Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Cal
Uploaded by
Risky Riyansh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views20 pagesELECTRICAL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentELECTRICAL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views20 pagesElectric Cal
Uploaded by
Risky RiyanshELECTRICAL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
ELECTRICAL POWER SUPPLY
The generation, transmission and
distribution system of electrical power is
called Supply System.
The Transmission System is used to deliver
bulk power from power station to the load
centers and large consumers beyond the
economical service range of the regular
primary distribution lines where as
distribution system is to deliver power from
power station to various consumers.
The Distribution System may further be
delivered into feeders, distributor and
service main.
Feeders are the conductors which connect
the station to the area to be fed by those
stations.
Distributors are the conductors from which
numerous tapings for the supply to the
consumers are taken.
Service mains are the conductors, which
connect the consumers terminal to the
distributors.
SUB STATIONS
Sub-Station server as sources of energy
supply for the local areas of distribution in
which they are located and their main
function is to receive energy transmitted at
high voltage from the generating stations
and to step down the voltage to a value
appropriate for local distribution and provide
facilities for switching.
INTRODUCTION OF MAIN INSTALLED AT
11 KV SUB STATION:(1)TRANSFORMER
The Transformer is simple in
construction and consists of Magnetic Circuit
linking with two winding known as Primary
and Secondary Winding. Besides Magnetic
Circuits and Windings it consists of a
suitable container for the assembled core,
winding, tank and suitable bushings for
insulating and bringing out terminals of the
winding from the container. Temperature
Gauges are used for measurement of
temperature of hot oil or hottest spot
temperature and oil gauge to indicate the oil
level inside tank. Gas operated
relay(Buchholz Relay) in order to give alarm
to indicate the presence of gas in case of
some minor fault and take out the
transformer out of circuit at the event of
serious fault.
CORE CONSTRUCTION OF POWER
TRANSFORMER
Since Core is Magnetic Link between the
systems connected to the Transformer and
itself contain a lot of energy, therefore, it is
not by an means the passive component as
it appears.
(2)CURRENT TRANSFORMERS (CT)
As the Current Transformer is used in
conjunction with current measuring device,
its primary winding is designed to be
connected in series with the line to the ratio
of primary secondary turns ratio.
A Current Transformer
comprises a laminated core (usually high
permeability steel) core carrying a large
number of turns of line insulated wire for the
secondary.
(3)POTENTIAL TRANSFORMER (PT)
Potential Transformer is used for
measurement of high voltage by means of
low range voltmeters or for energizing the
potential coil of wattmeter and energy
meter. This also used for energizing relay
and other protective devices.
The Potential Transformer
(PT) operates on the same principle as a
Power Transformer. Both Primary and
Secondary Windings are wound on a high
voltage winding is on the outside. The
Potential Transformer is always step down
transformer since this meant for reducing
the voltage to a reasonable operating value
(4)CIRCUIT BREAKER
Circuit Breaker is a mechanical device
designed to close or open contact members,
thus closing of an electrical circuit under
normal or abnormal conditions.
There are many types of Circuit
Breakers:Oil Breakers:- In Oil Circuit Breaker the
circuit make and breaking Oil. Nowadays it
is less in use.
Air Blast Circuit Breaker:- In Air Blast Circuit
Breaker the circuit operated by Air Pressure
and its yard.
Air Break Circuit:- In Air Circuit Breaker the
circuit make and break in natural air it is use
only for Low Voltage.
Sulphur Hexaflouride Breaker:- SF6 Circuit
Breaker is that in which SF6 with pressure is
to extinguish the arc. SF6 gas has excellent
Dielectric Arc Quenching, Chemical and
open Arc Quenching medium such as oil or
air. It has very high dielectric strength. So it
is used nowadays in Substations.
Vacuum Circuit Breaker:- in Vacuum Circuit
Breaker the Circuit Breaker breaks and
makes in Vacuum Interrupter. It is the safest
circuit makes and breaks process and used
widely nowadays.
(5)CAPACITY VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER
(C.V.T.)
Capacity Voltage Transformer is used to
remove the carrier and fundamentals
frequency. Capacity Voltage Transformer
output for carrier 0 to 10 volt.
