Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advanced Level Physics Practical Techniques 2010
Uploaded by
abdulrehman999Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced Level Physics Practical Techniques 2010
Uploaded by
abdulrehman999Copyright:
Available Formats
Planning an experiment
Know the difference between precise (fineness of scale
devisions) and accurate (closeness to true value).
Explain the advantages of dataloggers.
When timing oscillations measure at least 20 twenty in
total (e.g. a minimum of 2 sets of 10 oscillations).
Rather than single results take a range to plot a graph,
best fit a curve and take a gradient that is less sensitive to
random error.
Taking results
Place a ficidual mark to aid the timing of a pendulum (this
must go under the pendulum at the equilibrium position
for minimum transition time).
Place a ficidual mark to improve accuracy when measuring
the extension of a material.
Use a mirror to eliminate parallax error.
Be able to draw a sketch of the above three techniques.
Use a set square to ensure an object (e.g. metre rule) is
vertical. This needs to be placed at two perpendicular
surfaces to ensure the object is vertical in both planes.
Units that are name after people must start with a capital
letter e.g. Volt.
Ensure the independent variable is given at the precision
used e.g. 5.0cm not 5cm if measuring with a ruler
because you are controlling it doesnt mean it should be
truncated.
Measure the diameter of cylindrical objects (e.g. wire) by
using the instrument at three different angles in three
different positions (at least take more readings if there is
a lot of variation).
Record results to the max number of sig fig available.
Record zero as 0.00 if you are measuring to 2 dp (marks
are removed if you do not do this.)
Plotting graphs
If a variable is defined in a question (e.g. x = deflection of
metre rule) then use it on the axes label.
A best fit curve or line must not be drawn with thick pen, it
must not be sketchy or feint. It must have an even number
of data points on either side.
Ensure numbers are put on scale at least every 5cm.
The examiners penalise marks for points marked as blobs
or dots. They require that points are marked with + (and
not x)
Analysing data
Use a mirror to draw a normal to a best fit curve.
Use a protractor to place a tangent perpendicular to the
normal.
Draw a large triangle extending from a tangent in order to
calculate gradient or inverse gradient.
Draw construction lines and label with values to show how
you took the gradient unless clear evidence of working
is show full credit cannot be given.
Understand that in the context of practical papers
Evaluate can mean work out e.g. Evaluate the force if
the mass = 3kg and the acceleration =10ms -2 .
Express answers to the minimum number of sig fig given
in the question.
Dont truncate the significant figures during working.
Dont give the final answer to more than 4 sig. fig.
Dont truncate valid data e.g. 638mm
64cm.
When multiplying and dividing add %error.
When adding and subtracting add uncertainties.
Describing experiment
Where a lot of marks are given use bullet points to ensure
all are achieved.
Include instruments used, measurements to be made,
graphs to be plotted, results processing required.
Be specific (pedantically so) e.g. when asked how to check
that a ruler was horizontal students answered that they
measured the height from the floor at both ends. They
were not awarded a mark as they omitted to say that they
check that both heights were the same.
