Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DSK Audio4 Reva 1
Uploaded by
Blâçk ÂrmÿOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DSK Audio4 Reva 1
Uploaded by
Blâçk ÂrmÿCopyright:
Available Formats
DSK_AUDIO4
Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
for the
Texas Instruments TMS320C6X11/6713/6416T/5510
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Starter Kits
(Board Revision A)
Educational DSP, LLC
www.educationaldsp.com
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
2
3
4
5
Hardware ...........................................................................................................2
1.1
General Precautions .....................................................................................2
1.2
Installation ..................................................................................................2
1.3
Audio Connections .......................................................................................3
1.4
Clock Operation ...........................................................................................3
Programming the Codecs ....................................................................................4
2.1
Hardware Requirements ...............................................................................4
2.2
Application Programming Interface (API) ......................................................5
Advanced Codec Configuration .......................................................................... 10
3.1
Cautions.................................................................................................... 10
3.2
Application Programming Interface (API) .................................................... 10
Schematic Diagram .......................................................................................... 11
Board Layout ................................................................................................... 14
Page 1
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
1 Hardware
The DSK_AUDIO4 is a four-channel audio input/output daughtercard designed to
operate on the Texas Instruments TMS320C6211, TMS320C6711, TMS320C6713,
TMS320C6416T, and TMS320C5510 DSP Starter Kits (DSK). It has two stereo line
outputs, and 4 input channels that be selected from line level or microphone sources.
The daughtercard is designed so that on power-up it is compatible with software
written for the previous DUAL3006 audio daughtercard. In this mode it operates at a
48kHz sample rate using stereo line-level inputs and outputs with 0db gain. The
daughtercard can then be programmed by the DSP application to set amplifier gains,
select the input source, and control various codec capabilities. The programming
interface uses the CNTL0/1 and STAT0/1 on the DSKs Peripheral Interface connector.
Four-channel operation is not possible on TMS320C6211 DSKs. When
using the daughtercard on TMS320C6211/6711 DSKs, jumper JP1 must
be installed on the DSK in order to make the McBSPs available on the
Peripheral Interface connector.
1.1 General P recautions
Proper electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions should be observed at all times when
handling the DSK_AUDIO4 daughtercard. Failure to do so may result in damage to the
circuitry on the daughtercard or the DSK. Do not install or remove the daughtercard
while power is supplied to the DSK.
1.2 I nstallation
Installation should only be accomplished in an ESD-safe area. Disconnect all power to
the DSK. Install the DSK_AUDIO4 daughtercard on the DSKs Peripheral Interface
connector (J3 on the 6211/6711/6713/6416T DSKs). Pay careful attention to the pin 1
keying on the connectors. Fasten the daughtercard to the DSK using the supplied
12mm stand-off and hardware.
Even with the 12mm stand-off installed, the numerous audio cables
attached to the daughtercard can place stresses on the
daughtercard/DSK connection, possibly damaging the daughtercard
and/or DSK. It is recommended that the daughtercard be securely
attached to the DSK using an enclosure panel (available from
Educational DSP) or similar arrangement to prevent stress on the
daughtercard to DSK connection.
Page 2
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
1.3 Audio Connections
The audio connectors on the DSK_AUDIO4 daughtercard are design to accept standard
3.5mm (1/8) stereo mini-plugs. When inserting plugs into the audio connectors, it is
advisable to use your finger to maintain pressure on the rear of the connector housing
to prevent stressing the connectors. Each codec has a stereo line output jack, a stereo
line input jack, and two microphone input jacks. The microphone inputs are biased to
be compatible with most electret microphones, and can also be used as line-level inputs
as desired. The PCM3794 codec used on the DSK_AUDIO4 daughtercard has a
maximum input range of 1VRMS (+/-1.41V).
The audio connector locations as seen from the top of the daughtercard are as shown
below.