(6)WAVE TRAP:A device is used to exclude wanted
frequency component such as noise or other
interface of a wave. It blocks the high
frequency about 62kHz to 500 kHz. Wave
Trap only hang red phase for 132KV. And for
220 kHz above it hang on yellow phase.
(7)LIGHTING ARRETER:Lighting is a huge spark, which is due to the
electrical discharge taking place between
the clouds, with in the same clouds, with in
the some cloud between the cloud and
earth. An instrument which is used to
reduce the effect of surge produced by the
lighting is known as Lighting Arrester.
Lightning Arrester act as a safety valves
designed to discharge electric surge
resulting from lightning strokes, switching or
other disturbance which would otherwise
flash over insulator for puncture insulation,
resulting in a line outage and possible failure
of equipment.
(8)MAIN ISOLATOR:Main Isolator is used in Sub Station yard in
incoming side of line of isolating the Sub
Station supply in normal condition (i.e. in off
load position) for carried out general
maintenance work.
(9)LINE EARTH SWITCH:Line Earth Switch is for purpose for Line
Earthing purpose and for carried out
maintenance work on line in normal
conditions.
(10)CT; PT UNIT:It is joint unit of two types devices i.e.
current transformer and potential
transformer for measuring current and
voltage for metering-protection purpose.
(11)NEUTRAL CURRENT
TRANSFORMER:To measure the neutral current of any
winding of transformer. The Neutral Current
is always star connected transformer should
be zero. If increase in neutral current shows
that there is fault in transformer winding. It
operate the REF relay to switch off the
supply of transformer.
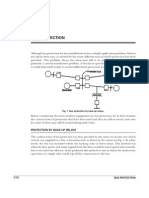
BUS BAR ARRANGEMENTS IN
SUBSTATION:
Bus Bar term is used for a main bar or
conductor carrying electric current to which
may connections may be made. Thus
electric bus bar is the collector of electric
energy at one location. Bus bars are merely
convenient means of connecting switches
and other equipment into various
arrangements. The usual arrangement of
connections is most of the Sub stations
permits working on almost any piece of
equipment without interruption to incoming
or outgoing feeders. The bus bars are
usually of Aluminum.
THERE ARE SEVERAL TYPES OF BUS
BAR ARRANGEMENTS:1) Single Bus Bar Arrangements:This is the simplest arrangement consisting
of a single set of bus bars for the full length
of the switch board and to this set of bus bar
are connected all the generators.
Transformer and feeders. The chief
advantages of such a bus bar arrangement
are low initial cost, less maintenance and
simple operation. The drawback of the
system is that in case of fault on the bus bar
whole of the supply system is affected and
all the healthy feeders are disconnected.
2)MAIN AND TRANSFORMER BUS
ARRANGEMENT:-
This arrangement has been quite frequently
adopted were the load and continuity of
supply stiff additional costs. This
arrangement provides additional flexibility.
Continuity of supply and allows periodic
maintenance without total shutdown. Such
as arrangement is suitable for highly
interconnected power network in which
flexibility is very important.
ADVANTAGES:
It ensures continuity of supply in case of
bus fault in the event of occurrence of
fault on one of the bus; the entire load
can be transferred to the other bus.
Repair and maintenance can be carried
out on the main bus without, interrupting
the supply as the load can be transferred
to the auxiliary bus.
Each load can be supplied from either
bus.
3)DOUBLE BUS DOUBLE BREAKER
ARRANGEMENT:In very imprint power station two circuit
breakers are employed for each circuit.
Such a bus bar arrangement does not
require any bus coupler and permits
switch over from bus to the other
whenever desired without interruption.
This bus arrangement is very costly and its
maintenance cost is also high. This
arrangement provides maximum. A circuit
breaker can be opened for repairs and
usual checks and the load can be shifted
on the other circuit breaker easily.
PROTECTION OF POWER T/F:-
The following relays are installed at
substation for protection power T.F. for any
abnormal condition i.e. for any fault in the
system. The relays command the
controlling circuit breaker and isolated
faulty portion.
(1)OVER CURRENT AND EARTH FAULT
PROTECTION:There are three numbers (R,Y,&B) over
current and one number earth fault
protection (relay) provided on C and
R(control and relay) panel. These relay are
provided to protect the T/F involving the
fault on over current and earth fault. The
time setting of these relays is made less
than the time setting of incoming line and
more than time setting of outgoing line.
