Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Environmental Legal Register
Uploaded by
muthuswamy77Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Environmental Legal Register
Uploaded by
muthuswamy77Copyright:
Available Formats
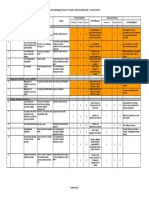
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
As required by ISO 14001 clause 4.3.2: The following environmental legislation has been identified as being applicable to MRF Name
Ref
E1
Aspect
Waste Management
General
Legislation/Enforcement
The Environmental Protection
(Duty of Care) (England)
(Amendment) Regulations 2003
and the Waste Management
Duty of Care Code of Practice
1996.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
Wastes to be stored securely.
Disposal of waste arising
from factory and office
activities.
Controlled wastes to be
disposed of to a licensed
waste carrier.
Vetting of waste carriers.
Evidence of compliance:
Documented transfer of
waste from the
organisation to a waste
carrier signed by both
parties. Retained for 2
years.
Appointment of waste
authorities.
E2
Waste Management General
Environmental Protection Act
1990: Part II Waste on Land.
Prohibition on unauthorised
disposal of waste.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
Granting of licences for
treatment, keeping and
disposal of any specified
waste in or on specified land.
The Clean Neighbourhood and
Environment Act 2005.
E3
Waste Management General
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA and Local
Authority.
Use licensed carriers.
Prohibition on unauthorised
disposal of waste.
Additional powers to agencies
dealing with fly-tipped waste.
Fines up to 50,000 and five
years imprisonment for those
found guilty of fly-tipping.
Environmental Legal Register
Use licensed carriers.
Compliance
All waste streams
are securely
stored in labelled
cages/containers?
All waste carriers
licence are valid
and on file?
All waste carriers
licences are valid
and on file for all
transport/waste
carriers?
All waste carriers
licences are valid
and on file for all
transport
carriers?
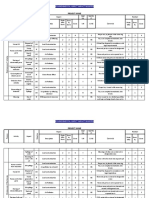
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
Aspect
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
Hazardous Waste is so called
because it has hazardous
properties that may render it
harmful to human health or
the environment.
All businesses in England
and Wales that produce
Hazardous Waste must:
E4
Waste Management
Hazardous Waste
The Hazardous Waste
Regulations 2005.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
1. Annual registration to
Environment Agency (EA).
2. No pre-notification to EA
except when delivered to
Scotland or Northern Ireland..
3. Quarterly returns to EA.
4. Keep consignment notes for
three years..
If premises are not
exempt, the producer
must register - even if the
premises produce less
than 200kg of Hazardous
Waste.
Environmental Legal Register
Relevance/Controls
Disposal of hazardous
wastes arising from
factory and office
activities (hazardous
chemicals, solvents and
solvent-based paints, inks,
waste oils, oily residues,
fluorescent light tubes
etc.
Compliance
Registered with
the Environment
agency
Premises code:
?.
Only classified
hazardous wastes
are removed?
The Environmental
Regulator tracks the
movement of Hazardous
Waste through a
consignment note system.
This ensures that waste is
managed responsibly from
its point of origin until it
reaches a suitably
licensed or exempt facility
to be recovered or
disposed of.
The consignment note
system needs to allow for
a consignment note copy
to be sent to the waste
producer as proof of waste
receipt.
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E5
Aspect
Waste Management
Non-Hazardous
Waste
Legislation/Enforcement
Landfill (England and Wales)
Regulations 2002, SI 2002 No.
1559, as amended, e.g. by the
Landfill (England and Wales)
(Amendment) Regulations 2005.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
Environmental Protection (Duty
of Care) (England) (Amendment)
Regulations 2003 (SI 2003/63).
E6
Waste Management Documentation
Enforced by the Waste Collection
Authority.
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
New rules mean that from
October 2007 non-hazardous
waste must be treated before
it is disposed of at a landfill
site and liquid waste will be
banned from any landfill.
Treatment is defined by a
three-point test, and all
criteria must be satisfied for
the waste to have been
treated. The criteria are that
the treatment must:
1. Be a physical, thermal,
chemical or biological
process including sorting.
2. Change the
characteristics of the
waste.
3. Change the waste to
reduce its volume or
hazardous nature,
facilitate its handling or
enhance its recovery.
If you are a waste
producer you are not
obliged to treat the waste
yourself many will
simply buy this service
from a waste contractor.
