Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Form 2 Math
Uploaded by
Lywee NeoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 2 Math
Uploaded by
Lywee NeoCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank
Chapter 1
10. Solve
(a) 12 (3) 6 + (14),
(b) (25 + 11) (7).
Directed Numbers
1. Find the value of each of the following.
(a) 12 + (14) (25)
(b) 25 (+10) + 24
Chapter 2
2. Calculate the value of each of the following.
(a) 18 (2) 6
(b) 21 (7) (4)
1. Evaluate each of the following without using a
calculator.
1 2
1 2
(a) 2
(b) 3
2
3
3. Solve
5 + 9 ,
(a)
7
14
3
2 .
(b)
8
5
1 2
2
2
3. Evaluate
(a) AB2 ABB
18 ,
6. Find the value of
8 ,
(a) 3
125
ABBBBB
61 .
1
ABBBB
64
8 .
7. Find the value of 5 ABBBBB
125
2
(b)
(b)
8. Solve
(a) (2)3 + AB
4 ,
7. Find the value of each of the following and express
your answer as a single fraction in its lowest
term.
1
3 1.3
(a) 1
2
5
1
1
(b) 4 1 + 2
4
3
ABBB
27 32.
9. Solve
0.008 ,
(a) ABBB
144 0.32 3ABBBB
ABB
1 2 4
1 3.
(b)
3
2
9
1 2
1 2
10. The total surface area of a cube is 54 cm2. Find the
volume of the cube, in cm3.
8. Find the value of each of the following and give
your answer in decimal.
2 (1.45)
(a) 5.4
5
3
(b) 9 (0.4) + 0.8
4
Chapter 3
Algebraic Expressions II
1. Simplify 6m 4(2 + m).
9. Evaluate
10 (5)
(a) ,
7 + 2
0.08 (0.2)
(b) .
0.004
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
AB5 ABB
20 .
2
2 1
(b)
5. Find the value of each of the following.
1 3
(a) 0.33
(b) 1
2
6. Find the value of each of the following and give
your answer in decimal.
1 + (2.6) + 10
(a) 1
4
3 8
(b) 9.6
5
1
1
4. Find the perimeter of a square of area 144 cm2.
5. Solve
5 2
1 ,
3
(a)
6
4
10
3
(b) 13 + 4.24 .
4
2. List all the perfect squares between 20 and 140.
4. Solve each of the following.
(a) 0.6 + (2.7)
(b) 5.3 1.9 (3.4)
Squares, Square Roots,
Cubes and Cube Roots
2. 5(h 3k) 5k 1 =
3. Simplify
3 a (20bc),
(a)
8
2 (5m 10p + 15q).
(b)
5
80
4. If x = 3, y = 2 and z = 5, find the value of
2x + y2 3z.
2 2pr.
5. If p = 1, q = 2 and r = 4, evaluate p2 +
q
1. Find the ratio of
(a) 45 minutes to 2 hours,
(b) 0.8 kg to 250 g.
6. In the algebraic term 4p2qr, state the coefficient
of
(a) p2,
(b) pqr.
7. Simplify
2 (18a2b),
(a)
3
8. Simplify
10hk ,
(a)
25k
2.
R
4 cm
(b) 3de (2ef).
10 cm
The diagram shows a rectangle PQRS. Find the
ratio of its length to its perimeter.
(b) 49pq
.
14qr
3. A sum of RMx is divided between Faizal and Ghafar
in the ratio 3 : 8. If Faizal receives RM225, find the
value of x.
9. Simplify each of the following.
(4mn)(5pq)
(12x2y)(yz3)
(a)
(b)
12
4xyz
4. Simplify the following ratios.
(a) 5 : 25 : 10
(b) 2.4 : 4 : 1.2
2 (10m 15p).
10. Simplify 2(3m 4p)
5
Chapter 4
Ratios, Rates and
Proportions
Chapter 5
5. Given that p : q : r = 1 : 5 : 3, find the ratio of
(a) p + q : r,
(b) p : q r.
