Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Pointers (2015)
Uploaded by
paradoxendazzlingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Pointers (2015)
Uploaded by
paradoxendazzlingCopyright:
Available Formats
ME2114 Pointers to Worksheet on Energy Methods
Q1. Convert the indeterminate problem to a determinate problem with unknown reaction
force, R. Find R from / = 0.
=0
=
Truss analysis:
5
, = ,
6
2
2
2
, = + ,
3
Q2. Convert the indeterminate problem to a determinate problem with unknown reaction
force, R. Find R from / = 0. Deflection of left end is given by = .
P
A
L
B
k=EI/L3
x
P
A
L
B
k=EI/L3
=0
= +
(( ))
1 2
=
+
2
2
0
ME2114 Pointers to Worksheet on Energy Methods
Q3. To find the deflection at B, add a force Q at B and apply Castiglianos Theorem,
=
|
=0
P
=
|
=0
B
Q
A common difficulty is to obtain expressions of T and M in the curved beam. From the free
body diagram below and the definition of used,
={
0
2
+ , 0
2
M
(1 + ) , 0
2
={
(1 ) + (1 + ), 0
2
A
B
P
Q=0
0
2
2
=
(
+
+
+
)|
2 2
2 2
=0
Hint : Do the differentiation first, then set Q=0 before attempting the integration. You will
find that the integral from /2 to 0 becomes zero and the integral from 0 to /2 is greatly
simplified.
ME2114 Pointers to Worksheet on Energy Methods
Q4. Convert the indeterminate problem to a determinate one by looking at half the ring
carrying half the load Q=P/2 as shown. Note that there will be a bending moment M0
when the ring is cut in half since the two halves are from a single continuous ring, i.e.,
M0=0 if the 2 halves are hinged together. This bending moment keeps the top and bottom
ends of the half-ring from rotating, i.e., = = 0
0
Q=P/2
P/2
M0
A
M M 0 QR sin
U
0
M2
Rd
2 EI
P/2
Determine M0 in terms of Q from = 0. Then find = |
0
=/2
Q5. Convert the indeterminate problem to a determinate one by replacing the support at C
with a vertical reaction force Q and a reaction moment Mc.
P
A
B
x
R
L
C
Mc
Q
Use Castiglianos Theorem to find Q and MC by solving simultaneously,
= 0,
=0
/2 2
For section BC: = (1 ) + , = 0
For section AB: = ( + ) + + , =
2
2
0 2
ME2114 Pointers to Worksheet on Energy Methods
Q6. Before applying PMPE, enforce y=0 at x=0, and y=0 at x=L.
Q7. y2 should give a better approximation because it has zero slope at the ends to correctly
represent fixed boundary conditions.
Q8. Find the PE in terms of u1, u2 and u3 from = + , where
2
2
2
=
( ( ) + ( ) + ( ) ),
2
2
3
= ( + + )
0
Q9. The following are intermediate results for you to check.
Rod
cos
sin
AC
EA / 4 3
0o
6 kN
AB
EA / 4
-30o
3/2
-1/2
BC
EA / 4
30o
3/2
1/2
4 3m
30
4m
30
B
4m
EA=50e6 N
0
0.75 0.4330 u B 0
1.5
0
0.5
0.4330 0.25 0 B y
EA
0.4330 uC 0
4 0.75 0.4330 1.3274
0.4330
0.25 vC 6e3
0.4330 0.25
(1)
0.75 0.4330 u B 0 u B 0.0011
1.5
EA
0.75 1.3274 0.4330 uC 0 uC 0.0014
4
0.4330 0.4330
0.25 vC 6e3 vC 0.0063
and from the deleted row in (1),
By
EA
0.4330uc 0.25vc 12000 N
4
(2)
ME2114 Pointers to Worksheet on Energy Methods
Q10. The following are intermediate results for you to check.