However, it is good
practice to complete a
written declaration
stating:
This legislation provides
powers for the relevant
Waste Collection Authority to
serve a notice on any person
required to keep copies of
transfer notes, requiring that
person to provide copies of
transfer notes within a
specified time. This is in
addition to the powers of the
Environment Agency.
Necessary documentation
controlled by procedures.
Environmental Legal Register
1. Whether you have
treated the waste.
2. The type of
treatment that has
occurred (if any).
3. If relevant, the
amount of waste
sorted out for
recovery or
alternative treatment.
Compliance
Written
statement
declaring amount
of waste to be
treated by?
Evidence that
subsequent
holder of waste
has treated waste
before landfill as
per regulations?
Duty of care
collections note
completed for
collections?
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E7
Aspect
Waste Management
Storage of Skips
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
Highways Act 1980 (England and
Wales)
Environmental Protection Act
1990
Environment Act 1995.
This legislation requires that
waste in skips must be
secure from access by the
public. MRF Name ensures
that the site is secure from
the general public and that
no waste is stored outside
customers premises.
Security on site.
Locked/secure bins.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
E8
Waste Management
Movement of
Waste
Control of Pollution
(Amendment) Act 1989
Controlled Waste (Registration of
Carriers and Seizure of Vehicles)
Regulations 1991 (SI 1991/1624)
Controlled Waste (Registration of
Carriers and Seizure of Vehicles)
(Amendment) Regulations 1998
(SI 1998/605).
Under the Control of Pollution
(Amendment) Act 1989, and
the above Regulations, it is a
criminal offence for a waste
carrier to transport waste
without being registered.
MRF Name has a Duty of
Care process to ensure
that any of its own
contractors carrying their
waste themselves hold a
current carriers licence.
To meet this requirement,
MRF Name shall retain a
copy of all relevant
current licences.
Compliance
Controls in place?
All waste carriers
licence are valid
and on file?
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
Landfill Tax Regulations 1996.
E9
Waste Management
Enforced by Customs and Excise.
Tax payable for landfill waste
to reflect the full
environmental costs of
disposing of waste to landfill.
Environmental Legal Register
Tax affects cost of
disposal. Higher tax for
active waste than for
inert.
Annual waste
tra
nsf
er
not
e?
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
Aspect
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
Environmental Protection Act
1990, Part II: Waste on Land.
MRF Name is required to
meet all of the requirements
of the licences as defined in
the licence documents (Ref.
EAWML/75188).
Under the EPA 1990, the
party to whom the licence
is issued has to be a fit
and proper person. The
competence needed to
meet this requirement is
determined through COTC
qualifications held by
members of staff.
Current COTC
qualifications?
Noise (waste compactor,
compressors).
Dust (waste compactor).
Waste litter in yard.
Smells (contaminated
plastics and tins).
Evidence of
statutory
complaints?
Competent persons must
service equipment
regularly.
Evidence of
regular
maintenance?
Waste Management Licensing
(England, Wales) (Amendment
and related provisions) Regs
2005 (SI 803).
E10
Waste Management
Licence
Waste Management Licensing
(Amendment) Regulations 1996
(SI 1996/1279).
Waste Management Licensing
(Amendment) (England)
Regulations 2002 (SI 2002/674).
(Waste Management
Licensing legislation
amended on 04-01-07
from Regs 1994, to Regs
2005 (Amendments to
cover exemptions for
requiring a waste
management licence).
Compliance
Is MRF Name
complying with
the waste
tonnage limits
outlined within
the Waste
Management
Licence?
Enforced by the Environment
Agency or SEPA.
E11
Emissions to Air
Environmental Protection Act
1990: Part III Statutory Nuisance
and Clean Air.
Nuisance (Noise, Dust,
Smells).
Activities not to be source of
statutory nuisance.
Heating oil emissions.
Clean Air Act 1993.
E12
Emissions to Air
Enforced by Local Authority and
Secretary of State.
The Act contains provisions
relating to the control of grit,
smoke and dust. The Act
prohibits, subject to
conditions, emissions of dark
and black smoke from
chimneys serving boilers and
industrial plant.
Environmental Legal Register
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E13
Aspect
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
The Control of Asbestos
Regulations 2005.
The Control of Asbestos
Regulations came into
force on 13 November
2006. As well as the
requirement for
accreditation, the
Regulations introduced
other changes including:
A single control limit of
0.1 fibres per cm3 of air
for work with all types of
asbestos.
Specific mandatory
training requirements for
anyone liable to be
exposed to asbestos.
Enforced by HSE.
