Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 01
Uploaded by
er_paramjeetgillCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 01
Uploaded by
er_paramjeetgillCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 01:
1. Aim: To study constructional details and prepare layout of front engine/ rear engine drive
lines.
2. Theory: The Drive Train/lines has two main functions, it carries power from the engine via
the transmission or gearbox to the wheels and it varies the amount of torque delivered from
power. Power from the engine is transferred through the engaged clutch to the input shaft of the
transmission. Gears in the transmission housing alter the torque and speed of this power input
before passing it on to other components in the drive train. There are a few different types of
drive train layouts, front engine front wheel drive, front engine rear wheel drive, front engine
four wheel drive, rear engine rear wheel drive, The main components of drive lines includes the
clutch, gearbox, universal joints, differential, axles and drive shafts.
3. Working:
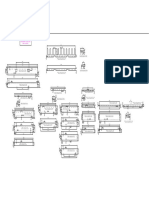
3.1 Front Engine Rear Wheel Drive:
In Front engine rear wheel drive vehicles propelled by rear wheels use a transmission system.
The transmission gearing is located within an aluminium or iron casing called the transmission
case assembly. The transmission case assembly is attached to the rear of engine, which is
normally located in the front of the vehicle. A drive shaft links the engines output shaft to
transmission with the differential and drive axle located in a separate housing at rear of the
vehicle. The differential splits the driveline power and redirects it to the rear drive axles, which
then passes it on to the wheels. For many years, rear wheel drive was the conventional method of
propelling vehicles.
3.2 Front Engine Front Wheel Drive:
Front wheel drives are propelled through the front wheels. Unlike the transmission used in rear
wheel drive and four wheel drive, here the mechanism is called Transaxle. A transaxle combines
the clutch, gearbox, differential and drive axle connections into a single case aluminium housing
located in front of vehicle.
Major advantage of this type of drive is the good traction on slippery roads due to the weight of
the drive train components being directly over the driving axle of the vehicle.
3.3 Front Engine Four Wheel Drive:
In front engine four wheel drive the power is distributed in all the four wheels. Front wheel
drives typically use a transmission and transfer case. The transfer case mounts on the side or
back of transmission. A chain or gear drive inside the transfer case takes power from the
transmission and transfers it to two separate drive shafts. One drive shaft connects to the
differential on front drive axle. The other drive shaft connects to differential on rear drive axle.
The major application of four wheel drive is in sports utility vehicles.
3.4 Rear Engine Rear Wheel Drive:
Rear engine rear wheel drive layout is one which places both the engine and drive wheels at the
rear of the vehicle. By placing the engine at the rear of the vehicle it can be made as a unit that
incorporates the clutch, gearbox and final drive assembly. The rear wheels act as the driving
wheels and the front wheels swivel to allow the vehicle to be steered. One advantage attributed
to a rear-engined layout is that it increases the load on the rear driving wheels, giving them better
grip of the road. The disadvantages is that placing the engine outside the wheelbase creates
significant problems for steering.
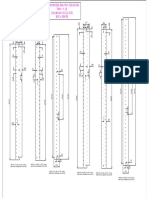
Front engine rear wheel drive
Front engine front wheel drive
Rear engine rear wheel Drive
You might also like
- Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers LTD.: WWW - Grse.inDocument22 pagesGarden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers LTD.: WWW - Grse.iner_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Idealization of Cad Geometry Using Design and Analysis Integration Features ModelsDocument11 pagesIdealization of Cad Geometry Using Design and Analysis Integration Features Modelser_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- EERAL A Rev00Document1 pageEERAL A Rev00er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Appel Gerlach Crusius 2016 The Interplay Between Facebook Use Social Comparison Envy and DepressionDocument6 pagesAppel Gerlach Crusius 2016 The Interplay Between Facebook Use Social Comparison Envy and Depressioner_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Hart: Handbook of Jealousy, Theory, Research, and Multidisciplinary Approaches 9781405185790 - 4 - 000 Final Proof 16.2.2010 5:11pmDocument3 pagesHart: Handbook of Jealousy, Theory, Research, and Multidisciplinary Approaches 9781405185790 - 4 - 000 Final Proof 16.2.2010 5:11pmer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- In - Gov.transport RVCER PB08AV1473Document1 pageIn - Gov.transport RVCER PB08AV1473er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- B.O.M - 130 & 139Document6 pagesB.O.M - 130 & 139er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Personal Therapy FormDocument2 pagesPersonal Therapy Former_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Petrol and Other BillDocument7 pagesPetrol and Other Biller_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- IvrDocument3 pagesIvrer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Eil-6!14!0003 Rev 5 Installation ProcedureDocument16 pagesEil-6!14!0003 Rev 5 Installation Procedureer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Your Tuesday Ride To Sarai RohillaDocument1 pageYour Tuesday Ride To Sarai