D
C
Rod
2m
A
B
P
2m
2m
cos
sin
1/ 2
1/ 2
AC
EA / 2 2
45
AB
EA / 4
0o
CD
EA / 2
180o
-1
BC
EA / 2 2
135o
-1 /
1/ 2
EA=80e6N
0.5 u B 0
1.2071 0.5 0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5 10e 3 B y
EA
0.5 2.4142
0 uC 0
2 2 0.5
0.5
0
1 vC 0
0.5
The 1st, 3rd and 4th eqn of the above simultaneous eqns can be written as
0 EA
(0.5)(10e 3)
0.5
0.5 u B
1.2071 0
2 2
0.5 0.5
y
0.5
0.5 10e 3
EA
EA
(0.5)(10e 3)
0 2.4142
0 uC 0
2 2 0.5
2 2
EA
v
0
.
5
0
0
1
(0.5)(10e 3)
C
0
2 2
u B 0.0017
uC 0.0017
vC 0.0041
ME2114 Pointers to Worksheet on Energy Methods
Q11. You only need to consider half the problem because of symmetry and you only need the
2nd equation in [K][u]=[f] to solve for va.
A
Zero x
displacement and zero
y reaction force
A 2
C L/2
fixed
L/2
fixed
[][] = []
(**) Solve va from 2nd eqn in [K][u]=[f]
i.e.,
2 + 5 ( 22) 6 ( 22) + 7 ( 2)
8 ( 2) = 0
So only need to determine 2nd row of [K]
matrix
0
8
22
22
[
]
[
2
]
Q12.
y
0
~
Using the given formula B 0 x
x y
~
~
for the 2 elements below, B a B b
Element a
Element b
x , it can be shown that
y
2L
2L
This means k local b k local a because k local
t ~T
~
B E B .
4A
u c P 1
For given problem, [K ]
2 1
vc
0 uc P 1
Et 0.6563
1.2188 vc
L2 0
2 1
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ignazio Basile, Pierpaolo Ferrari (Eds.) - Asset Management and Institutional Investors-Springer International Publishing (2016) PDFDocument469 pagesIgnazio Basile, Pierpaolo Ferrari (Eds.) - Asset Management and Institutional Investors-Springer International Publishing (2016) PDFrhinolovescokeNo ratings yet
- Impact of World War I Treaty of VersaillesDocument4 pagesImpact of World War I Treaty of VersaillesparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Mind (Jenkins & Sullivan) (2012)Document199 pagesPhilosophy of Mind (Jenkins & Sullivan) (2012)Claudenicio Ferreira100% (2)
- Comparison Between Full Order and Minimum Order Observer Controller For DC MotorDocument6 pagesComparison Between Full Order and Minimum Order Observer Controller For DC MotorInternational Journal of Research and DiscoveryNo ratings yet
- TIMO Selection Primary 5Document2 pagesTIMO Selection Primary 5Qurniawan Agung Putra100% (5)
- Universal Basic IncomeDocument32 pagesUniversal Basic IncomeparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Gaming SocialDocument15 pagesGaming SocialparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Hips (High Impact Polystyrene) : Advantages of HIPS: Applications IncludeDocument1 pageHips (High Impact Polystyrene) : Advantages of HIPS: Applications IncludeparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- UTS2101 Syllabus AY2015 Sem 1Document7 pagesUTS2101 Syllabus AY2015 Sem 1paradoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- EG2401 Lec 6 14-15sem2 (Compatibility Mode)Document31 pagesEG2401 Lec 6 14-15sem2 (Compatibility Mode)paradoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- ME3122 Handbook of Heat Transfer Equations 2014Document22 pagesME3122 Handbook of Heat Transfer Equations 2014howsky31No ratings yet
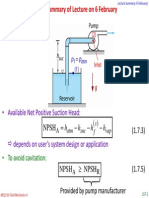
- Cavitation in Pumps: NPSH (1.7.3)Document2 pagesCavitation in Pumps: NPSH (1.7.3)paradoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
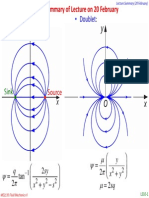