Emissions to Air
A requirement to analyse
the concentration of
asbestos in the air with
measurements in
accordance with the
1997 World Health
Organisation
recommended method.
Relevance/Controls
Compliance
Evidence of
inspection
reports?
Evidence of
routine checks?
All potential asbestos clad
buildings to be
investigated with samples
sent for analysis to UKAS
accredited laboratories.
Maintenance of asbestos
materials to be strictly
controlled to ensure staff
are adequately protected
from any potential
asbestos airborne fibres.
All work with asbestos
containing materials,
whether licensed or not,
must be undertaken by
trained workers following a
risk assessment and in
accordance with appropriate
controls to prevent exposure
to asbestos fibres.
Environmental Legal Register
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
Aspect
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
Packaging (Essential
Requirements) Regulations 2003
(SI 2003/ No.1941).
The qualifying criteria remain
unchanged at 2 million
turnover and 50 tonnes of
packaging handled per year.
Also the recycling and
recovery targets for 2006
2010 detailed in Schedule 2
are unchanged.
Packaging (Essential
Requirements) (Amendment)
Regulations 2004 (No.1188).
E14
E15
Resource
Consumption
Resource
Consumption
Enforced by Weights and
Measures Authorities in Great
Britain.
The Producer Responsibility
Obligations (Packaging Waste)
Regulations 2007 (SI 2007 No.
871) entered into force on 16
March and replace the Producer
Responsibility Obligations
(Packaging Waste) Regulations
2005.
Finance Bills 1999 and 2000
Climate Change Levy.
Enforced by Customs and Excise.
Product packaging shall be
minimised consistent with
the safe and hygienic
transport and handling of the
product.
Packaging shall be designed
to permit re-use or recovery.
Printing inks shall not involve
the use of heavy metal
pigments.
(Packaging legislation
amended on 07-06-06
from Regs 1998, to Regs
2003).
HM Government announced
a climate change levy or
carbon energy tax on the
industrial and commercial
use of energy to apply from
April 2001, exempting energy
from new forms of renewable
energy, e.g. solar, wind
power.
Basis for charging Vehicle
Excise Duty on new
passenger vehicles is related
to the vehicles CO2
emissions.
Environmental Legal Register
Relevance/Controls
Revisions include:
Provision for submitting
documents and
maintaining registers in
electronic form; An
increase in the
registration fee charged
by EA/SEPA from 768 to
776. (The fee for small
producers).
Compliance
Packaging Usage
figures for
2007/8?
Need for
compliance?
Supply chain.
Potential to recycle
drums, pallets, paper,
cardboard, plastic
containers, etc.
Energy and fuel
consumption.
Production of carbon.
All vehicles and
electricity data
was recorded and
monitored
through out
2006/7?
Use of finite resources.
Administration of the fleet
of company cars.
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E16
Aspect
Resource
Consumption
Legislation/Enforcement
The Waste Electrical and
Electronic Equipment
Regulations (SI 2006 No.3289)
were laid before Parliament on
12th December 2006 and came
into force on 2nd January 2007.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency.
Anti-Pollution Works Regulations
1999 (SI 1999/1006).
E17
Releases to Water
Enforced by the Environment
Agency.
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
Aims: To reduce the waste
arising from electrical and
electronic equipment.
Disposal is free if you
were sold the equipment
after 13th August 2005 or
if you are replacing with
equivalent EEE. This
service will be delivered
through the producer
take-back scheme. You
must pay for WEEE where
you are discarding EEE
purchased before 13th
August 2005, or where
you are not replacing EEE
with an equivalent.
Payment must also be
made if you cannot trace
the producer or their
compliance scheme, or if
you choose to negotiate
with producers to accept
the cost of treating and
disposing your WEEE.
To improve the
environmental performance
of all those involved in the
life cycle of electrical and
electronic products.
Any businesses using EEE
must comply with the new
regulations, meaning you
must store, collect, treat,
recycle and dispose of WEEE
separately from your other
waste. Similar to Waste
Transfer Notes, you must
obtain and keep proof that
your WEEE was given to a
reputable waste
management company and
treated and disposed of in an
environmentally sound way.
Under the Anti-Pollution
Works Regulations 1999 (SI
1999/1006) The Environment
Agency can serve an AntiPollution Works Notice on a
company if they perceive
that an activity is causing or
may cause pollution to
controlled waters. This
means primary responsibility
for carrying out and funding
the works can be placed with
the polluter.
Environmental Legal Register
Compliance
Choice to reuse
equipment or
donate before
recycling.
