Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RPDOnlineQuestions (FullS Small00center10 1995563
Uploaded by
ranujainbhandariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RPDOnlineQuestions (FullS Small00center10 1995563
Uploaded by
ranujainbhandariCopyright:
Available Formats
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
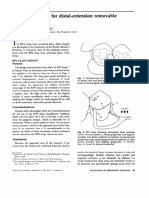
In reference to the partially edentu
lous arch and accompanying fram
ework shown---what is the Kenned
y classication? Class I, Modicatio
n 0 Class II, Modication 1 Class III,
Modication 0 Class IV, Modicatio
n 0 Does this RPD have an axis of
rotation? If so, where is it located?
Whataccompanying
class(s) of RPDs
do not
havet
The
gure
depicts
an
axis
of
rotation?
he lingual surface on the lower ant
erior teeth of a patient who is curr
ently wearing a bilateral distal ext
ension removable partial denture t
hat was fabricated 5 years ago. W
hat do you think is the most likely
cause for the tissue damage that h
Your
patient on
hastooth
teeth#22?
20-29
remai
as
occurred
The
low
ning.
You plan
to should
use mesial
er
anterior
teeth
haverests
been
and I-bars
both
terminal
abutm
plated
and on
were
not.
The patient's
ents.hygiene
Because
are lingual
tor
oral
is there
poor and
tissue bre
i present,
you willpocket
need to
use ling
akdown
followed
formation
uoplating
in the
premolar
on
the distal
of tooth
#22. areas.
A rest Tp
he
illustration
a lingual
view
of bt
reparation
andisrest
should
have
eeth
27-29. on
Thetooth
dotted
lineA on
#29
een placed
#22.
cast
ci
represents
theclasp
height
of
contour
(s
In the maxillary
class
III used
RPD
show
rcumferential
was
on to
urvey
line).
What
should
rel
n
either
a palatal
strap
orbe
anthe
anter
oth
#22----it
should
have
been
wro
ationship of ught
the
superior
of
ior-posterior
palatal
strapborder
major co
wire.
the plating
and
survey
Th
nnector
may
bethe
used.
If anline?
anterio
e
plating should
r-posterior
strap extend
design above
is to bethe
co
survey
line.
platingbetween
should end
nsidered,
theThe
opening
the
at or below
surveypalatal
line. The
pl
anterior
andthe
posterior
strap
must
exactly
at the
surv5
sating
should
beend
at least
_______
mm.
ey line. The plating
must end belo
10 15 20
w the survey line.
Because there are no movable tissues on the palate, the borders of
maxillary major connectors may be located farther from the gingiv
al margins than those of mandibular major connectors. True False
On the mandibular class III framew
ork shown, circumferential clasps
have been used on the canine, pre
molar, and molars. Which one of t
he following statements regarding
the clasping is TRUE? The retentiv
e arms on the canine and premola
r should be wrought wire while tho
se on the molars should be cast. T
he
arms
on the molars
On lingual
the RPD
framework
shown, are
the
frequently
the numbers
retentive 20
arms
rests on teeth
andbeca
28
use
are
often noand
usable
facia
are there
indirect
retainers
function
lwhen
undercuts.
If the bites
undercut
the patient
downon
onthe
th
second
on the
distofaci
e distalpremolar
extensionisarea.
True
False
al, the circumferential retentive ar
m would most likely be changed to
I-bars. In order to ensure adequate
retention, the tips of both the bucc
al and lingual arms on the molars
Guide surface preparations should
be completed
rest seat p
should
be placedbefore
in undercuts.
reparations. True False
The correct answer is 1 According
to the Kennedy Classication, the p
artially edentulous arch shown is a
Class I, Modication 0. There are b
ilateral posterior extension areas
with no other modication (edentul
ous) space(s) present. All class I R
PDs have an axis of rotation. To be
very
specic,
axis of
rotation
3 1 INCORRECT. Although plating
may
help tothe
prevent
this
situation
will pass
through
the rigid
metal
from occurring, denitive rest seats
under
the plating
would
stillclbe
osest
to the can
edentulous
space
that b
required. 2 INCORRECT. Poor oral
hygiene
contribute
to tissue
lies
above is
the
surveybyline
(height
reakdown. However, this type of
damage
caused
trauma
from
ofRPD
contour).
the design
is correct A
the downward movement of the
duringIffunction.
3 CORRECT.
and the laboratory
and clinicalofpro
rest preparation and rest are essential
to proper functioning
the
are is
carried
out caused
properly,
RPD. The damage shown in thecedures
illustration
primarily
byt m
axis ofduring
rotation
shouldSuch
passdama
thr
ovement of the RPD toward thehe
tissues
function.
the
most
distal
rests
on
each
would
not must
have end
occurred
if ough
aatgood
rest
seat
and
rest were
pres
3ge
The
plating
exactly
the
survey
line
(height
of contour
axis
of
rotation
forspace
this ctiss
ent.
4 INCORRECT.
The
typethe
of side.
clasp The
arm
has
nothing
to a
do
with
). If the
plating ends
below
survey
line,
there
will be
be
ase
indicated
by the
black line.
ueof
trauma
of is
this
type.
tween the superior edge
the plating
and
the tooth
creating
a food
Class
I and
Class
II RPDs
hato
trap. In addition, the edge of the
plating
will
stand
away always
from the
an axis
of rotation.
Classabove
III RP th
oth and may be irritating to theve
tongue.
If the
plating ends
Ds never
axis
of of
rotation.
e survey line, it will pre-empt the
mesialhave
rest.an
The
axis
rotation
Class IV
seldom
an axis
will pass through the plating instead
of RPDs
the rest.
The have
I-bar will
conta
of axis
rotation---some
people
ct the tooth in front of this "new"
of rotation and
will consider
engage th
that
Class toward
IV RPDsthe
have
an axis
of
e tooth when the extension base
moves
residual
ridge.
rotation
if on
all an
theinclined
incisorsplane,
and both
Also,
since the
will act
like
a rest
there
3 Although
the plating
exact space
required
is somewhat
arbitrary, we
gen
are missing,
creating an
"
will
be feel
the tendency
to push should
thecanines
tooth
functi
erally
that the opening
be toward
at leastthe
15 facial
mm. Ifduring
the openin
anterior
extension"
area. line m
The fact
the plating
mustgained
end
exactly
on the survey
gon.
is less
thanthat
15 mm,
the benet
from uncovering
the tissue
akes
fabrication
much "sensitivity"
more dicultoffor
laboratory
s mayframework
be oset by
the increased
thethe
tongue
to the t
echnician. Therefore,
whenever
possible,
avoid
plating
terminal
abu
multiple major connector borders.
tments on distal extension RPDs.
True Major connectors on the maxillary arch should be at least 6 m
m from the gingival margin. On the mandibular arch, the proximity
of movable tissues will not permit this amount of distance. In gener
al, mandibular major connectors should be at least 3 mm from the
gingival margin.
2 Incorrect. All of the clasps should be cast. Since there is no functi
onal movement of a class III RPD, there is no need for the stress-br
eaking eects of wrought wire clasps. Correct. Lower molars, partic
ularly second or third molars, frequently have no facial undercuts. I
n addition, the normal drift of the teeth is to the lingual, accentuatin
g lingual undercuts and minimizing facial undercuts. Incorrect. Modif
ied T-bars would be the retainers of choice if the undercuts were on
the distofacial. I-bars could be used but the tiny space between the
I-bars
and the denture
base
wouldnumbers
create food
traps
mak
False Although
the rests
on teeth
21 and
28and
arewould
indirect
re
e
the
plastic
very
dicult
to
nish
properly.
In
addition,
the
I-bars
tainers, they function when the extension base attempts to move w
a
ould from
tend the
to be
very short
and ridge)---not
inexible. Incorrect.
Only
one arm
o
way
tissues
(residual
toward the
residual
ridge
f each
clasp
assembly
should
extend
an These
undercut
(beare
retentive
as
would
occur
when the
patient
bitesinto
down.
rests
called
).
The other
arm must
be rigid
providethe
bracing
or reciprocation
a
indirect
retainers
because
they to
increase
eectiveness
of the dir
thus cannot
extend
into
an undercut
and provide
retention.
ectnd
retainers
(clasps)
when
there
is an attempt
to dislodge
the pros
thesis.
True The tooth structure removed during guide surface preparation
will adversely aect the shape and contour of the rest seat prepar
ation. Thus, the guide surfaces should be created BEFORE rest seat
s are prepared.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
In the class II mandibular RPD sho
wn to the right, the clasp on tooth
#27 should be wrought wire BECA
USE the cingulum rest acts like a d
istal rest and the tip of the retenti
ve arm is in front of the axis of ro
tation. True False
When tripoding a cast, the vertical arm of the surveyor must be loc
ked in position. True False
Referring to the maxillary class II
RPD design shown to the right, whi
ch of the following statements is T
RUE? A short thick I-bar clasp coul
d be used on tooth #6. A wrought
wire circumferential clasp could be
used on tooth #6. It is sometimes
not necessary to use any clasp on
tooth
#6. 2 and
3 are both
true
The
following
statement
refers
to t
he drawing of the class I RPD to th
e right: The clasp arm on tooth #2
0 should be wrought wire BECAUS
E functional forces cause tissuewar
d movement of the denture base,
the denture rotates around the res
t (which is on the distal), and the cl
asp
arm
engages
the Itooth,
tendin
In
the
maxillary
class
RPD shown
g to
it distally.
The statement
at
thetiltright,
the posterior
border a
o
the
reason
aremajor
true AND
relate
fnd
the
palatal
plate
connector
d.
The statement
theforward
reason a
should
be locatedand
as far
but are
NOT
related. The
s
sreistrue
possible
while
maintaining
eno
tatement
true
but theapproximat
reason is
ugh
widthisfor
strength
false.
the statement
norbor
th
ely
20Neither
mm behind
the anterior
e reason is
der approximately
10true.
mm anterior
to the fovea palatini at the posteri
or palatal seal area
All components of a maxillary major connector should cross the pal
ate at right angles to the midline and curves in the major connector
should be located to one side of the midline. True False
In the case shown to the right, whi
ch is the most eective indirect re
tainer? The rest on tooth #19. The
rest on tooth #21. The rest on too
th #27. The rest on tooth #28.
What is the most signicant proble
m with the rest shown on the man
dibular canine to the right? The res
t should be wider inciso-gingivally.
The rest should be located more t
oward the incisal edge. The rest s
hould be thicker buccolingually. Th
e rest should be located in a prepa
red rest seat.
True Both the statement and the reason are true. The rigid metal lo
cated above the survey line (height of contour) and closest to the e
dentulous space is that portion of the rest where it joins the guide
plate/minor connector. The tip of the clasp lies in front of the axis o
f rotation and the clasp will be activated when the extension base
moves toward the residual ridge. Thus, the clasp must be exible t
o provide stress relief for the abutment.
True The purpose of tripoding is to allow re-orientation of the cast i
n the same position at a later date. Tripoding is based on the geom
etric principle that three points determine a plane. If the vertical ar
m of the surveyor moves during the tripoding process, the plane in
dicated by the marks would not be the same as that currently being
used.
4 Incorrect. Cast clasps should not be used anterior to the axis of r
otation. Incorrect. #2 is a true statement but not the BEST answer.
The most commonly used solution would be to use a WW clasp. The
WW clasp would provide stress-relief through its increased exibilit
y: an important attribute in this case since the abutment tooth is in
front of the axis of rotation. Incorrect. #3 is a true statement but n
ot the BEST answer. If the patient is an experienced RPD wearer an
d retention is of minor importance, one might consider leaving the
retentive arm o tooth #6. This would be more likely if esthetics we
re
a major
consideration.
goodand
option
might beThe
to include
theclasp
WW
1 The
statements
are bothA true
are related.
tip of the
clasp
initially
check
forrotation
the clasp
after
Thisen
w
arm would
lieand
in front
ofthe
theneed
axis of
and
the delivery.
clasp would
ould
be
done
by
merely
bending
the
clasp
slightly
away
from
the
to
gage the tooth during functional movement of the extension base.
oth and
having
patient
the to
prosthesis
for a few
days.
If th
Thus,
the
clasp the
needs
to bewear
exible
provide stress
relief
to the
a
e patient managed the RPD without
retention from the clasp, it coul
butment.
d be cut o. Correct. #4 is the BEST answer. Both 2 and 3 are true
statements.
4 Incorrect. The palatal plate major connector is selected because it
provides maximum support and denture style retention. Moving the
posterior border forward negates both of these attributes. Incorrect
. There is no such relationship between the anterior and posterior b
orders of a maxillary palatal plate major connector. Incorrect. One
of the primary reasons a full palate is used is to create "denture sty
le retention." Termination of the major connector 10 mm anterior to
the fovea palatini would place the bead on the hard palate and a "s
eal" would be very dicult to achieve. Correct. The border should b
e placed in the posterior palatal seal area and should be beaded. O
ne of the primary reasons a full palate is used is to create "denture
True Crossing
the
right angles
seems
to create
situatio
style
retention."
Tomidline
do so, at
a "seal"
must be
created
at the a
posterior
n which
is less noticeable
thesoft
tongue.
border
by slightly
depressingtothe
tissues.
2 The rests on #19 and #28 are not indirect retainers. Rests on #2
1 and #27 are indirect retainers. The rest on #21 is further from a
line connecting the tips of the retentive arms on theeth numbers 19
and 28 and is thus more eective than the rest on tooth #27. In rea
lity, the rest on #27 could be omitted without appreciable loss of in
direct retention.
4 Rests must be placed in prepared rest seats. This is particularly i
mportant on anterior teeth where, without prepared rest seats, res
ts lie on inclined planes. Downward pressure on the rest will tend to
push the abutment buccally. Note: the rest could be a little wider inc
isogingivally and it could also be a little thicker. However, these pro
blems pale in comparison to the fact that there is no rest preparati
on.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
In the RPD shown to the right, the
guide surface - guide plate contact
s on the distal surfaces of teeth nu
mbers 20 and 29 determine a de
nite path of displacement/dislodge
ment. True False
The all plastic maxillary RPD should be avoided in all partial dentur
es except where the prosthesis is considered transitional and loss o
f the remaining teeth is imminent. True False
Tooth-supported RPDs require physiologic relief of the guide plates.
True False
The superior border of a mandibular lingual bar major connector m
ust be at least _____ mm below the gingival margins. 1-2 2-3 3-4 45
False The guide surface - guide plate contacts DO NOT determine a
denite path of insertion in this case. If the minor connectors to the
rests on the mesial occlusal surfaces of the premolars are in intima
te contact with the abutments, they may help to ensure a denite p
ath of insertion/dislodgement. However, it is safest to place the tips
of the I-bar retentive arms just in front of the greatest mesiodistal
curvature of the facial surface of the abutments. If the tips are plac
ed at or behind the greatest mesiodistal curvature, it would be pos
sible for the RPD to move slightly upward and backward allowing th
e retentive arms to escape the undercuts without exing. Under the
seplastic
circumstances,
RPD and
would
nottoexhibit
retention.
True All
RPDs lack the
rigidity
tend
encourage
plaque coll
ection. Also, most lack adequate rests. They should only be used o
n a temporary basis or when the dentition is "terminal."