Linear Equations
6. Given that a : b : c = 3 : 5 : 2 and a = 15, find the
value of b + c.
1. Given that 3x 5 = 10, find the value of x.
m = 2, find the value of m.
2. Given that 8 +
5
7. If p : q : r = 4 : 1 : 3 and p + q + r = 40, find the
value of q.
3. Solve the equation 5k 4 = 14 4k.
8. Given that x : y = 8 : 3 and y : z = 6 : 5, find the
ratio x : y : z.
e5
4. If = 1, find the value of e.
4
9. The lengths of the sides of a triangle are in the
ratio 2 : 5 : 6. If its perimeter is 78 cm, find the
length of its longest side.
1 , find the value of m.
2m = 1
5. If
2
3
6. Given that 6y 3 = 5 + 2y, find the value of y.
10. There are 58 marbles in a box. 18 of them are red,
24 of them are yellow and the rest are green. Find
the ratio of the number of yellow marbles to the
number of green marbles.
m 4 = 5.
7. (a) Solve
2
n = 4, find the value of n.
(b) If 7
3
8. Solve the following equations.
m+1
(a) = 2
4
n
+
2
n
(b) =
5
4
Chapter 6
1.
9. Solve the following equations.
(a) 5 3x = 14
(b) 4y + 6 = 2(y + 6)
Pythagoras Theorem
1.6 cm
x cm
1.2 cm
The diagram shows a right-angled triangle. Find
the value of x.
p5
p
10. (a) Solve = .
4
2
5 q 1 = 9, find the value of q.
(b) If
3
81
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
2.
8.
10 cm
x cm
4 cm
10 cm
T
5 cm
7 cm
The diagram shows a right-angled triangle. Find
the value of x, give your answer correct to two
decimal places.
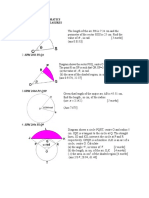
3.
In the diagram, PTR and QRS are straight lines. T is
the midpoint of PR. Calculate the length of QS.
14 cm
12 cm
Chapter 7
Set squares and protractors are not allowed to be used for
all questions.
9 cm
The diagram shows a trapezium. Calculate the
perimeter, in cm, of the trapezium.
4.
10 cm
Geometrical Constructions
1. Construct a triangle PQR such that PQ = 3 cm
and QR = 2 cm. Start your construction using the
straight line PR given below.
6 cm
S
In the diagram, PQRT is a square. Calculate the
area, in cm2, of the whole figure.
5.
2. The diagram below shows a straight line KL.
Construct a triangle JKL in which JKL = 45 and
JLK = 60.
P
17 cm
Q
4 cm
R 6 cm
6.
In the diagram, PQR and RST are straight lines.
Find the length of ST.
3. The diagram below shows a straight line PQ.
Construct a perpendicular bisector to line PQ.
5 cm
y cm
34 cm
The diagram shows a right-angled triangle. Find
the value of y.
7.
12 cm
8 cm
4. The diagram below shows a straight line PR.
Construct a line that passes through point Q and
is perpendicular to PR.
The diagram shows a trapezium JKLM. Given
that JL = 13 cm, find the area, in cm2, of the
trapezium.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
82
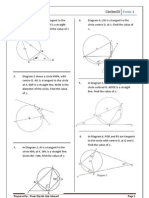
5. Construct PQR = 120 in the diagram below.
3. The diagram below shows a Cartesian plane.
(a) State the coordinates of point P based on the
diagram.
(b) Mark the point (4, 2) with Q on the
diagram.
6. By using a pair of compasses and a ruler, construct
a triangle PQR such that PQR = 30 and
PR = 4 cm. Start your construction by using the
line QR given below.
y
P
2
R
7. The diagram below shows a triangle PQR. Start
with the triangle given, construct
(a) the parallelogram PQRS,
(b) QT, the bisector of PQR, where T lies on the
line PR.
