Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Cold War and The Americas2
Uploaded by
Cathy CherubinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Cold War and The Americas2
Uploaded by
Cathy CherubinCopyright:
Available Formats
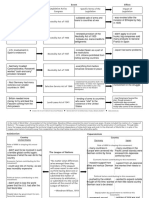
THE COLD WAR AND THE AMERICAS: Cathy Cherubin Per.
1
Complete this chart:
President
Key Domestic Policies
Truman
-1949 Fair Deal: Little success - Truman Doctrine - which
- Declared the right to the United - Responses since many countries
due to Congress.
stated that the U.S. would
States to be able to intervene in that accepted US money to help
support Greece and Turkey
Latin America and stabilize any the economy thought it would
- Rapid Peacetime reconversion
with economic and military aid country that needed help
do greater good than harm. That
after WWII.
to prevent them from falling
wasnt the case, especially in
into the Soviet sphere and later - Wanted to make sure to have
countries like Argentina. Many
- Wage/Price Control to reduce
extended to other countries that allies in Latin America to aid
Latin American countries
inflation(Failed.)
Us when needed
practiced non-communist
realized that the US was
ideologies
starting to be very controlling
- Put an end to labor unrest/
and wanted them out of their
strikes.
- Policy of containment
countries.
- Desegregation of the military
and the civil sercive.
Foreign Policies
Policies on Latin America
Reaction in Latin America
- (OAS) Over US objections
articles 15/16 of the charter
prohibited intervention
including economic and
diplomatic coercion into the
affairs of other signatory
nations.
Eisenhower
- Middle Road
- Continued containment policies - focused on helping Latin
- Latin American countries were
American countries to not get very appreciative of
- Did not remove New Deal
- Containment was not enough to into the Soviet Sphere of
Eisenhowers help even though
entirely.
stop Soviet expansion influence.
they doubted how the US was
adopted a policy know as
playing a part in their country.
- Role of Government was to
Massive Retaliation (U.S was - In order to show this, the US
balance the budget/ create
prepared to use atomic
provided support to Latin
- For instance, in Guatemala, the
infrastructure to promote
weapons if they were to be
American countries that needed president who was trying to
continued economic growth.
attacked)
help with their domestic
present democracy in the
policies as well as their
country was worried that
- Avoided tax cuts.
- Eisenhower Doctrine - stated
international policies if needed. Guatemala was going to
that a nation could request
become dependent on the US
- The Federal-Aid Highway Act: economic and military
for its economy
allowed faster transportation.
assistance from the United
States if it was being attacked
- decided to make sure that
- Did not pay much attention to
by a communist nation (drafted
Guatemala had its own
the poor.
in part as a response to an
independent economy.
increasing spread in
- Eisenhower encouraged the
- Great hostility due to harsh
communism, and tensions in
removal of McCarthy from
dictatorships working only for
the Middle East
behind the scenes.
the benefit of US.
- Ended Korean War
- Appointed Warren as Chief
- Hostility decreased (not much)
Justice Brown v. Board.
- Didn't get involved in the
after increase in US economic
Vietnam War but funded 80%
assistance and the fall of
- Was half-hearted supporter of
of battle costs to France and
Batista.
civil rights; wanted gradual
went to the Geneva conference,
change.
which split Vietnam at the 17th
parallel to create South
- Executive used army for
Vietnam
American children to attend
white school.
Kennedy
- New Frontier.
- Bay of Pigs Crisis
- mostly focused on Cuba due to
the missile crisis. However,
- Promised federal funding for - Cuban Missile Crisis- strained Kennedy did try to be on good
education, medical care, gov.
relationship between Soviet
terms with other countries to
intervention in economy, and
Union
avoid going through the same
economic aid in rural regions.
thing with Cuba.
- Sought to contain the perceived
- Promised to end racial
threat of communism in Latin - did try to avoid military
discrimination.
America by establishing the
conflicts with all these
Alliance for Progress which
countries.
- Income tax reduction proposed. sent aid to some countries and
sought greater human rights
- Removed death penalty in D.C. standards in the region
- Executive Order 10925- Peace corps
government contractors to treat
applicants equally without regard - Berlin speech
for color, race, etc.
