Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Year 11 Worksheet Air
Uploaded by
Mohamad El MawlaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 11 Worksheet Air
Uploaded by
Mohamad El MawlaCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 11 chemistry worksheet: Air and water
Read pages 182-189 in the textbook completely before
attempting questions, and then use these pages to
research proper answers to the following questions
Complete the following table showing the composition of dry,
unpolluted air. List the most abundant gases first.
Gas
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen
Argon
Formula
O2
CO2
N2
Ar
Abundance %
21
0.04
78
0.9
The natural humidity of air varies across the globe. What is the
general range of % water in the atmosphere? Between 1% and
4%.
Name and briefly describe the process used to obtain pure
nitrogen and oxygen gases from air.
Air is cooled and compressed to form a liquid, and then the liquid is fractionally distilled
to obtain each of the different components in the air.
Name three uses for pure oxygen gas (do not include normal
breathing).
-
Oxygen gas is poisonous to bacteria that cause gangrene. Therefore, it is used to kill
them.
Oxygen is used as a step in the production of antifreeze and polyester polymers. The
polymers are then used to make plastic and fabrics.
Pure oxygen is used to ensure the complete combustion of different chemicals.
Name two uses for Nitrogen gas, and explain why it is so useful.
-
Nitrogen is used in high temperature thermometers where mercury cannot be used. This
is because mercury boils at 356 C and cannot be used in such thermometers.
Nitrogen mixed with argon is used in electric bulbs to provide an inert atmosphere. It
helps in prevention of oxidation and evaporation of the filament of the bulb, giving it a
longer life.
Name an industrial process that uses nitrogen gas as a reactant
(Hint: you should have revised this process by now!) and state the
main products.
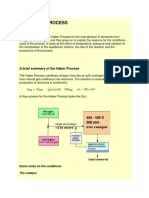
Haber Process
This reaction is reversible.
The forward reaction (from left to right) is exothermic.
Nitrogen + hydrogen
N2(g)
3H2(g)
ammonia (+ heat).
2NH3(g) (+ heat)
The industrial conditions are
1) Temperature between 450 C and 500 C.
2) Pressure of 200 atm (200 atmospheres).
3) Use an iron catalyst.
Only about 15% of the reactants are converted into products
under these conditions.
Ammonia is cooled and liquefied at the reaction pressure,
and then removed as liquid ammonia.
The remaining mix of nitrogen and hydrogen gases (85%)
are recycled and fed in at the reactant stage.
The process operates continuously.
List the most common pollutants in the table, with their sources
and hazards.
Pollutant
Source
Hazard
Why do nitrogen oxides form in exhaust gases? Write a balanced
equation.
What is fitted to car exhausts to remove nitrogen oxides? Write
and equation to show how two toxic gases are reacted together to
produce less harmful gases.
One of these less harmful gases is still a major environmental
concern. Which gas is it, and what is the concern?
There are four main greenhouse gases. List them in the table
below.
Greenhouse gas
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Source
Burning fossil fuels in power stations
and cars.
Cows, pigs and sheep release a lot of
methane by bacterial action in their
digestive systems.
Produced by bacteria in the soil.
Nitrous oxide
CFCs
Depletion of the ozone layer which
surrounds earth.
Read pages 180-181 in the textbook completely before
attempting questions, and then use these pages to
research proper answers to the following questions
There are two chemical tests for water. Name them both, and
write equations to explain and demonstrate the colour changes.
1: Copper (II) sulfate
2:
Label the diagram showing the stages of water treatment.
Settlement tank
Aluminum
sulfate added
Chlorine
Sand filter
Why is chlorine added to the water supply?
Chlorine is a highly efficient disinfectant, and is added to public water supplies to kill
disease-causing pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses that commonly grow in water
supply reservoirs, on the walls of water mains and in storage tanks.
