Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Controlling jury access to information in trials
Uploaded by
Evangelides80%(20)80% found this document useful (20 votes)
6K views2 pagesThis document discusses principles of relevance and character evidence in trials. It provides guidance on:
1) Determining if evidence is relevant based on its probative value and if it relates to a fact of consequence in the case.
2) Conditional relevance where the relevance of evidence depends on establishing another fact.
3) Balancing the probative value of evidence against the risk of unfair prejudice as outlined in Rule 403.
4) Exceptions to the general prohibition on character evidence to prove conduct, including for defendants and victims in criminal cases.
Original Description:
two page attack outline for law school evidence course
Original Title
Evidence Attack Outline
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses principles of relevance and character evidence in trials. It provides guidance on:
1) Determining if evidence is relevant based on its probative value and if it relates to a fact of consequence in the case.
2) Conditional relevance where the relevance of evidence depends on establishing another fact.
3) Balancing the probative value of evidence against the risk of unfair prejudice as outlined in Rule 403.
4) Exceptions to the general prohibition on character evidence to prove conduct, including for defendants and victims in criminal cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
80%(20)80% found this document useful (20 votes)
6K views2 pagesControlling jury access to information in trials
Uploaded by
EvangelidesThis document discusses principles of relevance and character evidence in trials. It provides guidance on:
1) Determining if evidence is relevant based on its probative value and if it relates to a fact of consequence in the case.
2) Conditional relevance where the relevance of evidence depends on establishing another fact.
3) Balancing the probative value of evidence against the risk of unfair prejudice as outlined in Rule 403.
4) Exceptions to the general prohibition on character evidence to prove conduct, including for defendants and victims in criminal cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
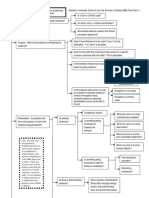
Controlling jury access to info
1)
d)
POLICY: trials must end, constitutional limits, privacy and
privileged communications, Unlike a bench trial, jury verdict
reasons are off limits to review: Goal right result
e)
General Principles of Relevance
2)
3)
4)
Probativeness and Materiality = Relevant
a)
401: Evidence is relevant if:
b)
401a: Probative= evidence that has a tendency to make a
fact more or less probable- Brick not wall (bare relevance)
c)
401b: Material= fact is of consequence in deciding the
matter (conditionally Relevant)
d)
ANALYSIS: what does evidence show?
e)
STANDARD: Preponderance of the Evidence- more likely
than not- inference
f)
402: Evidence Admissible Unless Prohibited by:
Constitution, Federal Statute, FRE/SCOTUS rules
g)
US v James- what D believed true was corroborated by
wrongfully excluded evidence- overturned exclusion
Conditional Relevance: exists in context
a)
104b: Relevance that depends on a fact. When the
relevance of evidence depends on whether a fact exists,
proof must be introduced sufficient to support a finding
that the fact does exist. The court may admit the proposed
evidence on the condition that the proof be introduced
later.
b)
104b STANDARD: Preponderance of the Evidence- more
likely than not (inference)
c)
Cox v State- testimony dependent on inference of what
reasonably known by D- jury can use common sense to
assess
Probativeness v Risk of Unfair Prejudice
a)
ANALYSIS- always do 403 analysis even if evidence is
admissible under other rules
b)
403: Excluding Relevant Evidence. Fact intensive
balancing test. court may exclude relevant evidence if its
probative value is substantially outweighed by a danger of
one or more of the following: unfair prejudice, confusing
the issues, misleading the jury, undue delay, wasting time,
or needlessly presenting cumulative evidence. However,
we do not force Ps to present case through stipulation
alone- nuances
c)
STANDARD- deference to trial judge
d)
GOAL: present evidence with fair weight
e)
ANALYSIS: look for improper influence evidence will
show a propensity for crime; Who is the target of the
prejudice? The D or perpetrator?
f)
State v Bocharski- Relevant evidence (6 gruesome
photos) should be excluded when the probative value of
the evidence is outweighed by the risk of prejudice to a Dcould have admitted fewer
g)
Tyco Videotape- over the top birthday party edited for
prejudice
h)
US v James- documentation of Vs crimes can lead jury to
ask did he do it? instead of, what did she believe?- Unfair
prejudice- evidence that makes the jury want to come to a
conclusion not based on the evidence but based on a
another motivation- like emotion
i)
People v Collins- mathematical odds based on unvalidated estimates are not admissible as evidence to
identify a D in a criminal proceeding- cast a light not a
spell do not usurp juries ability to assess defects beyond
the math
j)
Old Chief v US- to present prejudicial evidence
unfettered would encourage construction of cases in such
a way as to not try cases on their own merit,
k)
If it violates 404 it also violates 403- if the probative
value does not substantially outweigh the prejudice
f)
g)
h)
i)
j)
k)
l)
m)
n)
o)
p)
q)
6)
7)
8)
9)
Subsequent Remedial Measures
a)
407: Fixing After Harm Bars subsequent remedial
measures (by D) to prove negligence, culpable conduct,
product defect, or need for warning, may be admitted
(unless negotiate otherwise) to impeach or, if disputed,
prove ownership, control, feasibility- do 403 test
b)
POLICY: encourage fixing after harm
Compromise offer/Payment of Med. Exp.
