Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Iron-Iron Carbide (Fe-Fe3C) Phase
Uploaded by
Recep VatanseverOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Iron-Iron Carbide (Fe-Fe3C) Phase
Uploaded by
Recep VatanseverCopyright:
Available Formats
Materials Science I
6-Iron and Steel
6-1-The IronIron Carbide (FeFe3C) Phase
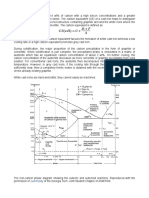
The iron-carbon phase diagram is important in engineering as it provides the basis for understanding all cast
irons and carbon steels and their heat treatment. For structural and mechanical applications, steels and other
alloys based on iron (the ferrous alloys) are the dominant engineering alloys. They are intrinsically stiff,
strong and tough, and mostly low cost.
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Page 1
Materials Science I
Phases in the FeFe3C & Fee-Fe3C System
Phase
C.Struc
Description and Comments
Liquid
Liquid solution of C in Fe.
b.c.c
(austenite)
f.c.c.
(also called ferrite)
b.c.c
Fe3C (iron carbide or
cementite)
Complex
Pearlite
Ledeburite
.-
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Random interstitial solid solution of C in b.c.c. Fe. Maximum
solubility of 0.08 wt% C occurs at 1492C. Pure Fe is the stable
polymorph between 1391C and 1536C
Random interstitial solid solution of C in f.c.c. Fe. Maximum
solubility of 1.7 wt% C occurs at 1130C. Pure Fe is the stable
polymorph between 914C and 1391C
Random interstitial solid solution of C in b.c.c. Fe. Maximum
solubility of 0.035 wt% C occurs at 723C. Pure Fe is the stable
polymorph below 914C
A hard and brittle chemical compound of Fe and C containing 25
atomic % (6.7 wt%) C.
The composite eutectoid structure of alternating plates of and
Fe3C produced when containing 0.80 wt% C is cooled below
723CPearlite nucleates at grain boundaries. It occurs in low,
medium and high carbon steels. It is sometimes, quite wrongly,
called a phase. It is not a phase but is a mixture of the two separate
phases and Fe3C in the proportions of 88.5% by weight of to
11.5% by weight of Fe3C. Because grains are single crystals it is
wrong to say that Pearlite forms in grains: we say instead that it
forms in nodules.
The composite eutectic structure of alternating plates of g and
Fe3C produced when liquid containing 4.3 wt% C is cooled below
1130C. Again, not a phase! Ledeburite only occurs during the
solidification of cast irons, and even then the g in ledeburite will
transform to a + Fe3C at 723C
Page 2
Materials Science I
Microstructures During the Slow Cooling of Pure Iron from the Hot Working Temperature
Microstructures During the Slow Cooling of a Eutectoid Steel from the Hot Working
Temperature
microstructure of a 0.76%C steel
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Page 3
Materials Science I
Microstructures During the Slow Cooling of a Hypoeutectoid Steel from the Hot Working
Temperature
microstructure of a 0.38%C steel
Microstructures During the Slow Cooling of a Hypereutectoid Steel.
