Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Closed Book Api 572-A (55-65) - 2
Uploaded by
slxantoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Closed Book Api 572-A (55-65) - 2
Uploaded by
slxantoCopyright:
Available Formats
Southern Inspection Services
Closed Book API 572
1. What must be considered important in the inspection of a metallic
lining?
a.
b.
c.
d.
That there are no dissimilar welds
That the linings made of pure alloy only
The vent holes exist in all liners.
That there are no holes or cracks present in the lining.
2. Of the following tools which should the inspector have on hand for
vessel inspections?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Pencil and note pad, flash light and scraper
Social security card.
Clean fire retardant clothing
Electrical conductivity testing equipment to test liners.
3. Many of the problems that develop in operating vessels may be traced
to;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Cold winters
On-stream inspections
Electrical shorts
Faulty materials and workmanship
4. The primary cause of deterioration in pressure vessels is;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Corrosion
Operating conditions
Improper installation
Water damage
5. High pressure may develop in a vessel as a result of;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Rapid venting of a vessels pressure source
Lowering heat below normal operating conditions
Thermal contraction of trapped fluids
Blocking off against a pressure source
6. Which of the following techniques is considered the primary means to
determine the minimum thickness of a vessels components?
a.
b.
c.
d.
A boat sample remove from a thin area
Measuring from a corroded area
Any suitable destructive method of examination
Ultrasonic thickness measurements.
API 510 DAY 4
Page 55
Southern Inspection Services
7. before starting the inspection of a pressure vessel, especially one is
severe service the inspector should determine;
a. The pressure and temperature conditions under which the vessel
been operated since the first inspection
b. The pressure and temperature conditions under which the vessel
been operated during the period since the last two inspections.
c. The pressure and temperature conditions under which the vessel
been operated since the current inspection
d. The pressure and temperature conditions under which the vessel
been operated since the last inspection
has
has
has
has
8. The inability to draw the products of fractionation or distillation from
certain trays may
a.
b.
c.
d.
Indicate fouling or loss of tray parts in a process tower
Indicate that instrumentation is giving false readings.
Prove that the piping diameter is too small
Indicate that the trays have lost all bubble caps or tray valves, or
possibly the tray has collapsed
9. Before any repair to a pressure vessel in accordance with its code of
construction, what if any additional requirements for inspection may
need to be considered?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Jurisdictional requirements that might override the API 510 code
Who is doing the repair?
The quality of the repair materials
The need for qualified welding procedures
10. Some jurisdictions require that welded repairs to a pressure vessel be
documented by the completion and filing of;
a.
b.
c.
d.
A detailed report of the location and extent of repairs
A qualifications record of all repair personnel
A permit issued by the jurisdiction
The national Board of Boiler and pressure vessel inspectors form R-1
API 510 DAY 4
Page 56
Southern Inspection Services
11. While inspecting an operating vessel you observe that cracks are
present in the connecting welds for a gauge glass, you also notice
vibrations are occurring in the assembly. Before you recommend
corrective actions you should;
a. Re-evaluate the materials used in the fabrication of the gauge glass
b. Write a report of the location with a recommendation for the type of
repairs needed
c. Research the inspection records for previous failures of this type
d. Check with a pressure vessel engineer to see if the cracks are caused
by fatigue failure
12. The two types of graphitization are
a.
b.
c.
d.
Localized and random graphitization
Ferritic and martensite graphitization
Austenitic and martensitic graphitization
Circular or globular graphitization
13. The main reason(s) for inspecting heat exchanger bundles after removal
and prior to cleaning is/are;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Location of scale on tubes can reveal non-operational problems.
Deposits on the tubes can reveal acid contamination problems
Color of the tube ends can reveal de-zincification
Color of deposits and scale can scale can reveal corrosion problems
14. Hydrogen chloride becomes a problem when,
a. Exposed to air, it will thermally react and result in a fire.
b. Exposed to water, it forms hydrochloric acid.
c. Exposed to water it becomes unstable and can form an explosive
compound
d. Exposed to water and air it produces formic acid
15. Which one of the following types of coating failures may not easily
detected?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Film lifting
Rust
Blisters
Film dispersions
API 510 DAY 4
Page 57
Southern Inspection Services
16. A vessel is in a service that subjects it to acidic fluids, what is a major
concern for this type of service?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Graphitic induced corrosion
Caustic blistering
Caustic embrittlement and cracking
Accelerated corrosion, Hydrogen blistering and Hydrogen induced
cracking
17. Ordinarily non-metallic coatings and linings can be most effectively
inspected by what technique?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Law holiday tester
Radiography
Hammer testing
Using a high voltage low current brush type electrode device (spark
Tester)
18. A major concern(s) when inspecting a nozzle flange face is /are;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Brand name of the flange
Brand name of the gaskets used in the flange.