a)
408: Compromise Cant use settlement talks (after claim
is made) to show disputed liability or to impeach, may be
admitted to prove witness bias, lack of undue delay, or
efforts to obstruct criminal investigation
b)
POLICY: may be motivated by desire for peace,
encourage compromise
c)
409 Medical Expenses specific statements to pay cant be
used to prove liability
d)
POLICY: encourage humane impulse/assistance
Liability Insurance
a)
411 Liability insurance cant be used to prove negligence
or wrongful action, may be used to prove witness bias or
agency, ownership, or control
b)
POLICY: unlikely insured are more careless than the
uninsured- discourages a windfall for P
c)
Williams v McCoy- cure wrong application by giving
jury limiting instructions
Pleas in Criminal Cases
a)
410 Pleas bars admittance against D of guilty please later
withdrawn, nolo contender plea, statements in plea
proceedings, statements in plea talks with P, may be
admitted for perjury prosecution if under oath, on record,
and in counsels presence- may not be used to impeach, D
can use, P can not
b)
POLICY: exclusion promotes plea bargaining, innocent
party may plead guilty to avoid risks of trial- no barriers to
pleas
Constitutional exception- criminal Ds have right to a defense and
right to confrontation- 6th am. Due process right
Character Evidence
10)
The Character-Propensity Rule
a)
Meant to Prevent:
i)
unfair prejudice- jury may give excessive weight,
or a preventative conviction 1) jury could fear
greater danger, or think 2) deserves punishment
ii)
Juror Confusion and Waste of Time
b)
404a1 Prohibited Uses of Character Evidence. Evidence
of a persons character or character trait is not admissible
to prove that on a particular occasion the person acted in
accordance with it.
c)
404a2 Exceptions for a D or V in a Crim. Case
12)
13)
Impeachment and Character for Truthfulness
14)
15)
r)
s)
t)
11)
See 404b2, above
General relevance test- is it a brick?
Special relevance two part testi)
does the evidence have special relevance on a
material issue independent of its tendency to show
propensity?
(1)
an exact match to prove is not necessary
(2)
the sum of lesser features does have
significant probative value- even when
individually they may not be sufficient
ii)
then apply 403 balancing test
u)
on appeal examine for abuse of discretion
v)
make at least two logical connections
i)
connect D and the past conducteven if acquitted,
or accusations
ii)
connect the past conduct and the charged offense
w)
when judging the probative nature of the special skill
the larger the pool of people who know how to do that
skill the less probative the evidence is
x)
A motion in limine- a hearing to eliminate evidence at the
threshold of the trial- before the trial begins
y)
US v Trenkler- proper to allow evidence of another
bombing because the two bombings were so similar. The
court also found that no prejudice to D existed.
i)
flaws go to weight not admissibility
z)
Huddleston Standard: given 404(b)2 Could a reasonable
jury looking at all the evidence find this fact by a
preponderance of the evidence possible? Does not have to
be a conviction (Conditional relevance)
i)
4 sources of protection against unfair prejudice
(1)
404b- evidence offered for a proper
purpose
(2)
402/104b- must be relevant
(3)
403- is probative value substantially
outweighed by potential for unfair
prejudice
(4)
105- limiting instr. to jury
Propensity Evidence- Sexual Assault Cases
a)
Exceptions to 404- 403/hearsay still apply
b)
Presumption for admittance no SoL
c)
Requires testimony of specific acts
d)
Disclosure to the D. If P intends to offer evidence, the P
must disclose it to the D, including Ws statements or a
summary of the expected testimony. The P must do so at
least 15 days before trial or at a later time that the court
allows for good cause.
e)
413a permitted uses. In a criminal case in which D is
accused of sexual assault, may admit evidence that the D
committed any other sexual assault, may be considered on
any matter relevant.
f)
413b See disclosure above
g)
414a Permitted Uses. In criminal case in which D is
accused of child molestation, may admit evidence that the
D committed any other child molestation, may be
considered on any matter relevant.
414b See disclosure above
415a Permitted Uses. In a civil case involving a claim for
relief based on a partys alleged sexual assault or child
molestation, the court may admit evidence that the party
committed any other sexual assault or child molestation.
The evidence may be considered as provided in 413/414
j)
415b See disclosure above
k)
US v Guardia- Analysis.
i)
Three threshold requirements
(1)
Accused of Sex offense
(2)
Evidence of commission of another sex
offense
(3)
Must be relevant
ii)
Then balance (403) and consider if the prejudicial
effect of the evidence can be minimized through a
less elaborate method of presentation
l)
US v Mound- the cautionary instruction to the jury
guarded against unfair prejudice, and in light of the
instruction, the court exercised its discretion in a proper
manner.
Proof of the Ds and the Vs Character
a)
See 404a2A and 404a2B
b)
405 Methods of Proving Character
c)
(a) By Reputation or Opinion. When a persons
character or character trait is admissible, it may be proved
by reputation/opinion. On cross-examination of character
W, the court may allow an inquiry into relevant specific
instances of the persons conduct.
d)
(b) By Specific Instances of Conduct. When a persons
character or character trait is an essential element of a
charge, claim, or defense, the character or trait may also
be proved by relevant specific instances of the persons
conduct.
Evidence of Habit
a)
406 Habit: Routine Practice Evidence of a persons habit
or an organizations routine practice may be admitted to
prove that on a particular occasion the person or
organization acted in accordance with the habit or routine
practice. The court may admit this evidence regardless of
whether it is corroborated or whether there was an
eyewitness.
i)
Habit is a repetitive pattern of conduct that is
so regular it is predictable
ii)
Habit is an automatic action done almost
without volition
(1)
Not violence (fact dependent) or drinking
(Disease)
h)
i)
Routes around the box
Specialized Relevance Rules- Public Policy
5)
404a2A D can offer evidence to build their own charactersubj. to rebuttal
404a2B D may offer evidence of Vs pertinent trait- subj.
to rebuttal, 412 and evidence of Ds same trait; Im
violent- youre violent
404a2C in homicide case P may offer evidence of Vs trait
of peacefulness
404a3 Exceptions for a Witness- evidence of a Ws
character may be admitted see 607, 608, 609
404b Crimes, Wrongs or Other Acts
404b1Prohibited Uses: evidence of a crime, wrong, or
other act is not admissible to prove a persons character in
order to show that on a particular occasion the person
acted in accordance with that character
404b2Permitted Uses: civil or criminal -may be
admissible to prove motive, opportunity, intent, prep, plan,
knowledge, identity, absence of mistake, or lack of
accident.