- Founder of the US-Israeli
- Established the Presidents
military alliance
Committee on Equal
Employment Opportunity
- Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
- Civil Rights Act of 1964
proposed.
- Equal Pay Act of 1963.
- Apollo Program man on the
moon after his death.
- Most of the reactions in Latin
America were negative because
the countries did not want the US
to have legislature over their
government.
- In Cuba, the Cubans were very
negative about US involvement
in Cuba and wanted to do their
won thing.
- Relations between Latin
America and US improved due
to US aid in improving living
conditions for the majority of
Latin Americans.
- ~Peace Corps assistance and
massive military spending
improved perception of
Americans.
Johnson
- Civil Rights Act of 1964
passed: A. Americans can vote.
- Civil Rights Act of 1968
passed: equal housing
- Fair Housing Act passed.
-Passed Immigration Act of 1965
which changed policy from NonEuropeans.
- Great Society Program aid in
education, Medicare/aid, urban
renewal, conservation, fight
against poverty/ disease, etc.-->
passed.
- Poverty declined
- Medicare covered millions of
Americans.
- Gun Control Act of 1968
- Greatly invested in the Vietnam - did not so much focus on Latin - became involved in Vietnam
war - 500,000 American troops America like the past presidents was because the US was against
in South Vietnam and no end in and rather he focused on
communism and that is what
sight to the conflict
Vietnam to make sure that the
the north was promoting.
north and the south did not
- tried to initiate a peace treaty completely destroy each other. - OAS cooperated with the
but it only went into affect after
removal of a Castro-style
he left office
government undermined its
credibility (Was seen as a
- Johnsons policy toward Latin
puppet to the US)
America became increasingly
interventionist, culminating
- Hostile relations returned.
with the deployment of U.S.
soldiers to Santo Domingo to
prevent another communist
takeover in the Caribbean.
Nixon
- Economic goal was to reduce
inflation by ending the war.
- Practiced Detente(open
relations)
- Maintained close relations with
Cuban-American exile
community and he assured
- Proposed grants to the state - Opened up communication
soviets and Cubans that he
did nothing but boost his political with China and Russia (signed would not attack Cuba.
credit.
a Nuclear Arms Treaty SALT)
- When Chile elected Allende as
- Announced temporary price/
- Reduction of Nuclear
their president, Nixon made
wage control, let dollar float vs.
Weapons eased the Cold War
sure to convert resistance
other currencies.
tensions.
against the Marxist leader.
- Wage/price controls ended after - Ended American involvement
unpopularity.
in the war in Vietnam
( replacing American troops
- New Federalism
with the Vietnamese troops,
also called "Vietnamization")
- Devolve power to state and
local elected officials.
- Strongly supported General
Yahya Khan of Pakistan during
- Conservation Movement
the Indo-Pakistan War of 1971
despite widespread human
- Environmental Protection
rights violations against the
Agency, Clean Air Act of 1970,
Bengalis, particularly Hindus,
vetoed Clean Water Act of 1972
by the Pakistan Army
due to excessive spending, but
overrode by Congress.
- Private health insurance
reform HMOs
- War on Drugs
- Civil Rights large scale
integration of public schools.
- Endorsed the Equal Rights
Amendment.
- Printed anti-Allende messages
to be published in Chile and
after economic, political and
social unrest; Pinochet came to
power in Chile.
- Comes to show how effective
Nixons resistance against
Allende really was.
- Severely damaged US- Latin
American relations.
Ford
- Economic Policy Board by
Executive Order.
- Inherited Richard Nixon's
- policies in Latin America were - The fact that Ford was in office
foreign policies and his foreign mainly based on alliances that for such a short amount of time is
policy advisers.
were not very good
why he did not really gain the
- Whip Inflation Now
trust of some Latin American
campaign (WIN)
- Continued the dtente policy - sent after unpopular policies countries.
with both the Soviet Union and that were against human rights
- Reduce spending/consumption. China, to ease the tensions of the standards.