microstructure of a 1.4%C steel
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Page 4
Materials Science I
5-2-Austenite Transformation
5-3-Steels
Low Carbon Steels
C < 0.25 wt% (may include HSLA with Cu, V, Ni,
Mo additions)
1. Most steels are low carbon steels
2. Least hardenable
3. Relatively soft/weak but tough/ductile
Medium Carbon Steels
O.25 wt%< C <0.60 wt%
1. Low hardenability improved by Cr, Ni
2. Heat treat by normalising and tempering
3. Stronger but less ductile/tough than low
carbon steels
High Carbon Steels
O.6 wt% < C < 1.4 wt%
1. Strongest but least ductile
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Page 5
Materials Science I
2. Often used in hardened and tempered
condition
3. Cutting tools contain Cr, V, W, Mo carbide
formers
4. Used in knives, razor blades, springs, wire
Stainless Steels
1. Cr used for improving corrosion resistance
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
2. Cr content > 11wt%
3. Ni and Mo increase corrosion resistance
4. Martensitic, ferritic, and austenitic stainless
steels
5. Austenitic stainless steels not heat treatable
Page 6
Materials Science I
5-4-Cast Irons
Gray Iron
C - 2.5 - 4%, Si - 1.0 - 3%, Silicon is a
graphite stabilizer, Weak and brittle in tension,
as graphite flakes act as cracks. graphite flakes,
weak & brittle in tension, stronger in
compression, excellent vibrational dampening,
wear resistant
Ductile Iron
Mg or Ce causes the graphite to form nodules,
or spheres. Can have pearlite or ferrite
surrounding. Can have high strength and
reasonable ductility. raphite as nodules not
flakes, matrix often pearlite tronger but less
ductile
White Iron
1 % Si, Carbon exists as cementite. Hard and
very brittle
Maleable Iron
Heat white iron to 800-900C for long times
in neutral atmosphere. Cementite forms
graphite clusters. Strong and reasonably
ductile
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Page 7
Materials Science I
Dr Ali Salami Golezani
Page 8
You might also like
- Heat TreatmentDocument179 pagesHeat TreatmentDebye101100% (1)
- Welding Metallurgy of Carbon Steel PDFDocument17 pagesWelding Metallurgy of Carbon Steel PDFwessamalex100% (1)
- 03 - Iron - Iron CarbideDocument35 pages03 - Iron - Iron CarbidebotobotoakbarNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis at Deep Drawing of Low Carbon SteelsDocument7 pagesFailure Analysis at Deep Drawing of Low Carbon SteelsPaul RosiahNo ratings yet
- Cast IronsDocument8 pagesCast IronsAlberto LunaNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Metallic Microstructure Cu-Based AlloysDocument51 pagesCharacterizing Metallic Microstructure Cu-Based AlloysjuegyiNo ratings yet
- 09 Cast IronDocument34 pages09 Cast IronyogeshmangulkarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04-CCT and TemperingDocument17 pagesLecture 04-CCT and TemperingRudy Dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys ProcessingDocument83 pagesTheory of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys ProcessingHimanshuDeepNo ratings yet
- Effect of Elements in SteelDocument3 pagesEffect of Elements in SteelJayakrishnan Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- Heat TreatmentDocument21 pagesHeat TreatmentChernet MerknehNo ratings yet
- Duplex Stainless Steel 329 or 1.4460 PDFDocument2 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel 329 or 1.4460 PDFtien100% (1)
- Extrusion of Metals: Mr. Jay Vora Faculty, School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarDocument27 pagesExtrusion of Metals: Mr. Jay Vora Faculty, School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarAdityasinh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Aluminium and Its Alloys: EF420 Lecture 11 John TaylorDocument48 pagesAluminium and Its Alloys: EF420 Lecture 11 John TaylorzorazhrNo ratings yet
- Extrusion and Its ApplicationDocument28 pagesExtrusion and Its ApplicationLakhan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Steel and Its AlloyDocument23 pagesSteel and Its AlloyHemang ChopraNo ratings yet
- 211 2aDocument33 pages211 2aMada ChohNo ratings yet
- Distortion Reduction in Gear by Simple Heat Treatment Process by Simple FixtureDocument7 pagesDistortion Reduction in Gear by Simple Heat Treatment Process by Simple FixtureVireshVerma100% (1)
- Aisi 305Document3 pagesAisi 305Aditya PratapNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heat TreatmentDocument5 pagesEffect of Heat TreatmentsupNo ratings yet