1.4 Clock Operation
Both PCM3794 codecs operate as slave devices, with the DSP serial port McBSP1
providing all required serial communications signals to both codecs and McBSP0. The
DSP serial port McBSP1 does this by using its Sample Rate Generator (SRG) hardware
with a master clock input from the daughtercard. As shipped, the DSK_AUDIO4
daughtercard is configured to operate using the 12.288MHz onboard oscillator, resulting
in a 48KHz sample rate as the default configuration. To obtain variable sample rates by
changing the master clock frequency, the DSPs TIMER1 output can be used to supply
the master clock to the daughtercard. To use TIMER1, a jumper block (not supplied)
must be installed at J10 as follows;
Cut the trace on the board between J10-2 and J10-3.
Solder a standard 0.050 spacing 3-position header strip at J10.
Install a shunt between J10-1 and J10-2. This will connect the DSKs TIMER1
output as the PCM3794 master clock.
Page 3
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
To return to the 12.288MHz master clock, place the shunt between J10-2 and
J10-3.
The range of sample rates over which the PCM3794 will operate is discussed in the
PCM3794 datasheet available from Texas Instruments. Note that the sample rate can
also be varied by changing the McBSP configuration and/or the PCM3794 configuration.
(See the Advanced Codec Configuration section for more information.)
2 Programming the Codecs
The daughtercard programming interface provides control over a number of codec
functions. Simple C-language function calls provide access to these functions. Source
code and sample projects are available on the Educational DSP website. A simplified
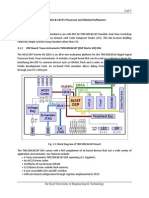
block diagram of the PCM3794 codec signal flow is shown below. The programming
interface permits control of the functions that are highlighted in yellow.
2.1 Hardw are Requirem ents
The programming interface uses the CNTL0/1 and STAT0/1 signals on the DSKs
Peripheral Interface connector. In general, you should not write to the DSK CPLD
register (DC_REG) that controls these signals when using the daughtercard. The
daughtercard also uses the daughtercard reset signal. If the daughtercard reset signal
is asserted and released, the daughtercard codecs will be reprogrammed to their
default configuration.
Page 4
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
2.2 Application Program m ing I nterface (AP I )
The functions that make up the codec configuration API are listed below.
void DskAudio4_Init(void);
o This function must be called before any other API function.
Int16 DskAudio4_ResetDaughtercardToDefaults(void);
o Resets the daughtercard to the default power-up configuration.
Int32 DskAudio4_GetDaughtercardInfo(void);
o Returns information on the daughtercard type and version.
Int16 DskAudio4_SelectInputSource(Uint8 codec, Uint8 lsrc, Uint8 rsrc);
o Selects whether to use line or microphone input sources.
Int16 DskAudio4_SetAdcAnalogGain(Uint8 codec, Uint8 channel, float gain);
o Sets the gain of the input amplifiers.
Int16 DskAudio4_SetDacInputAttenuation(Uint8 codec, Uint8 channel, float
gain);
o Sets the gain of the DAC digital attenuator.
Int16 DskAudio4_SetLineOutAnalogGain(unsigned char codec, unsigned char
channel, float gain);
o Sets the gain of the output amplifiers.
Int16 DskAudio4_WriteCodecSetting(Uint8 codec, Uint8 address, Uint8 data);
o Writes arbitrary data to any codec register. Misuse of this function can
cause damage to the daughtercard and/or DSK. See the the Advanced
Codec Configuration section for more information.
Individual API functions are described in detail below. Note that the data types used are
established by the tistdtypes.h include file for portability across platforms.
Page 5
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
DskAudio4_Init
void DskAudio4_Init(void);
Return Value
None.
Parameters
None.
Remarks
Does a hardware reset of the daughtercard and initializes the API variables. Always call
this function before calling any other API function.
DskAudio4_ResetDaughtercardToDefaults
Int16 DskAudio4_ResetDaughtercardToDefaults();
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Parameters
None.
Remarks
Causes the daughtercard to restore both codecs to the power-up default configuration
(DUAL3006-compatible operation).