Evidence of
contractual
arrangement with
? to dispose of
WEEE?
Consignment
note numbers will
be used when
disposing of
equipment?
Evidence of risk
assessments?
Chemicals, solvents,
diesel oil and other.
Substances/materials
used on site.
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
Aspect
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
Deliveries of raw
materials or fuels to your
site should be supervised,
to reduce the risk of
overfill and spillage.
Use of drip trays for fill
pipes outside the
secondary containment
system.
E18
Releases to Water
Control of Pollution (Oil Storage)
(England) Regulations 2001 No.
2954.
Enforced by the Environment
Agency.
In England, if you store oil
(such as petrol, diesel,
vegetable, synthetic or
mineral oil) in a container
with a storage capacity of
over 200 litres (44 gallons)
then you may need to
comply with the Control of
Pollution (Oil Storage)
(England) Regulations 2001.
Compliance
Evidence of
routine site
inspections?
Examples of
contamination
issues?
Fuels and chemicals
should be stored in
containers that are clearly
labelled and "fit for
purpose" and sited within
or provided with
secondary containment
facilities.
Secondary containment
should provide a capacity
of at least 110% of the
largest vessel or 25% of
the total volume being
stored, whichever is the
greater, and should be
impermeable to the
substance stored.
Any accumulated
rainwater should be
removed as part of
regular maintenance and
inspection. If the
rainwater is
contaminated, then it will
have to be appropriately
treated or disposed of.
Contaminated rainwater
may be considered
Hazardous Waste and, if
so, will have to be dealt
with accordingly.
Environmental Legal Register
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
Aspect
Legislation/Enforcement
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
Request for supply.
Water Industry Act 1999.
E19
Releases to Water
Enforced by DG of Water
Services, Environment Agency
and Local Authorities.
Charges.
Permission to use water
on site.
Adequate supply to support
works.
Energy used to produce
water.
(Water industry act
amended on 04-01-07
from Regs 1991, to Regs
1999).
Water consumption.
Water Resources Act 1991.
E20
Releases to Water
Enforced by Environment Agency
and Secretary of State.
Environment Act 1995: Part III.
E21
Land Contamination
Enforced by Local Authority.
Storage of chemicals and
other hazardous substances.
Local authorities and the
Environment Agency to
identify contaminated land
and to serve remediation
notices. Notices served on
the people who created the
contamination if they can be
identified. Otherwise the
current owner or occupier is
responsible.
Under the Water
Resources Act it is an
offence to cause pollution
of any watercourse.
Spillages of chemicals,
solvents and other
substances used on site.
Interpretation:
Contaminated Land (England)
Regulations 2000.
E22
Land Contamination
Enforced by Local Authority.
(Contaminated land Regs
amended on 04-01-07 from
Regs 2000, to Regs 2006).
Significant harm is being
caused or there is significant
possibility of such harm
being caused; or
Pollution of surface waters
and ground water is being, or
is likely to be, caused.
Spillages of chemicals,
solvents and other
substances used on site.
Compliance
Water usage data
is recorded and
monitored?
No incidents
reported. Spill
kits located in
proximity to open
drains?
No spillages
recorded
Potential spillage
from solvents,
spill kits in place
and staff trained
in procedures?
No spillages
recorded
Potential spillage
from solvents,
spill kits in place
and staff trained
in procedures?
Remediation notices for
measures to restore
controlled waters to
acceptable standard that
have been affected by
contaminated land.
Environmental Legal Register
10
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E23
Aspect
Land Contamination
Legislation/Enforcement
CHIP refers to the Chemicals
(Hazard Information and
Packaging for Supply)
Regulations 2002. These are
sometimes also known as CHIP3.
Enforced by HSE.
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
CHIP is the law that applies
to suppliers of dangerous
chemicals. Its purpose is to
protect people and the
environment from the effects
of those chemicals by
requiring suppliers to provide
information about the
dangers and to package
them safely.
All hazardous materials
will require labelling at all
times up to and during
collection by an
authorised waste transfer
authority. Reference to
European Waste
Catalogue codes are
required.
Check hazardous
materials for
correct
identification?
Owner must submit
application for
development permission
to include: site, design,
external appearance, land
use, means of access and
landscaping.
All previous
developments
applications have
been notified to
the Council?
Town and Country Planning Act
1990 (TCPA).
E24
Nuisance
Town and Country Planning
(Development Plan) Regulations
1999 (SI 1999 No. 3280).