404b2A on request P must provide notice of use,
404b2B unless judge excuses for good cause
i)
and then do 403 analysis
NOTE: scope of cross exam will match the Ds witnesses
testimony- this is why the defense does not usually bring
in character evidence- the P can go after anything brought
up- very broad!
i)
You can narrow the testimony to just
peacefulness- P could not then bring in conduct
about lying
Michelson v USi)
P is not allowed to introduce evidence of Ds evil
character to establish probability of guilt.
ii)
However, if a D calls a character W then the P
may pursue the inquiry for the limited purpose of
impeaching the Ws credibility.
iii)
POLICY: character Ws are only believable if can
establish they know character of the D.
see 413, 414, 415 May allow proof of sexual propensities
in sex offense trials
People v Zackowitz- In a criminal prosecution, character
is never an issue unless the D chooses to make it one.
ANALYSIS: Explain that it is character trait and P is only
introducing to try to show that D did this act on this day
i)
401 and 402- is it relevant? propensity is relevant
but not admissible under 404b
ii)
404- not admissible- prosecution cannot introduce
evidence of Vs character
(1)
go ahead and argue that the prior act is
evidence of skill or knowledge- but know
it is not likely to win the day if it is not
unique
iii)
405- methods of proving character(1)
defense brings up by reputation or opinion
only
(2)
prosecution can respond with specific
acts, cross examination, and their own
witnesses
iv)
then go to 403- was the probative value
substantially outweighed by the prejudicial nature
of the evidence
(1)
speculative = inadmissible
(2)
how probative is it? Too much of a good
thing?
v)
Then go to 105 for a limiting jury instruction
16)
17)
Modes of impeachment Cast doubt on the Ws accuracy or
trustworthiness
Non-Character- Based Impeachment
a)
ERROR: calling a witness mistaken
i)
challenge- not by character but by traits:
(1)
Their perception- poor eyesight, hearing,
lighting
(2)
Their memory- passage of time, witnesss
age
(3)
Their narrative skills- suggest the witness
misspoke
ii)
Offer counter witnesses
iii)
Thresholds 401 and 403
b)
LIE: suggest W lying now, one lie at a time, not that have
a tendency to lie non-character based accusation
i)
Contradict with conflicting evidence
ii)
Contradict with past inconsistent statement
iii)
Present evidence of bias-like motive
Impeachment by Opinion, Reputation, and Cross Examination
about Past Lies
a)
Character based impeachment- 404a3 authorizes
evidence of a witnesss character for truthfulness as
permitted by:
i)
607- Any party, including the party that called the
W, may attack the Ws credibility
ii)
608a Reputation or Opinion Evidence. permits
any litigant to offer evidence of a witnesss
character for truthfulness or untruthfulness in the
form of opinion or reputation (not peacefulness,
temperance, etc) (bias is not character)
iii)
608b Specific Instances of Conduct. on cross
examination any party may ask a witness about
specific instances of a witnesss conduct if
probative of propensity to lie or speak the truthbut It is a dead end if they lie- no extrinsic
evidence can be offered
(1)
no restriction on evidence to show witness
lied in this case
Impeachment with Past Convictions
a)
609- may impeach with past conviction of a sufficiently
serious or deceptive crime
b)
609a1 if crime was punishable by death or imprisonment
for more than one year,
c)
609a2 crime involved dishonesty and false statementsespecially probative of ones propensity to lieautomatically admissible
i)
subject to 609b, 609c, 609d
ii)
not subject to 403
iii)
differentiate between deceit and stealth- sneaking
up or in is not a lie
iv)
must be readily apparent that the elements of the
crime required deceit or dishonesty- no mini trials
d)
609b rebuttable presumption on Limit for Using
Evidence After 10 Years from conviction or release from
jail (which ever is later) to date of
indictment, presumption that it will come in unless
substantially outweighed by prejudice and must give
adverse party reasonable written notice of intent- so has
opportunity to contest.
e)
609c Not admissible if Pardoned, Annulled, or issues a
Certificate of Rehabilitation.
f)
609d juvenile adjudications are never admissible in civil
cases or to impeach the testimony of criminal Ds
g)
Us v Breweri)
609a balancing test- the probative value of the
evidence must outweigh its prejudicial effect (not
18)
like 403 where it must substantially outweigh)
Factors:
(1)
Nature of the crime- Violence does not
speak to honesty or veracity
(2)
Time of conviction and subsequent
history Does time lapse demonstrate
rehabilitation?
(3)
Similarity between past crime and
charged crime- too similar a crime is
prejudicial- he did it again
(4)
Importance of Ds testimony
(5)
Centrality of the credibility issue
h)
Luce v US- Conditions for appeal: D may not appeal 609
ruling unless two conditions met:
i)
The D must have testified at trial
ii)
The P must have introduced evidence of the
contested conviction
i)
Ohler v US- once a D admits a prior conviction in court,
they forfeit the right to appeal the decision that the
evidence was admissible.