You might also like
- Phys 91168 GuidelinesDocument8 pagesPhys 91168 Guidelinesapi-276915681No ratings yet
- As Level Physics Practical Paper 3Document7 pagesAs Level Physics Practical Paper 3Asif AyazNo ratings yet
- As Physics Practical NotesDocument6 pagesAs Physics Practical NotesUltramix100% (1)
- Physics Practical Skills (IGCSE)Document175 pagesPhysics Practical Skills (IGCSE)Mabrur Quaderi100% (1)
- Analysing Results and Assessing ValidityDocument6 pagesAnalysing Results and Assessing ValidityrahmaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Observations: Paper 4 - Alternative To Practical PaperDocument4 pagesMeasurement and Observations: Paper 4 - Alternative To Practical PaperjoeNo ratings yet
- ISA Preparation: 3 CourseworkDocument45 pagesISA Preparation: 3 CourseworkHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- AS Level Physics Practical Paper 3Document15 pagesAS Level Physics Practical Paper 3dulinawishwishNo ratings yet
- Lab ReviewDocument12 pagesLab ReviewAftab SaadNo ratings yet
- Skills Needed For Paper 6 (ATP)Document5 pagesSkills Needed For Paper 6 (ATP)Dhuhaa YusufNo ratings yet
- Lab ReviewDocument12 pagesLab ReviewEmaan MunsheyNo ratings yet
- AS Physics Practical Tips Notes - Formatted by Kaushik ReddyDocument8 pagesAS Physics Practical Tips Notes - Formatted by Kaushik Reddysathvikpranavaug28No ratings yet
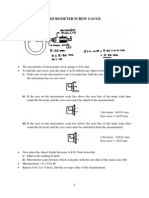
- Micrometer Screw GaugeDocument5 pagesMicrometer Screw Gaugepraphul4uNo ratings yet
- Experimental Methods For Results and UncertaintiesDocument8 pagesExperimental Methods For Results and UncertaintiesMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics PDFDocument42 pagesPhysics PDFashNo ratings yet
- AS Level Physics Practical Paper 3Document9 pagesAS Level Physics Practical Paper 3Rupali Samriddhi InalaNo ratings yet
- Graph TechDocument4 pagesGraph TechVision VictorNo ratings yet
- 9702 Physics Paper3Document3 pages9702 Physics Paper3Asmara Tayyeb100% (3)
- Chemistry ActivityDocument3 pagesChemistry ActivityRubz BulquerinNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Drawing GraphsDocument2 pagesGuidelines For Drawing GraphsLordJayNo ratings yet
- Physics and Physical Measurement: Topic 1.1 The Realm of Physics Range of Magnitudes of Quantities in Our UniverseDocument86 pagesPhysics and Physical Measurement: Topic 1.1 The Realm of Physics Range of Magnitudes of Quantities in Our UniversePeter LiNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Guide To Physics PracticalsDocument20 pagesCH 2 - Guide To Physics PracticalsNong Hm100% (2)
- Gceguide Com Resources Notes Physics 9702 Level Physics PracDocument14 pagesGceguide Com Resources Notes Physics 9702 Level Physics PracLio EditzNo ratings yet
- Physics P5 in 5 MinutesDocument2 pagesPhysics P5 in 5 Minutesyaseer786No ratings yet
- Practical Skills 4 - Evaluate Observations and DataDocument5 pagesPractical Skills 4 - Evaluate Observations and DatarobinsonNo ratings yet
- Physics (9702) Practicals - Tips & Points - Revise ZoneDocument12 pagesPhysics (9702) Practicals - Tips & Points - Revise Zonehamza100% (1)
- As Physics P3 Exam TipsDocument4 pagesAs Physics P3 Exam Tipsmtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- Graphs-Presentation of DataDocument5 pagesGraphs-Presentation of DataUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Experimental SkillsDocument6 pagesExperimental SkillsAkhilesh Maurya [USG]No ratings yet
- Ehsen Shaikh: Instructions For AS Practicals Type I QuestionsDocument5 pagesEhsen Shaikh: Instructions For AS Practicals Type I QuestionsiYaasirNo ratings yet
- 9702 Physics Practical ExamDocument8 pages9702 Physics Practical ExamIts Maria JerónimoNo ratings yet
- Physics P3 in 5 MinutesDocument3 pagesPhysics P3 in 5 MinutesMuneeb_2kNo ratings yet
- ATP NotesDocument17 pagesATP NotesAli LakhwairaNo ratings yet
- ATP - Guidelines and Expeimental TechniquesDocument9 pagesATP - Guidelines and Expeimental TechniquesHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Good Graphs:: Scaling Example: in A Given Experiment in Which The Current Is Being Measured, TheDocument2 pagesEssential Elements of Good Graphs:: Scaling Example: in A Given Experiment in Which The Current Is Being Measured, TheNahtanhoj TTenrabNo ratings yet
- Practical Physics Handbook (REVISED)Document6 pagesPractical Physics Handbook (REVISED)Fathin Khairunnisa0% (1)