Page 6
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
DskAudio4_ GetDaughtercardInfo
Int32 DskAudio4_GetDaughtercardInfo();
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Otherwise, returns information about the daughtercard compressed into the 32-bit
integer.
Byte 3 (MSB) - daughtercard type (0x30 for DSK_AUDIO4)
Byte 2
- daughtercard hardware revision (0x10 for PCB rev A)
Byte 1
- daughtercard firmware revision (high byte)
Byte 0 (LSB) - daughtercard firmware revision (low byte)
Parameters
None.
Remarks
Can be used to test for daughtercard compatibility within a DSP application.
DskAudio4_SelectInputSource
Int16 DskAudio4_SelectInputSource(Uint8 codec, Uint8 lsrc, Uint8 rsrc);
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Parameters
codec
Selects the desired codec. Set to 0 for codec 0 or 1 for codec 1.
lsrc
Selects the input source for the codecs left channel. The following symbols are defined;
DSK_AUDIO4_INPUT_LINE
- use line input
DSK_AUDIO4_INPUT_MIC_0DB - use microphone, no preamp
DSK_AUDIO4_INPUT_MIC_20DB - use microphone with 20db preamp
rsrc
Selects the input source for the codecs right channel. See lsrc.
Remarks
Selects the left and right input sources for the specified codec.
Page 7
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
DskAudio4_ SetAdcAnalogGain
Int16 DskAudio4_SetAdcAnalogGain(Uint8 codec, Uint8 channel, float gain);
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Parameters
codec
Selects the desired codec. Set to 0 for codec 0 or 1 for codec 1.
channel
Selects codec channel. Set to 0 for left channel, 1 for right channel.
gain
Sets the analog input PGA gain from +30db to -12db in 1db steps.
Remarks
Sets the gain of the ADC analog input programmable-gain amplifier (PGA) from +30db
to -12db in 1db steps. The gain parameter is truncated to the nearest valid value.
DskAudio4_ SetDacInputAttenuation
Int16 DskAudio4_SetDacInputAttenuation(Uint8 codec, Uint8 channel, float gain);
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Parameters
codec
Selects the desired codec. Set to 0 for codec 0 or 1 for codec 1.
channel
Selects codec channel. Set to 0 for left channel, 1 for right channel.
gain
Sets the DAC digital input attenuation from 0db to -62db in 1db steps.
Remarks
Sets the DAC digital input attenuation from 0db to -62db in 1db steps. The gain
parameter is truncated to the nearest valid value. Setting the gain to less than -62
mutes the DAC input.
Page 8
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
DskAudio4_ SetLineOutAnalogGain
Int16 DskAudio4_SetLineOutAnalogGain(Uint8 codec, Uint8 channel, float gain);
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Parameters
codec
Selects the desired codec. Set to 0 for codec 0 or 1 for codec 1.
channel
Selects codec channel. Set to 0 for left channel, 1 for right channel.
gain
Sets the line output PGA gain from +6db to -70db.
Remarks
Sets the gain of the line output programmable-gain amplifier (PGA) from +6db to
-70db. The gain step size is 0.5db from +6db to -11db, 1.0db from -12db to -24db,
2.0db from -26db to -42db, and 4.0db from -46db to -70db. The gain parameter is
truncated to the nearest valid value.
DskAudio4_ WriteCodecSetting
Int16 DskAudio4_WriteCodecSetting(Uint8 codec, Uint8 address, Uint8 data);
Return Value
Returns -1 on error, indicating a problem communicating with the daughtercard.
Parameters
codec
Selects the desired codec. Set to 0 for codec 0 or 1 for codec 1.
address
The address of the codec register to write to.
data
The data to write to the selected codec register.
Remarks
For advanced users, this function supports the programming of any register in the
PCM3794 codec. It should not be used without a thorough understanding of McBSP
configuration, the PCM3794 codec, and the DSK_AUDIO4 schematic diagram. See the
the Advanced Codec Configuration section for more information.