4. Find the distance between P(5, 3) and Q(5, 9).
5. Given points R(2, 4) and S(4, 10). Find the
coordinates of the midpoint of straight line RS.
6. Given points E(9, 6) and F(9, 4). Find the distance
of EF.
7.
y
6
8. Start with the straight line PQ given below,
construct
(a) the triangle PQR, such that PR = 3 cm and
QR = 4.5 cm,
(b) the perpendicular to PQ passing through R.
4
2
0
Q
R
2
On the Cartesian plane above, points P, Q and R
are three of the vertices of the parallelogram PQRS.
State the coordinates of point S.
P
Chapter 8
8. Given points H(3, 6) and K(3, 10), calculate the
coordinates of the midpoint of straight line HK.
Coordinates
9.
1. Calculate the distance between the points (5, 4)
and (8, 4).
H(8, 8)
M
2.
4
0 G(2, 0)
The diagram shows a Cartesian plane. M is the
midpoint of straight line GH. Find
(a) the coordinates of point M,
(b) the length of GH.
2
P
10. Given points P(x, 4) and Q(5, y). M(3, 1) is the
midpoint of the straight line PQ. Find the values
of x and y.
The diagram shows a Cartesian plane. Based on
the diagram, state the coordinates of the midpoint
of line PQ.
83
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 9
Loci in Two Dimensions
1. Construct the locus of a moving point which is
equidistant from the points E and F.
R
6. The diagram below shows a rectangle ABCD. E is
the midpoint of AD. On the same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of a moving point X, such
that EX = 2.5 cm,
(b) construct the locus of a moving point Y, such
that AY = 3 cm,
(c) mark the point of intersection between the
two loci with the symbol .
2. Construct the locus of a moving point which is
equidistant from the lines PQ and QR.
P
R
3 cm
3. In the diagram below, GH is a straight line of
length 3 cm. On the same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of a moving point P, such
that PG = 2 cm,
(b) construct the locus of a moving point Q, such
that GQ = QH.
(c) mark all the points of intersection between
the two loci with the symbol .
3 cm
5 cm
8. The diagram below shows a triangle JKL. P and
Q are points moving inside the triangle. On the
same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of P, such that PJ = PK,
(b) construct the locus of Q, such that
JQ = 3 cm,
(c) mark the point of intersection between the
two loci with the symbol .
L
5. The given diagram shows an equilateral triangle,
PQR. On the same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of a moving point X, such
that XP = XR,
(b) construct the locus of a moving point Y, such
that Y is equidistant from PR and PQ,
(c) mark the point of intersection between the
two loci with the symbol .
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
7. The diagram below shows a straight line PQR. Q is
the midpoint of PR. On the same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of a moving point X, such
that X is 2 cm from the line PQR,
(b) construct the locus of a moving point Y, such
that Y is 2.5 cm from Q,
(c) mark all the points of intersection between
the two loci with the symbol .
4. In the diagram below, PQ is a straight line of
length 5 cm. On the same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of a moving point X,
which is 2 cm from the line PQ,
(b) construct the locus of a moving point Y, such
that Y is equidistant from P and Q,
(c) mark all the points of intersection between
the locus of X and the locus of Y with the
symbol .
5 cm
84
5 cm
9.
3.
2 cm
O
B
The diagram shows a sector with centre O. Given
that the perimeter of the sector is 25 cm, find the
22
value of x. Use =
7
The diagram shows a rectangle ABDE. X is a point
moving within the rectangle. Describe completely
the locus of X in each of the following cases.
(a) AX = XE.
(b) X is equidistant from AB and BC.
(c) X is 2 cm from F.
4.
Q
O
10. The diagram below shows a rectangle PQRS. X and
Y are points moving inside the rectangle. On the
same diagram,
(a) construct the locus of X, such that X is 2 cm
from line PQ,
(b) construct the locus of Y, such that Y is
equidistant from PQ and PS,
(c) mark the point of intersection between the
two loci with the symbol .