- Very low point in US-Latin
Cold War
American relations.
- Supporter of Equal Rights
Amendment.
- SALT treaty still in place
- Opposed Roe v. Wade; would
later become pro-choice.
- Gave military aid and
humanitarian assistance to
South Vietnam
- Education for all Handicapped
Children Act of 1975.
- Trips to Japan and China, a
10-day European tour, and
- Unemployment increased
cosponsorship of the first
Advocated tax reduction and
international economic summit
signed Tax Reduction Act of
meeting
1975.
- Preventing a new war between
the Arab-Israeli opponents was
a major objective
- "Shuttle diplomacy" in the
Middle East
- More aid to both Israel and
Egypt-interim truce agreement
(didn't last)
Carter
- Issued executive order declaring - Camp David Accords
- Believed that the Latin
unconditional amnesty for
success(14 months of
American policies should
Vietnam War-era draft evaders.
diplomatic efforts by Egypt,
reflect its highest moral
Israel, and the United States)
principles. In Latin America,
- Head Start program was
expanded
- Hoped to continue the policy of - Wanted to promote human
dtente with the Soviet Union rights as a standard relation
- Many health and welfare acts
but had several major
with Latin American countries
passed.
confrontations with the
- to decrease the import of
Russians
- Child Nutrition Amendments of
weapons into Latin America
1978, Federal Mine Safety and - Recognition of China
Health Act of 1977, Pregnancy
Discrimination Act of 1978, Age - Iran Hostage crisis (escalated
discrimination in employment
tensions)
Act Amendments of 1978, etc.
- Proposed a bill for universal
national health insurance, later it
became limited. Proposed
mandatory hospital cost control:
failed.
- Control on oil prices during
energy crisis.
- Economy falls in recession after
short period of economic growth.
- United States Department of
Energy: conserve energy.
- Signed National Energy Act
- not successful in his diplomacy
but wanted moral principles and
to promote human rights between
the latin american countries and
US
You might also like
- APUSH Period 7 TestDocument10 pagesAPUSH Period 7 Testdannyal Alphones100% (1)
- AMSCO Chapter 26 NotesDocument3 pagesAMSCO Chapter 26 NotesMelissa Nunez92% (13)
- George HW Bush Is Really George H Scherf Jr.Document37 pagesGeorge HW Bush Is Really George H Scherf Jr.jdfarrell4575% (4)
- Apush Chapter 28 NotesDocument14 pagesApush Chapter 28 NotesatreyisNo ratings yet
- c121 Task4Document6 pagesc121 Task4Willie HarringtonNo ratings yet
- APUSH Exam 1996Document15 pagesAPUSH Exam 1996gophillies4000No ratings yet
- History Ib Notes On VietnamDocument3 pagesHistory Ib Notes On VietnamAnalía Piacentini Chinni100% (1)
- Moral Diplomacy and WilsonDocument13 pagesMoral Diplomacy and WilsonDavid Wang100% (1)
- Nathan Dunlap Photos and NarrativeDocument4 pagesNathan Dunlap Photos and NarrativeMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- USH Final Study GuideDocument11 pagesUSH Final Study GuideErica TranNo ratings yet
- USA History NotesDocument30 pagesUSA History NotesAayushiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: The Common Good: General Terms and EventsDocument4 pagesUnit 5: The Common Good: General Terms and EventsLailaS17No ratings yet
- Final ReviewDocument83 pagesFinal ReviewAlexandra TaylorNo ratings yet
- Danika Being AwesomeDocument7 pagesDanika Being AwesomeNihal ThapaNo ratings yet
- Cuban RevoultutionDocument5 pagesCuban RevoultutionCodeen WhiteNo ratings yet
- US GeoDocument7 pagesUS GeoserpilNo ratings yet
- Post-War One PagerDocument2 pagesPost-War One PagerParth JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 NotesDocument4 pagesUnit 7 NotesrachelNo ratings yet