Page 9
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
3 Advanced Codec Configuration
3.1 Cautions
The DSK_AUDIO4 daughtercard is designed to synchronize the sampling of the two
codecs by operating McBSP1 in master mode and having it supply the CLKX/CLKR and
FSX/FSR signals to both codecs and McBSP0. A 74LVC2G34 dual buffer (U5) is used to
drive the CLKX1/FSX1 signals from McBSP1 onto the CLKX0/FSX0 signals for McBSP0
and the attached PCM3794 codec 0 (U1). To prevent signal contention, do NOT
configure codec U1 or McBSP0 as master devices. If you wish to operate U1 or
McBSP0 as a master, then U5 must be removed from the board in order to isolate the
McBSP CLKX and FSX signals.
3.2 Application Program m ing I nterface (AP I )
The DskAudio4_WriteCodecSetting function can be used to write any value to any codec
register. No checking is performed on the address or data passed to the function. As
discussed in Cautions above, operating codec 0 (U1) as a master will cause contention
and possible damage unless U5 is removed from the board. Also, McBSP1 must be
operated as a slave whenever you operate codec 1 (U2) as a master.
Page 10
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
4 Schematic Diagram
Page 11
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
Page 12
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
Page 13
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
DSK_AUDIO4 Four-Channel Audio Daughtercard
5 Board Layout
Page 14
(Last updated August 17, 2010)
You might also like
- DSP Lab Manual - UpdatedDocument70 pagesDSP Lab Manual - UpdatedSatya kavyaNo ratings yet
- Adx + Programming ManualDocument205 pagesAdx + Programming ManualRajesh Kumar69% (13)
- RS232 CommunicationsDocument37 pagesRS232 CommunicationsNoor Kareem100% (1)
- Samsung NP300E5A PDFDocument55 pagesSamsung NP300E5A PDFLuiz LandtechNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing LabDocument36 pagesDigital Signal Processing Labavinash_yuvarajNo ratings yet
- 6713 User ManualDocument92 pages6713 User Manualsningle100% (1)
- Ccs Manual 1Document53 pagesCcs Manual 1VicathorNo ratings yet
- DSP LabmanualDocument82 pagesDSP LabmanualHemanth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tms320c6713 User ManualDocument60 pagesTms320c6713 User ManualJagannath Vishnuteja Desai100% (1)
- Real-Time DSP Laboratory1:: An Introduction To The TMS320C6713 DSKDocument20 pagesReal-Time DSP Laboratory1:: An Introduction To The TMS320C6713 DSKNeha PankiNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab 3Document11 pagesDSP Lab 3fahadsaeed930% (1)
- Ares Ii Dac: Owner'S ManualDocument17 pagesAres Ii Dac: Owner'S ManualCarlos HCNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab 21-09-2021Document78 pagesDSP Lab 21-09-2021POORNIMA PNo ratings yet
- TMS320C6713 DSKDocument4 pagesTMS320C6713 DSKshifaliNo ratings yet
- DSP Sp3 ManualDocument51 pagesDSP Sp3 Manualapi-26783388No ratings yet
- DSP Lab Manual PDFDocument84 pagesDSP Lab Manual PDFHoàng PhượngNo ratings yet
- D.S.P/MATLAB Theory & ExperimentsDocument57 pagesD.S.P/MATLAB Theory & ExperimentsNandagopal Sivakumar50% (4)
- Brooklyn AdcDocument20 pagesBrooklyn AdcdavidartefactNo ratings yet
- Terminator-Plus Dac: Owner'S ManualDocument19 pagesTerminator-Plus Dac: Owner'S Manualelectricdan2No ratings yet
- DRS4 Manual Rev40Document36 pagesDRS4 Manual Rev40МилицаБајићNo ratings yet
- Motorola: 24-Bit Digital Signal ProcessorDocument110 pagesMotorola: 24-Bit Digital Signal ProcessorNguyễn Văn LượmNo ratings yet
- Real-Time DSP Laboratory1:: An Introduction To The TMS320C6713 DSKDocument25 pagesReal-Time DSP Laboratory1:: An Introduction To The TMS320C6713 DSKNagaraju NeelaNo ratings yet