Rohillaer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- 452 As Built DrawingDocument6 pages452 As Built Drawinger_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- The Therapeutic Presence of The Art TherapistDocument9 pagesThe Therapeutic Presence of The Art Therapister_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Booking Confirmation On IRCTC, Train - 12455, 03-Dec-2019, 2A, DEE - BTIDocument1 pageBooking Confirmation On IRCTC, Train - 12455, 03-Dec-2019, 2A, DEE - BTIer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Part Drawing HMEL 2702 4Document1 pagePart Drawing HMEL 2702 4er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Permission to carry Mobile at GGS Refinery SiteDocument1 pagePermission to carry Mobile at GGS Refinery Siteer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-11-19 11.34.56Document2 pagesNew Doc 2019-11-19 11.34.56er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Part Drawing HMEL 2702 5Document1 pagePart Drawing HMEL 2702 5er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Part Drawing HMEL 2702 6Document1 pagePart Drawing HMEL 2702 6er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Data Folder IndexDocument4 pagesManufacturing Data Folder Indexer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Part Drawing HMEL 2702 1Document1 pagePart Drawing HMEL 2702 1er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Mockup Assembly WitnessDocument1 pageMockup Assembly Witnesser_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Part Drawing HMEL 2702 3Document1 pagePart Drawing HMEL 2702 3er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Part Drawing HMEL 2702 2Document1 pagePart Drawing HMEL 2702 2er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Material List Entry 08-02-2020Document1 pageMaterial List Entry 08-02-2020er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Coveralll Requirement-1 PDFDocument1 pageCoveralll Requirement-1 PDFer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- MRPL Schedule-1 PDFDocument1 pageMRPL Schedule-1 PDFer_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Installation Procedure.Document11 pagesInstallation Procedure.er_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- COLUMN - Installation Schedule 7410000355 UpdatedDocument12 pagesCOLUMN - Installation Schedule 7410000355 Updateder_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- H D B I, S, M M: Ydraulic ISC Rake Nstallation Ervice Aintenance AnualDocument9 pagesH D B I, S, M M: Ydraulic ISC Rake Nstallation Ervice Aintenance AnualOsscar Charlee PahpahNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal UN Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesLatihan Soal UN Bahasa InggrisSeptyan AnggaNo ratings yet
- Karakteristike Ulja IPONEDocument3 pagesKarakteristike Ulja IPONEJelena Boban PesicNo ratings yet
- Springboard Grammar Handbook 2 PDFDocument32 pagesSpringboard Grammar Handbook 2 PDFPrincess SelenaNo ratings yet
- Chain CouplingDocument3 pagesChain CouplingJong JavaNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - Sprocket Pack - CampagnoloDocument8 pagesTechnical Manual - Sprocket Pack - CampagnoloGica JoeNo ratings yet
- Lane Widths, Shoulders and Surfacing StandardsDocument26 pagesLane Widths, Shoulders and Surfacing Standardssharfutaj100% (2)
- I. Grammar and Vocabulary IA. Tick (: ShallDocument5 pagesI. Grammar and Vocabulary IA. Tick (: Shallmasc1127100% (1)
- Smart ForTwo Accessory BrochureDocument36 pagesSmart ForTwo Accessory BrochuremuskystoatNo ratings yet
- British Cycling Training Plan Week 13 Rest and Threshold TestDocument4 pagesBritish Cycling Training Plan Week 13 Rest and Threshold TestelsribeiroNo ratings yet
- BromptonDocument7 pagesBromptonVe Wee100% (1)
- TREK INCITE Bicycle Computer Owner's ManualDocument10 pagesTREK INCITE Bicycle Computer Owner's ManualbigwhaledorkNo ratings yet
- SE Bikes - 2020 Ripper X - Bike ArchivesDocument2 pagesSE Bikes - 2020 Ripper X - Bike ArchivesMark ArchambeaultNo ratings yet
- Sistema de TrasporteDocument3 pagesSistema de TrasporteArmida SucasaireNo ratings yet
- Ridley enDocument62 pagesRidley enEduBelleiNo ratings yet
- MTB Suspension Diagram & Tech for Trek Fuel EX 9.8Document2 pagesMTB Suspension Diagram & Tech for Trek Fuel EX 9.8Juan David Orrego100% (1)
- Mongoose 2011Document13 pagesMongoose 2011mountainbikerusNo ratings yet
- T NATION - The High Performance Training MatrixDocument5 pagesT NATION - The High Performance Training MatrixturbobrikNo ratings yet
- Triathlon Practice PlanDocument10 pagesTriathlon Practice Planapi-403982187No ratings yet
- UK Distributor for Carla Cargo TrailerDocument8 pagesUK Distributor for Carla Cargo TrailerKristian KruuseNo ratings yet
- GoEnduro 2017 Results by CategoriesDocument4 pagesGoEnduro 2017 Results by CategoriesmtbsiNo ratings yet
- MG3 BrochureDocument36 pagesMG3 BrochureReunion St Augustines100% (1)
- Aashto Lane Width PDFDocument1 pageAashto Lane Width PDFnywd806033No ratings yet
- Avigo Girly Girl Bike ManualDocument125 pagesAvigo Girly Girl Bike ManualkcmarkNo ratings yet
- Cars and PersonalityDocument32 pagesCars and PersonalityelquerecibeNo ratings yet
- Mile High Cycles Flexible BudgetsDocument7 pagesMile High Cycles Flexible BudgetsParamjit SinghNo ratings yet
- FIM Ice Speedway Gladiators World Championship Finale 4 - InzellDocument5 pagesFIM Ice Speedway Gladiators World Championship Finale 4 - InzellАлексей Полянцев100% (1)
- Lake Placid IronmanDocument2 pagesLake Placid IronmanLarry DeemNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Electric Car With PVC PipesDocument27 pages1.1. Electric Car With PVC PipesSubbu VarmaNo ratings yet
- Mint MagazineDocument116 pagesMint MagazineSamantha WoodNo ratings yet