- Rectilinear Motion Objectives: X V T A T V V A TDocument5 pagesRectilinear Motion Objectives: X V T A T V V A THastiti MurtiNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument3 pagesGraphsshana neilNo ratings yet
- Course Number, and Lab Title (In Words, Not A Number) On The First Page of The Lab ReportDocument2 pagesCourse Number, and Lab Title (In Words, Not A Number) On The First Page of The Lab ReportWilliam Andrew BrahamsNo ratings yet
- Graph Plotting Experiment ManualDocument3 pagesGraph Plotting Experiment ManualReem AlhadiNo ratings yet
- HistogramDocument10 pagesHistogramGalkandaNo ratings yet
- LaboratoryReporting Rethinkphysics BlogspotDocument2 pagesLaboratoryReporting Rethinkphysics BlogspotSuraj GopaulNo ratings yet
- General Tips For Paper 4Document4 pagesGeneral Tips For Paper 4Naillah SabaNo ratings yet
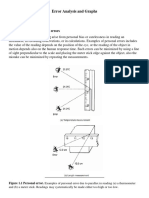
- Error Analysis and GraphsDocument8 pagesError Analysis and GraphsAli Almutairi100% (1)
- Error Analysis and PropagationDocument7 pagesError Analysis and Propagationpauljkt1No ratings yet
- Pratical Skills HandbookDocument30 pagesPratical Skills HandbookinayazeeshanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Written QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Written QuestionsSijNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The Philippines College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument13 pagesTechnological University of The Philippines College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentJeshua LloreraNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics - Flying Start: M0.2 Recognise and Use Expressions in Decimal and Standard FormDocument9 pagesAs Level Physics - Flying Start: M0.2 Recognise and Use Expressions in Decimal and Standard FormNiall QuadrosNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 (Lab Report) - Alban, Ronel D.Document4 pagesActivity 1 (Lab Report) - Alban, Ronel D.Ronel AlbanNo ratings yet
- Physics Atp TipsDocument2 pagesPhysics Atp TipsFehmeed Alchemy78% (9)
- Physics and Graph WorkDocument8 pagesPhysics and Graph WorkJharell CaravlhoNo ratings yet
- CC140 PPT Unit-1Document30 pagesCC140 PPT Unit-1hudasalhadinNo ratings yet
- A2 Edexcel Physics Unit 6 RevisionDocument45 pagesA2 Edexcel Physics Unit 6 RevisionNazrul mohammedNo ratings yet
- Plotting Graphs: There Are Lots of Different Types of GraphDocument4 pagesPlotting Graphs: There Are Lots of Different Types of GraphschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NOTES From Past PapersDocument3 pagesUnit 3 NOTES From Past PapersAlif37No ratings yet
- Best Physics Practical NotesDocument9 pagesBest Physics Practical NotesHuzaifah Punjani88% (25)
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Definition: A System of Linear Equations Is Said To Be Homogeneous If It Can Be Written in The Form A X 0. Otherwise, It Is Non-HomogeneousDocument8 pagesDefinition: A System of Linear Equations Is Said To Be Homogeneous If It Can Be Written in The Form A X 0. Otherwise, It Is Non-Homogeneousabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Mit18 06scf11 Ses2.5sumDocument4 pagesMit18 06scf11 Ses2.5sumabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Pureit Excella User Manual PDFDocument31 pagesPureit Excella User Manual PDFabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Social ScienceDocument4 pagesSocial Scienceabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Causes of Separation of East PakistanDocument27 pagesCauses of Separation of East Pakistanabdulrehman99969% (16)
- Practical 12 Object: Tasks: Working With Arrays in C++Document6 pagesPractical 12 Object: Tasks: Working With Arrays in C++abdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Practical-8 To 10Document18 pagesPractical-8 To 10abdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Benedict's Test For Reducing SugarDocument2 pagesBenedict's Test For Reducing SugarMohammed Parfals100% (2)
- Benedict's Test For Non-Reducing SugarsDocument2 pagesBenedict's Test For Non-Reducing SugarsSamer Ehab75% (4)
- Practical # 07 (16EL84)Document9 pagesPractical # 07 (16EL84)abdulrehman999No ratings yet