However time setting of T/F should be kept
as min as possible to clean the fault in
least time.
(2)DIFFERENTIAL RELAY:The relay is provided to protect the
equipment in the zone between incoming
current transformer to outgoing current
transformer. It detect balancing in the
current between these zone and trip
simultaneously.
(3)RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT RELAY
(REF):It is also called instantaneous fault relay
operates in zero time. It sees the zone
between primary C.T. to secondary C.T.
(4) BUCHHOLZ RELAY:It is gas and oil actuated protective device
and it is partially universally used on all oil
immersed transformer having rating more
than that 750 kva. It is installed in the pipe
joining the main tank of the transformer to
the conservator and is used to give alarm in
case of minor faults and to disconnect the
transformer from supply mains in case of
several internal faults. The use of such a
relay is possible only with transformers
having conservators.
It consists of two elements
mounted in a small chamber located in the
pipe connections between the conservators
and the transformer tanks. When minor fault
occur, heat is produced due to current
leakage, some of oil in the transformer tank
evaporates and some vapors collects in the
top of the chamber while passing to the
conservator. When a predetermined amount
off vapor accumulates in the top of the
chamber, the oil level falls, the mercury type
switch attached to the float is tilted and
closes the alarm circuit to ring the bell. A
release clock is provided at the top of the
chamber to refill the oil. When severe fault
occur large volume of gas is evolved so that
the lower element containing a mercury
switch mounted on a hinged type flap is
tilted and the trip coil is energized. A test
cock is provided at the bottom.
(5) MASTER RELAY/ TRIPPING RELAY:It is used to extend tripping command to the
circuit breaker and operates when ever
receives command from other protection
relays, also acts as blocking relay for
breaker operation. Used for extending inter
tripping commands.
(6)DC SUPERVISION RELAY:It makes a continuous supervision of DC
supply in the C & R panel and in case of its
operation initiates alarm contacts to the AC
buzzer.
(7) AC/DC CHANGE OVER:Without flag relay for change over of AC and
DC supply. It is provided in all the panels.
The indication automatically gat connected
to DC supply.
(8) DISTANCE PROTECTION MAIN-1,
MAIN-2
Impedance relays are whenever over current
relays do not provide adequate protection.
The function even if the short circuit current
is relative low. The speed of operation is
independent of current magnitude.
Measures the apparent impedance between
the relay and the short circuit. The apparent
impedance is measured by computing the
ratio between voltage and current at the
relay. The relays which are almost always
directional are typically employed on
transmission lies where impedance is both
predictable and constant.
(9) BUS BAR PROTON TIP RELAY:Used to isolate the fault bus by tripping all
the circuit breakers connected to the faulty
bus.
(10) LOCAL REMOTE SWITCH:Used as a selector switch for remote or local
operation of the circuit breaker.
(11) AIR GAS PRESSURE ALARM:-
Initiates the low air/gas alarm and lockout
contacts.
(12) GAS PRESSURE CONTRACTOR:It is a contractor in the circuit breaker used
to lock the breaker in case sf-6 gas pressure
falls below permissible limit.
(13) OVER FLUX RELAY:Generally installed on 220 kv C & R panels
of 220/132/66KV T/F and operates if the V/f
exceeds a preset value to avoid saturation
of magnetic circuits and to avoid excessive
core/iron losses in the T/F generally its
setting is 115% of normal value.
(14) BREAKER AUX. CONTACTS:Auxiliary contacts of the breaker used for
various purpose such as indication, tripping,
closing, interlock etc.
D.C. BATTERY
Battery se are produced at the D.C. supply
to meet out the required of system of
various for tipping protection system of
various equipment at substation. This D.C.
battery normally provided at the
substation are of 100, 150, 200AH
according to the required of D.C. load
normally 220V D.C. supply is required for
substation protection system, this battery
comprises of 110 cells of volt each making
220 volt. All the tripping system protection
system is based on D.C.
These 2 Volts D.C. generally are of
lead sulfate. They are certain parameter to
check the healthiness of the battery.
(1)SPECIFIC GRAVITY:It is the ratio of gravity of the solution in
the cell to the gravity of water normally a
healthy cell must have specific gravity
between 1.185 to 1.210. This is also
measure of charging of battery and also
shows the indicate of its health
consequent as charging/discharging.