Imposes controls over landuse and new development.
Enforced by Local Planning
Authority.
Road Traffic Act 1988 (EU
Directive 91/441/EEC) and EU
Directive 94/12/EEC).
E25
Transport
Enforced by Local Authority.
Possible future enforcement
of Road traffic act 1991
(C40).
Compliance
Fees are payable.
Local Planning Act may
grant conditional
approval.
It is an offence to use a
vehicle if it is emitting
"smoke, visible vapour, grit,
sparks, ashes, cinders or oily
substances" in such a way as
is likely to cause "damage to
any property or injury or
danger to any person.
Environmental Legal Register
Owned vehicles need to
be maintained properly.
Outside delivery vehicles
to be reported using note
book?
All company
vehicles to be
monitored for
maintenance and
insurance?
11
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E26
Aspect
Substances
Legislation/Enforcement
Control of Substances Hazardous
to Health (Amendment)
Regulations 2004 (SI 2004 No.
3386) COSHH).
Enforced by HSE and HM
Customs and Excise regarding
import bans.
Key Requirements
To protect employees and
other persons likely to be
affected against risks to their
health resulting from
exposure to substances
hazardous to health.
Control of hazardous
substances amended on
04-01-07 from Regs 2002,
to Regs 2004.
Wildlife and Countryside Act
1981.
Wildlife and Countryside
(Amendment) Act 1991.
E27
Nature Conservation
Wildlife and Countryside Act
1981 (Amendment) Regulations
1995 (SI 1995 No. 2825).
To strengthen protection for,
and provide off-site powers
to ensure the conservation
of, various endangered
species of wildlife including
wild birds.
Enforced by Natural England and
Secretary of State.
Environmental Legal Register
Relevance/Controls
In order to protect
employees and the
environment, employers
must use, as necessary,
control measures, training
plus routine exposure
monitoring and health
surveillance.
The assessment records
need to meet the
requirements of COSHH
also support
environmental risk
assessment in terms of
the properties of
hazardous chemicals
present.
To control the escape of
materials from the site
due to high winds and to
prevent contamination to
land and pollution to
storm water drains.
The installation of security
fencing to control wind
borne waste.
Housekeeping and
environmental training
procedures to control and
monitor contamination of
land and pollution of
drains.
Compliance
Maintain MSDS
records?
Conduct an
annual COSHH
assessment?
Identify Health,
Safety and
Environmental
risks and
controls?
Evidence of
environmental
awareness
training?
Evidence of
routine site
inspections?
12
MRF Name Environmental Legal Register
Ref
E28
Aspect
NEW LEGISLATION
Resource
Consumption
Legislation/Enforcement
The Carbon Reduction
Commitment (CRC) is a new
scheme, announced in the
Energy White Paper 2007.
Enforced by Local Planning
Authority.
Key Requirements
Relevance/Controls
The Carbon Reduction
Commitment (CRC) is the
new name for the Energy
Performance Commitment
proposal on which the
Government consulted in
2006. The name of the
scheme has been changed to
prevent any confusion with
Energy Performance
Certificates.
CRC allowances will be
issued to participants via
an auction process. Within
the context of the scheme
cap, participants will be
able to determine their
own emissions targets. In
order to ease participants
into the regime, and to
allow Government to
establish more accurate
data on emissions across
the target sector, CRC will
feature an introductory
phase, with a simple fixed
price sale of allowances.
The CRC will target emissions
from energy use by large
organisations whose annual
mandatory half hourly
metered electricity use is
above 6,000MWh focusing
on those emissions outside
the Climate Change
Agreements (CCAs) and
outside the direct emissions
covered by the EU Emissions
Trading Scheme (EU ETS). In
addition, firms with more
than 25% of their energy use
emissions in Climate Change
Agreements would be
completely exempt.
Environmental Legal Register
Compliance
Monitor
consumption on
quarterly basis.
Current usage?
Is business
covered by
legislation?