False Because tooth-supported RPDs do not exhibit movement towa
rd the tissues during function, physiologic relief is not necessary. Ex
tension RPDs, on the other hand, do exhibit functional movement a
nd do require physiologic relief. This is accomplished as follows: rs
t coat the guide plates with chloroform and rouge or another disclo
sing medium, seat the framework in the mouth, and push toward th
e tissues over the extension areas; then relieve the guide plate with
a ne textured stone. Repeat as necessary. It is very important tha
t the guide plates do not bind against the abutments during functio
nal movement --- otherwise they will pre-empt the planned mesial r
3 3-4 mm is a minimum. Numerous
ests.studies have shown that placing
the superior border of the major connector less than 3 mm away fr
om the gingival margin leads to increased plaque collection and sub
sequent increased marginal inammation.
For maxillary major connectors, except where plating is used, the b
order of the major connector should be at least ______ mm away fr
om the gingival margin. 1 3 5 6
4 At least 6 mm can almost always be obtained since one does not
have the space limitations created by the oor of the mouth---as in
the mandibular arch. Depending on the anatomy of the arch and th
e width and strength requirement of the elements of the major con
nector, more than 6 mm can often be obtained.
For the anterior-posterior palatal strap maxillary major connector, t
he anterior, posterior, and lateral straps should be about ______ m
m wide. 4-6 6-8 8-10 at least 10
2 6-8 mm allows for adequate strength while allowing for maximum
tissue exposure both over the palate and in the area of the margin
al gingiva.
The basic philosophy of dental treatment for a partially edentulous
patient is to preserve what remains and restore what is missing re
place the missing teeth improve the path of insertion reshape rotat
ed teeth
1 Restoring what is missing is rather obvious. It should be equally o
bvious that the restoration will ultimately fail if what remains is not
preserved. While answers 2, 3, and 4 play a role in RPD design and
treatment, they don't represent a "philosophy" and are certainly se
condary to "preservation and restoration."
It is best not to use a balanced occlusion when mandibular RPDs op
pose maxillary complete dentures. True False
False It is best to use balanced occlusion when a complete denture
opposes a partially edentulous arch restored with a removable parti
al denture.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
The function of the guide plate is to help establish a denitive path
of insertion/dislodgement. stabilize the RPD by controlling its horizo
ntal position. provide contact with the adjacent tooth. all of the abo
ve
What is the design error in the ma
xillary RPD framework shown to th
e right? The anterior teeth should
have been plated. An anterior-post
erior palatal strap major connector
should have been used. There sho
uld be a cast circumferential clasp
on tooth #6. The posterior border
of the major connector should cros
s the palate at right angles to the
midline.
What would be the best denture base connector
when there is limit
ed interocclusal space (<3 mm). Open latticework Meshwork All me
tal base All plastic base
4 Guide plates serve all the functions listed under 1, 2, and 3. Ther
efore, the best answer is 4 (all of the above).
4 Incorrect. There is no information given that would lead one to be
lieve that the anterior teeth should be plated. In this particular case
, plating the anterior teeth would denitely be the exception rather
than the rule. Incorrect. In the situation shown, an A-P palatal strap
would be dicult to design. The space between teeth 3 and 6 is mu
ch better suited to the use of a modied palatal plate---if it is done
correctly. Incorrect. Tooth #6 lies bodily in front of the axis of rotati
on and a cast circumferential clasp should denitely NOT used. If a
neededbase
or desired,
it should
be wrought
wire.very
Correct.
Forth
3clasp
The is
all-metal
would be
very strong
even with
limited
many people,
thefor
tongue
would
be sensitive
toeither
the lack
of symmetr
ickness.
In order
plastic
to extend
beneath
latticework
or
ymeshwork,
of the major
in the network
area of the
midline
theridge
palate.
It
theconnector
metal retentive
must
be oofthe
by a
would be better
the would
posterior
border
midline
at a righ
millimeter
or so. ifThis
leave
little crossed
space forthe
plastic
external
to
t angle
and then
extended
backward
more
or less parallel
tofor
theade
re
the
network.
There
simply is
not enough
interocclusal
space
sidual
ridge.
quate thickness of BOTH plastic
and
metal. The all plastic base woul
d be very weak because of the limited thickness and is therefore no
t indicated.
The rst consideration in developing occlusion is the evaluation and
establishment of the correct position of the occlusal plane. This ma
y be compromised by super-erupted and malposed teeth. True False
Your patient's partially edentulous
arch is depicted in the illustration t
o the right. The missing teeth (with
the exception of the third molars)
were extracted three weeks ago.
What would be the best denture b
ase/replacement teeth combinatio
n in this instance? Open latticewor
k Metal bases with beads for attac
hment of processed tooth colored
A wrought wire clasp is NOT used in which of the following situation
acrylic resin. An all metal base Tub
s? On a terminal abutment of an extension RPD. As an embrasure
e teeth
clasp. On a tooth with an indirect retainer on it. Both 1 and 2 above
.
In designing a RPD framework for
the partially edentulous arch to the
right---if at all possible, circumfere
ntial clasps should be used on the
numbers 28 and 30. They would b
e preferred to infrabulge retainers.
True False
Determining areas for physiologic relief is accomplished by marking
the framework intraorally. This process includes adjusting the castin
g to allow for functional movement on Class I and II RPDs to relieve
stress on the terminal abutment teeth. True False
True Partially edentulous arches often exhibit unusual occlusal plan
es due to malposed natural teeth. More often than not, the nal occl
usal plane is a compromise necessitated by super-eruption and drift
ing.
1 Because of the "green" residual ridges, open latticework is the be
st choice. Relining is easier after the tissues heal completely. In fact
, the other choices all involve some type of metal base and relining
after healing is almost impossible.
2 Incorrect. Wrought wire clasps are commonly used on terminal ab
utments for extension RPDs. Correct. Wrought wire clasps should n
ot be used as embrasure clasps. It is dicult to bend the clasp acc
urately through the embrasure and the slightest nick in the wire or
wear from occlusion will predispose the clasp to breakage in the are
a where it passes over the occlusal surfaces of the teeth. Incorrect.
Wrought wire clasps are frequently used on teeth that have indirect
retainers on them. A good example would be a class II modication
1 RPD where the anterior abutment on the tooth-supported side has
a rest that acts as an indirect retainer. If this tooth also has a clasp
True
onlyshould
one tooth
is missing
onbecause
a tooth-supported
RPD,
infr
on
it, When
the clasp
be wrought
wire
the tooth lies
bodily
abulge
retainers
should
be
avoided.
The
descending
and
ascending
in front of the axis of rotation. Incorrect. Answer 4 is incorrect beca
portions of the arms use
are answer
so close3together
that they form food trap
is incorrect.
s.
True The statement is an accurate description of "physiologic adjust
ment." Class III and Class IV RPDs do not require physiologic adjust
ment since there is no movement of the prosthesis during function.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Reciprocation between bracing and retentive components requires I
-bars be used bracing components contact after retentive compone
nts correct timing of contact during seating and removal of the RP
D both 2 and 3
Infrabulge clasps originate above the height of contour below the h
eight of contour above the 0.01" undercut above the occlusal surfa
ce of most premolars
3 Incorrect. The type of clasp (retentive arm) is not an important co
nsideration in determining whether or not reciprocation occurs. Inco
rrect. For reciprocation to occur, retentive and bracing components
must contact the teeth at the same time. Correct. For reciprocation
to occur, retentive and bracing components must contact the teeth
at the same time. As the retentive tips pass over the height of cont
our, the rigid opposing elements must maintain contact with the ab
utments. This issue of TIMING is critical in the concept of reciprocati
on.
If the rigid
elements
only contact
teeth when
the RPD
sea
2
Incorrect.
Clasps
originating
above the height
of contour
areissupr
ted, they
will function
for meaning
bracing but
not for
reciprocation.
Incorrec
abulge
retainers,
"supra"
above.
Correct.
"Infra" means
be
t. Since
#2 isoriginate
incorrect,
#4 isthe
also
incorrect.
low so infrabulge
clasps
below
height
of contour and a
pproach the undercut from a gingival direction. Incorrect. Infrabulge
clasps approach the undercut from below---from a gingival direction
. Also, by denition, supra or infrabulge categories are based on a r
elationship to the "bulge" or height of contour, not to the amount o
f undercut. Incorrect. An approach from above the occlusal surface
would constitute "suprabulge". Such an approach is also impractical
and nonsensical.
A modied palatal plate is used in maxillary class II cases and may
or may not include lingual plating True False
True Modied palatal plate major connectors are used in maxillary C
lass II RPDs. Plating is not common but can be used.
All of the following clasps are infrabulge clasps except? I-bar Modi
ed T-bar Roach clasp Akers clasp
4 All the clasps mentioned except the Akers clasp approach the und
ercut from a gingival or infrabulge direction. "Akers" is the old nam
e for a circumferential clasp which is, of course, a suprabulge clasp
.
A clasp assembly should have a retentive arm with adequate length
and taper for exibility have a retentive arm that terminates in an
undercut have elements that considered together, provide 180 deg
ree encirclement all of the above
4 A clasp assembly should have all of the attributes described in 1,
2, and 3.
The partial denture that will be co
mpleted on the framework shown
to the right can do all of the follow
ing except transfer stresses to the
abutment teeth transfer stresses a
cross the arch minimize supererup
tion of opposing teeth act as an or
thodontic retainer for the lower inc
isor teeth.
Maxillary class II RPDs do not have an axis of rotation because no f
unctional movement will occur over the hard midline suture of the
palate. True False
In a Class III modication 1 RPD, the rests are usually placed on the
canines away from the modication space in the area of the opposi
ng occlusal contact adjacent to the modication space.
4 Incorrect. The statement is true. The RPD will transfer stresses to
the abutment teeth through the rests, guide plates, major and mino
r connectors, and retentive arms. Incorrect. The statement is true.
The RPD will transfer stresses across the arch through the rests, gui
de plates, major and minor connectors, and bracing and retentive a
rms. This is an important positive attribute because it is through thi
s mechanism that stresses are dissipated throughout the arch rathe
r than being concentrated in one area. Incorrect. The statement is t
rue. The completed RPD (with denture teeth in the posterior edentul
ous areas) will help to minimize super-eruption of the opposing teet
h. It should be pointed out, however, that super-eruption will not be
False
class
RPDs
do have
an axis
rotation.
It is
not a
totallyMaxillary
prevented.
AsIIthe
plastic
denture
teethofwear,
some
super-er
ected
by the
midline plating
suture.would prevent perm
uption will take place.
Correct.
Although
anent tooth movement to the lingual, it will not prevent movement
to the facial which is the normal direction of migration, particularly i
n the presence of periodontal disease.
4 Incorrect. Although answer 1 is possible, it is not the BEST answe
r because the stem of the question does not speciy that the canin
es are adjacent to the edentulous areas. Incorrect. In tooth-support
ed RPDs, rests are usually placed immediately adjacent to the eden
tulous space(s). Incorrect. Areas of opposing occlusal contacts shoul
d be avoided whenever possible. Correct. In tooth-supported RPDs,
rests are usually placed immediately adjacent to the edentulous sp
ace(s).
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
A mandibular lingual bar major co
nnector such as the one shown in t
he RPD to the right requires a mini
mum of _____mm of vertical heigh
t between the gingival margin and
the oor of the mouth. 4 5 7 8
The presence of mandibular lingual tori would indicate the need for
a metal base lingual plating tube teeth extra indirect retainers
The illustration to the right shows
a framework for a mandibular clas
s II RPD. The indirect retainer on t
ooth 21 functions when the patient
chews on something hard the patie
nt chews on something soft the pa
tient chews on something sticky th
e patient bites the bullet
An anterior-posterior palatal strap maxillary major connector has gr
eater strength and rigidity than a horseshoe design. True False
Your patient has the mandibular ar
ch form shown to the right. A rest
on which tooth would be the most
eective indirect retainer? 20 21 2
2 27
Your patient exhibits the mandibul
ar class II modication 1 arch show
n to the right. Tooth #30 is tilted m
esiolinguallly and has very little tis
sue undercut on the lingual. What
is the best clasp for this situation?
Cast circumferential clasp utilizing
a distolingual undercut Cast I-bar
utilizing a mesiolingual undercut C
ast ring clasp utilizing a mesiolingu
al undercut Wrought wire circumfe
Rigid metal retention is associated with a dual path of insertion a cl
rential clasp utilizing a distolingual
ass IV RPD the need for excellent esthetics all of the above
undercut.
The palatal strap maxillary major connector is primarily used in sho
rt span maxillary class III modication 1 RPDs. True False
3 At least 3 mm is required for the space between the superior bor
der of the major connector and the gingival margin and at least 4
mm is required for the vertical height of the lingual bar. 3 + 4 = 7
mm minimum.
2 Incorrect. There is no relationship between the presence of tori a
nd the selection of a metal base. Correct. The major connector can
not extend below the height of contour of the tori and consequently
, there is seldom the 7 mm minimum vertical space needed for a lin
gual bar. Incorrect. There is no relationship between tori and the sel
ection of tube teeth. Incorrect. It is certainly not the BEST answer.
However, there is some logic for answer #4. Since the tissue over t
he tori is very thin and not tolerant to any vertical pressure, one co
uld
argue that
additional
indirect
couldwhen
be used
to safegua
3 Incorrect.
Indirect
retainers
DO retainers
NOT function
the patient
bit
rd down.
againstIttissue
trauma
the the
major
connector.
However,
#2Ini
es
doesn't
matterunder
whether
substance
is soft
or hard.
s really Correct.
the bestIndirect
answer.retainers come into pl
correct. Same as #1 above.
ay AFTER the patient bites down and then begins to open again. Th
e sticky nature of the material attempts to pull the denture base aw
ay from the residual ridge. The indirect retainers prevent the RPD f
rom simply rotating around a line connecting the tips of the direct r
etainers (clasps, retentive arms). They assist the direct retainers in
resisting dislodgement of the prosthesis. Incorrect. Humor???
True The anterior-posterior palatal strap has greater strength and ri
digidty because of its circular shape and because the metal straps li
e in several dierent planes.
4 Incorrect. A rest on #20 would be a primary rest, not an indirect
retainer. Incorrect. Tooth #21 would often have a rest on it and this
rest would function as an indirect retainer. However, it would not b
e the MOST EFFECTIVE indirect retainer. Incorrect. This tooth would
seldom have a rest in the partially edentulous situation shown. Eve
n if it did, it would not be the MOST EFFECTIVE indirect retainer. Co
rrect. The rest on #27 would be a very eective indirect retainer b
ecause it lies furthest from a line connecting the tips of the direct r
etainers (clasps).
2 Incorrect. Due to the mesiolingual
tilt of the tooth, it is unlikely th
at there will be a usable distolingual undercut. Correct. The mesioli
ngual I-bar will work very well. It must be on the mesiolingual corne
r of the tooth and it must emanate from the inferior border of the
major connector so that it has adequate length to be exible. Incorr
ect. This is not the best selection unless there is a severe tissue un
dercut that will cause the mesiolingual I-bar to stand out in the oor
of the mouth and irritate the tongue. Incorrect. Due to the mesioling
tilt of the
tooth
it is unlikely
that
a usable
distoling
4ual
Incorrect.
The
statement
is true
butthere
is notwill
thebeBEST
ANSWER.
The
ual
In addition,
there
is no
reason
use a WW
in th
dualundercut.
path of insertion
allows
rigid
metal
to betoplaced
in anclasp
undercut
is situation---no
need for is
increased
stress-breaking.