P
7 cm
P 15 cm R
In the diagram, OPQR is a sector with centre O.
OPR is an equilateral triangle. Find the length of
22
arc PQR. Use =
7
5.
E
F
72 5 cm
The diagram shows a sector centred O. Calculate
22
the area of the sector. Use =
7
4 cm
5 cm
6.
R
Chapter 10
1.
Circles
120
Q
P
21 cm
In the diagram, OPQ and ORS are two sectors
with a common centre, O. Given that OQ = QS =
7 cm, calculate the area of the shaded region.
22
Use =
7
120
Q
The diagram shows a sector centred O. Find the
22
length of arc PQ. Use =
7
2.
7.
O
60 r cm
A
The diagram shows two semicircles with diameters
22 , calculate the perimeter
PQ and OQ. Using =
7
of the shaded region.
The diagram shows a sector with centre O. Given
2 cm, find the value
that the length of arc AB is 3
3
22
of r. Use =
7
7 cm
85
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
8.
2. The diagram below shows a quadrilateral drawn
on a Cartesian plane. On the diagram, draw the
image of the quadrilateral under a reflection in
the y-axis.
Q
14 cm
P
In the diagram, OPQR is a square and ORS is
a quadrant with centre O. POS is a straight
line. Calculate the area of the whole diagram.
22
Use =
7
4
2
9.
10 cm
M
Q
Q 7 cm R
4. The diagram below is drawn on a square grid. On
the grid provided, draw the image of triangle ABC
under a clockwise rotation of 90 about point P.
12 cm
In the diagram, PQR is a quadrant centred R. QRS
is a straight line. Calculate the area of the whole
22
diagram. Use =
7
Chapter 11
3. The diagram below is drawn on a square grid. On
the grid provided, draw the image of triangle M
under a reflection in the line PQ.
The diagram shows a rectangle JKMN. L is the
midpoint of KM. JKL and LMN are two quadrants
inside the rectangle. Calculate the perimeter of
the shaded region. (Use = 3.14)
10.
Transformations
1.
y
P
5.
P
2
R
Q
P
R
In the diagram, P is the image of P under a
translation h . Find the values of h and k.
k
12
P
2
In the diagram, triangle PQR is the image of
triangle PQR under an anticlockwise rotation of 90.
State the coordinates of the centre of rotation.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
86
6.
The diagram shows a Cartesian plane. State the
coordinates of the image of point P under
(a) a reflection in the x-axis,
(b) a reflection in the y-axis.
y
6
4
10.
2
0
y
4
The diagram shows a Cartesian plane. State
the coordinates of the image of point T under a
translation 3 .
3
2
0
1 2
4
2
The diagram above is drawn on a Cartesian plane.
Given that P is the image of P under a certain
reflection.
(a) State the axis of reflection.
(b) Find the coordinates of the image of point Q
under the same reflection.
y
K
2
4
7.
Chapter 12
Solid Geometry II
The diagram above is drawn on a Cartesian plane.
State the coordinates of the image of point K under
a clockwise rotation of 90 about the point (0, 1).
1. The total surface area of a cube is 150 cm2. Find its
volume, in cm3.
8.
2. A cuboid is 2.4 m long, 1.5 m wide and 0.8 m high.
Find its total surface area, in m2.
y
4
P
4
3. Find the surface area of a sphere with a radius of
10 cm. (Use = 3.142)
2
0
4.
In the diagram above, triangle P is the image of
triangle P under a certain transformation. Describe
completely the transformation.
9.
4
Q 6 cm R
5. The area of the curved surface of a cone is 220 cm2.
If the radius of its base is 5 cm, find the length of
22
its slant height. Use =
7
The diagram shows a right pyramid with a square
base PQRS. M is the midpoint of PQ. Given that
VM = 8 cm, calculate the total surface area of the
pyramid.