- Source: - DoubletDocument4 pagesSource: - DoubletparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sept 12Document39 pagesChapter 1 Sept 12paradoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- ME2135 Lecture Summary 21janDocument4 pagesME2135 Lecture Summary 21janparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Theory Test 1 NotesDocument6 pagesTheory Test 1 NotesparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- V U Vds Udx Vdy Dxdy Dxdy X Y: Counterclockwise Line IntegralDocument1 pageV U Vds Udx Vdy Dxdy Dxdy X Y: Counterclockwise Line IntegralparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Gatsby: Chapter SevenDocument1 pageGatsby: Chapter SevenparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- ME2135 QUIZ - February 2010Document6 pagesME2135 QUIZ - February 2010paradoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- FI NotesDocument1,069 pagesFI NotesparadoxendazzlingNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 AnthropometryDocument23 pagesModul 1 Anthropometryssoppriok 12No ratings yet
- Basic ProbDocument12 pagesBasic ProbChaaaNo ratings yet
- Integrals of Differential Binomials and Chebyshev's CriterionDocument4 pagesIntegrals of Differential Binomials and Chebyshev's CriterionEnrique GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Attribution ModelsDocument7 pagesAttribution Modelsjade1986No ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Maths Higher Paper 2 June 2022 Mark SchemeDocument26 pagesEdexcel GCSE Maths Higher Paper 2 June 2022 Mark SchemeZia Saad ANSARINo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study Between Experimental and Theoretical Buckling Load For Hollow Steel ColumnDocument7 pagesA Comparative Study Between Experimental and Theoretical Buckling Load For Hollow Steel ColumnSaurabh SahuNo ratings yet
- Assignment Brief and Guidance:: P Standard Atmospheric Pressure (101.3 Kpa) R Gas Constant Its Value For Air Is 286.9Document7 pagesAssignment Brief and Guidance:: P Standard Atmospheric Pressure (101.3 Kpa) R Gas Constant Its Value For Air Is 286.9Khanur AysahNo ratings yet
- Echo Park Community Design OverlayDocument4 pagesEcho Park Community Design OverlayechodocumentsNo ratings yet
- Math 139-1 Lesson 6 and 7Document52 pagesMath 139-1 Lesson 6 and 7jenny teresa50% (2)
- Jadavpur University: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument65 pagesJadavpur University: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyArchisman HazraNo ratings yet
- Presentation 11 April 2019Document38 pagesPresentation 11 April 2019Anas HameedNo ratings yet
- (Clifford) Advances in Engineering Software PDFDocument796 pages(Clifford) Advances in Engineering Software PDFNguyễn Tấn LậpNo ratings yet
- Let Us C SolutionsDocument81 pagesLet Us C Solutionsneonav100% (2)
- Lecture 10Document19 pagesLecture 10M.Usman SarwarNo ratings yet
- Gpu Applications CatalogDocument56 pagesGpu Applications CatalogWaris La Joi WakatobiNo ratings yet
- Year 6Document53 pagesYear 6Baiat FinutzNo ratings yet
- Data Mining With Weka: Ian H. WittenDocument33 pagesData Mining With Weka: Ian H. WittenQuân PhạmNo ratings yet
- NMDocument12 pagesNMShravan KumarNo ratings yet
- PTM Phy F.4.Ch.2.4Document13 pagesPTM Phy F.4.Ch.2.4Bazil BoliaNo ratings yet
- STA642 Handouts Topic 1 To 187 by Mahar Afaq Safdar MuhammadDocument1,739 pagesSTA642 Handouts Topic 1 To 187 by Mahar Afaq Safdar Muhammadhumairamubarak2001No ratings yet
- MBR Session 20Document78 pagesMBR Session 20mariamabbasi2626No ratings yet
- ch11 SolDocument20 pagesch11 SolJohn Nigz PayeeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics III 2015 Solved Question Papers For VTU All Semester 3 PDFDocument25 pagesEngineering Mathematics III 2015 Solved Question Papers For VTU All Semester 3 PDFAbishek Abh50% (2)
- Ojimc 2021 (Imo Mock)Document8 pagesOjimc 2021 (Imo Mock)NonuNo ratings yet
- Study of Process - Improving Efficiency of Closed Die Hot Forging ProcessDocument69 pagesStudy of Process - Improving Efficiency of Closed Die Hot Forging ProcessMrLanternNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Topic 2 AS-Level English Language School DubaiDocument28 pagesMechanics: Topic 2 AS-Level English Language School DubaiHamza ShabbirNo ratings yet