. Incorrect.
The statement
true but exibility
is not theor
BEST
ANSWER. Rigi
d metal retention is not used exclusively in class IV RPDs but certai
nly is commonly used in such situations. Incorrect. The statement is
true but is not the BEST ANSWER. Rigid metal retention eliminates t
he need for clasps on anterior teeth and produces excellent estheti
cs. This is the reason it is often used on class IV RPDs. Correct. 1, 2
, and 3 are all true statements.
True If the edenulous areas of maxillary class III RPDs are larger, o
ne is more apt to select an anterior-posterior palatal strap.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Your patient has the class I arch sh
own to the right. The axis of rotati
on is most frequently determined
by: the placement (location) of the
primary rests the type of clasp ar
ms selected the placement of the
minor connectors the placement o
f the indirect retainers
In maxillary RPDs, the bead line is approximately _______mm thick (
deep). 4 3 2 1
1 Correct. The axis of rotation passes through the rigid metal that li
es above the height of contour and closest to the edentulous space
. This should be the rests, as all other rigid metal lies on inclined slo
pes. In the case shown, the axis of rotation would pass through the
rests on teeth numbers 20 and 27. Incorrect. The axis of rotation is
not determined by the type or location of the clasps. Incorrect. The
location of the minor connectors has no relation to the axis of rotati
on. Incorrect. The axis of rotation passes through the PRIMARY rest
s and is important when the extension base moves toward the tissu
4es.
(meaning
1mm)
Becausefunction
the metal
exhibits
very littlebase
dimensional
The indirect
retainers
when
the extension
moves
change
in the
can
light.of
Itsthe
prima
away from
thecasting
tissuesprocess,
and are the
not bead
related
tobe
thevery
location
axi
ry purpose is to provide positive
contact
with
the
tissues
so
food
do
s of rotation.
es not get under the major connector. At the posterior border of a
palatal plate major connector, it may also help provide denture styl
e retention.
The C + 1 rule Does not apply to class IV RPDs Does not apply to cl
ass III RPDs Gives a general rule for the number of clasps Both 1 a
nd 3
4 Incorrect. Although answer 1 is a true statement, it is not the BES
T answer. Incorrect. With very few exceptions, the C+1 rule does a
pply to class III RPDs. Incorrect. Although answer 3 is a true statem
ent, it is not the BEST answer. Correct. Statements 1 and 3 are bot
h correct.
Which of the following maxillary major connectors possesses the le
ast strength and rigidity? Anterior-posterior palatal strap Horse-sho
e Palatal plate Modied palatal plate
2 The horse-shoe maxillary major connector has the least strength
and rigidity unless it is very bulky. For this reason, it is the least de
sirable of all the maxillary major connectors.
A cingulum rest is normallly placed between the middle and incisal
thirds of the maxillary incisors in order to avoid occlusal interferenc
es. True False
False The statement is false. Rests on maxillary incisors generally n
eed to be placed as far gingivally as possible to avoid the opposing
occlusion. This is generally no further incisally than the junction of t
he gingival and middle thirds.
Your patient exhibits the mandibul
ar class II modication 1 arch show
n to the right. Tooth #30 is tilted m
esiolingually, but has a very sever
e tissue undercut on the lingual. W
hat is the best clasp for this situati
on? Cast circumferential clasp utili
zing a distolingual undercut. Cast I
-bar utilizing a mesiolingual underc
ut. Cast ring clasp utilizing a mesio
lingual undercut.
wire agree
circ
All methods of measuring the vertical
dimensionWrought
of occlusion
umferential
clasp (speaking
utilizing a and
distolin
on one major principle: In physiologic
functions
swall
gual undercut.
owing) the teeth should make contact.
True False
3 Incorrect. Due to the mesiolingual tilt of the tooth, it is unlikely th
at there will be a usable distolingual undercut. Incorrect. The mesiol
ingual I-bar would be appropriate EXCEPT that there is a severe tiss
ue undercut. In this instance, the I-bar would stand out in the oor o
f the mouth and would have signicant potential for irritating the to
ngue. Correct. The ring clasp is the best selection because there is
a severe tissue undercut that would cause a mesiolingual I-bar to st
and out in the oor of the mouth and irritate the tongue. The buccal
portion of the ring clasp must be heavy enough to be rigid and stro
ng, and an auxiliary distal rest should be used. Incorrect. Due to th
False
The teeth tilt
willofcontact
during
as there
the mandible
e mesiolingual
the tooth,
it isswallowing
unlikely that
will be abrac
usa
es
against
the
maxilla.
However,
the
teeth
should
NOT
ble distolingual undercut. In addition, there is no reasoncontact
to use duri
aW
ng speech. If they do,Wthe
vertical
dimension
clasp
in this
situation.of occlusion is too gre
at.
Malposed or super-erupted teeth may cause a discrepancy between
centric relation and centric occlusion. Therefore, it is recommended
that the opposing teeth not touch during the making of a centric rel
ation record for mounting of diagnostic casts. True False
True Contact of the natural teeth during making of a centric relation
record is a common cause for error in the record. When the teeth c
ontact, they may cause the mandible to deect or move away from
centric relation.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
The purpose of the centric relation record is to record the exact po
sition of the maxilla to the mandible in a protrusive relation. True Fa
lse
False The relation of the maxilla and the mandible in a protrusive p
osition is a "protrusive record" not a "centric relation record."
If abutment teeth require crowns, the RPD design is prepared after
the crowns are cemented. True False
False The RPD design should be determined BEFORE the crowns are
fabricated so that the appropriate rest seats and contours can be in
corporated into the crowns.
Alginate impression materials have excellent dimensional stability o
ver time and seldom lead to over extended vestibular extensions. T
rue False
False The statement is false on both counts. Alginate has poor dime
nsional stability over time and should be poured as soon as possibl
e. Its consistency often leads to over-extenstions in the vestibules,
especially if a stock tray is used.
Master casts for patients with lone-standing abutments should be po
ured in "Silky Rock" stone. True False
True Lone-standing abutments are more likely to fracture when the i
mpression is separated from the cast and the extra strength of "Sil
ky Rock" or some other "improved" stone minimizes this problem.
The altered cast impression technique is often used on Class I and
Class III RPDs. True False
False The altered cast impression is used on class I and class II RPD
s. Almost never on class III RPDs.
Your patient exhibits the partially e
dentulous mandibular arch shown
to the right. The maxillary arch is t
o be restored with a complete den
ture. Teeth 20 and 29 will receive c
rowns. There are no contraindicati
ons to any type of clasping. Which
of the following clasp assemblies
would
you use
on 20the
andpartially
29. Mesie
Your
patient
exhibits
al
rests and
I-bars Mesial
rests
and
dentulous
mandibular
arch
shown
modied
T-bars
restsarch
andisWt
to
the right.
The Distal
maxillary
Wbe
circumferential
Distal den
res
o
restored withclasps
a complete
ts and
cast20
circumferential
clasps.c
ture.
Teeth
and 29 will receive
rowns. There are very high labial f
renal attachments on both sides.
Which of the following clasp assem
blies patient
would you
use on
and 29?
Your
exhibits
the20
partially
e
Mesial
rests
and I-bars arch
Mesial
rests
dentulous
mandibular
shown
and
modied
T-bars
Distal arch
rests is
ant
to
the
right. The
maxillary
do WW
circumferential
clasps Distal
be restored
with a complete
den
rests The
and undercuts
cast circumferential
ture.
on 20 andclas
29
are on the distalps.
portion of the faci
al surface. There are no contraindi
cations to either infrabulge or supr
abulge retainers. Which of the foll
1 With our philosophy, the number one choice of clasp assemblies f
or extension RPDs is mesial rests and I-bar retentive arms---so that
the clasps will RELEASE during functional movements of the extensi
on bases. The appropriate rest seats and undercuts should be incor
porated into the crowns.
3 Distal rests and WW clasps should be used since there is a contrai
ndication to bar clasps---the high frenal attachments. The rest seats
and appropriate mesiofacial undercuts must be incorporated into th
e crowns.
2 The primary indication for modied T-bar infrabulge retainers occ
urs when the undercuts are adjacent to the edentulous area (on the
distofacial in this case). One must be sure the vertical portion of th
e arm contacts the tooth in front of the greatest mesiodistal curvat
ure.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Reciprocation of clasps is related to the timing of contact between t
he bracing and retentive clasp arms in order to prevent undue forc
es on the abutment teeth during seating and removal of the RPD. T
rue False
Your patient has the partially eden
tulous arch shown to the right. The
undercuts on 21 and 28 are on the
mesiofacial surfaces. The most co
mmonly used clasp assemblies on
the premolars would be: Distal res
ts and I-bars Distal rests and modif
ied T-bars Distal rests and cast circ
umferential
Distal
restseden
and
Your patientclasps
has the
partially
WW
circumferential
tulous
arch
shown to theclasps
right. The
undercuts on 21 and 28 are on the
distofacial surfaces. There are no
contraindications to any types of cl
asps. Under these circumstances,
the most commonly used clasp as
semblies on the premolars would b
e: Distal
rests
and
I-bars
Distal
res
Your
patient
has
the
partially
eden
ts and arch
modied
T-bars
Distal
rests
tulous
shown
to the
right.
The
and cast circumferential
clasps
Dis
undercuts
on 21 and 28 are
on the
tal
rests andsurfaces
WW circumferential
cl
mesiofacial
and there are
asps to suprabulge
no contraindications
or infrabulge retainers. The long r
ange prognosis for the molars is p
oor but your patient does not wan
t them
extracted
at this
time.eden
Sev
Your
patient
has the
partially
eral
alterations
the usual
design
tulous
arch forminshown
to the
righ
could
madehave
to facilitate
later co
t.
The be
molars
drifted mesially
nversion
of the
prosthesis
to a cla
and
lingually.
With
these factors
in
ss
I RPD.
One
of them
involves
the
mind,
rigid
metal
retention
could
b
clasp
assemblies
on the
premolars
e
considered
for use
on the
molars
. Your recommendation?
. True False Distal res
ts and I-bars Distal rests and modif
ied T-bars Distal rests and cast circ
umferential clasps Distal rests and
WW circumferential clasps
Which one of the following classes of RPDs NEVER has an axis of ro
tation? Class I Class II Class III Class IV
What is the major problem with th
e RPD framework shown to the rig
ht? Teeth numbers 21 and 28 shoul
d be plated. The plating on the ling
ual surfaces of the anterior teeth s
hould cover the cinguli. Distal rests
would be better than mesial rests
on teeth numbers 21 and 28. Cast
circumferential
clasps are
preferre
Which of the following
could
be re
d
with the
rests
teeth lin
nu
ason(s)
formesial
choosing
theondouble
20 and 29.shown to
gual bar mbers
major connector
the right? Large interproximal spac
es have resulted from periodontal
surgery. The patient exhibits a hig
h oor of the mouth. There is over
lapping of the anterior teeth. Both
a and b above.
True In order to provide true reciprocation, the timing must be corr
ect. The bracing arm must be in contact with the abutment as the r
etentive arm passes over the bulge and into the undercut.
3 For tooth supported RPDs, whenever the undercut is in the appro
priate area---opposite the point of origin of the clasp (away from th
e edentulous area)---a cast circumferential clasp is the retainer of c
hoice.
2 The undercuts are in the appropriate location for modied T-bars.
Either mesial or distal rests can be used since the RPD is tooth-supp
orted and exhibits no functional movement.
4 Incorrect. If the molars were lost, the I-bars would be cast clasps i
n front of the axis of rotation. It is possible that I-bars could be use
d but the rests should be changed to the mesial. Incorrect. The und
ercuts are not in the appropriate location for modied T-bars. In ad
dition, if the molars were lost, the cast clasps would be in front of t
he axis of rotation. Incorrect. If the molars were lost, the tips of the
cast circumferential clasps would be in front of the axis of rotation.
Correct. If the molars were lost, the WW clasps would provide stres
s
relief
for the
abutments
to their
exibility)
the extensio
True
In this
case,
there are(due
normally
undercuts
onwhen
the mesial
surfac
n base moves
residual
ridge.
es of the molars---due
to thetoward
drifting.the
If only
partial
blockout is done
on the mesial surfaces of the molars during framework fabrication,
the rigid metal of the guide plates will slide into the undercuts and t
hen the anterior part of the RPD is rotated downward into position.
Now the posterior portion of the RPD cannot be dislodged unless th
e clasps on the premolars release rst allowing the anterior portion
of the RPD to move upward and forward.
3 Incorrect. Class I RPDs always have an axis of rotation. Incorrect.
Class II RPDs always have an axis of rotation. Correct. Class III RPD
s never have an axis of rotation. Incorrect. Class IV RPDs usually d
o not have an axis of rotation but many people consider that if all t
he incisors and the canines are missing, the anterior edentulous are
a is so extensive that there is essentially an "anterior extension" an
d an accompanying axis of rotation.
2 Incorrect. While teeth numbers 21 and 28 could be plated, there i
s nothing in the stem of the question indicating that this is necessar
y. Answer #1 is not the BEST answer. Correct. As shown, the platin
g ends at the tooth tissue junction---essentially in the sulcus. Plating
must extend to the contacts interproximally and must cover the cin
guli. When possible, rest seats should be prepared on the incisor te
eth and must be prepared at least on the canines. Incorrect. Assum
ing the undercuts are appropriate for I-bars and there is no contrain
dication
to If
infrabulge
retainers,
mesialindirect
rest, I-bar,
distalfrom
guide
pl
1 Correct.
there is the
need tothe
provide
retention
the
ate is theteeth
preferred
clasp
assembly. Simply
changing
the
restsfrom
to th
anterior
but large
interproximal
spaces
exist, the
metal
e
distal
would
place
thebe
I-bars
(which
are cast clasps)
front
the
the
lingual
plate
could
visible
and unsightly.
In this in
case,
a of
doubl
axis
of rotation.
Incorrect.
Mesial However,
rests, distal
guide
and cast
e lingual
bar might
be indicated.
it is
NOT plates,
a commonly
us
circumferential
claspsIncorrect.
composeThe
the inferior
clasp assembly
called
thelingual
"RPA"
ed major connector.
bar of the
double
.bar
This
is notconnector
the recommended
the rigid
major
must meetdesign
all thebecause
requirements
for originating
a conventi
portion
of the
cast
clasp often lies
height
contour
onal
lingual
bar.
Consequently,
the above
doublethe
lingual
barofcannot
beand
use
like
a rest
on an
inclined
plane. Overlapping an
d when there is acts
a high
oor
of the
mouth.
Incorrect.
terior teeth pose the same problems for the upper bar of the doubl
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
When possible, plating on maxillary RPDs should be avoided due to
the potential for interfering with speech and occlusion. True False
True Plating on maxillary RPDs occasionally causes problems with s
peech and frequently interferes with normal occlusion of the maxill
ary and mandibular teeth.
The survey line (height of contour) of a full contour wax-up for a cr
own for an RPD abutment tooth can be visualized using red wax zin
c stearate powder border wax pressure indicating paste
2 After the surface of the wax-up is lightly covered with zinc stearat
e, the analyzing rod is passed over the surface of the wax. The hei
ght of contour will appear darker than the surrounding powdered su
rface.