2
4
87
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
6.
2.
Area P
Area Q
Area R
represents 25 trees
4 cm
The pictogram shows the number of trees planted
in three areas in a certain month. Find the total
number of trees planted in these three areas.
The diagram shows a right pyramid with a square
base of sides 3 cm. Draw the net of the pyramid.
7.
3.
7 cm
January
February
March
represents 30 calculators
15 cm
The diagram shows a cylinder. Calculate the total
22
surface area of the cylinder. Use =
7
8. The surface area of a sphere is 256 cm2. Find the
radius of the sphere.
The incomplete pictogram shows the number of
calculators sold in a book shop in three months.
If the total number of calculators sold is 390, how
many symbols of must be drawn for the month
of February?
9.
4.
4 cm
Profit (RM)
10 cm
8 cm
10 cm
15 cm
The diagram shows a right prism. Find the total
surface area of the prism.
5.
14 cm
The diagram shows a solid made of a hemisphere
and a cylinder. Find the total surface area of the
22
solid. Use =
7
1.
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May
Month
Statistics
The line graph shows the monthly expenditure of
Daisy. Based on the line graph, calculate the mean
monthly expenditure, in RM.
32 16 25 28 25 24
28 28 24 16 28 16
The data shows the temperature, in C, of twelve
towns of a certain day. State the temperature
with
(a) the highest frequency,
(b) the lowest frequency.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Expenditure (RM)
The line graph shows the profit made by a
cafeteria in five days. Find the difference between
the highest and the lowest profit made in the five
days.
5 cm
Chapter 13
Mon. Tue. Wed. Thu. Fri.
Month
10.
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
88
7.
week 4
10. The incomplete bar chart below shows the daily
saving of Joey in five days. If the total saving in
the five days is RM24, complete the bar chart
below for Thursday.
Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr.
Month
Saving (RM)
Number of cars
week 3
The line graph shows the number of books read
by a group of students in four weeks. Find the
percentage increase of number of books read in
Week 4 as compared to the number of books read
in Week 1.
The bar chart shows the number of students in
a class who scored grade A in six Mathematics
monthly tests. Find the greatest increase between
two consecutive months.
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
week 2
0
Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May June
Month
The bar chart shows the monthly production of
cars in a factory for the first four months of a year.
Find the ratio of the number of cars produced in
January to the total number of cars produced in
the four months.
8.
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
week 1
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
Number of books read
9.
Number of students
6.
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Mon. Tue. Wed. Thu.
Fri.
Day
Factory A
Factory B
Factory C
represents 40 males
represents 40 females
The pictogram shows the number of male and
female workers in three factories. Find the total
number of female workers in the three factories.
89
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- Coordinate Geometry Ver 2012Document19 pagesCoordinate Geometry Ver 2012Tee Pei LengNo ratings yet
- 2D and 3D ShapesDocument21 pages2D and 3D ShapesRoobendhiran Sivasamy67% (3)
- Maths Form2 - RevisionDocument23 pagesMaths Form2 - RevisionNK2884% (49)
- Add Maths SPM Forecast PapersDocument16 pagesAdd Maths SPM Forecast PapersShanmuganantha KathiraveluNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Answer ALL Questions. Write ALL The Answers On The Answer Sheets ProvidedDocument6 pagesInstructions: Answer ALL Questions. Write ALL The Answers On The Answer Sheets ProvidedYuenHei Kwok100% (2)
- Maths Form 2Document22 pagesMaths Form 2HaziraAzlyNo ratings yet
- Form 2 MathematicsDocument7 pagesForm 2 Mathematicsyokekeann0% (1)