Surface corrosion in the bolt circle.
Distortion of the flange and the condition of the gasket seating
surfaces.
19. If there are leaks in a vessels insulation system or protective coatings,
corrosion can occur. At below what temperature is this corrosion
most likely to be a problem?
a.
b.
c.
d.
250F
212F
350F
275F
20. which of the following is subject to de-alloying when exposed to steam
containing sulfur compounds?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Cuppro brass
Naval brass
Admiralty brass
Monel
API 510 DAY 4
Page 58
Southern Inspection Services
21. Titanium alloys are subject to loss of ductility in certain environments
what is this condition called?
a.
b.
c.
d.
High temperature embrittlement
Low temperature embrittlement
Hi-alloy effect
Hydriding
22. Which of the following describes a crack in metal?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Cracks run parallel to the surface
Cracks run at right angles to the surface
Cracks are usually wide at one end and narrow at the other
Cracks run at obtuse angles to the surface
23. Which of the following describes a lamination in metal plate?
a. Laminations usually represent large cavities
b. Laminations are fish mouth type openings and are only found on the
edges of plate
c. Laminations run at a slant to the plate surface
d. Laminations run at an obtuse angle to the plate surface
24. Above what temperature must hydrogen attack be considered a concern
in an operating carbon steel vessel?
a.
b.
c.
d.
above 650F
below 650F
below 450F
above 450F
25. After removing an exchanger bundle you find a Prussian blue coating
on the tubes, what do you suspect causes this coating?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Amino acid
Cyanide
Ferri-ferrocyanide
Phosphoric acid
26. One major area of concern when inspecting guy wires for a vessel is
crevice corrosion where does this occur?
a.
b.
c.
d.
On the free end of the turn buckle
In the threaded areas
On the guy wires
Where the wires contact the ground
API 510 DAY 4
Page 59
Southern Inspection Services
27. You are inspecting a failure in a vessel wall, what conditions would you
look for if it was believed that the fracture was brittle?
a.
b.
c.
d.
There is almost a no lack of ductility
The fractured surfaces has a smooth surface
The surface of the crack would have jagged edges.
There is an almost complete lack of ductility and the failure site will
have a faceted surface
28. Carbon dioxide considered corrosive when?
a.
b.
c.
d.
When combined with glycol
When combined with water
When combined with ethylene
When combined with water and high temperatures
29. If white salts are found at cracks in a vessel;
a.
b.
c.
d.
It is an indication that the vessel contains an alkaline based chemical
It is an indication that the vessel contains an acidic based chemical
It is an indication that the vessel contains a low pH chemical
It is an indication that the vessel had been operated above normal
temperatures.
30. A poor choice of material for ammonia service would be;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Stainless steels
Copper based alloys
Carbon steels
Carbon Molybdenum steels
31. when manufacturing lubricating oils and aromatics the following
chemical is used.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Phenol
Ammonia
Hydrogen cyanide
glycol
32. Aluminum chloride can affect stainless steel in which of the following
ways?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Severe pitting corrosion only
Intergranular cracking only
Stress corrosion cracking only
Stress corrosion cracking and/or intergranular cracking can occur
API 510 DAY 4
Page 60
Southern Inspection Services
33. The low temperature corrosion of gray cast irons is called;
a.
b.
c.
d.
graphitic corrosion
temper embrittlement
brittle fracture
incipient melting
34. Most active of sulfur compounds found in refinery service is;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Mercaptans
organic sulfur compounds
hydrogen sulfide
polymorphic sulfides when combined with polymer products.
35. Which of the following is an example of a microstructure change in
metal?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Graphitization
Interstial Corrosion
Dembrittlement
Embossing
36. A common corrosive compound found in crude oil is;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Nitrogen compounds.
Phenolic acid
Napthinic acid.