Your patient has only teeth numbers 20 through 29 remaining. You
have tried in the framework and are border molding the extension
areas in preparation for an altered cast impression. The distobuccal
area is shaped by the? Buccinator muscle Masseter muscle Internal
pterygoid muscle Mylohyoid muscle
Your patient has teeth numbers 20
through 29 remaining. The survey
line and undercut (shaded area) fo
r tooth #29 are as shown on the ri
ght. There is no contraindication to
the use of an infrabulge clasps but
there is a very solid contact in the
mesial-occlsual fossa. What would
be your
rest
location
an
(Image did not appear on website)
Yourchoice
patientfor
has
teeth
numbers
retentive
Distal rest
and caar
20 through 29 remaining. The d
survey
line arm?
and undercut
(shaded
circumferential
clasp
Distal
rest
ea) for tooth #29 are as shownston
the right. There
is no
contraindic
and
cast and
I-barthere
Mesial
rest
cast pr
ation to the use of an infrabulge
clasps
are
no and
occlusal
and best
WW choice
circumfer
oblems aecting rest location. I-bar
WhatDistal
wouldrest
be the
for r
claspMesial rest an
est location and retentive arm? Mesial restential
and I-bar
d modied T-bar Mesial rest and WW circumferential clasp Distal re
st and WW circumferential clasp
Your patient has teeth numbers 20
through 29 remaining. The survey
line and undercut (shaded area) fo
r tooth #29 are as shown on the ri
ght. There is no contraindication to
the use of an infrabulge clasps. Th
e opposing occlusion is provided b
y a complete denture. What would
be your choice for rest location an
d retentive
arm? Mesial
rest andYou
IYour patient has only teeth numbers
20 through
29 remaining.
bar
Mesial
rest
and
modied
T-bar
have tried in the framework and are border molding the extension
Mesial
rest
and cast circumferenti
areas in preparation for an altered
cast
impression.
The distolingua
al clasp
Distal rest
andInternal
WW circum
l border molding is shaped by the?
Masseter
muscle
pteryg
ferential
clasp
oid muscle Superior constrictor muscle Mylohyoid muscle
As a general rule, plating is indicated for the maxillary arch if there
are less than three contiguous maxillary incisor teeth remaining. Tr
ue False
2 Incorrect. The buccinator muscle is a relatively weak muscle and i
ts bers run anterior-posteriorly. It has very little if any eect on th
e shape of the distobuccal corner of the denture base. Correct. The
masseter muscle is a powerful muscle whose bers run more or les
s superiorly-inferiorly. Upon contraction, it pushes the buccinator m
uscle and other tissues into the distobuccal corner of the denture b
ase. Incorrect. The internal pterygoid muscle has no eect on the di
stobuccal corner of the mandibular denture base. Incorrect. The my
muscle
no eect
on the
buccal
of the
denture
b
4lohyoid
Incorrect.
NO! has
NEVER!
Incorrect.
The
I-bar aspect
would lie
in front
of the
ase. It would not release during func
axis of rotation and is a cast clasp.
tion and would have the potential to torque the tooth. Incorrect. Alth
ough the undercut is appropriate for an I-bar, a mesial rest cannot
be used due to the occlusion and, if a distal rest is used, the cast Ibar would lie in front of the axis of rotation. Correct. Since the occl
usion precludes the use of a mesial rest, the rest must be moved t
o the distal. Virtually any type of clasp will place the retentive tip in
front
of the axis
rotationisand
of the
clasp
is of
paramo
2 Incorrect.
The of
undercut
not exibility
appropriate
for an
I-bar.
The
I-bar
wrought
wire.
must be placedunt
justimportance---thus,
in front of the greatest
mesiodistal
curvature o
f the facial surface. In this case, most of the undercut is behind the
greatest mesiodistal curvature of the facial surface. Correct. Most o
f the undercut is behind the greatest mesiodistal curvature of the f
acial surface and that is where the retentive tip should be placed. T
he vertical approach arm must be placed in front of the greatest m
esiodistal curvature so that the clasp cannot simply move upward a
ndCorrect.
backward
withoutrest
exing.
If thisiscould
happen,
theThe
clasp
would
1
A mesial
and I-bar
the best
choice.
I-bar
lies n
a
retentive.
Incorrect.
A circumferential
clasp cannot
be used b
totorbe
behind
the axis
of rotation
and would release
during functional
ecause
the undercut
is adjacent
the
edentulous
on thei
movement
of the denture
base. to
It is
our
#1 choicearea
if the(and
undercut
same
side
of the tooth
as the iforigin
of the arm).
Incorrect.
Samean
re
s in the
appropriate
location,
an infrabulge
clasp
can be used,
asontoas
#3.
d if there is no contraindication
placement
of a rest on the mesio
-occlusal surface. Incorrect. Although a modied T-bar could work, it
is not the rst choice, especially when most of the undercut lies on
the mesiofacial surface. Incorrect. This would be the "RPA" concept.
problemThe
is that
the originating
portion
of the
is rigid and
3The
Incorrect.
masseter
muscle has
no eect
onclasp
the contour
of th
would
lie ange.
above the
surveyThe
line.internal
It would
function muscle
like a rest
e
lingual
Incorrect.
pterygoid
hason
noan
ei
nclined
plane---not
a
good
idea!
Incorrect.
Although
a
distal
rest
an
ect on the lingual denture ange. Correct. The superior constrictor
d WW circumferential
clasp
could
workofinthe
thislingual
situation,
it is Ifnot
our
muscle
aects the most
distal
portion
ange.
you
a
rst
choice. We would
a clasp arm
that releases
re
overextended
in thisrather
area, have
the patient's
complaint
will oftenduring
be th
functional
movement
(downward,
tissueward)
movement
of the
den
at he/she has
a sore throat.
Incorrect.
The mylohyoid
muscle
aect
base.
s the lingual ange but notture
at its
most posterior (distal) aspect.
True The plating will provide cross arch stability and will also provid
e a mechanism for adding articial teeth to the RPD should any of t
he remaining teeth be lost. Also, plating will close up small, one too
th openings in the framework.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
All of the components listed below may be involved in the 180 degr
ee encirclement rule EXCEPT I-bar Minor connector Guide plate Ope
n latticework
What is the correct relationship of the foot of an I-bar to the surve
y line (height of contour) on a terminal abutment for an extension
RPD? The foot should be entirely above the survey line. The foot sh
ould be partially above and partially below the survey line. The foot
should be totally below the survey line. The relationship of the foot
of the I-bar and the survey line is of no consequence.
4 Incorrect. An I-bar (or any type of retentive arm) can be one com
ponent that helps establish 180 degree encirclement of an abutme
nt. Because retentive arms are exible, they may not be quite as e
ective as some other components but they still contribute. Incorre
ct. Because of their location and their rigidity, minor connectors are
very eective contributors to 180 degree encirclement. Incorrect. B
ecause of their location and rigidity, guide plates are very eective
contributors to 180 degree encirclement. Correct. Open latticework
(or any type of denture base retentive element) has no relation to t
he 180
degree
encirclement
3 Incorrect. The foot
cannot
extend
above therule.
survey line or it will
not release during functional movements of the extension base. Inc
orrect. Same reasoning as #1. Correct. The foot should be totally b
elow the survey line so that it will release during functional movem
ents of the extension base. Incorrect. It DOES make a dierence.
The primary indication for and Oddo clasp occurs when an anterior
abutment has excessive labial inclination so that the retainer (clasp
) would be very close to the incisal edge. True False
True The statement is true---the primary reason for using an Oddo
hinge clasp is to improve esthetics by moving the clasp arm gingiva
lly. Less frequently, Oddo hinge clasps may be used to prevent infr
abulge arms from standing out in the vestibule. While Oddo clasps
are more commonly used in the maxillary arch for esthetic reasons
, they may be used in either arch to prevent infrabulge arms from
standing out in the vestibule.
The purpose of the altered cast impression procedure is to obtain t
he maximum support possible from the edentulous areas of class I
and class II RPDs. True False
True The altered cast impression captures the tissues of the edentul
ous ridges in relation to the way the framework ts in the mouth (n
ot on the cast). Hopefully, the two would be the same but that is no
t always the case. With an altered cast impression, one also tends t
o avoid the overextension that is prevalent with a cast made from
an alginate impression in a stock tray.
When there are extensive edentulous areas present in both arches
and no opposing teeth meet, we should establish the vertical dimen
sion of occlusion prior to making a centric relation record. True Fals
e
True It is always a good idea to establish the VDO before making a
centric relation record. In theory, the VDO could be adjusted on the
articulator after the casts are mounted if a face-bow transfer has b
een done. However, since the type of face-bow transer we do is "ar
bitrary" and since some inaccuracy is to be expected, it is best to
make the centric relation record at the correct VDO whenever possi
ble.
You are fabricating maxillary and mandibular RPDs for your patient.
At the framework try-in appointment, both frameworks should initia
lly be placed in the mouth to check for occlusal interferences. True
False
False The frameworks should be tried in one at a time. First, each s
hould be checked for t. Then the occlusion should be adjusted with
each of the frameworks in place without the other. Finally, the occlu
sion is adjusted with both frameworks in place.
A protrusive record is made with the mandibular anterior teeth app
roximately 6 mm forward of centric relation (or with the mandibular
and maxillary anterior teeth in an edge to edge relationship). This r
ecord is used to set the horizontal condylar guidance on the articul
ator. True False
True After the protrusive record is made, the casts, prostheses, or r
ecord bases and the record are placed on the articulator. The horiz
ontal guidance controls on each side are loosened and rotated until
the record and teeth or keys t together as accurately as possible.
The space that opens between the posterior teeth during anterior
movement of the mandible is called Christensen's Phenomenon. Th
is posterior separation is increased if the incisal guidance is increas
ed. True False
True The amount of posterior separation is aected by both the inci
sal guidance and the horizontal condylar guidance. The separation i
s increased as both IG and HCG increase---the eect of IG is greate
r anteriorly and the eect of HCG is greater posteriorly.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Before trying in a framework, you should inspect the master cast f
or damage and inspect the framework for sharp ns. True False
Your RPD framework ts the cast but does not t in the mouth. On
e should assume that the impression for the cast was inaccurate an
d that a new impression will need to be made. True False
The fewer teeth that remain, the more like a denture the RPD beco
mes and the more likely the need for a custom impression tray. Tru
e False
Reason(s) for selecting a mandibular lingual plate major connector i
s/are? The presence of lingual tori. Anticipated loss of one or more
of the remaining teeth. A high lingual frenum. 1, 2, and 3 above
Your patient has teeth 20 through
29 remaining. Tooth #29 exhibits t
he tooth contours and undercut sh
own in the illustration to the right.
Which of the clasp assemblies liste
d has the GREATEST DANGER of to
rquing the abutment during functio
nal movements of the extension b
ase? Mesial rest and cast I-bar Dis
tal rest and WW circumferential cl
asp RPA clasp assembly with a cas
Which of the following clasps commonly
lingualthe
undercuts?
t clasp All utilize
have about
same po Ri
ng clasp Extended arm clasp Half and tential
half clasp
Both 1 and 3
danger
Which of the abutments in the part
ially edentulous arch to the right h
as the greatest potential for utiliza
tion of a ring clasp? #18 #21 #28
None of the abutments have any p
otential for the use of a ring clasp.
Metal denture bases are most commonly used over well-healed pos
terior ridges where vertical space is a problem. True False
True If the master cast has been damaged in the tting of the fram
ework to the cast, there is a high probability that the framework wil
l not t in the mouth. The areas of damage should be the rst area
s adjusted if the framework does not t. Sharp ns are very prone
to damaging the cast and thus also very suspect if the framework
does not t---but sometimes the damage to the cast caused by tiny
ns is very dicult to see.
False The impression and/or the cast may be inaccurate and thus b
e the cause of the problem. However, because of the time and cost
involved in making the framework, all other possible causes should
be eliminated before making a new impression. Scarring of the cast
or sharp ns or protuberances on the framework might be correcta
ble by analyzing the metal contacts with the teeth with some type o
f disclosing medium and relieving the metal. Inaccuracies from very
minor tooth movement may also be corrected in this manner. If att
empts
t theteeth
framework
theedentulous
mouth areareas
unsuccessful,
then one
True
Astofewer
remain,tothe
become larger.
In
can assume
thattray
either
impression
or the in
cast
is inaccurate
andr
general,
a stock
willthe
perform
adequately
areas
where teeth
the impression
need to be
remade.
emain but relatively
poorer inwill
edentulous
areas.
This is one of the
major reasons an altered cast impression is done. However, when t
he number of teeth is very few and the edentulous areas are very l
arge, it is sometimes easier to make a custom tray and border mol
d before the impression is made. In this way, the altered cast proce
dure can usually be omitted.
4 Answers numbers 1, 2, and 3 are all very valid reasons for selecti
ng a linguoplate major connector.
Incorrect. The I-bar should release and thus, should create little dan
ger of torquing the abutment. Incorrect. Since the WW arm is exibl
e, it provides some stress-breaking eect and the danger of torqui
ng the abutment should be minimized. Correct. Even though the RP
A clasp has a mesial rest, the originating portion of the circumferen
tial clasp will lie above the height of contour and will act like a dista
l rest on an inclined plane. The tip of the cast arm will now lie in fro
nt of the axis of rotation. Incorrect. One of the other choices is muc
h more potentially damaging to the abutment.
4 Both the ring clasp and the half and half clasp use lingual underc
uts almost exclusively.
1 Ring clasps are used almost exclusively on lower molars that hav
e drifted mesially and lingually. We would generally prefer to use a
mesiolingual I-bar but in cases where there is considerable undercu
t below the abutment, a ring clasp is just about the only alternative
.
True The primary indication for metal bases is limited vertical space
. However, the ridges should be well-healed because relining is alm
ost impossible.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Referring to the partially edentulou
s arch shown to the right. The guid
e plates on teeth 21 and 28 should
curve buccolingually and extend li
ngually just short of the distolingu
al line angles. True False
False The guide plates should extend just beyond the distolingual lin
e angles to provide 180 degree encirclement, bracing, and, in some
cases, reciprocation.
A cingulum rest should be placed between the occlusal and middle
thirds of the incisor teeth. above the middle third of the incisor teet
h. at the junction of the gingival and middle thirds of the incisor tee
th. on the disto-incisal edges of the incisor teeth.
3 Incorrect. Too high. It is dicult to prepare an adequate rest seat
and the potential for torquing forces on the abutment teeth are incr
eased. In the maxillary arch there would also be the increased pote
ntial for interference with the opposing occlusion. Incorrect. Too hig
h. Same reasoning as for answer #1. Correct. This location places t
he rest seat and rest just above the cingulum but as low as possibl
e so that potential torquing forces on the abutment are minimized. I
ncorrect. Totally nonsensical.
The external nish line is the external junction of framework metal
and denture base plastic. the external junction of framework metal
and supporting tissues. the external junction of the framework met
al and the natural teeth. the external junction of the natural teeth a
nd the denture base plastic.
1 By denition, the external nish line is the external junction of the
framework metal and the denture base plastic.
As a general rule, a removable partial denture needs C+1 clasps w
here C=Kennedy classication number. True False
True The "Wiebelt" rule for determining the number of clasps for a r
emovable partial denture. [# of clasps = Kennedy classication + 1]
A "bead" line" is used only on mandibular major connectors is a sea
l at the interface of framework metal and tissues should taper o a
s it approaches the marginal gingiva of the abutment teeth both 2
and 3 above
4 Answer #1 is false. A "bead line" is used only on maxillary major
connectors. Answers #2 and #3 are both true so answer #4 becom
es the best answer.