Rehabilitation, Use of Extrinsic Evidence
a)
Can rehabilitate after an attack by offering evidence of
truthful character consistent with rule 608
b)
Bias Is not character evidence- can offer evidence
supporting truthfulness in this case- not general character
for truthfulness
c)
On cross examination specific act can be asked about a W
truthfulness- attacking their character for truthfulness, but
state can take steps to rehabilitate
i)
the door to character evidence has been opened by
the attack
ii)
bolster his truthfulness by bringing in character
evidence about his reputation for truthfulness
(1)
not about specific act which would be
extrinsic evidence about a specific act
(2)
not ask about an extenuating
circumstances or justification
d)
if witnesss testimony is not challenged you can still bring
in witnesses to support the facts in the statement but not to
bolster your witnesses truthfulness without an attack on
that truthfulness
e)
EVIDENCE ANALYSIS
i)
Identify the purposes of introducing the evidencecould be multiple
ii)
Is one of the purposes UNRELATED to the
character for truthfulness
(1)
If only relates to character not allowed to
talk about specific instances
(2)
But if there is a purpose otherwise
iii)
If yes, is that purpose otherwise permissible (eg
under rule 404)
iv)
If yes, are there any other reasons to exclude it (eg
403 balancing)
f)
Bias is exculpatory not character and may be established
by extrinsic evidence
g)
BALANCING STANDARDS
i)
criminal witness not the D- use 403- is the
probative value is substantially outweighed by the
risk of unfair prejudice
ii)
criminal D- stricter 403- does the probative value
of the evidence outweigh its prejudicial effect (not
substantially) more like preponderance of the
evidence
iii)
juvenile adjudication evidence- only if admitting
the evidence is necessary to fairly determine guilt
or innocence
iv)
evidence of 10year+ since convicted or released
from confinement- presumption of
inadmissibility- wouldve to be very relevant
v)
perjury- is admissible unless it is over 10 years
old or in a juvenile adjudication
vi)
larsony- not admissible if punishable by less than
a year and does not involve deceit- more likely
involves stealth
The Rape Shield Law
h)
i)
j)
k)
l)
m)
n)
o)
p)
Factors for proving rape:
i)
Prove actual physical resistance by V
ii)
Prove substantial force by aggressor
iii)
Show corroboration of the Vs account
iv)
Penalize Vs who do not promptly complain
v)
Vs prior sexual history goes to Consent and
Credibility
vi)
Policy for change: V being violated by both
aggressor and the justice system
412a Prohibited Uses. The following evidence is not
admissible in a civil or criminal proceeding involving
alleged sexual misconduct:
i)
(1) evidence offered to prove that a V engaged in
other sexual behavior; or
ii)
(2) evidence offered to prove a Vs sexual
predisposition.
412b Exceptions.
412b1 Criminal Cases. The court may admit the
following evidence in a criminal case:
412b1A evidence of specific instances of a Vs sexual
behavior, offered to prove that someone other than the D
was source of semen, injury, or other physical evidence;
412b1B evidence of specific instances of a Vs sexual
behavior with respect to the person accused of the sexual
misconduct, if offered by the D to prove consent or if
offered by the P;
412b1C evidence whose exclusion would violate the Ds
6th Am. rights.
412b2 Civil Cases. may admit evidence offered to prove
a Vs sexual behavior or sexual predisposition if its
probative value substantially outweighs the danger of
harm to any V and of unfair prejudice to any party. The
court may admit evidence of a Vs reputation only if the V
has placed it in controversy.
412c Procedure to Determine Admissibility.
q)
412c1 Motion. If a party intends to offer evidence
under Rule 412(b), the party must:
412c1A file a motion that specifically describes the
evidence and states purpose for which it is to be offered;
s)
412c1B 14 days before trial
t)
412c1C serve the motion on all parties
u)
412c2 Hearing. Before admitting evidence must conduct
an in camera hearing and give right to be heard. Unless
court orders otherwise, the motion, related materials, and
record of the hearing must be sealed.
v)
ANALYSIS- look at 3 exceptions in 412 and 404/403
i)
Requirements: needs to be critical to the defense
and have strong markers of trustworthiness
Rape Law in Force
a)
State v Smith- We do not consider prior false allegations
of sexual misconduct to be sexual behavior
b)
Olden v Kentucky- The 6th Am. right to be confronted
with the witnesses against the accused, includes the right
to conduct reasonable cross-examination.
s)
r)
19)
t)
u)
v)
w)
x)
y)
Competency of Witnesses
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
601- everyone is competent unless they are not
602- A W may testify to a matter only if evidence is
introduced sufficient to support a finding that the W has
personal knowledge of the matter. Evidence to prove
personal knowledge may consist of the Ws own
testimony. This rule does not apply to a Ws expert
testimony under Rule 703.
603- Before testifying, a W must give an oath or
affirmation to testify truthfully. It must be in a form
designed to impress that duty on the Ws conscience.
610 Evidence of a Ws religious beliefs or opinions is not
admissible to attack or support the Ws credibility.
Childs Competency Factors:
i)
If perceive and remember events accurately
ii)
If child can communicate effectively
iii)
If understands difference between truth and
falsehoods and the obligation to tell the truth
iv)
If child can respond intelligibly to questions posed
on cross examination
POLICY: Opposing party needs to be able to cross
The Rule Against hearsay
20)
Defining Hearsay (must do a 403 weighing)
a)
801 Exclusions to Hearsay The following definitions
apply under this article:
b)
801a Statement. Statement means a persons oral or
written assertion, or nonverbal conduct, if person intended
it as an assertion.
c)
801b Declarant. Declarant means the person who made
the statement.
d)
801c Hearsay. Hearsay means statement that:
i)
801c1 declarant does not make while testifying at
current trial or hearing; &
ii)
801c2a party offers in evidence to prove the truth
of the matter asserted
e)
801d Statements That Are Not Hearsay. If meets the
following conditions not hearsay:
f)
801d1 A Declarant-Witnesss Prior Statement. The
declarant must testifies and is subject to crossexamination about a prior statement, and the statement:
g)
801d1A is inconsistent with the declarants testimony and
was given under penalty of perjury at a trial, hearing, or
other proceeding or in a deposition;
h)
801d1B is consistent with the declarants testimony and is
offered
i)
to rebut an express or implied charge that the
declarant recently fabricated it or acted from a
recent improper influence or motive, or
ii)
to rehabilitate the declarant's credibility as a
witness when attacked on another ground; or
i)
Tome v US- A consistent statement that predates the
motive is a square rebuttal of the charge that the testimony
was contrived as a consequence of that motive
j)
801d1C identifies a person the declarant saw earlier.