Carbonic acid
37. Dezincification occurs by attacking metals which contain;
a. Copper Zinc alloys containing less than 95% of copper used in water
service
b. Copper Zinc alloys containing less than 85% of copper used in water
service
c. Copper Zinc alloys containing less than 85% of copper used in
caustic service
d. Copper Zinc alloys containing less than 95% of copper used in acidic
service
38. Which of the following describes a physical change in metal?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Intergranular conosion
Sensitization.
Banite solution.
Amphoric layering.
API 510 DAY 4
Page 61
Southern Inspection Services
39. When looking for surface cracks in a vessel made of ferrous material
which of the following is the most capable of detection?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Fluorescent Penetrant Method.
Radiography
Fluorescent Magnetic Particle Method.
Close visual Inspection with good lighting.
40. The majority of vessel foundations are constructed using;
a.
b.
c.
d.
High grade (load bearing) concrete compounds.
Structural steel fireproofed with concrete.
Concrete reinforced with polymers.
Structural steel overlaid with refractory.
41. Vanadium Oxide corrosion is not known to occur below;
a.
b.
c.
d.
1,050 F
1,100 F
950 F
800 F
42. Which of the following is a major concern when operating vessels that
utilize the fluidized bed principle?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Overheating
Erosion
Corrosion
Cracks
43. The inspection of a vessel to determine if a hydrogen blister is present
is often best performed by;
a.
b.
c.
d.
Researching the inspection records.
Determine the vessels material to see if hydrogen attack is likely.
Shining a flash light parallel to the vessels surface.
Recommending metallurgical tests for blisters in a laboratory.
44. When preparing to inspect a vessel which has had previous inspections
what is the initial step in preparation for the inspection?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Assemble all the required tools to perform the inspection.
Review previous inspection records.
Advice maintenance of any anticipated repairs.
Insure that all non-destructive examinations required have been
scheduled
API 510 DAY 4
Page 62
Southern Inspection Services
45. Which of the following best describes a Corrosion Button as might be
found in a pressure vessel?
a. Buttons made of highly corrosion resistant material from which
corrosion loss can be measured.
b. Buttons which corrode at about the same rate as the vessels material
and are used to estimate the vessels corrosion losses.
c. No such thing exists; there is however a corrosion tab used in vessels.
d. A form of corrosive product produced by certain chemicals in a vessel
when is constructed of high chrome alloy material.
46. Why should weld probe or trepan inspection methods be avoided if at
all possible?
a. The repair concern will normally charge more to repair these
destructive tests sites in the vessel
b. These types of destructive test site (holes) are difficult to repair and the
weld quality of such repairs is likely to be poor.
c. Most jurisdictions prohibit such destructive tests.
d. NDE personnel are ill equipped to test such sites prior to repairs.
47. pitting corrosion is usually found in a vessel by what means?
a. Thickness measurements at all the compass points at one foot
intervals.
b. Scratching with a pointed scraper.
c. Each shell course and head shall be subjected to abrasive blasting.
d. Each shell course and head shall be wire brushed thoroughly.
48. Heavy wall process hydro-carbon reactors operate at high pressures
and have special inspection requirements, chief among these
requirements are inspections for what type of problem?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Laminations of the heavy wall plates used in construction
Crack damage.
Upset trays and down comers.
Severe corrosion in the top head due to corrosive vapors generated in
the process.