You might also like
- Industrial Gases: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Hydrogen ManufactureDocument13 pagesIndustrial Gases: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Hydrogen ManufactureBiain A SecasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Industrial Gases+ Ammonia 2019Document49 pagesLecture 3 Industrial Gases+ Ammonia 2019Mohamed AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Annealing of Wire TechDocument4 pagesAnnealing of Wire TechJayabharath KrishnanNo ratings yet
- BTEX Removal From Natural GasDocument46 pagesBTEX Removal From Natural GasSurendar Babu S100% (1)
- Petrochemical Industry - Production ProcessDocument40 pagesPetrochemical Industry - Production ProcessAyie Arie AyitNo ratings yet
- Air and Water ChemistryDocument24 pagesAir and Water ChemistryShaman Samuel GodfreyNo ratings yet
- 1صناعاتDocument15 pages1صناعاتroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- CHEMICAL MONITORINGDocument11 pagesCHEMICAL MONITORINGLNo ratings yet
- C1b HomeworkDocument7 pagesC1b HomeworkWendywitch123No ratings yet
- Fertiliser Manufacturing Processes and Its Environmental ProblemsDocument69 pagesFertiliser Manufacturing Processes and Its Environmental ProblemsAulizar MarioNo ratings yet
- Haber AmmoniaDocument22 pagesHaber AmmoniaKabilanNo ratings yet
- Synthesis gas and ammonium nitrate productionDocument44 pagesSynthesis gas and ammonium nitrate productionyudiapnNo ratings yet
- Ethylene OxideDocument6 pagesEthylene OxideRabiya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Episode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingDocument31 pagesEpisode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingSAJJAD KHUDHUR ABBASNo ratings yet
- UreaDocument18 pagesUreaDian Anggraini PurbaNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia by Haber Bosch ProcessDocument5 pagesProduction of Ammonia by Haber Bosch ProcesszahidNo ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument10 pagesHaber ProcessTon5698No ratings yet
- Combustion of AlkanesDocument7 pagesCombustion of AlkanesA-ar FebreNo ratings yet
- Motors in Chemical Eng.Document6 pagesMotors in Chemical Eng.Guillermo CúmezNo ratings yet
- 1 AirDocument51 pages1 AirAli HarbNo ratings yet
- Ethylene 2520oxide Methods 2520of 2520productionDocument25 pagesEthylene 2520oxide Methods 2520of 2520productionmartin_2104No ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsDocument12 pagesAthmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Gas Preparation First Methane Is Cleaned To Remove Impurities That Would Poison The CatalystsDocument44 pagesSynthesis Gas Preparation First Methane Is Cleaned To Remove Impurities That Would Poison The CatalystsabdoNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL MONITORING AND MANAGEMENTDocument28 pagesCHEMICAL MONITORING AND MANAGEMENTdasdaNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Oxide and Ethanol Amines Production ProcessesDocument7 pagesEthylene Oxide and Ethanol Amines Production Processesمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Component Percentage% Nitrogen Oxygen Argon Carbon Dioxide Neon Krypton Nitrogen Dioxide Methane Ozone Helium Hydrogen XenonDocument4 pagesComponent Percentage% Nitrogen Oxygen Argon Carbon Dioxide Neon Krypton Nitrogen Dioxide Methane Ozone Helium Hydrogen XenonVitor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Properties of Non-MetalsDocument14 pagesPatterns and Properties of Non-MetalsiluvreadingbooksNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document8 pagesCH 19JayelleNo ratings yet
- PCS Trinidad Nitrogen Complex: Ammonia and Urea ProductionDocument8 pagesPCS Trinidad Nitrogen Complex: Ammonia and Urea ProductionLok Chen ChuangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Year 11 Depth Study: Frank DingDocument7 pagesChemistry Year 11 Depth Study: Frank DingFrankNo ratings yet
- Wet Air Oxidation of Alkanolamines: Chapter No. 3Document6 pagesWet Air Oxidation of Alkanolamines: Chapter No. 3Azam KhanNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Year 10Document34 pagesScience Notes Year 10Rishi Máran100% (2)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentVishal RajNo ratings yet