(Second image does no appear on
website) Your patient has the parti
ally edentulous arch shown in the i
llustration on the left. Tooth #28 h
as the survey line and undercut sh
own in the illustration on the right.
There are no contraindications to a
ny type of clasp or to any rest loc
Your
has the
eden
ation.patient
What would
bepartially
your rst
ch
tulous
in the lefton
illustr
oice forarch
the shown
clasp assembly
too
ation.
Tooth
#28
has
thecast
survey
lin
th #28?
distal
rest
and
circum
e
and undercut
shown
in the
ferential
clasp distal
rest
andillustr
WW
ation
on the right.
There
arerest
no an
co
circumferential
clasp
distal
ntraindications
to any
clas
d
I-bar clasp distal
resttype
and of
modi
p or to anyedrest
location.
T-bar
clasp What wo
uld be the most common choice fo
r the clasp assembly on tooth #28
? distal rest and cast circumferenti
The superior border of a mandibular
lingual
connector
al clasp
distalbar
restmajor
and WW
circum sh
ould be at least 3 mm from theferential
tooth/tissue
at least
2 mm
claspjunction
distal rest
and I-bar
from the tooth/tissue junction located
at
the
tooth/tissue
junction
clasp distal rest and modied T-baat
least 3 mm above the tooth/tissue
junction
r clasp
4 Incorrect. A circumferential clasp cannot be used when the under
cut is located on the side of the tooth (distal in this case) where the
clasp originates. Incorrect. A circumferential clasp cannot be used
when the undercut is located on the side of the tooth (distal in this c
ase) where the clasp originates. In addition, WW clasps are seldom
used on tooth-borne RPDs. Incorrect. In order for an I-bar to be use
d, the undercut should be just forward of the greatest mesiodistal c
urvature of the facial surface. Correct. When the undercut is adjace
nt
to the edentulous
a modied
an excellent
choice, m
a
1 Correct.
The RPD isarea,
tooth-borne
andT-bar
thus is
exhibits
no functional
ssuming
are not contraindications
the of
use
oftooth
an infrabulge
otion andthere
the undercut
is on the oppositetoside
the
from the
clasp.
point of origin of the clasp---a requirement
for a circumferential cla
sp. Incorrect. Although the undercut is appropriate for a distal rest
and WW circumferential clasp, there is really no need for WW since
there is no functional movement of the prosthesis. #2 is not the be
st answer. Incorrect. Although a distal rest and I-bar would work, it i
s not the rst choice clasp assembly unless esthetic demands dictat
e that the clasp be hidden. In this case, the I-bar might be better th
an a cast circumferential clasp. Not the best answer. Incorrect. Mos
t of the undercut is on the mesiofacial surface, not the distofacial a
1 The superior
border
of a lingual bar
should
be at
least 3 mm fro
s would
be appropriate
for a
modied
T-bar.
m the gingival margin---4 mm is preferred.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
The internal nish line is the butt joint between the metal and plasti
c on the tissue side of the edentulous area the butt joint between t
he metal and plastic on the outer surface of the RPD a type of post
erior palatal seal a special type of bead line
1 Answer #1 is correct by denition. Answer #2 denes the extern
al nish line. Answers #3 and #4 are unrelated to the stem of the q
uestion.
A class I modication 0 RPD normally has how many clasps? 1 2 3 4
2 According to the C+1 rule......1+1 = 2
Select a maxillary major connector
for the large Class III modication
1 RPD shown to the right. The resi
dual ridges are good and the abut
ment teeth are strong. Palatal stra
p Modied palatal plate Horse-shoe
Anterior-posterior palatal strap
When an RPD is fully seated, the tips of the clasp arms should exer
t very light pressure against the abutment teeth. True False
Your patient's partially edentulous
arch form is shown in the left illust
ration. The clasp assembly for toot
h #20 is illustrated on the right. W
hen is the retentive arm activated?
When the patient bites down on th
e extension base. When there is a
n attempt to dislodge the RPD. Wh
en the extension base moves towa
rd the tissues. It should never be a
ctivated.
Guide plates for tooth-supported RPDs may extend above the heigh
t of contour while those on extension RPDs should not. True False
Select a maxillary major connector
for the large Class III modication
1 RPD shown to the right. The resi
dual ridges are of medium quality
but the third molar abutment teeth
are weak. A wide single palatal str
ap An anterior-posterior palatal str
ap A modied palatal plate A hors
e-shoe
Select a maxillary
major connector
for the Class III modication 1 RPD
shown to the right. The residual rid
ges are of good quality and the r
st premolar and second molar abu
tment teeth are strong. Anterior-p
osterior palatal strap Horse-shoe M
odied palatal plate Palatal strap
4 Incorrect. Although it could be used, there would be undesirable ti
ssue coverage---especially since the ridges are good and the abutm
ents strong. Incorrect. A modied palatal plate is used for maxillary
class II RPDs. Incorrect. In general, a horse-shoe major connector is
undesirable because it lacks rigidity unless quite bulky. It is only use
d to circumvent large inoperable tori or when the patient is a big-ti
me gagger. Neither of these circumstances are mentioned in the qu
estion stem. Correct. These are perfect circumstances for an anteri
or-posterior palatal strap major connector. The tooth-borne areas ar
e large, the abutments are strong, and the residual ridges are of go
od size
and the
quality.
False When the RPD is fully
seated,
tips of the clasp arms shoul
d exert NO pressure against the abutment teeth---they should be to
tally passive.
2 Incorrect. When the patient bites down on the extension base, the
I-bar should RELEASE. It should only function when there is an atte
mpt to dislodge the RPD, i.e. move it away from the basal seat. Cor
rect. The retentive arm should be activated when dislodging forces
attempt to unseat the RPD---movement away from the basal seat. I
ncorrect. The retentive arm should be activated when dislodging for
ces attempt to unseat the RPD---movement away from the basal se
at. Incorrect. The retentive arm should be activated when dislodgin
g forces
attempt
to unseat RPDs
the RPD---movement
awaymovement,
from the bas
True
Since
tooth-supported
exhibit no functional
th
al seat.
e guide plates may extend above
the height of contour. Extension
RPDs do exhibit functional movement around an axis of rotation. T
he axis should pass through the rest closest to the edentulous area
. However, if the guide plates next to the edentulous areas extend
above the height of contour, they will pre-empt the planned rests a
nd act like rests on inclined planes. The retentive tips would now be
in front of the axis of rotation and have the potential for torquing th
e teeth Aduring
functional
movements
of the
extension
bases.
1 Correct.
wide palatal
strap
will add some
palatal
support
to the
RPD---a desirable characteristic considering that the abutments are
weak. Incorrect. Because of the weak abutments, more palatal sup
port is desirable and a wide palatal strap would be preferred. This i
s sometimes called a palatal plate because of its breadth. Other pe
ople prefer to restrict the term "palatal plate" for the connector use
d with large class I maxillary RPDs. Incorrect. A modied palatal pla
te is used for maxillary class II RPDs. Incorrect. In general, a horseshoe
major connector
is undesirable
because
it lacks
unless
4 Incorrect.
The breadth
of the edentulous
spaces
arerigidity
too small
to
quitean
bulky.
It is only
to circumvent
large
inoperable
or the
wh
use
A-P strap.
Theused
opening
would almost
surely
be lesstori
than
en the patient
is arequired.
big-time Incorrect.
gagger. Neither
of these
circumstances
minimum
15 mm
In general,
a horse-shoe
majo
are mentioned
in theit question
stem.
r connector is undesirable
because
lacks rigidity
unless quite bulk
y. It is only used to circumvent large inoperable tori or when the pa
tient is a big-time gagger. Neither of these circumstances are menti
oned in the question stem. Incorrect. A modied palatal plate is use
d for maxillary class II RPDs. Correct. The A-P dimension is small, th
e residual ridges are good, and the abutments are strong---all indic
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Select a maxillary major connector
for the Class III modication 1 arch
shown to the right. The residual rid
ges are of good quality and the r
st premolar and third molar abutm
ent teeth are strong. The patient r
elates a long history of gagging pr
oblems and, in fact, had major pro
blems with
the impressions
for on
the
(Second
picture
did not appear
study
casts.
pala
website)
YourAnterior-posterior
patient has the parti
tal
Horse-shoe
allystrap
edentulous
arch Modied
shown inpalat
the l
al palte Tooth
Palatal#28
strap
eft illustration.
has the s
urvey line and undercut shown in t
he right drawing. An infrabulge cla
sp CAN NOT be used due to a very
high frenal attachment immediatel
y below the abutment. What would
be your rst choice for the clasp o
tooth
A castthe
circumferentia
If a mandibular RPD abutment n
must
be#28?
crowned,
FPD impressio
l clasp
A wrought
wirea circumferen
n should include all the abutment
teeth
for the RPD
full arch impr
tialpads
claspall
A of
cast
e
ession the retromolar
thecircumferential
above
mbrasure clasp A wrought wire cir
cumferential embrasure clasp
A tissue undercut may preclude the selection of A suprabulge clasp
An infrabulge clasp A half and half clasp A combination clasp
2 Even though the horse-shoe major connector is not as rigid as oth
er major connectors, it probably will suce with good ridges and st
rong abutments. In this patient, the major problem will undoubtedly
be gagging and the horse-shoe connector should be more favorable
in this regard.
3 Incorrect. A conventional circumferential clasp cannot be used wh
en the undercut is adjacent to the origin of the clasp (in this case, t
he distal). Incorrect. Same reason as #1 and there is no reason to u
se WW since the RPD is totally tooth-borne. Correct. The cast clasp
would emanate from a mesial minor connector, pass through the e
mbrasure, cross the facial surface of the tooth and engage the dist
ofacial undercut. Incorrect. Do not use WW through an embrasure. I
t is dicult to adapt to the occlusal surfaces of the teeth and may i
nterfere
withAlthough
the opposing
occlusion.
In addition,
nick o
4 Incorrect.
the answer
is true,
it is not the slightest
BEST answer.
kink in the
wireshould
will ultimately
leadintothe
breakage.
All of the rabutment
teeth
be included
impression so th
at the best path of insertion/dislodgement for ALL abutments can b
e determined. Incorrect. Although the answer is true, it is not the B
EST answer. A full arch impression is required to capture all of the
abutments and the retromolar pads. Incorrect. Although the answer
is true, it is not the BEST answer. The retromolar pads may be imp
ortant in helping to establish the plane of occlusion. Although it is tr
ue that there would be many circumstances when the plane of occl
usion
would
be entirely
determinedthe
by use
the of
remaining
natural
2 Tissue
undercuts
contraindicate
infrabulge
claspsteeth,
beca
there
are
also will
circumstances
the location
of theor
retromolar
p
use
the
clasps
stand out inwhen
the oor
of the mouth
the vestibu
ads
would
provide
valuable
information.
Correct.
1,
2,
and
3
are
all
le and may be irritating to the tongue or lips/cheeks. The other choi
true.clasps and tissue undercuts hav
ces for answers are all suprabulge
e no bearing on these clasps.
A combination clasp assembly generally has a cast bracing arm a d
istal rest a wrought wire retentive arm all of the above
Your patient's partially edentulous
mandibular arch form is shown to
the right. Which of the abutment t
eeth would be likely to have a com
bination clasp? Not likely on any of
the abutments #20 very likely; #2
9 less likely #29 very likely; #20 l
ess likely #31 very likely; not likel
y on either
#20
or #29 abu
A modied
T-bar on
a terminal
tment for a Class I partially edentu
lous arch (such as the one shown)
is used with a distal rest is placed i
nto a distobuccal undercut should
have the vertical approach arm dis
tal to the greatest mesio-distal cur
vature of the facial surface both 1
and 2
Which of the following should be considered in diagnosis for an RPD
patient? interarch space tissue undercuts occlusal contacts all of th
e above
4 Answers 1, 2, and 3 are all correct. Therefore, the best answer is
#4, "all of the above."
2 A combination clasp (WW retentive arm, cast bracing arm) is MOS
T likely on tooth #20 because it lies bodily in front of the axis of ro
tation. A combination clasp may also be indicated on #29 if the me
sial rest, I-bar, distal guide plate clasp assembly cannot be used.
2 Incorrect. It is used with a MESIAL rest. Correct. The tip of the ar
m is placed in a distobuccal undercut. Incorrect. The vertical approa
ch arm must be placed just to the MESIAL of the greatest mesiodist
al curvature of the facial surface. This prevents the arm from relea
sing upward and backward without providing retention. Incorrect. Si
nce #3 is incorrect, so is #4.
4 Answers 1, 2, and 3 are all true and therefore, #4 is the BEST an
swer.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
For a removable partial denture abutment that must be crowned,
more than the normal occlusal reduction will be required. True False
True The extra reduction is required for the rest seat in the nal res
toration.
A lingual plate mandibular major connector may be selected becaus
e the mandibular incisors are tilted lingually there are mandibular t
ori present there is a high lingual frenum all of the above
4 Answers 1, 2, and 3 are all common reasons for selecting a lingu
oplate mandibular major connector. Therefore, the best answer is 4
.
A master cast for a RPD should be blocked out and duplicated befor
e overlapped incisors are recontoured rest preparations are prepar
ed the framework is waxed up all of the above
3 Incorrect. Overlapped incisors should be recontoured BEFORE the
nal impression is made and the master cast poured. Incorrect. Res
t seat preparations must be completed BEFORE the nal impression
is made and the master cast poured. Correct. The master cast is bl
ocked out and duplicated---poured in refractory material. Then the f
ramework is waxed up on the refractory cast. Incorrect. Since 1 an
d 2 are incorrect, 4 is also incorrect.
Rest placement on a terminal abutment of a Class I RPD depends o
n the opposing occlusion the tilt of the abutment tissue undercuts a
ll of the above
What is the problem (if any) with t
he design of the I-bar on tooth #2
8? The I-bar should be placed in fr
ont of the greatest mesio-distal cu
rvature, not behind it. The I-bar sh
ould be placed more distally, close
r to the guide plate. The I-bar shou
ld extend above the survey line. T
here patient
is no problem;
of
Your
has the the
archposition
form sho
the
I-barYou
is correct.
wn to the
right.
plan to use me
sial rests and I-bars but will need t
o plate the premolars due to the to
ri. What should be the relationship
of the superior border of the platin
g and the height of contour on the
lingual surfaces of teeth numbers
A
clasping
teeth
20general
and 29?rule
Thefor
plating
must
end w
b
hich lie
to contour.
the axis The
of rota
elow
theanterior
height of
pla
tion
#21
the illustrati
ting (e.g.
must tooth
end at
theinheight
of con
on
to The
the right)
a Class
modict
tour.
platinginmust
endII above
ation
1 RPD
AlwaysNone
use cast
cla
he height
ofis:
contour.
of the
sps Neverabove
use suprabulge
is correct. clasps U
se wrought wire clasps Use 0.030 i
nch undercut for stability
A general rule for rest placement on an abutment adjacent to an e
xtension area is? Place the rest on the occlusal surface on the oppo
site side of the tooth from the extension area. Place the rest on the
occlusal surface adjacent to the extension area. Place rests on both
the mesial and distal occlusal surfaces. Do not place a rest on this t
ooth.