13
You might also like
- Register of Legal and Other RequirementsDocument10 pagesRegister of Legal and Other RequirementsFairulhidayahNo ratings yet
- Legal RegisterDocument13 pagesLegal RegisterVictor Thembinkosi Makhubele50% (2)
- Legislation Register - ExampleDocument10 pagesLegislation Register - Exampleaitzaz5610% (1)
- Environmental Aspects and ImpactsDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Aspects and ImpactsCristina Coceasu100% (4)
- Environmental Aspect & Impact RegisterDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Aspect & Impact Registerpak-ksa life100% (1)
- Legal Register-QatarDocument62 pagesLegal Register-QatarRamasubramanian Sankaranarayanan80% (5)
- Legal Register Evaluation Feb '20Document61 pagesLegal Register Evaluation Feb '20Priyanka J100% (6)
- Environmental Aspects and ImpactsDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Aspects and Impactssharif khan100% (3)
- Aspect Impact RegisterDocument4 pagesAspect Impact Registermark_vyz100% (7)
- Legal - Register - Manufacturing Service (Aug '17) .Document8 pagesLegal - Register - Manufacturing Service (Aug '17) .jagshishNo ratings yet
- ISO 14001 2015 Environmental Aspects and Impacts Procedure SampleDocument6 pagesISO 14001 2015 Environmental Aspects and Impacts Procedure SampleEndah Yulita67% (3)
- Environmental Aspects and Impacts Evaluation REV-003Document12 pagesEnvironmental Aspects and Impacts Evaluation REV-003sunthu100% (1)
- Hallite Aspects ImpactsDocument1 pageHallite Aspects ImpactsRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- UAE Legal Register OK TO USEDocument11 pagesUAE Legal Register OK TO USEPriyanka J75% (4)
- Sample Only: Register of Environmental Objectives and TargetsDocument1 pageSample Only: Register of Environmental Objectives and TargetsRamasubramanian Sankaranarayanan0% (1)
- EHS ManualDocument16 pagesEHS Manualshalakabisht50% (2)
- Environmental Aspects and Impact Register TemplateDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Aspects and Impact Register TemplateCarlosNo ratings yet
- Environemental Management System - Risk Register - Aspect and Impacts RegisterDocument6 pagesEnvironemental Management System - Risk Register - Aspect and Impacts Registersjmpak100% (8)
- Hse Plan L & TDocument69 pagesHse Plan L & TNarayanasami Kannan50% (2)
- Legal RegisterDocument10 pagesLegal RegisterShyam_Nair_9667100% (2)
- Environmental Aspects and ImpactsDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Aspects and ImpactsImtiyaz Akhtar80% (5)
- EM01-06 Aspects Register 2017Document7 pagesEM01-06 Aspects Register 2017Armand LiviuNo ratings yet
- Legal Register 1Document51 pagesLegal Register 1VictorNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspect Impact RegisterDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Aspect Impact Registernikhilearat100% (7)
- Legal Compliance RegisterDocument1 pageLegal Compliance RegisterravikpandeyNo ratings yet
- Aspects and Impacts Register 160415Document1 pageAspects and Impacts Register 160415Roselyn SharronNo ratings yet
- Safety Audit PlanDocument23 pagesSafety Audit Planpkitchen25100% (4)
- Environmental AspectsDocument31 pagesEnvironmental AspectsNachar A N100% (4)
- Manual PreviewDocument16 pagesManual PreviewMuhammad Yasin67% (6)
- EMS - Sample Environmental Aspects & Impacts RegisterDocument7 pagesEMS - Sample Environmental Aspects & Impacts RegisterBalaji_Rajaman_228025% (4)
- EMS-1B Environmental Aspects and Impacts Register (Summary)Document12 pagesEMS-1B Environmental Aspects and Impacts Register (Summary)ezal2No ratings yet
- EMS Aspect Impact Work BookDocument52 pagesEMS Aspect Impact Work Bookcdmguide5985100% (3)
- OSHAD Tittle 2019Document2 pagesOSHAD Tittle 2019anish7785No ratings yet
- Veera Iso 45001-2018nutshellDocument11 pagesVeera Iso 45001-2018nutshellVeerabahu Nallasivam0% (1)
- Sample SOP For Legal and Other Requirements PDFDocument2 pagesSample SOP For Legal and Other Requirements PDFanoushia alviNo ratings yet
- Aspects and ImpactsDocument3 pagesAspects and ImpactsrexivyNo ratings yet
- EMS 01 ISO14001 2015 Environmental ManualDocument26 pagesEMS 01 ISO14001 2015 Environmental Manualyenesew mulluNo ratings yet
- Register of Aspect Impact - IMSM 4.3.1 R02Document7 pagesRegister of Aspect Impact - IMSM 4.3.1 R02jrpatel18853100% (2)