API 510 DAY 4
Page 63
Southern Inspection Services
Closed Book API 572 ANSWERS
Q.No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
ANSWER
LOCATION OF ANSWER
D
A
D
A
D
D
D
A
A
D
D
A
D
B
A
D
D
D
A
D
D
B
C
D
C
B
D
B
A
B
A
D
A
C
A
A
API 572 10.4.5
API 572 10.2.2
API 572 8.4
API 572 8.2
CHAPTER II 206.021 - .023
API 572 10.5
API 572 10.1
API 572 9.2
API 572 11.0 (see note in text body)
API 572 11.0 (see note in text body)
API 572 10.3.10
CHAPTER 2 204.022
API 572 A.9.1
CHAPTER II 202.022
API 572 10.3.11
CHAPTER II 202.022
API 572 10.4.6
API 572 10.3.8
CHAPTER II 202.042
API 572 8.3.3
API 572 8.3.7
API 572 10.4.4
API 572 10.4.4
CHAPTER II 204.035
API 572 A.9.2
API 572 10.3.7
CHAPTER II 205.01
CHAPTER II 202.024
API 572 10.3.12
CHAPTER II 202.037
CHAPTER II 202.033
CHAPTER II 202.039
CHAPTER II 202.063
CHAPTER II 202.23
API 572 8.3
CHAPTER II 202.021
API 510 DAY 4
Page 64
Southern Inspection Services
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
B
A
C
B
B
B
C
B
A
B
B
B
API 510 DAY 4
CHAPTER II 202.66
API 572 8.3
API 572 10.4.4
API 572 10.3.3
CHAPTER II 202.054
CHAPTER II 202.32
API 572 10.3.13
API 572 10.4.3
API 572 10.5
API 572 11.0
API 572 10.4.4
API 572 10.4.4
Page 65
You might also like
- API 510 Exam Study GuideDocument6 pagesAPI 510 Exam Study GuidetayyabNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsFrom EverandCorrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsNo ratings yet
- Examination Question 510Document12 pagesExamination Question 510ohengjkt100% (1)
- Casti CourseDocument43 pagesCasti CoursekazumiyutoriNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Arc Length: The Distance From The Tip of The WeldingDocument7 pages3.4 Arc Length: The Distance From The Tip of The WeldingMohammed IlliasuddinNo ratings yet
- API 577 Questions Scope and DefinitionsDocument10 pagesAPI 577 Questions Scope and DefinitionsmaorealesNo ratings yet
- Api 578-Mock 1 - KeyDocument28 pagesApi 578-Mock 1 - KeysheikmoinNo ratings yet
- Open Book API 510 Practice Exam B Do Not Mark On Your Exam, Use The Answer Sheets ProvidedDocument16 pagesOpen Book API 510 Practice Exam B Do Not Mark On Your Exam, Use The Answer Sheets ProvidedBeantickNo ratings yet
- 1 API 653 Memories March 2014 ExamDocument16 pages1 API 653 Memories March 2014 ExammajidNo ratings yet
- Undercut (Per API 577, Table 6) Can Be Corrected by (Practical Solution Column)Document2 pagesUndercut (Per API 577, Table 6) Can Be Corrected by (Practical Solution Column)korichiNo ratings yet
- API 510 Closed Questions GuideDocument5 pagesAPI 510 Closed Questions GuideEinsteinw2No ratings yet
- 63 Multiple Choice Questions: No Answer GivenDocument16 pages63 Multiple Choice Questions: No Answer GivenAnonymous Q4YUvR100% (1)
- API 510 Certification Prep: 60-hr Pressure Vessel Inspector CourseDocument1 pageAPI 510 Certification Prep: 60-hr Pressure Vessel Inspector CourseAbu Huraira0% (1)
- API-570 SAMPLE Closed Book ExamDocument12 pagesAPI-570 SAMPLE Closed Book ExamuttamNo ratings yet
- (PDF) PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR API RP 577 Quizlet - Gustavo HC - Academia - EduDocument4 pages(PDF) PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR API RP 577 Quizlet - Gustavo HC - Academia - EduKumar R100% (1)
- API 570 Libro Abierto GeneralDocument26 pagesAPI 570 Libro Abierto GeneralWveimar BriceñoNo ratings yet
- 17 Multiple Choice Questions: No Answer GivenDocument5 pages17 Multiple Choice Questions: No Answer GivenAkram AlhaddadNo ratings yet
- API 510 Prep Course QuestionsDocument30 pagesAPI 510 Prep Course QuestionsRanaweera AriyamanjulaNo ratings yet
- 17 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pages17 Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous Q4YUvR100% (1)