- Joshua Campe Sunny Chawla Brandon HardwickeDocument19 pagesJoshua Campe Sunny Chawla Brandon HardwickeWalida AdauwiyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Nitrogen and SulfurDocument10 pagesChapter 13 - Nitrogen and SulfurNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Ammonia PlantDocument16 pagesAmmonia Plantganeshan67% (6)
- CH 11 Air and WaterDocument6 pagesCH 11 Air and Waterlayan alharbiNo ratings yet
- Production of AmmoniaDocument29 pagesProduction of AmmoniaBhavna Bajpai83% (6)
- Introduction to Ammonia Production and PropertiesDocument15 pagesIntroduction to Ammonia Production and PropertiesHameed Akhtar100% (1)
- Ammonia Process InformationDocument4 pagesAmmonia Process InformationRishikesh AwaleNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea Production ProcessDocument10 pagesAmmonia and Urea Production ProcessSameer PanditaNo ratings yet
- Sem1Fin SummaryDocument6 pagesSem1Fin SummarySharonNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea ProductionDocument10 pagesAmmonia and Urea Productionwaheed_bhattiNo ratings yet
- 9.5 Industrial ChemistryDocument33 pages9.5 Industrial ChemistrykevNo ratings yet
- As Notes Final 2023docxDocument53 pagesAs Notes Final 2023docxMuhammad HashimNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Applications: FertilzersDocument20 pagesNatural Gas Applications: FertilzersTamanna Kumari100% (1)
- Topic.10 Chemistry of Our EnviromentDocument12 pagesTopic.10 Chemistry of Our EnviromentJoyce AmirNo ratings yet
- Ammonia production from natural gas and nitrogen separation technologiesDocument7 pagesAmmonia production from natural gas and nitrogen separation technologiespragati agrawalNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen's triple covalent bond and lack of reactivityDocument5 pagesNitrogen's triple covalent bond and lack of reactivityThapelo SebolaiNo ratings yet
- Core Topic 3 - Chemical Monitoring and ManagementDocument20 pagesCore Topic 3 - Chemical Monitoring and ManagementD RayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson 21Document5 pagesChemistry Lesson 21Ali HaidarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FolioDocument43 pagesChemistry Folioharshini1010No ratings yet
- Optimization of Synthesis Gas (Autothermal) Reactor in Methanol Production Process Using Natural Gas As Feed StockDocument18 pagesOptimization of Synthesis Gas (Autothermal) Reactor in Methanol Production Process Using Natural Gas As Feed StockainmnrhNo ratings yet
- Water Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsFrom EverandWater Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Direct Methane to Methanol: Foundations and Prospects of the ProcessFrom EverandDirect Methane to Methanol: Foundations and Prospects of the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Waves 7 - Refractive Index HWDocument3 pagesWaves 7 - Refractive Index HWMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Study Blank TimetableDocument2 pagesStudy Blank TimetableObfuNo ratings yet
- Desert Ecosystems and Bushmen AdaptationsDocument13 pagesDesert Ecosystems and Bushmen AdaptationsMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 CollisionsDocument22 pagesCh.3 CollisionsMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Refugee Blues - Analytical Essay: W. H. AudenDocument1 pageRefugee Blues - Analytical Essay: W. H. AudenMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Indicator Species Reveal Environmental ChangesDocument6 pagesIndicator Species Reveal Environmental ChangesMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Guidance Notes On Experimental Work (Edexcel New Spec AS & A2)Document11 pagesPhysics: Guidance Notes On Experimental Work (Edexcel New Spec AS & A2)arya12391% (33)
- Desert Ecosystems and Bushmen AdaptationsDocument13 pagesDesert Ecosystems and Bushmen AdaptationsMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Leanbody Labrada CalendarDocument3 pagesLeanbody Labrada CalendarJaviDiazNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 KinematicsoDocument46 pagesCh.2 Kinematicsotoney lukaNo ratings yet
- Refugee Blues - Analytical Essay: W. H. AudenDocument1 pageRefugee Blues - Analytical Essay: W. H. AudenMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- 0417 w10 QP 2Document8 pages0417 w10 QP 2Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesHafiz HazizanNo ratings yet