(2)VOLTAGE:There are two terminal are provided to
meant the voltage between two terminal it
should be within the range of 1.9to 2.1
over charging and under charging of
battery must be avoided for better life of
battery normally that life of battery is
estimated as 10 years.
(3) AMPERE HOUR:It is the unit to show the capacity of the
battery means as if 10 ampere hours
taken it can give 10 ampere for an hour
continuously without any dipper voltage,
i.e. fully charged. Normally 2 volt is used
in series t50 from 220 volt having certain
advantages.
1. Cost of one cell is less.
2. It cell is damage may be kept out of
circuit without effecting the D.C. o/p
considerably.
(4) BATTERY CHARGER:Battery Charger is used at the substation
to charge the D.C. battery cells on the
appropriate voltage level. This is basically
a convenient type device which convert
the A.C. for charging purpose. There are
two modes of charging.
1. Boost
2. Float
When high charging is required in less
time boost is applied and in normal case
the float operates to make care of normal
charging/discharging of battery cells.
Normally there output is 220 voltD.C.
You might also like
- Instructor Engr. Muhammad YaseenDocument33 pagesInstructor Engr. Muhammad Yaseenbedilu77No ratings yet
- 220 KV Sub-StationDocument17 pages220 KV Sub-StationJaat Pankaj BurraNo ratings yet
- 400kv SubstationDocument5 pages400kv SubstationJothi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Batch - 14 - Protection Scheme of Busbars and Transmission LinesDocument26 pagesBatch - 14 - Protection Scheme of Busbars and Transmission LinesYugendran KumaravelNo ratings yet
- KP PPTDocument22 pagesKP PPTSaurabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Elec 5204 Review Quizzes AnsDocument9 pagesElec 5204 Review Quizzes Ansveljal6317No ratings yet
- Intoduction To 400Kv Switchyard: Single Line Diagram of 400kV SubstationDocument3 pagesIntoduction To 400Kv Switchyard: Single Line Diagram of 400kV SubstationPratik LahaneNo ratings yet
- SwitchyardDocument33 pagesSwitchyardAafaque QureshiNo ratings yet
- Reduced Voltage Starting Using Part Winding Technique of 3-Phase Cage Rotor Induction MotorDocument8 pagesReduced Voltage Starting Using Part Winding Technique of 3-Phase Cage Rotor Induction MotorKennethNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection: Shoaib Ahmed Shaikh Lecturer (EE) Sukkur IBA UniversityDocument67 pagesPower System Protection: Shoaib Ahmed Shaikh Lecturer (EE) Sukkur IBA Universityfaizan100% (1)
- High Voltage Engineering: Chapter 4 Generation of High VoltagesDocument75 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering: Chapter 4 Generation of High VoltagesSunny ModiNo ratings yet
- Structure of PowerDocument7 pagesStructure of Powerkala6006No ratings yet
- Designing of A GSS and Power Line CommunicationDocument36 pagesDesigning of A GSS and Power Line CommunicationGabriela MaerskNo ratings yet
- Capacitor BankDocument16 pagesCapacitor BankKyaw Soe0% (1)
- RTCC Report 1Document36 pagesRTCC Report 1Shubham Ghongade100% (1)
- Current Transformer OperationDocument6 pagesCurrent Transformer Operationsurya892No ratings yet
- Midway Report: Project Semester: Study of 220KV Substation and SLDCDocument15 pagesMidway Report: Project Semester: Study of 220KV Substation and SLDCdamanpreet singhNo ratings yet
- ONLOAD 2007 enDocument46 pagesONLOAD 2007 enpokojang100% (1)
- Transformer Protection: Power Transformers and Power AutotransformersDocument29 pagesTransformer Protection: Power Transformers and Power Autotransformersmoham akhNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformer: National Power Training Institute of NigeriaDocument34 pagesInstrument Transformer: National Power Training Institute of NigeriaMůąxxïęm à MøhďNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesDocument43 pagesChapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Busbar Differential ProtectionDocument19 pagesBusbar Differential ProtectionVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 FailureDocument80 pages1 FailureSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Voltage Stability AnalysisDocument29 pagesVoltage Stability Analysisyohannis masreshaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Electric Power Transmission and DistributionDocument100 pagesIntroduction of Electric Power Transmission and DistributionUmair BeygNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Capacity CalculationDocument11 pagesTransmission Line Capacity CalculationRajesh Pillai88% (16)