- 2-Questions API 650 Question N°02 2022Document3 pages2-Questions API 650 Question N°02 2022korichiNo ratings yet
- Api 577 Reponse01Document3 pagesApi 577 Reponse01korichiNo ratings yet
- API-510 Exam Prep Course Practice Exam #3 SolutionsDocument14 pagesAPI-510 Exam Prep Course Practice Exam #3 SolutionsKarim MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Boost Your API-570 Piping Inspectors Exam ScoreDocument6 pagesBoost Your API-570 Piping Inspectors Exam Scorejaire esparzaNo ratings yet
- Additional API 571 Practice Questions flashcardsDocument4 pagesAdditional API 571 Practice Questions flashcardsMohammad Aamir Perwaiz100% (1)
- API 510 Preparatory Course GuideDocument7 pagesAPI 510 Preparatory Course GuideRanaweera AriyamanjulaNo ratings yet
- Sis Book1Document99 pagesSis Book1Hamza AlamNo ratings yet
- API.570. Closed Book 3Document31 pagesAPI.570. Closed Book 3Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- API RP 571 corrosion questionsDocument5 pagesAPI RP 571 corrosion questionsأحمد صبحى100% (1)
- API 510 QUIZ No.4Document5 pagesAPI 510 QUIZ No.4Hatem RagabNo ratings yet
- API 510 Data Sheets - QuizletDocument1 pageAPI 510 Data Sheets - Quizletads_1203No ratings yet
- API 510.jan 2022 (Open & Closed)Document79 pagesAPI 510.jan 2022 (Open & Closed)Ali BEN YESAADNo ratings yet
- API 510 TestDocument3 pagesAPI 510 Testshabbir626No ratings yet
- Test - API 577 - Quizlet 145qDocument38 pagesTest - API 577 - Quizlet 145qAnonymous Q4YUvRNo ratings yet
- API 510 PC 20 31 Aug05 Bench MarkDocument4 pagesAPI 510 PC 20 31 Aug05 Bench MarknikafiqNo ratings yet
- API 570 - Mockup CB - Paper 2Document16 pagesAPI 570 - Mockup CB - Paper 2Shanawas Abdul Razak100% (1)
- API 570 - CL Book 111122112010 R0... Mockup 3Document18 pagesAPI 570 - CL Book 111122112010 R0... Mockup 3patvinderNo ratings yet
- Api 510 Q&a-2Document32 pagesApi 510 Q&a-2Mohammed ShakilNo ratings yet
- C Closed B Losed B Ook Ook P Practice Que Ractice Questio Stio Ns NsDocument10 pagesC Closed B Losed B Ook Ook P Practice Que Ractice Questio Stio Ns NsElankumaran Periakaruppan100% (1)
- API 510 Mid Session Closed0Document10 pagesAPI 510 Mid Session Closed0مبشر أحمد100% (2)
- 10 MCQS API 510 Anees Ul HasnainDocument126 pages10 MCQS API 510 Anees Ul HasnaintayyabNo ratings yet
- Test - API 577 - Quizlet 72qDocument23 pagesTest - API 577 - Quizlet 72qAnonymous Q4YUvRNo ratings yet
- MSTS Mark's API 510 STUDY GUIDE.Document30 pagesMSTS Mark's API 510 STUDY GUIDE.Hares SlalNo ratings yet
- Open Book For API 653Document10 pagesOpen Book For API 653gopiNo ratings yet
- Closed Book API RP 578 Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesClosed Book API RP 578 Practice QuestionsIsmail Jamaluddin100% (1)
- API 510 Case Study - 7Document2 pagesAPI 510 Case Study - 7Khaled FatnassiNo ratings yet
- Daily Points To Recall (Day 8) : Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesDaily Points To Recall (Day 8) : Page 1 of 3chowhkNo ratings yet
- API 576 Pressure Relief Device QuestionsDocument1 pageAPI 576 Pressure Relief Device QuestionsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- API 570 Questions 06Document22 pagesAPI 570 Questions 06Ravindra S. Jivani75% (4)
- API 570 Exam Prep TrainingDocument3 pagesAPI 570 Exam Prep Trainingalouis100% (1)
- API 570 Exam 574 QuizDocument3 pagesAPI 570 Exam 574 Quizessnelson100% (2)
- API 570 Bench Mark Quiz (1-55)Document56 pagesAPI 570 Bench Mark Quiz (1-55)Christopher Randolph100% (5)
- Api 510 QDocument25 pagesApi 510 QShyam Singh100% (1)
- 510 Closed Exam B, Rev8Document20 pages510 Closed Exam B, Rev8yrdna nawaiteosNo ratings yet