k)
801d2 An Opposing Partys Statement. The
statement is offered against opposing party &:
l)
801d2A was made by the party in an individual or
representative capacity;
m)
801d2B is one the party manifested that it adopted or
believed to be true;
n)
801d2C was made by a person whom the party authorized
to make a statement on the subject;
o)
801d2D was made by the partys agent or employee on a
matter within the scope of that relationship and while it
existed; or
p)
801d2E was made by the partys coconspirator during and
in furtherance of the conspiracy.
i)
Conspiracy existed at time statement made
ii)
Conspiracy included both parties
iii)
Made in the course of or furtherance of the
conspiracy
q)
ANALYSIS:
i)
Is it hearsay? Was the statement meant to
communicate or was assertive conduct?
(1)
A threat can be by verbal conduct NH
(2)
Are the words asserting ToM?
(3)
Reputation is hearsay
ii)
Non hearsay uses of out of court statement:
(1)
Impact on listener
(2)
Prove legal right or duty
(3)
Inconsistent statement to impeach
(4)
Involuntary expressions
r)
803 Exceptions Applicable Regardless of the
Declarants availability
i)
present sense impressions
ii)
excited utterances
iii)
Stmts of the existing mental, emotional or
physical condition
iv)
Stmts made for medical diagnosis or treatment
v)
recorded recollections
vi)
Business Records
vii)
Public Records and Reports
804 Exceptions applicable only when the Declarant is
Unavailable
i)
Former Testimony- predecessor in interest crossed
ii)
Dying declarations- must think dying
(1)
St. of mind- future more weight than past
iii)
Statements against interest- pecuniary or jail
iv)
Forfeiture by wrongdoing
US v Owens neither the Confrontation Clause nor FRE
802 is violated by admission of an identification statement
by a witness who is unable, because of memory loss, to
testify concerning the basis of the identification.
US V Duenas- Does the old the cross have same objective
807 Residual Exception- best evidence of a material fact
i)
look for trustworthiness and to serve justice
612- refresh a Ws memory if exhausted
803(5)- Recorded Recollection- W must be on stand and
unable to recall well enough to testify fully and
accurately- records made when memory fresh and
accurately reflects Ws knowledge
US v Ince Under 607, a Ws credibility may be attacked
through impeachment testimony, but when testimony lacks
any probative value and carries a high risk of prejudice,
the evidence must be excluded, even when it meets the
technical requirements of Rule 607
Confrontation and Compulsory Process
21)
22)
23)
24)
25)
26)
27)
28)
29)
30)
Confrontation Clause 6th Am. In all criminal prosecutions, the
accused shall enjoy the ...right to be confronted with the witnesses
against him.
Crawford Rule: Testimonial Hearsay must be excluded unless 1)
the declarant is available at trial for cross, or 2) the declarant is
unavailable and the D, against whom the statement is sought to be
introduced, had an earlier opportunity to cross the declarant.
Testimonial: Preliminary hearing testimony, grand jury testimony,
former trial testimony, statements made in police interrogations.
Primary Purpose Test: If the purpose of the questioning was to
enable police to respond to an ongoing emergency.
Reliability Test: Does the statement have the indicia of reliability.
Documents: Documents reporting the results of tests implicate the
Confrontation Clause. Need lab tech.
Solemnity Test: Is the statement formal.
Does not apply: Statement not offered for its truth, offered in civil
cases or against P, declarant is a W at trial, the declarant is
unavailable and was previously cross examined about statement,
Ds wrongdoing, statement is nontestimonial.
The Bruton held that a defendants confrontation clause rights are
violated when a non-testifying codefendants confession naming
the defendant as a participant in the crime is introduced at their
joint trial, even if the jury is instructed to consider the confession
only against the defendant. Later decisions say limiting
instructions can be given and the statement redacted to eliminate
not only Ds name but their very existence!
Compulsory Process
a)
Will arise when D is trying to bring in evidence for his
defense and he is denied the admission of that evidence.
Not all evidence is admissible though.
i)
Evidence must be critical.
ii)
Evidence must be especially trustworthy.
Lay Opinions and Expert Testimony
31)
32)
33)
34)
701 Lay Opinions: Testimony as opinion limited to: rationally
based on witnesss perception; not based on scientific, technical,
or other specialized knowledge within the scope of 702.
702 Expert Testimony: Qualified expert may testify in the form
of an opinion or otherwise if: (a) experts scientific, technical or
otherwise specialized knowledge will help the trier of fact to
understand the evidence or determine a fact in the issue; (b) the
testimony is based on sufficient facts or data; (c) the testimony is
the product of reliable principles and methods; and (d) the expert
has reliably applied the principles and methods to the fact in the
case. Note: opinion can be based on inadmissible info as long as
reasonably relied on by experts in the field. IF the facts or data
would otherwise be inadmissible, the proponent may disclose
them to the jury only if the probative value in helping the jury
substantially outweighs their prejudicial effect. [703]
Mental State: No opinion of about mental state or condition that
constitutes an element of the crim. Matter for ToF. [704]
Ideas: W can be challenged on cross about facts, data, or methods
Authentication, Identification, and the Best Evidence Rules
35)
36)
37)
38)
To satisfy the requirement of authenticating or IDing an item of
evidence, the proponent must produce evidence sufficient to
support a finding that the item is what the proponent claims it is.