- SKD61-Forged Hot Work Tool SteelDocument1 pageSKD61-Forged Hot Work Tool SteelAgustine SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Physical MetallurgyDocument101 pagesPhysical MetallurgySheikh Sabbir SarforazNo ratings yet
- Retained Austenite and PittingDocument6 pagesRetained Austenite and PittingSuhaib AshrafNo ratings yet
- Outokumpu Supra Range DatasheetDocument12 pagesOutokumpu Supra Range DatasheetMichelNo ratings yet
- Alloys and Types of SteelDocument16 pagesAlloys and Types of SteelRajatNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus Segregation in CR - Mo - V Cast Steel After Regenerative Heat TreatmentDocument6 pagesPhosphorus Segregation in CR - Mo - V Cast Steel After Regenerative Heat Treatmentsanketpavi21No ratings yet
- Melting Practice, Casting Defects and Their Remedies in Aluminum AlloysDocument26 pagesMelting Practice, Casting Defects and Their Remedies in Aluminum AlloysShubham KaseraNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation On Magnesium SuperplasticityDocument23 pagesPowerpoint Presentation On Magnesium SuperplasticityashvaniNo ratings yet
- JI S (Japanes E) Stand Ards For ST EE L Ma TE RI ALSDocument2 pagesJI S (Japanes E) Stand Ards For ST EE L Ma TE RI ALSDamar Wardhana100% (1)
- W6 Lecture 6.surface Hardening of Steel PDFDocument28 pagesW6 Lecture 6.surface Hardening of Steel PDFYota KimireNo ratings yet
- A Model For The Graphite Formation in Ductile Cast Iron Part I Inoculation MechanismsDocument25 pagesA Model For The Graphite Formation in Ductile Cast Iron Part I Inoculation MechanismsAdams GodoyNo ratings yet
- Casting Material Austenitic Ductile Iron in ASTM A439Document3 pagesCasting Material Austenitic Ductile Iron in ASTM A439Alex007No ratings yet
- AlloysDocument91 pagesAlloysNiccoloNo ratings yet
- Steel CleanlinessDocument22 pagesSteel Cleanlinessdrbeyer100% (1)
- Riview On Cold Drawing Process PDFDocument7 pagesRiview On Cold Drawing Process PDFAmandeep Singh GujralNo ratings yet
- Sand Molding Processes: Thanuj Kumar MDocument47 pagesSand Molding Processes: Thanuj Kumar MVDNo ratings yet
- Casting Defects Analysis in Foundry and Their Remedial Measures With Industrial Case StudiesDocument11 pagesCasting Defects Analysis in Foundry and Their Remedial Measures With Industrial Case StudiesIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Masinski Materijali Za Prvi Razred - Brodomasinski Tehnicar-IV StepenDocument1 pageMasinski Materijali Za Prvi Razred - Brodomasinski Tehnicar-IV StepenBanghalorNo ratings yet
- Foundry DefectsDocument12 pagesFoundry DefectsVirendra Gupta100% (1)
- Effect of Alloying Elements On Steels Rev.BDocument402 pagesEffect of Alloying Elements On Steels Rev.BCharlie Chong100% (23)
- Material Definitions & TermsDocument3 pagesMaterial Definitions & TermsDr_M_SolimanNo ratings yet
- Aalco CatalogueDocument92 pagesAalco CatalogueNigin ParambathNo ratings yet
- 4 Ferrous MetalsDocument26 pages4 Ferrous MetalsLira AgbonNo ratings yet
- Proses Manufaktur - Fundamental of Metal FormingDocument35 pagesProses Manufaktur - Fundamental of Metal FormingAnatolium IrgrandeNo ratings yet
- Etching Specialty AlloysDocument6 pagesEtching Specialty AlloysNitin100% (1)
- The Precipitation Hardening SSsDocument3 pagesThe Precipitation Hardening SSsClaudia MmsNo ratings yet
- Welding of Stainless SteelsDocument48 pagesWelding of Stainless SteelsRamzi BEN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Steel Making - Open-Hearth TehniqueDocument5 pagesSteel Making - Open-Hearth TehniqueMarcelo Rodriguez FujimotoNo ratings yet
- Pin HolesDocument4 pagesPin HolesEr WidodoNo ratings yet
- AMCOL - MCST - TR - HeviSand - Chromite - Double - Skin Defect - On - Heavy - Steel - Casting PDFDocument12 pagesAMCOL - MCST - TR - HeviSand - Chromite - Double - Skin Defect - On - Heavy - Steel - Casting PDFSUNDRAMNAGANo ratings yet
- Steel CleanlinessDocument22 pagesSteel CleanlinessfondershellNo ratings yet
- O HC HCDocument101 pagesO HC HCIndustrial Infra Jobs100% (1)
- Thermomechanical Processing and Constitutive Strength of Hot Rolled Mild SteelDocument104 pagesThermomechanical Processing and Constitutive Strength of Hot Rolled Mild SteelvishwanathanskNo ratings yet
- Casting and Fabrication of High-Damping Manganese-Copper AlloysDocument28 pagesCasting and Fabrication of High-Damping Manganese-Copper Alloysbrad209No ratings yet