- ASME B16.5 practice questions and answersDocument66 pagesASME B16.5 practice questions and answersAbdul Qhadeer AnsariNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive Evaluation of Corrosion and Corrosion-assisted CrackingFrom EverandNon-Destructive Evaluation of Corrosion and Corrosion-assisted CrackingRaman SinghNo ratings yet
- API 510 PC 4sept04 Daily Exam 5 Closed PSJDocument12 pagesAPI 510 PC 4sept04 Daily Exam 5 Closed PSJMohammed Shakil100% (1)
- API 510 Exam 9 ReviewDocument6 pagesAPI 510 Exam 9 ReviewCss SfaxienNo ratings yet
- API 571 Exam Questions 2014Document8 pagesAPI 571 Exam Questions 2014Mansoor Ali100% (1)
- Api 510 Preparatory Final Exam (Closed Book) : Answers in A Separate Answer SheetDocument14 pagesApi 510 Preparatory Final Exam (Closed Book) : Answers in A Separate Answer SheetCss Sfaxien100% (1)
- Bgas Paint Faults, BittinessDocument49 pagesBgas Paint Faults, BittinessslxantoNo ratings yet
- ASME VIII CalculationDocument15 pagesASME VIII CalculationJoao Osmar Correa100% (1)
- Hydro Vs PneumaticDocument4 pagesHydro Vs PneumaticAnonymous rYZyQQot55No ratings yet
- Pid37451 PMAADocument6 pagesPid37451 PMAAslxantoNo ratings yet
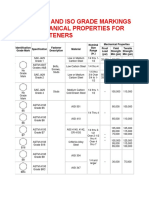
- Astm, Sae and Iso Grade Markings and Mechanical Properties For Steel FastenersDocument6 pagesAstm, Sae and Iso Grade Markings and Mechanical Properties For Steel FastenersCarlos Nina OchoaNo ratings yet
- API 510 Examination Sample ItemsDocument3 pagesAPI 510 Examination Sample ItemsMagira PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Overseas Jobs Times MumbaiDocument3 pagesOverseas Jobs Times MumbaislxantoNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Sand-Blasting Procedure PDFDocument5 pagesAbrasive Sand-Blasting Procedure PDFEko Kurniawan100% (5)
- H2S Safety CourseDocument98 pagesH2S Safety CourseWalter RuedaNo ratings yet
- ASTM and Grain Size MeasurementsDocument6 pagesASTM and Grain Size MeasurementsTomy George100% (1)
- BGas MaterialDocument65 pagesBGas Materialslxanto100% (4)
- Southern Inspection Services ASME SEC VIII QB and API 510 Exam QuestionsDocument15 pagesSouthern Inspection Services ASME SEC VIII QB and API 510 Exam Questionsslxanto100% (1)
- API Certification Exam Dates & Deadlines 2015Document2 pagesAPI Certification Exam Dates & Deadlines 2015slxantoNo ratings yet
- API Certification Exam Dates & Deadlines 2015Document2 pagesAPI Certification Exam Dates & Deadlines 2015slxantoNo ratings yet
- API Inspector Training CoursesDocument10 pagesAPI Inspector Training CoursesslxantoNo ratings yet
- API 2014 Exam ScheduleDocument1 pageAPI 2014 Exam ScheduleslxantoNo ratings yet
- Api510practiceexams 130208053530 Phpapp02Document138 pagesApi510practiceexams 130208053530 Phpapp02slxantoNo ratings yet
- Mos GRPDocument53 pagesMos GRPslxanto100% (3)
- API Inspector Training CoursesDocument10 pagesAPI Inspector Training CoursesslxantoNo ratings yet
- Radiation Hazards From Cell Phones and Cell Towers - Presentation at KEM HospitalDocument61 pagesRadiation Hazards From Cell Phones and Cell Towers - Presentation at KEM HospitalNeha KumarNo ratings yet
- Course BrochureDocument25 pagesCourse BrochureslxantoNo ratings yet
- Er.Sulthan's Ayurvedic Home RemediesDocument321 pagesEr.Sulthan's Ayurvedic Home Remediesarunram86100% (2)
- ASME B31.1 Power PipingDocument1 pageASME B31.1 Power Pipingslxanto25% (4)
- Evolution of Oilfield BatteriesDocument16 pagesEvolution of Oilfield BatteriesPasquale CutriNo ratings yet
- Documentation For: Bank - MasterDocument6 pagesDocumentation For: Bank - MastervijucoolNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure Experiment Data AnalysisDocument3 pagesVapor Pressure Experiment Data AnalysisRanaNo ratings yet
- Life 365 V 2 Users ManualDocument67 pagesLife 365 V 2 Users ManualAmanda VegaNo ratings yet
- R07-HC3C20-AAP-MTS-CI-0005 (02) Method Statement of Site Mobilization at Island (Revised)Document32 pagesR07-HC3C20-AAP-MTS-CI-0005 (02) Method Statement of Site Mobilization at Island (Revised)like saddamNo ratings yet
- Mousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeDocument1 pageMousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeMorteza AtaeiNo ratings yet
- Wae 22462 AuDocument8 pagesWae 22462 AuDaniel ManoleNo ratings yet
- Improved M16A2 - A3 - A4 Zero TargetDocument6 pagesImproved M16A2 - A3 - A4 Zero Targetbeetho1990No ratings yet
- Xlpe - Ls243Nta: - 1 Technical Data Sheet Crosslinkable Polyethylene CompoundDocument3 pagesXlpe - Ls243Nta: - 1 Technical Data Sheet Crosslinkable Polyethylene CompoundLe MinhNo ratings yet
- Applications: H D P TDocument2 pagesApplications: H D P TEnrique MurgiaNo ratings yet
- Queen Sala Celinda Del Rosario LECCION2 Actividad de Produccion 2.4Document4 pagesQueen Sala Celinda Del Rosario LECCION2 Actividad de Produccion 2.4Salustino AbreuNo ratings yet
- Performance Fluids Oh32 Oh150 Hydraulic OilDocument3 pagesPerformance Fluids Oh32 Oh150 Hydraulic Oilpancho7rNo ratings yet
- Column and Wall Load Take Down Spreadsheet v1.0 - CLDocument28 pagesColumn and Wall Load Take Down Spreadsheet v1.0 - CLBilal KhattabNo ratings yet
- PE Electromagnetic Pump Unit PE GB T1101 01-02-182Document4 pagesPE Electromagnetic Pump Unit PE GB T1101 01-02-182li geneNo ratings yet
- Furuno GMDSS Installation Manual PDFDocument64 pagesFuruno GMDSS Installation Manual PDFEric PskdNo ratings yet
- User Interface DesignDocument6 pagesUser Interface DesignpoojaqNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Biodiesel Melalui Transesterifikasi Minyak Goreng Bekas Berbasis Katalis Heterogen Cao Dari Limbah Cangkang Telur AyamDocument6 pagesSintesis Biodiesel Melalui Transesterifikasi Minyak Goreng Bekas Berbasis Katalis Heterogen Cao Dari Limbah Cangkang Telur Ayamkarim kasmudinNo ratings yet
- SUN 72M Mono Crystalline Module PerformanceDocument2 pagesSUN 72M Mono Crystalline Module PerformanceFernando VieiraNo ratings yet
- Demo-C Tfin52 67Document5 pagesDemo-C Tfin52 67namank005No ratings yet
- DDNS Management System User's Manual V1.0 - 20120301Document7 pagesDDNS Management System User's Manual V1.0 - 20120301judapiesNo ratings yet
- Pfaff 360 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument55 pagesPfaff 360 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- Sika PDS E SikaRep SDocument3 pagesSika PDS E SikaRep Slwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Adf Interview Questions and AnsewrsDocument85 pagesAdf Interview Questions and Ansewrsleninbabus100% (2)
- Control your ship with Kobelt electronic controlsDocument36 pagesControl your ship with Kobelt electronic controlsBERANGER DAVESNE DJOMALIA SIEWENo ratings yet
- Davao October 2014 Criminologist Board Exam Room AssignmentsDocument113 pagesDavao October 2014 Criminologist Board Exam Room AssignmentsPRC Board0% (1)
- Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5Document60 pagesCisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5JodieNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Service Parts List ForDocument49 pagesDiesel Engine: Service Parts List ForIgnacio OsorioNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing For Downhole ProcessDocument10 pagesCoiled Tubing For Downhole ProcessCristian BarbuceanuNo ratings yet
- SHIP HANDLING WITH ESCORT TUGS A REFERENCE MANUAL FOR MASTERS PILOTS GIANO Tug SpecsDocument8 pagesSHIP HANDLING WITH ESCORT TUGS A REFERENCE MANUAL FOR MASTERS PILOTS GIANO Tug SpecsMahmoud ElsherifNo ratings yet
- MIT OCW Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Lecture on Octahedral ML6 Sigma ComplexesDocument7 pagesMIT OCW Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Lecture on Octahedral ML6 Sigma Complexessanskarid94No ratings yet