4 Incorrect. It is a true statement but not the BEST answer. Deep in
terdigitation or tight contact in a particular fossa may negate its us
e as a rest area. Incorrect. It is a true statement but not the BEST
answer. A tilted terminal abutment may dictate the use of a distal r
est and WW clasp assembly because adequate physiologic relief of
the guide plate is impossible and the guide plate will pre-empt a pla
nned mesial rest. Incorrect. It is a true statement but not the BEST
asnwer. Tissue underucts may negate the use of an infrabulge clas
p
in turn,
a change
in there
the location
of the rest.
Correct.
1
1 and,
Correct.
In itscause
current
location,
is the possibility
that
the enti
, 2,
and upward
3 are alland
true.
re clasp assembly could
move
backward, allowing the Ibar to escape the undercut without exing. If this occurred, there w
ould be no retention. Incorrect. It is already too far distal. It needs t
o be moved anteriorly just in front of the greatest mesiodistal curv
ature of the facial surface. Incorrect. The I-bar cannot extend abov
e the survey line or it will not release during functional movements
of the extension base. Incorrect. There IS a problem. The I-bar is po
sitioned
far the
distally.
2 Incorrect. If the plating
ends too
below
height of contour, there wi
ll be a space between the superior edge of the plating and the tooth
---a food trap. Correct. The plating must end EXACTLY at the height
of contour. Incorrect. If the plating ends above the height of contou
r, it will pre-empt the planned mesial rest. It will be a rest on an inc
lined plane (which is no good) and the I-bar will lie in front of the ax
is of rotation (which is also no good). Incorrect.
3 Incorrect. NEVER use cast clasps for teeth which lie in front of the
axis of rotation. Incorrect. Suprabulge clasps are almost always use
d in this instance. Correct. WW clasps, because of their exibility, w
ill tend to place less stress on the anterior abutment when the exte
nsion base exhibits functional movement (movement toward the re
sidual ridge). Incorrect. 0.030 inch undercut is three times what is n
ormally used. Even a wrought wire clasp into this amount of underc
ut would place signicant stress on the abutment during functional
the extension
1 Correct. This ismovement
the generalofrule.
It ts with base.
our preferred clasp as
sembly of mesial rest, distal guide plate, and I-bar retentive arm. T
here are certainly many exceptions to the rule. You should know wh
at they are and the reasons for their selection. Incorrect. This woul
d not be your rst choice and would not be the general rule. Howev
er, there are several exceptions to the general rule. Do you know w
hat they are? Incorrect. There could be instances where rests are pl
aced on both the mesial and distal occlusal surfaces but it would ce
rtainly not be the general rule. (An example where both would be u
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Low fusing metal is associated with which of the following procedur
es? The altered cast impression. Physiological adjustment of the fr
amework. The RPD remount cast. Making records for RPDs.
Physiologic adjustment of the framework is usually done at deliver
y of the RPD. should be done at the framework try-in appointment.
is usually done at the records appointment. may be omitted in the
presence of strong abutments and good residual ridges.
An exception to the C+1 rule for number of clasps is the Class II m
odication 0 case. True False
Physiologic adjustment is related to the axis of rotation adjustment
of the framework to the teeth functional movement of the framewo
rk all of the above
If physiologic adjustment of the framework is not done on a Class I
modication 1 RPD, the clasps may not release in function. True Fal
se
The bracing arm of a circumferential clasp assembly must always li
e at or above the height of contour. True False
Your patient has the partially eden
tulous arch shown to the right. Wh
at would be the best clasps for too
th number 20 and 29 if they were
tilted mesially? Mesial rests and ca
st I-bars Mesial rests and WW I-bar
s Distal rests and WW I-bars Distal
rests and combination clasps
Your patient has the partially eden
tulous arch shown to the right. The
premolars are tilted lingually and t
here are no facial undercuts. Ther
e are, however, undercuts on the l
ingual. What would be the best cla
sps for this situation? Lingual I-bar
s Roach clasps Akers clasps Half a
nd Half clasps
3 Low fusing metal is used to make the remount cast. It is placed in
the areas where natural teeth remain.
2 Incorrect. Physiologic adjustment is seldom done at the delivery a
ppointment because the denture bases will prevent the exaggerate
d functional movement needed to adequately mark areas where th
e framework binds against the remaining natural teeth. Correct. At
the framework try-in appointment, there are no record bases or de
nture bases to interfere with the exaggerated functional movement
required to mark the areas of contact of rigid metal with the natura
l teeth. Incorrect. Physiologic adjustment is seldom done at the rec
ords appointment because the temporary bases will prevent the ex
aggerated functional movement needed to adquately mark areas w
here the framework binds against the remaining natural teeth. Inco
rrect.
adjustment 0ofRPD
the generally
framework
should
always
TruePhysiologic
A class II modication
has
2 clasps
not be
3. d
one for extension RPDs regardless of the strength of the abutments
or quality of the residual ridges.
4 Incorrect. It is a true statement but not the BEST answer. Marking
of the framework for physiologic relief occurs when one creates ex
aggerated movement of the RPD around the axis of rotation. Physi
ologic relief is only necessary on those RPDs that have an axis of r
otation. Incorrect. It is a true statement but not the BEST answer. T
he purpose of physiologic adjustment is to adjust the framework to
the teeth---to be sure the framework does not bind on the teeth dur
ing functional movements of the RPD. Incorrect. It a true statement
but not the BEST answer. Functional movement of the framework is
an integral
part metal
of physiologic
relief.
Correct.
Since 1,
2, and
3 are
True
If any rigid
(particularly
the
guide plates)
bind
during
fun
4 is this
the metal
BEST answer.
ctional movement correct,
of the RPD,
will pre-empt the mesial r
est and act like a distal rest on an inclined plane. The I-bar will then
engage the abutment during functional movement of the RPD--rath
er than release as it should.
True The bracing arm must be rigid and therefore cannot extend be
low the height of contour. It could not ex to get into and out of th
e undercut.
4 Incorrect. Because the abutments tilt mesially, the distal guide pla
tes will pre-empt the mesial rests and act like distal rests on incline
d planes. Physiologic relief would create a space between the guide
plates and the abutments. Thus, it is best to switch to disal rests. O
nce that decision is made, one must also change the type of retenti
ve arms. Incorrect. With very few exceptions, WW I-bars should be
avoided. It is dicult to position them properly, especially in relatio
n to the soft tissues. They are also prone to accidental bending. Th
e Incorrect.
other problem
here
is that,
abutments
tiltedIncorr
mesi
4
Lingual
I-bars
canbecause
ONLY bethe
used
on lower are
molars.
ally, Athe
guide
plates
willinfrabulge
pre-empt clasp
the mesial
rests. Thus,
distal
ect.
Roach
clasp
is an
that generally
utilizes
a res
fac
ts
be selected.
Incorrect.
Same T-bar.
reasoning
#3.
Be
ialshould
undercut---like
an I-bar
or modied
This as
type
ofCorrect.
clasp cann
cause
the abutments
tilt mesially,
plates would preot be used
here because
there arethe
no distal
facial guide
undercuts---infrabulge
empt
mesial
act lingual
like distal
rests on
inclined planes.
Ph
claspsthe
cannot
berests
used and
on the
surfaces
of premolars.
Incorre
ysiologic
relief would
create
a space between
guide plates circu
and t
ct. An "Akers"
clasp is
a circumferential
clasp.the
A conventional
he abutments.
it is
tobecause
use distal
rests.
Once
that decisio
mferential
claspThus,
cannot
bebest
used
there
are
no facial
underc
n
is made,
one
must
theistype
of retentive
arms
to WW
uts.
Correct.
The
halfalso
and change
half clasp
appropriate
for the
circumst
circumferential
Fortunately,
when teeth
are tilted
ances
describedclasps.
in the stem
of the question.
Because
thismesially,
type of clt
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
The external nish line on a maxillary Class I RPD originates from t
he lingual of the guide plate of the terminal abutment and ends at
the hamular notch. in the glenoid fossa. opposite the buccal pouch.
opposite Stenson's duct.
1 The nish line ends at the hamular notch. The other answers mak
e no sense.
The open latticework on a maxillary class I RPD covers the hamular
notch. covers the tuberosity. does not cover the tuberosity. does no
t require substantial interach space.
3 Incorrect. It does not extend back to the hamular notch. Incorrect
. Interarch space limitations usually preclude extension over the tub
erosity. Correct. Interarch space limitations usually preclude extensi
on over the tuberosity. Incorrect. Open latticework does require sub
stantial interarch space. That's the reason it does not usually exten
d backward to cover the tuberosity.
The partial denture design should be nalized prior to any emergen
cy treatment. any xed prosthodontic treatment. preparation of res
t seats. both 2 and 3 above.
Your patient has the partially eden
tulous arch shown to the right. The
root of #29 has been saved as an
overdenture abutment. True or Fal
se The presence of the overdentur
e abutment may change the axis o
f rotation but will not change the c
lasping considerations on tooth #2
8. True False
4 Incorrect. Emergency treatment can be done prior to the develop
ment of the RPD design. This is often simply a matter of getting the
patient out of pain. Even under these circumstances, it is best if on
e has a general idea of the ultimate design---so that potentially use
ful teeth are not extracted. Incorrect. A true statement but not the
BEST answer. Incorrect. A true statement but not the BEST answer.
Correct. Answers 2 and 3 are correct so 4 is the BEST answer. Only
emergency treatment should be done prior to development of the
RPD design.
False The overdenture abutment may change the axis of rotation a
nd in doing so would unquestionably aect the clasping of tooth #2
8. Therefore, the answer is false.
When placing the tripod marks on the diagnostic cast, the vertical a
rm of the surveyor should have the analyzing rod in place. should
be moved up or down to touch the tissues at widely separated area
s. Both 1 and 2 are true Neither 1 nor 2 are true
4 Incorrect. The lead should be in the vertical arm. Incorrect. The v
ertical arm must be locked in position so that the three marks will d
etermine a plane that can be used to reorient the cast. Incorrect. #
3 is incorrect since #1 and #2 are incorrect. Correct. Neither #1 no
r #2 are correct.
The internal and external nish lines are normally superimposed ov
er each other. normally oset from each other to avoid weakness i
n the framework. normally designed and placed independently. non
e of the above statements are true.
2 The nish lines must be oset. If they are superimposed over eac
h other, substantial weakness in the framework is created and fract
ure in this area would be very likely.
In general, lingual plating should be supported by the inclined surfa
ces of the mandibular incisors. with minor connectors. with bracing
arms. with rests.
4 Linguoplating should be supported by rests placed in rest seats (a
t least on the canines). Of course, the rests are under the plating a
nd would not be visible when the RPD is in place. Without the rest s
eats and rests, the plating would lie totally on inclined planes and c
ould, over time, move the teeth toward the facial.
A maxillary arch without three con
tiguous incisors (such as the one s
hown) usually requires plating of t
he remaining incisor should not be
plated should have a horse-shoe
major connector both 1 and 3 abo
ve.
1 Correct. As a general rule, if there are not three contiguous incis
ors present, the remaining incisor should be plated. Incorrect. See
#1 above. Incorrect. A horse-shoe major connector is related to the
presence of a torus or to gagging. It has nothing to do with the pres
ence or absence of three contiguous incisors. Incorrect. Although #
1 is correct, #3 is incorrect. Thus, #4 is incorrect.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
The external nish line on the dist
al extension side of the mandibula
r Class II modication 1 RPD for th
e partially edentulous arch shown
to the right runs from the lingual fr
enum to the retromolar pad. runs
from the lingual of the guide plate
to the oor of the mouth. runs fro
m the mesial of the guide plate to
the retromolar pad. cannot be det
ermined
without
more
Wrought wire retentive arms are usually
selected
for information.
distal extensi
on RPDs when the tips of the arms lie behind the axis of rotation. Tr
ue False
Occlusal rest preparations should be spoon shaped at least 1/3 the
buccolingual width of the occlusal surface at least one millimeter d
eep all of the above
Guide plates for anterior teeth should be kept to the labial for best
esthetics. should be kept to the lingual for best esthetics. be thinne
d on the labial aspect. both 2 and 3 above.
An anterior-posterior palatal strap major connector is less rigid than
a horse-shoe major connnector because it (the A-P strap) has less
width. The rst statement is true but the reason is false. The rst s
tatement is false and the reason is also a false statement. The rst
statement is true and the reason is true. The rst statement is fals
e but the reason is a true statement.
Your patient has the partially eden
tulous arch form shown. All of the
abutments have good bone suppor
t. On which one of the abutments
would you likely utilize a WW clasp
? #22 #29 #32 None of the above
.
2 Incorrect. It simply makes no sense. Correct. The statement accu
rately describes the location of the external nish line. Incorrect. Th
e nish line is located at the distal of the terminal abutment. It does
not run posteriorly from that point. Incorrect. The external nish lin
e is fairly standard in this situation and depends very little on any di
agnostic information.
False WW clasps are usually selected for distal extension RPDs whe
n the retentive tips lie in front of the axis of rotation.
4 Incorrect. A true statement but not the BEST answer. Rest seat p
reparations should be rounded and "spoon-shaped". This is particul
arly important in extension RPDs where the prosthesis needs to be
able to rotate around the rests during functional movement. Incorre
ct. A true statement but not the BEST answer. The width of the occl
usal rest seat is at least 1/3 the total width of the occlusal surface
but more often approaches 1/2 of the distance between the buccal
and lingual cusp tips. Incorrect. A true statement but not the BEST
answer.
RestThe
seat
preparations
be atand
least
1 mm on
deep.
Corre
4
Incorrect.
metal
should bemust
cut back
thinned
the labial,
ct. Sincein1,the
2, labial
and 3 direction.
are all true,
#4 is the
BEST
answer.is true
not extended
Incorrect.
The
statement
but #2 is not the BEST answer. The guide plate should be positione
d as much as possible to the lingual to limit the visible metal on the
nished prosthesis. Incorrect. The statement is true but #3 is not th
e BEST answer. The labial aspect of the guide plate should be thinn
ed so that the articial tooth or teeth can be shaped and positioned
to avoid exposure of metal. Correct. Both 2 and 3 are true stateme
nts so 4 is the BEST answer.
4 The anterior-posterior strap is more rigid than the horse-shoe con
nector unless the horse-shoe is made very bulky. The anterior-poste
rior strap has good rigidity in spite of the fact that it is very thin, d
ue to the closed circle design and the fact that the metal lies in ma
ny dierent planes.
4 WW clasps would not be used on any of the abutments unless the
prognosis for the molars was poor and there was a plan to re-adapt
the RPD when the molars were lost. That is not the situation describ
ed in the stem of the question.
Which of the following clasp assemblies utilize a primary rest and a
n auxiliary rest? RPA clasp Ring clasp Infrabulge clasp Extended ar
m clasp
2 A ring clasp has both a mesial primary rest and a distal auxiliary
rest. It is used almost exclusively on mandibular mesiolingually tilte
d molar abutments.
In a circumferential clasp assembly, only one of the arms may exte
nd into an undercut. True False
True One arm, the retentive arm, extends into an undercut. The oth
er arm, the bracing or reciprocating arm, must be rigid and therefo
re, cannot extend into an undercut.
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Which of the following steps is done LAST? Rest preparation Frame
work try-in Centric relation records Altered cast impression
Incisal rests are generally more positive vertical stops than cingulu
m rests. may interfere with the opposing occlusion. should not be u
sed on maxillary incisors. all of the above.