- English Grammar - LearnEnglish - British Council - Sentence StructureDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar - LearnEnglish - British Council - Sentence Structureabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Step-by-Step Calculator: Cosx Sin XDocument4 pagesStep-by-Step Calculator: Cosx Sin Xabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Mcqs - PaperpkinfoDocument8 pagesCost Accounting Mcqs - Paperpkinfoabdulrehman999100% (2)
- Exp00 - EA - Error Analysis PDFDocument14 pagesExp00 - EA - Error Analysis PDFUtkarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Mathematics 4004/2Document12 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council Mathematics 4004/2Tawananyasha Mukoriwo100% (6)
- 3-Fractions MergedDocument24 pages3-Fractions MergedZakaria SajolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument68 pagesChemistry WorksheetFaya MohammadNo ratings yet
- Lecture Pt. 3Document39 pagesLecture Pt. 3zy- SBGNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2022 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Primary Progression TestDocument10 pagesMathematics 2022 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Primary Progression TestTosu Nour100% (2)
- Numerical MethodsDocument132 pagesNumerical MethodsDISCOVERYNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 1-Mr 6points-1 - 095214Document101 pagesMath Paper 1-Mr 6points-1 - 095214Zacks Sibande87% (15)
- Lecture 1Document411 pagesLecture 1Hazrat AliNo ratings yet
- CSEC June 2008 Mathematics P1Document11 pagesCSEC June 2008 Mathematics P1Tamera GreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Units of Measurement and ApplicationDocument30 pagesChapter 3 Units of Measurement and ApplicationAaron KirkNo ratings yet
- CLASS 4 MathsDocument10 pagesCLASS 4 Mathsvincent adzinyoNo ratings yet
- Ambition Pulpy PhysicsDocument148 pagesAmbition Pulpy PhysicsRishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Week 1 & 2 (2) - For MergeDocument11 pagesWeek 1 & 2 (2) - For Mergelubna imranNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Term 1Document8 pagesScience Reviewer Term 1Sai KabilingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1Document47 pagesChemistry Chapter 1Madison CraterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5th Edition by Nivaldo J Tro ISBN Test BankDocument17 pagesChemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5th Edition by Nivaldo J Tro ISBN Test Bankkatherine100% (25)
- Higher Mathematics MathematicsDocument4 pagesHigher Mathematics MathematicsanzaaariNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Mathematics Chapter 1Document7 pagesForm 4 Mathematics Chapter 1Vincent Kok100% (25)
- 9702 w11 Er PhysicsDocument62 pages9702 w11 Er PhysicsmounirdNo ratings yet
- Oct 2022 Unit 2 MSDocument18 pagesOct 2022 Unit 2 MSEdexcelAcademyNo ratings yet
- Pushpalata British International School, Tirunelveli: Mock-1 (2021-2022) IGCSE MathematicsDocument14 pagesPushpalata British International School, Tirunelveli: Mock-1 (2021-2022) IGCSE MathematicssudeethNo ratings yet
- New Century Maths Year 8 Chapter 1Document34 pagesNew Century Maths Year 8 Chapter 1vivian25% (4)
- Uncertainties and Significant FiguresDocument3 pagesUncertainties and Significant FiguresMark Kevin AguilarNo ratings yet
- EURONORM 145 - 78 - Tinplate and Blackplate in Sheet Form Qualities, Dimensions and Tolerances PDFDocument16 pagesEURONORM 145 - 78 - Tinplate and Blackplate in Sheet Form Qualities, Dimensions and Tolerances PDFJaveed A. KhanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Math Question Paper 2 October/November 2004Document12 pagesIGCSE Math Question Paper 2 October/November 2004Mariam A.No ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY For First Years of Faculties of Science, Medicine and Pharmacy Part 1Document102 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY For First Years of Faculties of Science, Medicine and Pharmacy Part 1Mufaddal KaderbhaiNo ratings yet
- Static and Kinetic Coefficients of Friction of Plastic Film and SheetingDocument8 pagesStatic and Kinetic Coefficients of Friction of Plastic Film and SheetingekaNo ratings yet
- Reporting Results of Analysis of Water: Standard Guide ForDocument6 pagesReporting Results of Analysis of Water: Standard Guide ForSaravanan NatesanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 11th Notes PDFDocument99 pagesCHEMISTRY 11th Notes PDFMazar KhanNo ratings yet