc. - 17A - 10may2022Ming MaoNo ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument28 pagesEconomics AssignmentJoydeep NaskarNo ratings yet
- Cash Management Bank of IndiaDocument52 pagesCash Management Bank of Indiaakalque shaikhNo ratings yet
- Digital Dossier of Current AffairsDocument187 pagesDigital Dossier of Current Affairskandasamy004No ratings yet
- Sohn Investment Conference Presentation, June 9, 2022Document49 pagesSohn Investment Conference Presentation, June 9, 2022aitilopNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy Objectives-7Document5 pagesFiscal Policy Objectives-7Rahul ItankarNo ratings yet
- HE1002 Tutorial4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesHE1002 Tutorial4 QuestionsRaudhah Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Balances of Payments and Exchange Rates ExplainedDocument7 pagesBalances of Payments and Exchange Rates ExplainedAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chris Lori - Understanding Global FundamentalsDocument38 pagesChris Lori - Understanding Global FundamentalsRui Lopes100% (1)
- TariffContent 2014Document11 pagesTariffContent 2014gvsbabu63No ratings yet
- Economics of Sea Transport International Trade-2008 EXAMINERS REPORTDocument5 pagesEconomics of Sea Transport International Trade-2008 EXAMINERS REPORTMohd Shaji100% (2)
- List of Sub-Object Code - 20160322Document135 pagesList of Sub-Object Code - 20160322Julius AlemanNo ratings yet
- Cefap 2016-17 Online FullDocument328 pagesCefap 2016-17 Online FullDalipNo ratings yet
- 1UPSCPORTALMagazineCivil Services 2009 Pre Special PDFDocument113 pages1UPSCPORTALMagazineCivil Services 2009 Pre Special PDFManda Swamy100% (1)
- Strategic Analysis of United Bank LimitedDocument75 pagesStrategic Analysis of United Bank Limitedshahid_pak1_2611436480% (5)
- The Modern Financial System: Sargon NissanDocument40 pagesThe Modern Financial System: Sargon Nissanjagdishmisra2011No ratings yet
- Fritz Strengthening PFM 2014Document55 pagesFritz Strengthening PFM 2014amudaryoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Stock Market On Indian EconomyDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Stock Market On Indian EconomyIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Session: ArthashastraDocument27 pagesKnowledge Session: ArthashastraRomali DasNo ratings yet