- MODULE 14 Algebraic Exp Expand Factor Is at IonDocument6 pagesMODULE 14 Algebraic Exp Expand Factor Is at IonNyai Blorong KetombeNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect 7 (Algebra)Document8 pagesPractice Makes Perfect 7 (Algebra)dikwanzNo ratings yet
- AMATH QuadraticFunctionDocument14 pagesAMATH QuadraticFunctionLeneNo ratings yet
- 1st Payment ReminderDocument1 page1st Payment ReminderElysium RootNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Document18 pagesAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Test with 20 QuestionsDocument14 pagesTrigonometry Test with 20 QuestionsMohd TaufekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Coordinate GeometryDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - Coordinate GeometryshahrulkamilNo ratings yet
- SPM AddMath Permutations and CombinationsDocument7 pagesSPM AddMath Permutations and CombinationsLeneNo ratings yet
- HCF LCMDocument7 pagesHCF LCMBunga NoionlaNo ratings yet
- Guide to Properties of 2D and 3D ShapesDocument7 pagesGuide to Properties of 2D and 3D Shapesexplo4747No ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionDocument5 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionSabariah OsmanNo ratings yet
- Keep Your Kitchen SafeDocument13 pagesKeep Your Kitchen SafeVanessa VivNo ratings yet
- Circular Measures Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesCircular Measures Problems and SolutionspizamNo ratings yet
- Kebarangkali (BI)Document11 pagesKebarangkali (BI)smkpthoeNo ratings yet
- Modul Tok JiringDocument18 pagesModul Tok JiringShin AzwanNo ratings yet
- Key to excelling in Additional Mathematics/TITLEDocument124 pagesKey to excelling in Additional Mathematics/TITLEJia HuiNo ratings yet
- 6th Class Maths MCQsDocument4 pages6th Class Maths MCQsHassaan Ahmed SajidNo ratings yet
- LCM & HCFDocument5 pagesLCM & HCFArockia RajNo ratings yet
- BAB 7 MATE T3 Algebraic FormulaDocument1 pageBAB 7 MATE T3 Algebraic FormulacgnashNo ratings yet
- Exercise Alg FormulaeDocument6 pagesExercise Alg FormulaeLaavanes MurgayaNo ratings yet
- Math Mid Year f1 Paper 1Document8 pagesMath Mid Year f1 Paper 1Nurun Nadia MasromNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure CalculationsDocument17 pagesCircular Measure CalculationsRahman AnwarNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 2 Math Chapter 10Lywee Neo75% (4)
- Circles IIIDocument2 pagesCircles IIIHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Math MF2 Chapter 1 (Directed Numbers)Document1 pageMath MF2 Chapter 1 (Directed Numbers)compeil100% (4)
- 2 Klon SPM Quad Eqn 2003 - 2014 - EdDocument32 pages2 Klon SPM Quad Eqn 2003 - 2014 - EdAnonymous 0fagPbbloNo ratings yet
- Pt3 Mathematics Form 2 Revision KSSMDocument12 pagesPt3 Mathematics Form 2 Revision KSSMjx 08No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeCik Yana50% (2)
- SPM Trigonometry Functions Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageSPM Trigonometry Functions Problems and SolutionsRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- HotSpot Question in PT3 2017 Mathematics (Sample Question)Document1 pageHotSpot Question in PT3 2017 Mathematics (Sample Question)Cemerlang Studi100% (3)
- PT3 RevisionDocument26 pagesPT3 RevisionAnonymous Kx8TAybnXQNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Form 5 Probability Tanpa Jawapan Try ThisDocument32 pagesChapter 7 Form 5 Probability Tanpa Jawapan Try ThisNain MfNo ratings yet
- Standard Form Mathematics GuideDocument14 pagesStandard Form Mathematics GuideMathana SuriaNo ratings yet
- Math F2 Ujian 3 K1Document4 pagesMath F2 Ujian 3 K1compeilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Standard FormDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Standard FormWupo Ling100% (1)
- Modul 10 Set K2Document8 pagesModul 10 Set K2Ting ShiangNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Mathematics Chapter 1 (Indices) KSSMDocument2 pagesForm 3 Mathematics Chapter 1 (Indices) KSSMBONG TZER WEI MoeNo ratings yet