- 02 General Aspect Impact StudyDocument1 page02 General Aspect Impact StudymakdelNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects and Impacts RegisterDocument1 pageEnvironmental Aspects and Impacts Registerkev24586% (7)
- Aspect Impact Evaluation Procedure.Document3 pagesAspect Impact Evaluation Procedure.harshar2100% (1)
- IMS Project Implementation Plan - Rev 2 (111019)Document1 pageIMS Project Implementation Plan - Rev 2 (111019)Biell BaleNo ratings yet
- Legal RegisterDocument57 pagesLegal Registerवात्सल्य कृतार्थ100% (1)
- Legal Compliance Evaluation ProgramDocument7 pagesLegal Compliance Evaluation Programazee730% (1)
- Environmental Aspect & ImpactDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Aspect & ImpactBaran ShafqatNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspect and Impact Assessment EvaluationDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Aspect and Impact Assessment EvaluationRahul SiwakotiNo ratings yet
- Safety Department Checklist FormatDocument32 pagesSafety Department Checklist Formatrockyvinoo100% (18)
- HSE Capability AssessmentDocument5 pagesHSE Capability Assessmentsjmpak78% (18)
- IMS IQA Audit Check ListDocument123 pagesIMS IQA Audit Check ListMahesh Jadhav75% (4)
- Procedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowDocument3 pagesProcedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowMarjorie Dulay Dumol67% (3)
- Iso 14001 Sample ProceduresDocument19 pagesIso 14001 Sample ProceduresMichelle Baxter McCullochNo ratings yet
- SHEQXel Performance Monitoring ToolDocument105 pagesSHEQXel Performance Monitoring ToolEmil50% (2)
- H S Legal Register Abudhabi ADDC D 10590 B PDFDocument13 pagesH S Legal Register Abudhabi ADDC D 10590 B PDFsachin_micro100% (1)
- ISO 45001 Documents List of Required Policies & ProceduresDocument16 pagesISO 45001 Documents List of Required Policies & ProceduresBFNo ratings yet
- EHS Legal Regulations TrainingDocument125 pagesEHS Legal Regulations TrainingSudhir Barot100% (4)
- Synergic Safety Engineers: Environmental Aspect & It'S ImpactDocument22 pagesSynergic Safety Engineers: Environmental Aspect & It'S ImpactsgrsthNo ratings yet
- ISO 45001 Manual-Rev-00-06-07-2018-1 PDFDocument18 pagesISO 45001 Manual-Rev-00-06-07-2018-1 PDFAnonymous vmw7z1WHm83% (6)
- Aspects & Impacts Register v8.2 January 2015: S I G N I F I C A N C eDocument5 pagesAspects & Impacts Register v8.2 January 2015: S I G N I F I C A N C eShashank SaxenaNo ratings yet
- F Gas GuidanceDocument40 pagesF Gas GuidancePadraig SheahanNo ratings yet
- NC DetailsDocument3 pagesNC Detailsmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Resume Nandhakumar 31.12.2023Document2 pagesResume Nandhakumar 31.12.2023muthuswamy77No ratings yet
- SUPPLIER - PERFORMANCEDocument41 pagesSUPPLIER - PERFORMANCEmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- TOWN NEWS, Ayapakkam Edition, Tuesday, January 9,2024Document4 pagesTOWN NEWS, Ayapakkam Edition, Tuesday, January 9,2024muthuswamy77No ratings yet
- IATF Audit MandaysDocument1 pageIATF Audit Mandaysmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Risk Register Example PDFDocument1 pageRisk Register Example PDFmuthuswamy77100% (1)
- Effective Problem SolvingDocument1 pageEffective Problem Solvingmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- 2016 - 03 - 31 - ISO - 14001 - Dick Hortensius PDFDocument58 pages2016 - 03 - 31 - ISO - 14001 - Dick Hortensius PDFmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Work Instruction For Alarm Annunciator: 1. PurposeDocument2 pagesWork Instruction For Alarm Annunciator: 1. Purposemuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Ticket RedbusDocument1 pageTicket Redbusmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Grove TM1150Document4 pagesGrove TM1150muthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Ims - Awareness Training - JcsDocument86 pagesIms - Awareness Training - Jcsmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Heat Treatment AssesmentDocument53 pagesHeat Treatment Assesmentmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Monthly Plate Compactor Check ListDocument2 pagesMonthly Plate Compactor Check Listmuthuswamy7783% (6)