Examples:
a)
Testimony of W with knowledge;
b)
Non-Expert opinion about handwriting;
c)
Comparison by expert W or the ToF;
d)
Distinctive characteristics and the like;
e)
Opinion about a voice - Heard first hand or through
transmission or recording.
f)
Evidence about a phone conversation; evidence that a call
was made to the number assigned to:
i)
a particular person showing that the person
answering was the person
ii)
A particular business and the call related to
business reasonably transacted over phone
g)
Evidence about public records (excludes police reports)
i)
document was recorded or filed in public office as
authorized by law; or
ii)
a purported public record or statement is from the
office where this kind of item is kept.
h)
evidence about ancient document or data;
i)
In a condition that create no suspicion about it
authenticity and was as in a place where if
authentic it would likely be
The Best Evidence Rule A writing, recording or photograph in its
original form. Original is not required if all the originals are lost,
or destroyed and not in bad faith; or an original cannot be obtained
by available judicial means. Duplicates may be offered unless
there is a genuine question as to the authenticity of the original or
it would be unfair to admit the duplicate.
Note: Rule only applies when a party seeks to prove the contents
of the writing, not when it is used for some other purpose.
You might also like
- Business Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10From EverandBusiness Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10No ratings yet
- Evidence Outline and Case ChartDocument24 pagesEvidence Outline and Case ChartMichael Mroczka0% (1)
- lesSummaryChart Spring2012Document7 pageslesSummaryChart Spring2012kates218100% (13)
- Evidence Attack OutlineDocument12 pagesEvidence Attack OutlineArghavanPezeshkian100% (5)
- Passing the Uniform Bar Exam: Outlines and Cases to Help You Pass the Bar in New York and Twenty-Three Other States: Professional Examination Success Guides, #1From EverandPassing the Uniform Bar Exam: Outlines and Cases to Help You Pass the Bar in New York and Twenty-Three Other States: Professional Examination Success Guides, #1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Evidence Outline Fall 2018Document22 pagesEvidence Outline Fall 2018Rebecca WadeNo ratings yet
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume II of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Evidence, Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Constitutional Criminal Procedure: Law School Survival GuidesFrom EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume II of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Evidence, Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Constitutional Criminal Procedure: Law School Survival GuidesNo ratings yet
- Evidence Outline - Fisher CasebookDocument83 pagesEvidence Outline - Fisher Casebookice8080100% (6)
- Evidence, Law Essentials: Governing Law for Law School and Bar Exam PrepFrom EverandEvidence, Law Essentials: Governing Law for Law School and Bar Exam PrepNo ratings yet
- EVIDENCE CHECKLIST FOR RELEVANCE, AUTHENTICATION, AND CHARACTERDocument7 pagesEVIDENCE CHECKLIST FOR RELEVANCE, AUTHENTICATION, AND CHARACTERnicole100% (1)
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesFrom EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesNo ratings yet
- Rules Short Sheet (Evidence)Document4 pagesRules Short Sheet (Evidence)bcarroll89No ratings yet
- Law School Evidence OutlineDocument12 pagesLaw School Evidence Outlinem10simonNo ratings yet
- Evidence OutlineDocument24 pagesEvidence OutlineMary Wang100% (1)
- Evidence Study Guide: Relevance, Character, Hearsay, and MoreDocument51 pagesEvidence Study Guide: Relevance, Character, Hearsay, and MoreJimmy SnodgrassNo ratings yet
- Character Evidence ChartDocument1 pageCharacter Evidence Chartabassos100% (9)
- Evidence Attack SheetDocument11 pagesEvidence Attack SheetRebecca Stokoe-Gray100% (11)
- Evidence RULES OutlineDocument10 pagesEvidence RULES OutlineBrooke Clarke100% (4)
- Evidence FlowchartDocument4 pagesEvidence Flowchartmitchturb100% (3)
- EvidenceOutline MGGDocument226 pagesEvidenceOutline MGGJohnny Thach93% (14)
- Evidence Chart - HeasayDocument1 pageEvidence Chart - Heasayalinap0533% (3)
- Federal Rules of Evidence FlowchartDocument1 pageFederal Rules of Evidence FlowchartTraci Diamond100% (7)
- Evidence Checklist 11Document5 pagesEvidence Checklist 11afisher-poguelaw100% (11)
- Evidence RulesDocument18 pagesEvidence RulesChristina Hou100% (1)
- Evidence OutlineDocument49 pagesEvidence Outlinefallingup77100% (9)
- Hearsay Definition and Exceptions in 40 CharactersDocument1 pageHearsay Definition and Exceptions in 40 CharactersJennifer Koerner100% (3)
- Rulings and Evidence Admissibility GuideDocument12 pagesRulings and Evidence Admissibility Guidetamu12100% (3)
- Evidence Attack Outline SummaryDocument10 pagesEvidence Attack Outline Summaryseabreeze100% (3)
- Backward Looking - Everyday Decisions Look Forward, But Courts Determine Historical FactDocument28 pagesBackward Looking - Everyday Decisions Look Forward, But Courts Determine Historical FactMegan KelbermanNo ratings yet
- RELEVANCE 401Document15 pagesRELEVANCE 401Brigette MerzelNo ratings yet
- Evidence FlowchartDocument2 pagesEvidence Flowchartsuperxl200989% (9)
- Evidence Outline-ALL RULESDocument33 pagesEvidence Outline-ALL RULESTyb50% (2)