- 2012 Math F2 (Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots)Document1 page2012 Math F2 (Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots)compeilNo ratings yet
- Math MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)Document6 pagesMath MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)compeil100% (1)
- SPM 2003-2007 VECTORS, TRIGONOMETRY, PROBABILITY ANSWERSDocument9 pagesSPM 2003-2007 VECTORS, TRIGONOMETRY, PROBABILITY ANSWERSRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Algebraic FormulaeDocument1 pageChapter 3 Algebraic FormulaeTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Solving quadratic equationsDocument8 pagesSolving quadratic equationsjesunathan44@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Answer All The Questions. (A) Diagram 1 (A) Shows A Number LineDocument16 pagesAnswer All The Questions. (A) Diagram 1 (A) Shows A Number LineRosmah Abdullah89% (19)
- Chapter 11 Introduction To SetsDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Introduction To SetsJu WenNo ratings yet
- KembangkanDocument22 pagesKembangkanNURAIN BINTI REDZALINo ratings yet
- Linear Law P1Document2 pagesLinear Law P1mohamad_bidari0% (1)
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)Document4 pagesAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)HANIFAHNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3 Chapter 8 LociDocument15 pagesMathematics Form 3 Chapter 8 LociFrancesca CheeNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS Form 2Document22 pagesSTATISTICS Form 2Rosmah Abdullah80% (5)
- Form 3 Solid GeometryDocument23 pagesForm 3 Solid GeometryNg Kok ChingNo ratings yet
- Answers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)Document2 pagesAnswers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)compeil100% (2)
- Bab6 Mathf2Document2 pagesBab6 Mathf2cikguanuar100% (1)
- Modul 1 Persamaan Linear SerentakDocument5 pagesModul 1 Persamaan Linear SerentakPing Ping ThianNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ramalan Mathematics PMR 2009 Paper 2Document16 pagesSoalan Ramalan Mathematics PMR 2009 Paper 2kguna100% (1)
- Teknik Menjawab Matematik Spm2009Document25 pagesTeknik Menjawab Matematik Spm2009adeksam72No ratings yet
- Set 3 MawarDocument36 pagesSet 3 MawarAmu KevinNo ratings yet
- XPY Paper 2Document23 pagesXPY Paper 2Lim Wai Wai SmktpNo ratings yet
- CALCULATING DIRECTED NUMBERS, FRACTIONS AND OTHER ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONSDocument31 pagesCALCULATING DIRECTED NUMBERS, FRACTIONS AND OTHER ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONSAmu KevinNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soalan PT3 Matematik 2014Document3 pagesLatihan Soalan PT3 Matematik 2014Lywee Neo100% (5)
- JOB Application Form: Position Applied For: DateDocument1 pageJOB Application Form: Position Applied For: DateLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- WAJA Mathematics PMR - Line GraphsDocument11 pagesWAJA Mathematics PMR - Line GraphsLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Calculate Length of Paddy Field by Its Area and WidthDocument2 pagesCalculate Length of Paddy Field by Its Area and WidthLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- F2 Math Chapter 11Document5 pagesF2 Math Chapter 11Lywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Upsr Mat Trial 18 1Document15 pagesUpsr Mat Trial 18 1Nur FatiniNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 4Document3 pagesForm 2 Chapter 4Lywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 10 TESTDocument4 pagesForm 1 Chapter 10 TESTLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Whole Number and Fraction Word ProblemsDocument5 pagesWhole Number and Fraction Word ProblemsLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 4Document1 pageForm 2 Chapter 4Lywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 8 TestDocument2 pagesForm 2 Chapter 8 TestLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 MathDocument3 pagesForm 2 MathLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 4Document3 