- Funamental of MetallurgyDocument235 pagesFunamental of Metallurgysoumyo broto dasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Materials NotesDocument9 pagesClassification of Materials NotesJohn K KikwaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Ferrous AlloysDocument31 pagesLecture 9 - Ferrous Alloysmahmoud foudaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Alloys (Ferrous)Document103 pagesEngineering Alloys (Ferrous)Sukhwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Barrel Breakage.Document6 pagesBarrel Breakage.Recep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- The War Between Heraclea Pontica and Leucon I of BosporusDocument17 pagesThe War Between Heraclea Pontica and Leucon I of BosporusRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Karadeniz Ereğli Müzesi'Nden Herakles Aleksikakos'a Sunulan Bir Adağın DüşündürdükleriDocument17 pagesKaradeniz Ereğli Müzesi'Nden Herakles Aleksikakos'a Sunulan Bir Adağın DüşündürdükleriRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Steel Edge Snow Pusher - Kage InnovationDocument4 pagesSteel Edge Snow Pusher - Kage InnovationRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- A Group of Staters of Timotheus and - or Dionysius, Tyrants of Heraclea PonticaDocument9 pagesA Group of Staters of Timotheus and - or Dionysius, Tyrants of Heraclea PonticaRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Xian Xi 2021Document187 pagesXian Xi 2021Recep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Competition and Memory in An Ephebic VictorDocument15 pagesCompetition and Memory in An Ephebic VictorRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Memnon On The Siege of Heraclea Pontica by Prusias IDocument7 pagesMemnon On The Siege of Heraclea Pontica by Prusias IRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Nanostructured and Ultrafine-Grained Metallic ImplantDocument7 pagesCorrosion of Nanostructured and Ultrafine-Grained Metallic ImplantRecep Vatansever100% (1)
- KemikyapısıDocument42 pagesKemikyapısıRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Karadeniz Ereğli Müzesi'Nden Herakles Aleksikakos'a Sunulan Bir Adağın DüşündürdükleriDocument17 pagesKaradeniz Ereğli Müzesi'Nden Herakles Aleksikakos'a Sunulan Bir Adağın DüşündürdükleriRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Karadeniz Ereğli Müzesi'Nden Herakles Aleksikakos'a Sunulan Bir Adağın DüşündürdükleriDocument17 pagesKaradeniz Ereğli Müzesi'Nden Herakles Aleksikakos'a Sunulan Bir Adağın DüşündürdükleriRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Metallic Implant MaterialsDocument39 pagesMetallic Implant MaterialsRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Implantarmamentarium 170902170115Document99 pagesImplantarmamentarium 170902170115Recep Vatansever0% (1)
- Structure/Property Relationships in Irons and SteelsDocument21 pagesStructure/Property Relationships in Irons and Steelssuniljha121No ratings yet
- Steel MicrostructureDocument5 pagesSteel MicrostructureRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Heat Treatment of Heat Treatment of Steel Alloys Heat Treatment of Steel AlloysDocument42 pagesHeat Treatment of Heat Treatment of Heat Treatment of Steel Alloys Heat Treatment of Steel AlloysengrumairshahidNo ratings yet
- Super Bainite Yields Super-Strong Steel - World Industrial ReporterDocument5 pagesSuper Bainite Yields Super-Strong Steel - World Industrial ReporterRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Create Your Future: The Best Just Got Better: Smart Linear, Smart PulseDocument2 pagesCreate Your Future: The Best Just Got Better: Smart Linear, Smart PulseRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Some Phase Transformations in SteelsDocument8 pagesSome Phase Transformations in SteelsRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- SSAB - 912 en Bending of High Strength Steel PDFDocument8 pagesSSAB - 912 en Bending of High Strength Steel PDFchristos032No ratings yet
- High Strength Steel in FireDocument10 pagesHigh Strength Steel in FireRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Design For Assembly: Iit BombayDocument16 pagesDesign For Assembly: Iit Bombaytejap314No ratings yet
- KAMAX - Bolt and Screw CompendiumDocument60 pagesKAMAX - Bolt and Screw Compendiumjzaw65No ratings yet