Cast retentive arms are usually selected when the RPD is tooth sup
ported or when the retentive tips release during functional moveme
nts of extension RPDs. True False
3 Incorrect. Of the steps listed, rest preparation is the rst accompl
ished. Incorrect. Framework try-in must be completed before both t
he altered cast impression and records. Correct. Centric relation re
cords are generally done after the framework has been tried in and
the altered cast impression made and poured. Record bases are th
en added and the CR record is made using these bases. Incorrect. T
he altered cast impression is made before centric relation records a
re made.
4 Incorrect. The statement is true but not the BEST answer. Incisal r
ests on lower anteriors are generally used when the lingual slope of
the teeth is so steep that adquate rest seats cannot be prepared. If
the rest seats and rests "hook" over the incisal edges of the teeth,
the rests will provide very positive vertical stops. Incorrect. The sta
tement is true but not the BEST answer. Incisal rests certainly may
interfere with the opposing occlusion. For this reason, the incisal res
t seat must be deep enough that most or all of the rest will sit with
in the connes of the rest seat. Incorrect. The statement is true but
not the BEST answer. Incisal rests should not be used on maxillary i
ncisors because of esthetic considerations and because the minor c
True The statement
accurately
describes
when
arms
onnector
between the
major connector
and
the cast
rest retentive
often interferes
are
usually
selected.
with the occlusion. Correct. #4 is the BEST answer because 1, 2, an
d 3 are all true statements.
Cleaning a removable partial denture in sodium hypochlorite may r
esult in increased caries activity increased periodontal problems co
rrosion of the metal of the framework 1 and 2 above
3 Since sodium hypochlorite may cause corrosion of the metal of th
e RPD framework, it is not recommended for cleaning solutions for
partial prostheses.
Which of the following clasp assemblies utilizes a lingual undercut a
nd can be used on premolars for either extension or tooth-supporte
d RPDs? half and half clasp lingual I-bar lingual modied T-bar ring
clasp
1 Correct. Although certainly not a "rst choice" retainer, half and
half clasps are used to engage lingual undercuts and can be used o
n both extension and tooth-supported RPDs. Incorrect. Lingual I-bars
are only used on lower molars. Incorrect. Lingual modied T-bars ar
e seldom if ever used on any tooth. Incorrect. A ring clasp utilizes a
lingual undercut but is only used on molars.
If a metal base is to be used an altered cast impression should be
made after framework try-in a stock tray should be used for the n
al impression a custom tray should be used for the nal impression
interocclusal records must be made after tooth selection
When surveying to determine the height of contour of the abutmen
ts, the mark on the tooth must be made by the side of the lead ma
rker. True False
Clasps help stabilize the RPD by controlling occlusal movement. hel
p stabilize the RPD by controlling gingival movement. may also func
tion as indirect retainers. prevent excessive biting forces on the ab
utments.
3 Incorrect. An altered cast cannot be done because the metal base
must be incorporated into the framework. Incorrect. A stock tray sh
ould not be used for the nal impression as it is important to get a
n accurate, undistorted impression of the residual ridges and surro
unding soft tissues. Correct. A custom tray should be used as it is i
mportant to get an accurate, undistorted impression of the residual
ridges and surrounding soft tissues. The metal base will be incorpor
ated into the framework. Incorrect. Interocclusal records would be
made before tooth selection. The records could be made either bef
ore or after framework fabrication (usually after but if the interoccl
True
survey
line must
made
byteeth
the side
lead marker.
usal The
distance
is very
smallbe
and
metal
are of
to the
be incorporated
Otherwise
there
could
and
probably
would
be
marks
on
the
tooth th
with the base, records would have to be made before the
framewor
at do not represent the height
of contour. These would be very dec
k is fabricated).
eiving when formulating a design.
1 Correct. The primary purpose of clasps is to resist movement of
the RPD occlusally or away from the tissues and teeth---to resist dis
lodging forces. Incorrect. Gingival movement is prevented or contro
lled primarily by rests. Gingival movement may also be prevented
to a very minor degree by the rigid portions of clasps but remembe
r, these elements lie on inclined planes and cannot be the primary
elements resisting gingival movement of the prosthesis. #2 is den
itely not the BEST answer. Incorrect. Clasps do not function as indir
ect retainers. Rests and sometimes plating (supported by rests) ser
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Your patient exhibits the partially e
dentulous arch shown to the right.
Tooth #29 is tilted mesially. The un
dercut is on the mesiofacial surfac
e. What would be the best clasp a
ssembly for this situation? Distal re
st and cast circumferential clasp.
Distal rest and WW circumferential
clasp. Mesial rest and I-bar. Distal
rest and I-bar.
During biting, a maxillary Class I RPD will rotate around a line deter
mined by the rigid metal above the survey line and closest to the e
xtension areas. This line is called Camper's line Frankfurt line Dual
path line Axis of rotation
The WORST clasp assembly for a t
erminal abutment on a mandibular
class I RPD (such as #29 in the par
tially edentulous arch to the right) i
s Mesial rest and I-bar Distal rest a
nd cast circumferential clasp Mesia
l and distal rest and a 1/2 and 1/2
clasp Mesial rest and modied T-b
ar
The guide surface preparation should be curved mesio-distally bucc
o-lingually occluso-gingivally none of the above
2 Incorrect. The tip of the clasp would lie in front of the axis of rota
tion and the cast clasp has minimal exibility. Correct. You must us
e a distal rest because of the angulation of the tooth. Otherwise the
guide plate will pre-empt the planned mesial rest and will act like a
rest on an inclined plane. Attempts to physiologically relieve the gui
de plate would result in a space between the guide plate and the di
stal proximal surface of the tooth creating an unacceptable food tra
p. Once you have decided to use a distal rest, you must use a clasp
maximum
exibility
Incorrect.
Because
of design.
the tilt of
the
4with
Incorrect.
Camper's
line(WW).
has nothing
to do
with RPD
Incorr
tooth,
the distal
guidething
plateas
will
pre-emptline.
the mesial
restThere
and will
ac
ect.
There
is no such
Frankfort's
Incorrect.
is no
t
like
a
rest
on
an
inclined
plane.
The
I-bar
would
now
be
a
cast
cla
such term as "dual path line." Correct. If extension RPDs are proper
spdesigned,
in front ofthis
the line
axisshould
of rotation.
Incorrect.
The
I-bar
would
be aToca
ly
pass through
the
most
distal
rests.
b
st clasp
frontbe
ofcareful
the axis
of rotation.
e sure this is true,
oneinmust
that
there is no other rigid
metal above the survey line that is closer to the edentulous segme
nts.
2 Incorrect. A mesial rest and an I-bar is the BEST choice. Correct.
A distal rest and cast circumferential clasp has the greatest potenti
al for torquing the abutment during functional movement of the ext
ension base. Incorrect. Although the half and half clasp is not our
rst choice retainer, it is acceptable when lack of a facial undercut n
ecessitates the use of a lingual undercut. Incorrect. A mesial rest a
nd modied T-bar is an acceptable clasp assembly when the underc
ut is on the distofacial surface and when there is no contraindicatio
n to surfaces
the use of
a bar
(infrabulge)
clasp.
2 Incorrect. Guide
(and
guide
plates) are
seldom placed on
the buccal or lingual surfaces---the only ones that could curve mesi
odistally. Correct. Guide surfaces and guide plates should follow the
natural buccolingual curvature of the tooth. Incorrect. Guide surface
preparations and guide plates should be vertically parallel to the es
tablished path of insertion/dislodgement---not curved occluso-gingiv
ally. Incorrect.
Fill in the blank What are the indications for a linguoplate as a majo
r connector for a mandibular RPD?
The correct answer is High oor of the mouth (<7 mm of vertical h
eight) High lingual frenum Presence of lingual tori One or more mis
sing incisors Periodontially involved incisors with possible loss in the
future Lingually tilted mandibular anterior teeth
Fill in the blank. Name four types of suprabulge clasps.
The correct answer is Circumferential Embrasure Ring Hairpin
Fill in the blank. Your patient has te
eth numbers 20 through 29 remain
ing. The illustration to the right sh
ows the design for a modied T-ba
r retainer on tooth #29. The vertic
al line on the tooth represents the
greatest mesiodistal curvature of t
he facial surface. Do you see any
problems with the design?
Fill in the blank In the illustration s
hown to the right, what would be y
our rst choice for a retainer (clas
p) on tooth #6?
The correct answer is The approach arm of the modied T-bar mus
t be placed just to the mesial of the greatest mesio-distal curvature
of the facial surface. Otherwise there is the possibility that the entir
e RPD could be displaced upward and backward without the retentiv
e arm exing. In this case, the RPD would exhibit no retention.
The correct answer is Wrought wire circumferential clasp
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Fill in the blank Your patient has th
e partially edentulous arch shown
to the right. The molars have drift
ed mesially and lingually so that th
e only usable undercuts are on the
mesiolingual. What clasps would y
ou use on the molars if (1) there w
ere no large tissue undercuts and (
2) there were large tissue undercu
ts?
The answer is Part 1: mesiolingual I-bars Part 2: ring clasps with rig
id facial portions and auxiliary distal rests
Fill in the blank Which classes of mandibular RPDs require an altere
d cast impression?
The correct answer is Classes I and II
Fill in the blank Important factors in determining the path of insertio
n/dislodgement are:
The correct answer is 1. potential guide surfaces 2. undercuts for di
rect retention 3. hard and soft tissue interferences 4. esthetic consi
derations
Fill in the blank Incisal rests should generally not be used on maxill
ary incisors. Why?
The correct answer is Poor esthetics and interferences with the opp
osing occlusion.
Fill in the blank For tooth-supported RPDs, where are the primary re
sts normally placed?
The correct answer is In tooth-supported RPDs, primary rests are u
sually located on the tooth next to the edentulous space and on the
portion of the occlusal surface immediately adjacent to the edentul
ous space---thus avoiding additional minor connectors and gingival
coverage.
Fill in the blank For extension RPDs, where are the primary rests us
ually placed?
The correct answer is On the tooth next to the edentulous space bu
t on the portion of the occlusal surface away from the edentulous s
pace.
Fill in the blank What is/are the ind
ications for the use of a maxillary
palatal plate major connector whic
h is composed partly of metal and
partly of plastic? See example to t
he right.
The correct answer is Plastic in the posterior aspect of the major co
nnector allows for post-insertion revision of the posterior palatal se
al and for relining or rebasing over residual ridges that are still in t
he process of recontouring (healing).
Fill in the blank What are the indic
ations for the use of a maxillary h
orseshoe major connector?
The correct answer is A horse-shoe or U-shaped maxillary major co
nnector is indicated when a large, inoperable torus extends posterio
rly within 8 mm or less of the junction of the hard and soft palates
or when the patient cannot tolerate contact of the prosthesis with t
he posterior portion of the palate---a gagger!
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Fill in the blank The total retention for a RPD is obtained from
The correct answer is 1. denture style retention (adhesion, cohesio
n, interfacial surface tension) 2. frictional retention from guide surfa
ce/guide plate contacts 3. mechanical retention from clasps (direct r
etention)
Fill in the blank What are the components of a clasp assembly?
The correct answer is 1. one or two rests 2. a retentive arm 3. a br
acing or reciprocating element 4. one or more minor connectors
Fill in the blank An ideal clasp assembly should possess the followin
g qualities:
The correct answer is 1. support 2. bracing 3. reciprocation 4. 180
degree encirclement
SUPPORT for a RPD framework is provided by?
Fill in the blank Explain the dierence between bracing and reciproc
ation.
The correct answer is Support is provided almost entirely by rests.
Some support is furnished by other rigid metal located above the s
urvey line (e.g. the rigid portions of retentive arms and bracing and
reciprocating arms). However, these components usually lie on incli
ned surfaces and should never be expected to provide primary vert
ical support. In the maxillary arch, some support may also be provi
ded by the major connector if it covers a signicant portion of the
hard palate. When considering the RPD as a whole, the denture bas
es
provide
support,
much
more so inare
extension
RPDs than
toot
Thealso
answer
is Bracing
and
reciprocation
both provided
by rigid
RPDs. connectors. Under certai
portions of clasps, guide h-supported
plates, and minor
n circumstances, linguoplating may also provide bracing and recipr
ocation. Bracing occurs when the RPD is fully seated. Bracing eleme
nts distribute horizontal forces across the arch. Reciprocation is dyn
amic and requires timing. The rigid elements must contact the abut
ment teeth as the retentive arms pass over the height of contour d
uring insertion and removal of the prosthesis.
Fill in the blank Factors important in the selection of a particular cla
sp design include?
The correct answer is 1. tooth contour (location of undercut) 2. tiss
ue contour 3. exibility of the clasp arm 4. tooth coverage 5. esthet
ic requirements 6. the capacity for adjustment, maintenance, and r
eplacement 7. the ability to provide stabilization (bracing)
Fill in the blank What are indirect retainers and how do they functio
n?
The correct answer is Indirect retainers are rests that are located a
nterior to the retentive arms on distal extension RPDs. They functio
n when dislodging forces attempt to move the denture base away fr
om the basal seat tissues. By preventing downward movement of t
he anterior portion of the RPD, the indirect retainers force the direc
t retainers (clasps) to activate when movement away from the basa
l seat is attempted.
Fill in the blank ______________________________ are mechanical reta
iners that originate from a point at or above the height of contour--usually from a rest, minor connector, or guide plate---and angle do
wnward across the clinical crown where the tip is located in the pre
scribed undercut.
The correct answer is Suprabulge retainers
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
For a circumferential clasp, the undercut must be located on the sa
me side of the abutment as the point of origin. on the opposite sid
e of the point of origin.
2 on the opposite side
Fill in the blank What is a combination clasp?
The correct answer is A combination clasp is a circumferential clasp
assembly composed of a rest, a exible wrought wire retentive ar
m, and a rigid cast reciprocating/bracing arm.
Fill in the blank When is a combination clasp most commonly used?
The correct answer is The combination clasp is most commonly use
d for extension RPDs when 1. a tissue undercut below the terminal
abutment precludes the use of a bar clasp 2. the mesial tilt of the t
erminal abutment would cause the guide plate to pre-empt the mes
ial rest in an I-bar clasp assembly 3. a retainer is placed on a tooth
that lies bodily in front of the axis of rotation
Fill in the blank What is the "RPA" clasp concept and what is the pro
blem with the design?
The correct answer is The RPA concept has occasionally been reco
mmended for distal extension RPDs and includes a distal guide plat
e, a mesial rest, and a circumferential retentive arm originating fro
m the guide plate. Problem: If the originating portion of the arm lies
above the height of contour, it will pre-empt the mesial rest and wil
l act like a distal rest on an inclined plane. The retentive tip will now
engage the undercut during functional movement of the extension
base.
Fill in the blank What is the name
of the clasp assembly shown to th
e right?
The correct answer is The picture shows an embrasure clasp assem
bly (which is a type of circumferential or suprabulge clasp).
Fill in the blank What is the most si
gnicant error in the design shown
to the right. (Hint: the error is not
particularly easy to see but it invol
ves the major connector.)
The correct answer is The biggest problem with the design is that t
he major connector ends in the gingival sulcus of the anterior teeth.
If the intent is to plate these teeth, the plating must cover the cingu
li and extend interproximally up to the contact points. If plating is n
ot desired, the border of the major connector must be at least 6 m
m away from the gingival margins.