- Testing of DC Machines - UNIT IIIDocument34 pagesTesting of DC Machines - UNIT IIIKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Transformer PtotectionsDocument19 pagesTransformer Ptotectionsbiju singhNo ratings yet
- 01 - Power System Protection-Basics and Breakers v2 (Revised) PDFDocument55 pages01 - Power System Protection-Basics and Breakers v2 (Revised) PDFJawwad Sadiq Ayon100% (1)
- EHV Prot - 2011Document70 pagesEHV Prot - 2011NimeshNo ratings yet
- Substation LayoutDocument9 pagesSubstation LayoutReynan Gabriel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Six Week Industrial Training FinalDocument26 pagesSix Week Industrial Training FinalDilpreet Singh Ghuman100% (2)
- 132 33kv SubstationDocument44 pages132 33kv SubstationRatnesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line ProtectionDocument111 pagesTransmission Line ProtectionPankaj100% (1)
- Single Line Diagram of Power Supply SystemDocument29 pagesSingle Line Diagram of Power Supply SystemAakash Saravanan100% (1)
- Ssasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Document167 pagesSsasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Sunil Singh100% (1)
- SGP Question BankDocument3 pagesSGP Question BankSanjay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Busbar Protection Philedelphia Edu LibreDocument90 pagesBusbar Protection Philedelphia Edu Libreprakasa88No ratings yet
- A Project Report On Scada System: Submitted By:-Sanskar Sagar Electrical 2017/130Document27 pagesA Project Report On Scada System: Submitted By:-Sanskar Sagar Electrical 2017/130Sharma Saab100% (1)
- Over and Under Voltage Relay CharacteriticsDocument24 pagesOver and Under Voltage Relay CharacteriticsKashif RehmanNo ratings yet
- Bhel Lem ReportDocument33 pagesBhel Lem ReportHarshita GautamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Power System Overview and ModelingDocument8 pagesUnit 1: The Power System Overview and ModelingIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent RelayDocument10 pagesTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relayhasbi fadliNo ratings yet
- CT For Protection: Prof.O.V.Gnana SwathikaDocument24 pagesCT For Protection: Prof.O.V.Gnana SwathikaSarthak VatsNo ratings yet
- EXP-4 To Perform Vector Group Testing On 3 Phase Transformer.Document7 pagesEXP-4 To Perform Vector Group Testing On 3 Phase Transformer.sameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring of Instrument Transformers - POWERGRID ExperienceDocument36 pagesCondition Monitoring of Instrument Transformers - POWERGRID ExperiencebcqbaoNo ratings yet
- JCT College of Engineering and Technology: Pichanur, Coimbatore-641105, India ISO 9001:2008 Certified InstitutionDocument16 pagesJCT College of Engineering and Technology: Pichanur, Coimbatore-641105, India ISO 9001:2008 Certified InstitutionPrakash Chandran CNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Analysis of LLC Resonant Converter Using Closed Loop PI ControllerDocument3 pagesSimulation and Analysis of LLC Resonant Converter Using Closed Loop PI ControllerijaertNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Overcurrent ProtectionDocument9 pagesThe Importance of Overcurrent ProtectionR Is100% (1)
- Types of Neutral Earthing in Power Distribution Part 2Document7 pagesTypes of Neutral Earthing in Power Distribution Part 2shoham985No ratings yet
- Session 2-2 - Building System - Electrical System ComponentsDocument48 pagesSession 2-2 - Building System - Electrical System ComponentsCeino Rey QuimintanNo ratings yet
- EET414 Chapter 5Document46 pagesEET414 Chapter 5Lee Boon HongNo ratings yet