- Lec 7 Fe C DiagramDocument45 pagesLec 7 Fe C DiagramAdnan MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 20180504041238-Saarstahl Product CatalogueDocument72 pages20180504041238-Saarstahl Product CatalogueRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Control of Microstructure During Solidification & Homogenization of Thin-Slab Cast Direct-Rolling (TSCDR) Microalloyed SteelsDocument259 pagesControl of Microstructure During Solidification & Homogenization of Thin-Slab Cast Direct-Rolling (TSCDR) Microalloyed SteelsRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- A New Method For Glass-Fiber Reinforced Composites ManufacturingDocument4 pagesA New Method For Glass-Fiber Reinforced Composites ManufacturingRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Steel MicrostructureDocument5 pagesSteel MicrostructureRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- 750-0020 Seawaterecbiofouling Sept15Document8 pages750-0020 Seawaterecbiofouling Sept15Recep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- 9 SolutionsDocument31 pages9 SolutionsLaurertan TavaresNo ratings yet
- Iv-Sem DTDMDocument14 pagesIv-Sem DTDMAryanNo ratings yet
- THE EFFECT OF VANADIUM AND GRAIN REFINER ADDITIONS ON THE NUCLEATION OF SECONDARY PHASES IN 1XXX Al ALLOYSDocument17 pagesTHE EFFECT OF VANADIUM AND GRAIN REFINER ADDITIONS ON THE NUCLEATION OF SECONDARY PHASES IN 1XXX Al ALLOYSdrika100% (1)
- MCQ Phase DiagramsDocument3 pagesMCQ Phase DiagramsPrince AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inKanwarlal KharolNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196890422012109 MainDocument27 pages1 s2.0 S0196890422012109 MainPranav OmkarNo ratings yet
- Unit-3: Phase EquilibriaDocument94 pagesUnit-3: Phase EquilibriaNiboli K ZhimomiNo ratings yet
- Materials Science - Alloys System - 2Document16 pagesMaterials Science - Alloys System - 2Sumit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Iws Materials and Their Behaviour PDFDocument282 pagesIws Materials and Their Behaviour PDFkatfy1No ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Alloy, Phase Diagram & SteelsDocument26 pagesChapter 5. Alloy, Phase Diagram & SteelsLaxmi PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Casting Lab 1Document20 pagesCasting Lab 1john johnsonNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Written Test For Management Trainee PostsDocument9 pagesSyllabus For Written Test For Management Trainee PostsSanjeet thakurNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Iron-Carbide Phase Diagram - STEELS: 3SP3 - Gordana A. CingaraDocument69 pages10.1 Iron-Carbide Phase Diagram - STEELS: 3SP3 - Gordana A. CingaraRyan TorresNo ratings yet
- ME8491 Engineering Metallurgy COURSE PLANDocument4 pagesME8491 Engineering Metallurgy COURSE PLANKarthick NNo ratings yet
- MATE 215 - Lab 4 Phase DiagramsDocument13 pagesMATE 215 - Lab 4 Phase DiagramsKarina CampNo ratings yet
- Tutorials PT 1 - Materials ScienceDocument19 pagesTutorials PT 1 - Materials ScienceVassish DassagneNo ratings yet
- Bs Murthy ThermodynamicsDocument761 pagesBs Murthy ThermodynamicsGomathi VarshiniNo ratings yet
- Artigos SICDocument5 pagesArtigos SICMarli GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- 98materials Phase DiagramsDocument27 pages98materials Phase DiagramsHari PrasathNo ratings yet
- AlFeCu ReviewDocument25 pagesAlFeCu ReviewJaqueline Altidis100% (1)
- Re CrystallizationDocument18 pagesRe CrystallizationSeema SuranjikaNo ratings yet
- Aluminiumalloys Intech BookDocument327 pagesAluminiumalloys Intech BookSorin DraganNo ratings yet
- Assessment of High Alumina Refractories by Phase Diagram EvaluationsDocument5 pagesAssessment of High Alumina Refractories by Phase Diagram EvaluationsNhocSkyzNo ratings yet
- Phase Rule PDFDocument13 pagesPhase Rule PDFPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument16 pagesHeat TreatmentPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Cap 4. Termodinamica Fuera Del EquilibrioDocument34 pagesCap 4. Termodinamica Fuera Del EquilibrioEdgar Solis AlbarranNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 EmmDocument40 pagesUnit 1 EmmNagaaswin SNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument19 pagesPhase Diagramsget2csNo ratings yet
- Duplex Casting Cracking MechanismDocument5 pagesDuplex Casting Cracking Mechanismgokulakrishnan vNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 MetalsDocument22 pagesLesson 5 MetalsJake CanlasNo ratings yet