- 06.HR ManualDocument21 pages06.HR Manualmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Annex SL - ISO 9001 2015Document24 pagesAnnex SL - ISO 9001 2015Alex VargasNo ratings yet
- Resume - 01.03.2016Document5 pagesResume - 01.03.2016muthuswamy77No ratings yet
- 14 Management PrincipleDocument1 page14 Management Principlemuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- The Objectives:-: ' Say No To Crackers 'Document2 pagesThe Objectives:-: ' Say No To Crackers 'Rozy SinghNo ratings yet
- DVLA Rates of Vehicle TaxDocument2 pagesDVLA Rates of Vehicle TaxNaj BalochNo ratings yet
- Importance of Environmental Management and ProtectionDocument7 pagesImportance of Environmental Management and ProtectionJoao Saide BacarNo ratings yet
- 10-01 European Wood Heating Technology SurveyDocument157 pages10-01 European Wood Heating Technology SurveySteve DarmonNo ratings yet
- Voestalpine Permit Amendment Request 2019Document43 pagesVoestalpine Permit Amendment Request 2019callertimesNo ratings yet
- The International Climate Initiative (IKI)Document2 pagesThe International Climate Initiative (IKI)Daniel TobarNo ratings yet
- M101c - Costs&Benefits of Digital Technologies: Author: Prof. Dr. Meltem Ucal, KHAS, Turkey Ceren Takımlı, KHAS, TurkeyDocument18 pagesM101c - Costs&Benefits of Digital Technologies: Author: Prof. Dr. Meltem Ucal, KHAS, Turkey Ceren Takımlı, KHAS, Turkeymaia maiaNo ratings yet
- 0095 A0i3c5kubDocument4 pages0095 A0i3c5kubNandar Min HtetNo ratings yet
- EGR Valve Cooler Delete (BKD)Document75 pagesEGR Valve Cooler Delete (BKD)Rafael troyano cardenasNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Evs ProjectDocument12 pagesAir Pollution Evs ProjectSaharsh100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry CIE: 10.2 Air Quality & ClimateDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry CIE: 10.2 Air Quality & Climate50moreNo ratings yet
- gEOTHERmal Power PlantsDocument4 pagesgEOTHERmal Power PlantsVirtual almostNo ratings yet
- Est AnsDocument9 pagesEst Anspathanfarhankhan712No ratings yet
- The Carbonneutral Protocol Jan 2020Document76 pagesThe Carbonneutral Protocol Jan 2020Nicolas Navas HernandezNo ratings yet
- Kilpilahti Combined Heat and Power ProjectDocument3 pagesKilpilahti Combined Heat and Power ProjectAnonymous KduLd7No ratings yet
- Copy To:: This Is Computer Generated Order. Signature Is Not Required. 1Document12 pagesCopy To:: This Is Computer Generated Order. Signature Is Not Required. 1aswinNo ratings yet
- The LAPINDO Mud Disaster: Uguru Deng Aleji Rianto EdekeDocument18 pagesThe LAPINDO Mud Disaster: Uguru Deng Aleji Rianto Edekerusman_riantoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 2nd Summative m3-m4Document2 pagesScience 7 2nd Summative m3-m4Melannie MagalongNo ratings yet
- VI - Science Sample Question Paper-2Document8 pagesVI - Science Sample Question Paper-2jijosbstnNo ratings yet
- Manual For GASBOARD-6010 Opacity Meter Components Smoke HeadDocument10 pagesManual For GASBOARD-6010 Opacity Meter Components Smoke HeadJOSEPH CAJOTENo ratings yet
- Mine Gas Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesMine Gas Questions and AnswersMalayali StargazerNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Indo German Carbons LimitedDocument1 pageMSDS - Indo German Carbons Limiteddumb2471817No ratings yet
- VOLKSWAGENDocument11 pagesVOLKSWAGENNitika KingerNo ratings yet
- Carpet Green Label InfoDocument2 pagesCarpet Green Label InfoTariq KhurshaidiNo ratings yet
- Sample SummaryDocument1 pageSample SummaryLien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet As Per Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/830 Product: Aminoethylethanolamine (AEEA)Document6 pagesSafety Data Sheet As Per Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/830 Product: Aminoethylethanolamine (AEEA)Andrea GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Bio-Fuel PosterDocument1 pageBio-Fuel PosterElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Impact Assessment of Asphalt PlantDocument26 pagesEngineering Impact Assessment of Asphalt PlantSaxum AquaSamuelNo ratings yet
- Traffic Congestion: Cause and Effect EssayDocument24 pagesTraffic Congestion: Cause and Effect EssayBeste KarıkNo ratings yet
- 07-Air Quality EngineeringDocument49 pages07-Air Quality EngineeringAstra BeckettNo ratings yet