- DSP LabDocument56 pagesDSP LabKamal HasanNo ratings yet
- Interfacing The ADS7881 To The TMS320C6713 DSP: Application ReportDocument14 pagesInterfacing The ADS7881 To The TMS320C6713 DSP: Application ReportSashikanth BethaNo ratings yet
- DSP CasestudyDocument23 pagesDSP CasestudyShayani BatabyalNo ratings yet
- 4.3.2 ADC Evaluation Board AD9228 FeaturesDocument3 pages4.3.2 ADC Evaluation Board AD9228 FeaturesManjeer MajumderNo ratings yet
- Design and ImplementationDocument4 pagesDesign and ImplementationKrste DimitrievskiNo ratings yet
- PE3308 - Technical Summary For Cable1632 Rev DDocument2 pagesPE3308 - Technical Summary For Cable1632 Rev DJohn HallowsNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetSai Krishna BangaruNo ratings yet
- DMX512 Protocol Implementation Using MC9S08GT60 8-Bit MCU: Application NoteDocument12 pagesDMX512 Protocol Implementation Using MC9S08GT60 8-Bit MCU: Application NotesnehaNo ratings yet
- 7521 ServiceManualDocument122 pages7521 ServiceManualRicardo Alexis Fuentes LufittNo ratings yet
- Programming Cable Users GuideDocument13 pagesProgramming Cable Users GuideSahal AhammedNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 AdcDocument8 pagesExperiment No 3 AdcDakshata WaghNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: DVD PlayerDocument66 pagesService Manual: DVD PlayerJoel MarvalNo ratings yet
- Xapp495 S6TMDS Video InterfaceDocument16 pagesXapp495 S6TMDS Video InterfaceNông Văn DânNo ratings yet
- DSP Blocks InterfacingDocument30 pagesDSP Blocks Interfacingdolly aryaNo ratings yet
- En 25 F 80Document33 pagesEn 25 F 80mactocheNo ratings yet
- Matlab 6713Document15 pagesMatlab 6713ameiyappan5697No ratings yet
- EST Network Applications Installation SheetsDocument20 pagesEST Network Applications Installation SheetsleunamsayanNo ratings yet
- 420 Key EncoderDocument22 pages420 Key EncoderDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- TMS320C5535, C5534, C5533, C5532 Fixed-Point Digital Signal ProcessorsDocument152 pagesTMS320C5535, C5534, C5533, C5532 Fixed-Point Digital Signal ProcessorsNarendra BabuNo ratings yet
- Csi Cd2 ManualDocument22 pagesCsi Cd2 ManualYoryiNo ratings yet
- An2014 001-15229Document6 pagesAn2014 001-15229Lenin PozoNo ratings yet
- Music Synthesizer Senior Project - Individual ReportDocument39 pagesMusic Synthesizer Senior Project - Individual Report邓雪松No ratings yet
- STICK User ManualDocument34 pagesSTICK User ManualadordiNo ratings yet
- Nexys4-DDR RMDocument29 pagesNexys4-DDR RMDocente Fede TecnologicoNo ratings yet
- ZedBoard Examples Radio420SDocument17 pagesZedBoard Examples Radio420Srcollins06181675100% (1)
- Digital Signal Processing Lab: CODE NO: EC05177 List of ExperimentsDocument33 pagesDigital Signal Processing Lab: CODE NO: EC05177 List of ExperimentsSai SaranyaNo ratings yet
- dsk6416 TechRefDocument56 pagesdsk6416 TechRefAizaz Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- DSASL0037380Document40 pagesDSASL0037380Yaseen GhulamNo ratings yet
- Top View DSP DebuggerDocument0 pagesTop View DSP DebuggerVishnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Hardware InstallationDocument29 pagesHardware InstallationHarjass SinghNo ratings yet
- mp3 Decoder AT83SND2CMP3Document98 pagesmp3 Decoder AT83SND2CMP3Venkatesh KamathNo ratings yet
- DVX VHF Digital Voice Transceiver: Moe Wheatley, AE4JYDocument20 pagesDVX VHF Digital Voice Transceiver: Moe Wheatley, AE4JYPaulo FernandesNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To UWB Antenna TechnologyDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To UWB Antenna TechnologyjackNo ratings yet