- Evidence Outline (Concannon)Document76 pagesEvidence Outline (Concannon)Kaycee100% (1)
- Evidence ChartDocument12 pagesEvidence Chartadmiral30100% (19)
- Admissibility of Evidence FlowchartDocument10 pagesAdmissibility of Evidence FlowchartViana83100% (24)
- HugeFIU Evidence OutlineDocument78 pagesHugeFIU Evidence OutlineBrian Robert Kaam100% (2)
- 4A Analysis of Gov't Searches and Warrant ExceptionsDocument1 page4A Analysis of Gov't Searches and Warrant Exceptionsstephanie100% (1)
- Evidence Big Picture FlowchartDocument3 pagesEvidence Big Picture Flowchartweichoong92% (12)
- Evidence: FRE 104 - Preliminary QuestionsDocument77 pagesEvidence: FRE 104 - Preliminary QuestionsLeah_McLaughli_77691% (11)
- Federal Rules of Evidence ChartDocument20 pagesFederal Rules of Evidence ChartRebecca LB100% (2)
- Final Evidence OutlineDocument90 pagesFinal Evidence Outlinecandigirl5100% (4)
- Evidence Essay Issue SheetDocument4 pagesEvidence Essay Issue Sheettara100% (7)
- Relevancy (FRE 401)Document14 pagesRelevancy (FRE 401)seabreeze100% (1)
- Is It Hearsay?Document1 pageIs It Hearsay?Alex Faris0% (1)
- Character E FlowchartDocument2 pagesCharacter E Flowchartmischa29No ratings yet
- CEC Vs FREDocument3 pagesCEC Vs FRElawschool2013No ratings yet
- Evidence OutlineDocument66 pagesEvidence Outlinechicho953100% (9)
- Most Important Federal Rules of EvidenceDocument21 pagesMost Important Federal Rules of EvidenceJanelle Grigaitis100% (2)
- Obscenity and Indecency Case Law EvolutionDocument5 pagesObscenity and Indecency Case Law EvolutionBrittany Johnson100% (1)
- First Amendment 2011Document62 pagesFirst Amendment 2011DavidFriedmanNo ratings yet
- I. Types of Courtroom EvidenceDocument64 pagesI. Types of Courtroom EvidenceErick Edson100% (2)
- Con Law OutlineDocument25 pagesCon Law OutlineNader80% (5)
- Evidence Attack OutlineDocument2 pagesEvidence Attack OutlinePaulStaplesNo ratings yet
- Evidence AND: Evidence Outline W/O Hearsay I. Relevance (FRE 401 and 403)Document12 pagesEvidence AND: Evidence Outline W/O Hearsay I. Relevance (FRE 401 and 403)no contractNo ratings yet
- Relevance and Admissibility of EvidenceDocument18 pagesRelevance and Admissibility of EvidenceksskelsoNo ratings yet
- Multiple evidentiary issuesDocument15 pagesMultiple evidentiary issuesSean Austin Parker-O'Grady Pog100% (1)
- Character Evidence Rules: Introduction of Evidence Sufficient To Support A FindingDocument18 pagesCharacter Evidence Rules: Introduction of Evidence Sufficient To Support A FindingTanishka Vanessa CruzNo ratings yet
- Heavold Short Evidence OutlineDocument17 pagesHeavold Short Evidence OutlineChristopher YoungNo ratings yet
- Legal Professional Responsibility QuotesDocument1 pageLegal Professional Responsibility QuotesEvangelidesNo ratings yet
- 1L Contracts OutlineDocument10 pages1L Contracts OutlineEvangelides100% (3)
- Tax Outline 2014Document62 pagesTax Outline 2014EvangelidesNo ratings yet
- 1L Fall Civ Pro OutlineDocument11 pages1L Fall Civ Pro OutlineEvangelides100% (1)
- CSC V Magnaye FTDocument10 pagesCSC V Magnaye FTLuz Celine CabadingNo ratings yet
- R.A. No. 10022Document47 pagesR.A. No. 10022Sonny MorilloNo ratings yet
- Rafael Nadyahan V PeopleDocument1 pageRafael Nadyahan V PeopleJcoy BaccayNo ratings yet
- TMP 1679 12-16-2022 12001Document4 pagesTMP 1679 12-16-2022 12001FeNo ratings yet
- Indonesia-Malaysia Dispute over Sipadan and Ligitan IslandsDocument2 pagesIndonesia-Malaysia Dispute over Sipadan and Ligitan IslandsUbaidullah HalimNo ratings yet
- 2013 v13 PiDocument145 pages2013 v13 PiJessica ArtNo ratings yet
- Complaint and Jury Demand 01.17.19Document31 pagesComplaint and Jury Demand 01.17.19Anonymous GF8PPILW5No ratings yet
- Real Estate Contract Rescission and ForfeitureDocument2 pagesReal Estate Contract Rescission and ForfeitureJoyce CordonNo ratings yet
- CRPC ProjectDocument13 pagesCRPC ProjectThakur Prashant Singh0% (1)
- MRT Development Corp v Gammon Philippines construction dispute arbitrationDocument4 pagesMRT Development Corp v Gammon Philippines construction dispute arbitrationJeanne DumaualNo ratings yet
- CA-G.R. SP Nos. 70014 and 104604 DECISIONDocument68 pagesCA-G.R. SP Nos. 70014 and 104604 DECISIONBLP Cooperative90% (20)
- Pablito Murao Vs People of The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesPablito Murao Vs People of The Philippinesrgomez_940509No ratings yet
- 5158-LL T HandbookDocument32 pages5158-LL T HandbookEswar StarkNo ratings yet
- Estate Planning Intake FormDocument8 pagesEstate Planning Intake Formbash shangNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Criminology A Canadian Perspective 8th by Rick Linden PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Criminology A Canadian Perspective 8th by Rick Linden PDFedward.furr108100% (39)
- PTA Skeleton ArgumentDocument20 pagesPTA Skeleton ArgumentPeteNo ratings yet
- Filed: Patrick FisherDocument3 pagesFiled: Patrick FisherScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- COMMISSION ON AUDIT CIRCULAR NO. 92-391 November 25, 1992 TODocument2 pagesCOMMISSION ON AUDIT CIRCULAR NO. 92-391 November 25, 1992 TOpaoloNo ratings yet
- Opinion Notice of GarnishmentDocument3 pagesOpinion Notice of GarnishmentGil Arvin C. ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Manila Doctors College v. Emmanuel M. Olores Case on Reinstatement BackwagesDocument1 pageManila Doctors College v. Emmanuel M. Olores Case on Reinstatement BackwagesLara CacalNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Business Permit Tax Year 2017 Municipality of GAMUDocument1 pageApplication Form For Business Permit Tax Year 2017 Municipality of GAMUGamu DILGNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court On Delay NCDRCDocument5 pagesSupreme Court On Delay NCDRCPiyushNo ratings yet