pagesForm 2 Chapter 4Lywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Coordinate Systems ExplainedDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Coordinate Systems ExplainedLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Basic Plain Sponge CakeDocument3 pagesBasic Plain Sponge CakeLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Basic Plain Sponge CakeDocument3 pagesBasic Plain Sponge CakeLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- F2 Math Chapter 2 TestDocument2 pagesF2 Math Chapter 2 TestLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Skills Practice: TranslationsDocument1 pageLesson 1 Skills Practice: TranslationscraigNo ratings yet
- Cube Angle Print PlayDocument2 pagesCube Angle Print PlaybelengarridoNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet - PO 2 Class Viii-MathematicsDocument3 pagesRevision Worksheet - PO 2 Class Viii-Mathematicspriya srivastavaNo ratings yet
- MATHS Class XI - Revision Assignment (2022 - 23)Document10 pagesMATHS Class XI - Revision Assignment (2022 - 23)spy arrowNo ratings yet
- A Level Math Paper 2 Equlibrium of Three Forces Lamis Theorem 1Document7 pagesA Level Math Paper 2 Equlibrium of Three Forces Lamis Theorem 1George SsebNo ratings yet
- Elliptic Geometry Concepts and TheoremsDocument5 pagesElliptic Geometry Concepts and Theoremsrenzy3polaron3baylosNo ratings yet
- Centre of Gravity Micro-ProjectDocument10 pagesCentre of Gravity Micro-ProjectShubham Marwade100% (4)
- Straight Line Pair QuestionsDocument44 pagesStraight Line Pair QuestionsNipun MittalNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p1 Ex10cDocument5 pagesAlevelsb p1 Ex10ceduguideNo ratings yet
- Analytic ReviewDocument9 pagesAnalytic ReviewpsittacosisNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction and History PDFDocument22 pages01 Introduction and History PDFMichelle PalupitNo ratings yet
- Maths Syllabus - Form 1: Chapter 1: Whole NumbersDocument25 pagesMaths Syllabus - Form 1: Chapter 1: Whole NumbersDexter 福少No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Using Opengl, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyDocument56 pagesComputer Graphics Using Opengl, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleySakirin Bin Haji MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapter 4 WorksheetsDocument7 pagesGeometry Chapter 4 Worksheetsapi-3067202130% (3)
- Construction of Quadrilaterals: Class VIII. Maths WorksheetDocument2 pagesConstruction of Quadrilaterals: Class VIII. Maths WorksheetsanaNo ratings yet
- Volumes of Solids: Find The Volume of Each Figure. Round To The Nearest TenthDocument2 pagesVolumes of Solids: Find The Volume of Each Figure. Round To The Nearest TenthVer ClauNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFsamiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Mathematics (3 Year High School)Document6 pagesLesson Plan Mathematics (3 Year High School)Marla Jean FabroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Volume of SolidsDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Volume of SolidsSamsiah MustaffaNo ratings yet
- TOS in MathDocument5 pagesTOS in MathalexdelavegaNo ratings yet
- 4th Periodical Test in MATH 6Document7 pages4th Periodical Test in MATH 6anon_734597237No ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper 01 Maths Class 9Document3 pagesCBSE Sample Paper 01 Maths Class 9Anonymous M2tenErNo ratings yet
- Crack TCS NQT 2022 in One GoDocument3 pagesCrack TCS NQT 2022 in One GoshivanshNo ratings yet
- Segments and RaysDocument14 pagesSegments and Raystrade008paypalNo ratings yet
- List of Theorems and Postulates On CirclesDocument1 pageList of Theorems and Postulates On CirclesAlexandra86% (7)
- Find Ratios, LCM, Numbers from Ratio ProblemDocument3 pagesFind Ratios, LCM, Numbers from Ratio ProblemriddhiNo ratings yet
- Instructors Solutions To Elements of Electromagnetics 6th Edition by Sadiku p.4Document1 pageInstructors Solutions To Elements of Electromagnetics 6th Edition by Sadiku p.4nogwtfNo ratings yet