- WP - Driving The Costs Out of IPTVDocument26 pagesWP - Driving The Costs Out of IPTVshiuli1288No ratings yet
- ISO9141-2 On OBDIIDocument115 pagesISO9141-2 On OBDIILojze MiškovičNo ratings yet
- 204c Mil ServiceDocument51 pages204c Mil Servicekf8rdNo ratings yet
- Model LA-ST120: AC Distribution Panel UnitDocument2 pagesModel LA-ST120: AC Distribution Panel UnitDaniel JovelNo ratings yet
- Pioneer DDJ-1000SRT - W RRV4695Document99 pagesPioneer DDJ-1000SRT - W RRV469544g6psdxtpNo ratings yet
- Power Waves and The Scattering Matrix: V%+ Z%ibDocument9 pagesPower Waves and The Scattering Matrix: V%+ Z%ibsanjeevsoni64No ratings yet
- Semiconductor MemoryDocument17 pagesSemiconductor MemoryAnkit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- AD5930Document28 pagesAD5930Muhammad UMAIRNo ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument18 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerGulafshanNo ratings yet
- Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS)Document19 pagesIndian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS)neeraj aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Zed-F9P: U-Blox F9 High Precision GNSS ModuleDocument24 pagesZed-F9P: U-Blox F9 High Precision GNSS ModuleGhifari RakaNo ratings yet
- Usher X Series, CompassDocument8 pagesUsher X Series, CompassmilexconsultNo ratings yet
- Formula Bank For SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesFormula Bank For Semiconductorskrishna gargNo ratings yet
- Impulse: Operation ManualDocument8 pagesImpulse: Operation ManualRonggo SukmoNo ratings yet
- Mwn-Wapr150n User GuideDocument116 pagesMwn-Wapr150n User GuideDan WrysinskiNo ratings yet
- Cabalse - Keen LE7 NocodeDocument2 pagesCabalse - Keen LE7 NocodeKeen Gementiza CabalseNo ratings yet
- 501-380 Fieldbus Physical Layer Troubleshooting Guide PDFDocument29 pages501-380 Fieldbus Physical Layer Troubleshooting Guide PDFdiosjirehNo ratings yet
- Load Test TransformerDocument10 pagesLoad Test TransformerUpinder Pal Singh0% (1)
- Avionics Training Systems by Len Buckwalter1Document138 pagesAvionics Training Systems by Len Buckwalter1lol no100% (3)
- Microprocessor and InterfaceDocument16 pagesMicroprocessor and InterfaceMajid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Irhlf77214 250V Radhard N MosfetDocument9 pagesIrhlf77214 250V Radhard N MosfetarsebiscuitsNo ratings yet
- 20211112054904Document16 pages20211112054904Israel PinedaNo ratings yet
- EVDO Service FlowDocument32 pagesEVDO Service FlowSandeep MohantyNo ratings yet
- Waveform Digitizers: Digitizer Families Waveform Recording Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) ToolsDocument38 pagesWaveform Digitizers: Digitizer Families Waveform Recording Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) ToolsScarduelliNo ratings yet
- LTE TDD Basic Technology and Comparison With LTE FDD: LTE Product Import Team Wireless Product Service DeptDocument42 pagesLTE TDD Basic Technology and Comparison With LTE FDD: LTE Product Import Team Wireless Product Service Deptmohamed fadl100% (1)
- Metal Fire Alarm Station Ms-700U Series: FeaturesDocument2 pagesMetal Fire Alarm Station Ms-700U Series: FeaturesRicardo TitoNo ratings yet
- 2 MTP850S Product Information Manual PDFDocument228 pages2 MTP850S Product Information Manual PDFDaniel PresaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Topic: GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)Document26 pagesPresentation Topic: GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)Anonymous xsK0G4INo ratings yet