Fill in the blank The illustration sho
wn to the right was taken from an
advertisement that appeared in on
e of the dental journals. It suggest
s that a bar bridge/splint in combi
nation with a precision or semi-pre
cision removable partial denture is
appropriate treatment for "Geriatri
cFillReconstruction."
do youtothit
in the blank TheWhat
illustration
nkright
about
this type
of treatment?
he
shows
the tissue
surface o
f a maxillary removable partial de
nture. The arrows point to the junc
tion of the framework metal and t
he plastic denture base. What is th
is structure called?
There are many problems with this type of treatment for a large pe
rcentage of geriatrics patients. First of all, many older patients sim
ply do not have the manual dexterity to control the precise insertio
n and removal of this type of prosthesis. Secondly, the splinting of
teeth means the only means of assuring adequate interproximal pla
que control by use of oss threaders under the soldered contacts--also a very dicult task for people with marginal coordination and
dexterity. In general, one could say that plaque control is more di
cult for the geriatric population than for younger patients. Recurren
t decay around crown margins is common among geriatric patients.
Whenever possible, margins should be as accessible as possible---t
hat is not the The
casecorrect
with this
type of
The
rule of "KISS" (
answer
is restoration.
Internal nish
line
keep it simple stupid) may not have the best connotation but is tru
e most of the time and certainly in relation to removable prosthese
s for geriatric patients. Make insertion and removal of the prosthesi
s as easy as possible. Avoid precision attachments and the like. Allo
w for repair of the underlying restorations and design the RPD so th
RPD Online Questions (full set)
Study this set online at: http://www.cram.com/ashcards/rpd-online-questions-full-se
t-1995563
Fill in the blank The illustration to t
he right shows a tooth-supported s
egment of a mandibular removabl
e partial denture framework. The r
ed arrow is pointing to the raised e
dge of metal where the framework
and plastic denture base will meet.
What is this structure called?
The correct answer is External nish line
Fill in the blank The illustration to t
he right shows a maxillary class I
RPD framework with an anterior-po
sterior palatal strap major connect
or. What is the minimum acceptabl
e distance between the anterior an
d posterior straps (red arrow)?
The correct answer is 15 mm.
Fill in the blank What Kennedy clas
sication is the RPD shown in the p
icture to the right? What is the na
me of this type of major connector
?
The correct answer is Class II, modication 0 Modied palatal plate
Fill in the blank What is the Kenned
y classication of the maxillary RP
D shown to the right?
The correct answer is Class III, modication 0
Fill in the blank What is the Kenned
y classication of the maxillary RP
D shown to the right?
The correct answer is Class III, modication 1. If tooth #14 had not
been missing, it would have been a Class IV. However, no modicat
ion spaces are possible in a class IV RPD---any other edentulous are
a takes precedence in nomenclature.
Fill in the blank The red arrows poi
nt to a "ridge" of metal on the fra
mework where the framework and
the denture base plastic will meet.
What is this "ridge" called?
The correct answer is External nish line
Fill in the blank The illustration to t
he right shows a tooth-borne segm
ent of a mandibular RPD. There is
an I-bar retainer on the molar abut
ment. What is unusual about this r
etainer?
The correct answer is Generally, lingual I-bars on lower molars sho
uld be placed at the mesiolingual corner of the abutment. This help
s prevent the approach portion of the arm from standing out in the
oor of the mouth and irritating the tongue. Will this arm work? Pro
bably. There is very little tooth or tissue undercut so the arm may n
ot stand out in the oor of the mouth even though it is positioned f
urther posteriorly than would usually be desired.
Fill in the blank The illustrations ab
ove show a very large maxillary R
PD and a close-up of one of the re
tentive arms. What type of retenti
ve arms have been used on this pr
osthesis?
The correct answer is Oddo hinge clasp
You might also like
- RPD QuestionsDocument77 pagesRPD QuestionsDontoNo ratings yet
- RPD Review QuestionsDocument85 pagesRPD Review Questionsdeenm67% (3)
- Question 1Document62 pagesQuestion 1Saleh Al-naimiNo ratings yet
- RPD Test With KeyDocument14 pagesRPD Test With KeySaleh Al-naimiNo ratings yet
- Which Impression Technique Attempts To Simulate Tissue Conditions in A Preloaded, Pressurized State andDocument20 pagesWhich Impression Technique Attempts To Simulate Tissue Conditions in A Preloaded, Pressurized State andNaresh TeresNo ratings yet
- RPD Review Questions 1-10Document4 pagesRPD Review Questions 1-10SkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Deep and Cross Bite: Special EditionDocument28 pagesDeep and Cross Bite: Special EditionRoniAnasokaNo ratings yet
- Epi IDocument4 pagesEpi IAna-Maria MachidonNo ratings yet
- 13 - Class II, III and IV Students Partial Denture DesignDocument34 pages13 - Class II, III and IV Students Partial Denture DesignMona GalalNo ratings yet
- RPD BasicsDocument63 pagesRPD BasicsMahmud J. BarznjiNo ratings yet
- Kennedy I Design Tutorial-RevisedDocument34 pagesKennedy I Design Tutorial-RevisedAmanda Amaro100% (1)
- Direct RetainersDocument14 pagesDirect RetainersNidhiNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Pre-Adjusted Orthodontic Appliance Prescription For Anterior TeethDocument6 pagesChoosing A Pre-Adjusted Orthodontic Appliance Prescription For Anterior TeethYorisbeth SanNo ratings yet
- Trust The ProcesssDocument3 pagesTrust The ProcesssDana KostNo ratings yet
- 0002 9416 (58) 90024 1Document12 pages0002 9416 (58) 90024 1Durga VoraNo ratings yet
- Elias On 1983Document3 pagesElias On 1983JesusCordoba100% (2)
- MCQ in RPDDocument10 pagesMCQ in RPDIbrahim Ramadan Eltorky91% (11)
- Fractures of Distal End of RadiusDocument25 pagesFractures of Distal End of RadiusVenkee SaiNo ratings yet
- DR Balendra Pratap Singh BDS, MDS, Mams, Fisdr, Fpfa, Faamp, Icmr-If Assistant Professor Deptt. of ProsthodonticsDocument26 pagesDR Balendra Pratap Singh BDS, MDS, Mams, Fisdr, Fpfa, Faamp, Icmr-If Assistant Professor Deptt. of ProsthodonticsElavarasi GanesanNo ratings yet
- Designing RPD 321Document50 pagesDesigning RPD 321R MNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Design Sequence For RpdsDocument34 pagesLecture 7: Design Sequence For RpdsAmanda AmaroNo ratings yet
- Paper Molar Distalization SambalpurDocument21 pagesPaper Molar Distalization SambalpurAsmita RayNo ratings yet
- Expert Partial TechniciansDocument9 pagesExpert Partial Technicianssymac9999No ratings yet
- ملخصDocument11 pagesملخصhgfdsNo ratings yet
- Articulators and Related InstrumentsDocument4 pagesArticulators and Related InstrumentsUmut ASLANNo ratings yet
- Mclaughlin2003 PDFDocument19 pagesMclaughlin2003 PDFSreeramnayak MalavathuNo ratings yet
- C-Orthodontic Microimplant For Distalization of Mandibular Dentition in Class III CorrectionDocument9 pagesC-Orthodontic Microimplant For Distalization of Mandibular Dentition in Class III CorrectionNeeraj AroraNo ratings yet
- Indirect RetainersDocument4 pagesIndirect RetainerstakkykumasangNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Pre-Adjusted Orthodontic Appliance Prescription For Anterior TeethDocument7 pagesChoosing A Pre-Adjusted Orthodontic Appliance Prescription For Anterior TeethAadhirai GopinathNo ratings yet
- RPD ReviewDocument24 pagesRPD ReviewAnoush ZamaniNo ratings yet
- Mccracken'S Removable Partial Prosthodontics. Chapter 10 & 19Document50 pagesMccracken'S Removable Partial Prosthodontics. Chapter 10 & 19Al CarLozNo ratings yet
- 6.rpa Clasp DesignDocument3 pages6.rpa Clasp DesignbarbieNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Removable Partial Denture - Design and RetentionDocument72 pagesIntroduction of Removable Partial Denture - Design and RetentionDilesh Pradhan0% (1)
- Torque in OrthodonticsDocument157 pagesTorque in OrthodonticsVasundhra Mittal93% (15)
- Prepearing Teeth For RPDDocument14 pagesPrepearing Teeth For RPDShreyans DamadeNo ratings yet
- Using Intraoral Gothic Arch Tracing To Balance Full Dentures and Determine Centric Relation and Occlusal Vertical DimensionDocument15 pagesUsing Intraoral Gothic Arch Tracing To Balance Full Dentures and Determine Centric Relation and Occlusal Vertical DimensionAlfred OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Removablepartial Dentures Direct Retainers: DR - Mohammad Al Sayed 19L4/2008Document26 pagesRemovablepartial Dentures Direct Retainers: DR - Mohammad Al Sayed 19L4/2008ZaraNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j FSC 2020 09 002Document7 pages10 1016@j FSC 2020 09 002Ali LabafchiNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 3rd Class PDFDocument4 pagesLec 8 3rd Class PDFBrandon AviciiNo ratings yet
- Stage I and Stage Ii-Begg'S ApplianceDocument50 pagesStage I and Stage Ii-Begg'S ApplianceNaziya ShaikNo ratings yet
- FinishingDocument76 pagesFinishingsahar emadNo ratings yet
- RPD Design ConsiderationsDocument38 pagesRPD Design ConsiderationsSharad VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Final Review From WNTRDocument4 pagesFixed Final Review From WNTRmirfanulhaqNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Cavity PreparationDocument166 pagesEndodontic Cavity Preparationagusaranp0% (1)
- Cavity Preparation in Deciduous Teeth: Sum M AryDocument8 pagesCavity Preparation in Deciduous Teeth: Sum M AryNabilla FaralizaNo ratings yet
- FinalizaçãoDocument57 pagesFinalizaçãodentalnetworkNo ratings yet
- Answers - Seminar 7 ExpectationsDocument40 pagesAnswers - Seminar 7 Expectationsdrzana78No ratings yet
- Impression MaterialsDocument7 pagesImpression Materialsكاظم عبد الحسينNo ratings yet
- Intertrochanteric Fractures - Ten Tips To Improve ResultsDocument8 pagesIntertrochanteric Fractures - Ten Tips To Improve ResultsPetrarescu AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Texas: KY Louis S. JIT H - On-, L:.a., D.D.S., HoijstonDocument2 pagesTexas: KY Louis S. JIT H - On-, L:.a., D.D.S., HoijstonBenet BabuNo ratings yet
- Adult Class LLL Treatment Using A J-Hook Headgear To The Mandibular ArchDocument8 pagesAdult Class LLL Treatment Using A J-Hook Headgear To The Mandibular ArchRocioNo ratings yet
- RPIDocument17 pagesRPIishtiii100% (2)
- Removable Partial Dentures: Chapter 9 ProsthodonticsDocument3 pagesRemovable Partial Dentures: Chapter 9 Prosthodonticsمحمد امينNo ratings yet
- Orthodonticsdd2011-2012 DR GhadeerDocument62 pagesOrthodonticsdd2011-2012 DR GhadeerGhadeerHassaan100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyFrom EverandFundamentals of Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Test Ex.1 Read The Text. For Each Question, Choose The Best Answer (A, B, C or D) - (10 Points) Bird ResearcherDocument5 pagesTest Ex.1 Read The Text. For Each Question, Choose The Best Answer (A, B, C or D) - (10 Points) Bird ResearcherAndrei KazmarurkovNo ratings yet
- Jareds BoyDocument31 pagesJareds BoyAnaNo ratings yet
- California Zephyr Dining MenuDocument2 pagesCalifornia Zephyr Dining MenuekaterinaNo ratings yet
- English TestDocument13 pagesEnglish TestDJ MRNo ratings yet
- Arch105 Paper 2Document4 pagesArch105 Paper 2Bambi DragonNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) : Essential Newborn Care From Evidence To PracticeDocument3 pagesCare of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) : Essential Newborn Care From Evidence To PracticeAlec AnonNo ratings yet
- DX Roleplaying HandbookDocument520 pagesDX Roleplaying HandbookJeffrey Lee89% (9)
- Philippine LiteratureDocument93 pagesPhilippine LiteratureEthel Marie Casido Burce100% (4)
- Mandala Effects by Maryanne JohnsonDocument38 pagesMandala Effects by Maryanne JohnsonKaren MersonNo ratings yet
- Leishmania SPPDocument9 pagesLeishmania SPPanalyn123No ratings yet
- Animal DefensesDocument9 pagesAnimal DefensesSalma BazziNo ratings yet
- Meat Dishes: Tools, Utensils, and Equipment For Meat PreparationDocument6 pagesMeat Dishes: Tools, Utensils, and Equipment For Meat PreparationJohn Alloysius ZamaylaNo ratings yet
- Brain Imaging Technologies and Their Applications in NeuroscienceDocument45 pagesBrain Imaging Technologies and Their Applications in NeuroscienceNeea AvrielNo ratings yet
- The Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryDocument20 pagesThe Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryBertran RousseauNo ratings yet
- Case Taking FormatDocument29 pagesCase Taking FormatmadhukarNo ratings yet
- Annotated Reading LogDocument13 pagesAnnotated Reading LoggaureliNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Read MeDocument56 pagesCH 3 Read MeelzianhawkwindNo ratings yet
- Gagy Gygax's - Lejendary Adventure - Essentials Box Set - Moon SlavesDocument13 pagesGagy Gygax's - Lejendary Adventure - Essentials Box Set - Moon Slavesestibandumas100% (1)
- Zitelli Picture Review - GeneticsDocument101 pagesZitelli Picture Review - GeneticsEllagEszNo ratings yet
- Pest Control Services - ISSHIcareDocument11 pagesPest Control Services - ISSHIcarepromos10No ratings yet
- 15 - Minute English Test Unit 2Document2 pages15 - Minute English Test Unit 2Thế Hiền PhạmNo ratings yet
- The Wardrobe, The White Witch Has Magical Powers That Children Fear. She Can TurnDocument3 pagesThe Wardrobe, The White Witch Has Magical Powers That Children Fear. She Can Turnxxbbb ddssNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument41 pagesElectronicsKazelle BustamanteNo ratings yet
- The Amygdala Brain Physiology - Richard UttDocument33 pagesThe Amygdala Brain Physiology - Richard UttHuib Salomons100% (11)
- Ultimate Psionics GM ScreenDocument2 pagesUltimate Psionics GM ScreenEduardo Ferreira SuzartNo ratings yet
- Ars Poetica - Valzhyna MortDocument2 pagesArs Poetica - Valzhyna MortZeynep KocaadamNo ratings yet
- Ustrasana - Camel Pose - Yoga International PDFDocument8 pagesUstrasana - Camel Pose - Yoga International PDFToreØrnNo ratings yet
- 6530-01-533-4863 - Table Surgical ISO - HANDBOOK - INSERT - STARTUPDocument17 pages6530-01-533-4863 - Table Surgical ISO - HANDBOOK - INSERT - STARTUPViniciusNo ratings yet
- Advanced Sentence Correction For GMAT SCDocument27 pagesAdvanced Sentence Correction For GMAT SCharshv3No ratings yet
- Ajara-Rasayana KSRPrasadDocument56 pagesAjara-Rasayana KSRPrasadksr prasad100% (1)