- Voltage Control Techniques Session 1Document23 pagesVoltage Control Techniques Session 1Sumit SinghNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram: Simplified Single-Phase Balanced Three-Phase Single Line Apparatus SymbolsDocument25 pagesOne-Line Diagram: Simplified Single-Phase Balanced Three-Phase Single Line Apparatus SymbolsSafina SygNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 PDFDocument38 pagesChapter6 PDFJaved LakanwalNo ratings yet
- EE35T - Transformer Differential ProtectionDocument4 pagesEE35T - Transformer Differential ProtectionTanveer Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Technical Subjective QuestionsDocument52 pagesTechnical Subjective QuestionsEngr AHmed Ali DallNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Questions: Verilog Task Verilog FunctionDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Questions: Verilog Task Verilog FunctionProject TeamNo ratings yet
- Course - Assignment S1 2021 PDFDocument3 pagesCourse - Assignment S1 2021 PDFDJOB RogerNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: VLT® 4152 - 4652 VLT® 5122 - 5602 VLT® 6152 - 6652 VLT® 8152 - 8652Document158 pagesService Manual: VLT® 4152 - 4652 VLT® 5122 - 5602 VLT® 6152 - 6652 VLT® 8152 - 8652ArzymanNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument2 pagesCircuit Theoryroyal1979No ratings yet
- 08 Ta BWGF 000a B6eDocument3 pages08 Ta BWGF 000a B6eAmador AguilaNo ratings yet
- T7S 1250 PR231/P LS/I in 1250A 3p F FDocument3 pagesT7S 1250 PR231/P LS/I in 1250A 3p F FAldair PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument78 pages4th LectureNaveed RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Radar Systems: TEST - 01Document8 pagesRadar Systems: TEST - 01mounikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Basics-2-3Document40 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Basics-2-3Syed Zubair ZahidNo ratings yet
- GE Solar Modeling-V1-1 PDFDocument36 pagesGE Solar Modeling-V1-1 PDFRosyNo ratings yet
- DR AF T: Annex A Product Safety StandardsDocument4 pagesDR AF T: Annex A Product Safety StandardstatacpsNo ratings yet
- Highvoltage OpampDocument28 pagesHighvoltage OpampKamil Gökberk ErginNo ratings yet
- WojaduxexasodDocument2 pagesWojaduxexasodNovri AndiNo ratings yet
- Led TV: Service ManualDocument68 pagesLed TV: Service ManualZigma FNo ratings yet
- S60SC4M Mxqwqqs PDFDocument11 pagesS60SC4M Mxqwqqs PDFBaharak BaghiNo ratings yet
- 42tl016 Audio Transformer DiagramDocument2 pages42tl016 Audio Transformer DiagramMiguelangel Lopez MadridNo ratings yet
- Eaglerise Profile 2010Document18 pagesEaglerise Profile 2010李昊No ratings yet
- ELYM 115 2nd Opp Examination MC-2022-09-21 TTDocument3 pagesELYM 115 2nd Opp Examination MC-2022-09-21 TTTrevor TolibadiNo ratings yet
- Phase-Control Alternatives For Single-Phase AC Motors Offer Smart, Low-Cost, SolutionsDocument8 pagesPhase-Control Alternatives For Single-Phase AC Motors Offer Smart, Low-Cost, SolutionsAdedotun J. AgbemukoNo ratings yet
- Mounting Instructions - 123ignitionDocument5 pagesMounting Instructions - 123ignitionminimaniaNo ratings yet
- Sprinter DRB III Manual PDFDocument52 pagesSprinter DRB III Manual PDFRoger SegoNo ratings yet
- QS4 QuickstartDocument10 pagesQS4 QuickstartEvita Elizabeth Ramos CuevasNo ratings yet
- FR-E800 Instruction Manual - Function Ib0600868engeDocument534 pagesFR-E800 Instruction Manual - Function Ib0600868engeNguyễn Quang HảoNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: MODEL: 29A3DE / 29A3E / 29A3SHDocument19 pagesSchematic Diagram: MODEL: 29A3DE / 29A3E / 29A3SHCristhan Dwi AryaNo ratings yet
- Alums - GSM RF - Student GuideDocument262 pagesAlums - GSM RF - Student Guidecpatel49No ratings yet
- BLDC Trpezoidal Control PDFDocument35 pagesBLDC Trpezoidal Control PDFAlei El Din AliNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Attenuation and Scintillation Effects PrimeraDocument2 pagesAtmospheric Attenuation and Scintillation Effects Primeraph abeynayakeNo ratings yet
- Bzt52c2v4 Series g1804Document7 pagesBzt52c2v4 Series g1804Zlatko Mrki HrncicNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapterwise Weightage - EAMCETDocument2 pagesPhysics Chapterwise Weightage - EAMCETVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- References ThesisDocument7 pagesReferences ThesisFaizal IsmailNo ratings yet