- KolsDocument2 pagesKolsitsyousef118No ratings yet
- The Kidney: Filtration & Re-Absorption: Pickering ReferenceDocument8 pagesThe Kidney: Filtration & Re-Absorption: Pickering ReferenceMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Cold War TimelineDocument2 pagesCold War TimelineMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Weeexcretion QuestionsDocument1 pageWeeexcretion QuestionsMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Worksheet AirDocument4 pagesYear 11 Worksheet AirMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Melting and DissolvingDocument1 pageMelting and DissolvingMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Chap 17 - Water InfluxDocument57 pagesChap 17 - Water InfluxSlim.BNo ratings yet
- Dwyer 4000 SeriesDocument1 pageDwyer 4000 SeriesMuh RenandaNo ratings yet
- Hydrant Orifice CalculationDocument3 pagesHydrant Orifice CalculationM.Jabar ali100% (3)
- South-to-North Water Transfer Project: F3 GeographyDocument15 pagesSouth-to-North Water Transfer Project: F3 GeographyYu Hang FUNGNo ratings yet
- Affordable Portable Helium Sniffers For Leak Detection In EuropeDocument52 pagesAffordable Portable Helium Sniffers For Leak Detection In EuropeChristos StiapisNo ratings yet
- Report Iffco UREA PRODUCTIONDocument44 pagesReport Iffco UREA PRODUCTIONRahul BaghelNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Dossis Chemical RO Dan ClarifierDocument29 pagesPerhitungan Dossis Chemical RO Dan ClarifierAndi LeeNo ratings yet
- CHM142L Organic Chemistry Lab Report on Simple and Steam DistillationDocument5 pagesCHM142L Organic Chemistry Lab Report on Simple and Steam DistillationAdrian OblenaNo ratings yet
- Compare Properties of Gases, Liquids and SolidsDocument4 pagesCompare Properties of Gases, Liquids and SolidsRaymond MaristelaNo ratings yet
- CLO - Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesCLO - Fluid Mechanicstooba IshfaqNo ratings yet
- AltimeterDocument8 pagesAltimeterwolffoxxxNo ratings yet
- Activity NoDocument8 pagesActivity NoWilbert PialaNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument21 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure FluidsIR Ika EtyEtyka Dora100% (1)
- TOT 1718 999 9020 0019 (Gas Freeing and Inerting)Document11 pagesTOT 1718 999 9020 0019 (Gas Freeing and Inerting)Jahel LootiNo ratings yet
- Drive MechanismDocument48 pagesDrive MechanismtalhahafeezmNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Chemical EngineeringDocument143 pagesFluid Mechanics: Chemical EngineeringYADAV VikasNo ratings yet
- Gas Freeing Purging and Pressure TestingDocument5 pagesGas Freeing Purging and Pressure TestingbabaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Archimedes' PrincipleDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Archimedes' PrincipleShahrin Ahmad100% (2)
- 2004 Gas Lift SeminarDocument317 pages2004 Gas Lift SeminarThang LeNo ratings yet
- Meul703 TurbomachinesDocument2 pagesMeul703 TurbomachinesArun BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-5: Water Quality Parameters Course Code: ENV107L Section: 13Document7 pagesLab Report-5: Water Quality Parameters Course Code: ENV107L Section: 13Mehrab Jami Aumit 1812818630No ratings yet
- By: Anant Kumar Mishra Physics Revision Compendium: "Fluid Mechanics"Document4 pagesBy: Anant Kumar Mishra Physics Revision Compendium: "Fluid Mechanics"Shrey chandrashekher MishraNo ratings yet
- Lift Pump CalculationDocument15 pagesLift Pump CalculationamrNo ratings yet
- WASTE WATER TREATMENT: GRIT REMOVAL PROCESSDocument22 pagesWASTE WATER TREATMENT: GRIT REMOVAL PROCESSsarfaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument19 pagesRRLJBSNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument16 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantVishal guptaNo ratings yet
- 008.192 EN - Danfoss - Thermostatic Valve - AVTA-15Document16 pages008.192 EN - Danfoss - Thermostatic Valve - AVTA-15Ng MeriedNo ratings yet
- Venturi EffectDocument8 pagesVenturi EffectDwayne AndersonNo ratings yet
- TransientDocument888 pagesTransientBimantara PrayogoNo ratings yet