- Tuv Gee U 401HSDocument9 pagesTuv Gee U 401HSAshley Jiyhun WindsorNo ratings yet
- Cimb Bank BHD V Wellcom Communications (M) SDocument4 pagesCimb Bank BHD V Wellcom Communications (M) SFikri C-roNo ratings yet
- MOA LEASE (Repaired)Document2 pagesMOA LEASE (Repaired)RaysunArellano50% (2)
- Webfil LTD V Abhishek Kumar 395868Document13 pagesWebfil LTD V Abhishek Kumar 395868Vishwajit SawantNo ratings yet
- A.C. No. 5816Document2 pagesA.C. No. 5816Jumel John H. Valero100% (1)
- Babst vs. Court of Appeals (GR 99398, 26 January 2001) Doctrine: FactsDocument2 pagesBabst vs. Court of Appeals (GR 99398, 26 January 2001) Doctrine: FactsAgie MarquezNo ratings yet
- Uy v. CADocument6 pagesUy v. CAnakedfringeNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics: Legality of The Process in Cameroon: Joan B.AliDocument10 pagesDigital Forensics: Legality of The Process in Cameroon: Joan B.AliMbangse MarcelNo ratings yet
- Legal Writing in Plain English, Third Edition: A Text with ExercisesFrom EverandLegal Writing in Plain English, Third Edition: A Text with ExercisesNo ratings yet
- Everybody's Guide to the Law: All The Legal Information You Need in One Comprehensive VolumeFrom EverandEverybody's Guide to the Law: All The Legal Information You Need in One Comprehensive VolumeNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Legal Terms: Definitions and Explanations for Non-LawyersFrom EverandDictionary of Legal Terms: Definitions and Explanations for Non-LawyersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Nolo's Deposition Handbook: The Essential Guide for Anyone Facing or Conducting a DepositionFrom EverandNolo's Deposition Handbook: The Essential Guide for Anyone Facing or Conducting a DepositionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LLC or Corporation?: Choose the Right Form for Your BusinessFrom EverandLLC or Corporation?: Choose the Right Form for Your BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Power of Our Supreme Court: How Supreme Court Cases Shape DemocracyFrom EverandThe Power of Our Supreme Court: How Supreme Court Cases Shape DemocracyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Legal Writing in Plain English: A Text with ExercisesFrom EverandLegal Writing in Plain English: A Text with ExercisesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Torts: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandTorts: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastFrom EverandThe Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Nolo's Encyclopedia of Everyday Law: Answers to Your Most Frequently Asked Legal QuestionsFrom EverandNolo's Encyclopedia of Everyday Law: Answers to Your Most Frequently Asked Legal QuestionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Essential Guide to Workplace Investigations, The: A Step-By-Step Guide to Handling Employee Complaints & ProblemsFrom EverandEssential Guide to Workplace Investigations, The: A Step-By-Step Guide to Handling Employee Complaints & ProblemsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Legal Guide for Starting & Running a Small BusinessFrom EverandLegal Guide for Starting & Running a Small BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Legal Forms for Starting & Running a Small Business: 65 Essential Agreements, Contracts, Leases & LettersFrom EverandLegal Forms for Starting & Running a Small Business: 65 Essential Agreements, Contracts, Leases & LettersNo ratings yet
- Ukraine: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandUkraine: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (117)
- Nolo's Essential Guide to Buying Your First HomeFrom EverandNolo's Essential Guide to Buying Your First HomeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (43)
- Employment Law: a Quickstudy Digital Law ReferenceFrom EverandEmployment Law: a Quickstudy Digital Law ReferenceRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A Student's Guide to Law School: What Counts, What Helps, and What MattersFrom EverandA Student's Guide to Law School: What Counts, What Helps, and What MattersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- So You Want to be a Lawyer: The Ultimate Guide to Getting into and Succeeding in Law SchoolFrom EverandSo You Want to be a Lawyer: The Ultimate Guide to Getting into and Succeeding in Law SchoolNo ratings yet
- Form Your Own Limited Liability Company: Create An LLC in Any StateFrom EverandForm Your Own Limited Liability Company: Create An LLC in Any StateNo ratings yet
- Louisiana Notary Exam Sidepiece to the 2024 Study Guide: Tips, Index, Forms—Essentials Missing in the Official BookFrom EverandLouisiana Notary Exam Sidepiece to the 2024 Study Guide: Tips, Index, Forms—Essentials Missing in the Official BookNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Glossary of Legal Terms, Law Essentials: Essential Legal Terms Defined and AnnotatedFrom EverandComprehensive Glossary of Legal Terms, Law Essentials: Essential Legal Terms Defined and AnnotatedNo ratings yet
- Nolo's Essential Guide to Child Custody and SupportFrom EverandNolo's Essential Guide to Child Custody and SupportRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)