- History Sem 1 SGDocument7 pagesHistory Sem 1 SGRachel LewisNo ratings yet
- The Most Significant Political Reform That Progressives Accomplished at TheDocument5 pagesThe Most Significant Political Reform That Progressives Accomplished at TheJessica AdamNo ratings yet
- The Killing ZoneDocument17 pagesThe Killing ZoneDanielNo ratings yet
- SdggasDocument3 pagesSdggasCasey TaylorNo ratings yet
- Potential Short Answer Questions/Essay Topics Include:: Market Revolution This ThisDocument6 pagesPotential Short Answer Questions/Essay Topics Include:: Market Revolution This Thiss20190142No ratings yet
- USA Foreign PolicyDocument10 pagesUSA Foreign PolicyEdgar HernandezNo ratings yet
- KennedyDocument6 pagesKennedyapi-345327430No ratings yet
- America's History 8th Edition Chapter 31Document19 pagesAmerica's History 8th Edition Chapter 31Anonymous lFgKXClHNo ratings yet
- United States of AmericaDocument11 pagesUnited States of AmericaSergio Nakama Momichis RamírezNo ratings yet
- 10 - Washington1Document14 pages10 - Washington1api-234908816No ratings yet
- Cuban Independence From Spain From 1868 To 1898Document5 pagesCuban Independence From Spain From 1868 To 1898Alejandro Vargas CarrascalNo ratings yet
- ApushDocument9 pagesApushmenoahisloveNo ratings yet
- The Federalist Era1Document10 pagesThe Federalist Era1albertmorales82No ratings yet
- The American Revolution Power NotesDocument3 pagesThe American Revolution Power Notesapi-238207999No ratings yet
- Usa 1932-1969Document6 pagesUsa 1932-1969Augusto NuñezNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For FinalDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Finalrflores71400No ratings yet
- Li Ba JoDocument14 pagesLi Ba JoWania AbbasiNo ratings yet
- 055 The Washington Presidency PresentationDocument21 pages055 The Washington Presidency PresentationBianca CzarneckiNo ratings yet
- Study Guide U3Document20 pagesStudy Guide U3Trần Phan Gia ThưNo ratings yet
- Post WWII PresidentsDocument5 pagesPost WWII PresidentsVickyNo ratings yet
- Module 20 - Lecture SlidesDocument29 pagesModule 20 - Lecture Slidesapi-297591968No ratings yet
- Us His ReviewDocument7 pagesUs His ReviewMinh Nguyen DucNo ratings yet
- US HISTORY FROM 1865 To PresentDocument10 pagesUS HISTORY FROM 1865 To PresentGraceNo ratings yet
- A Survey: American History Alan Brinkley CH 27 NotesDocument5 pagesA Survey: American History Alan Brinkley CH 27 NotesRachel Colleen GrayNo ratings yet
- World War 1Document23 pagesWorld War 1api-277598276No ratings yet
- There Was Nothing New About The New DealDocument4 pagesThere Was Nothing New About The New Dealbdw39No ratings yet
- Chapter 19-25 NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 19-25 NotestheLimitingNo ratings yet
- Period 3 NotesDocument3 pagesPeriod 3 Noteschloechiang0No ratings yet
- Cold War Assignment 2Document3 pagesCold War Assignment 2Daidrill FlavorNo ratings yet
- PERIOD 4 GUIDE Growth and Expansion 1800-1848Document14 pagesPERIOD 4 GUIDE Growth and Expansion 1800-1848kendall knightNo ratings yet
- Apush 1900-1918Document3 pagesApush 1900-1918Aaron BautistaNo ratings yet
- Ib History Notes - Castro's Foreign Policy - The Cold WarDocument9 pagesIb History Notes - Castro's Foreign Policy - The Cold Warmimi incNo ratings yet
- Ib History Notes Castro S Foreign Policy The Cold WarDocument9 pagesIb History Notes Castro S Foreign Policy The Cold WarJournal ArtNo ratings yet
- Apush Unit 2 GuideDocument2 pagesApush Unit 2 Guideapi-121876090No ratings yet
- Chapter 5-7Document10 pagesChapter 5-7SclaffenNo ratings yet
- Foreign PolicyDocument10 pagesForeign PolicyRanaAshiqERasool100% (1)
- Chapter 19 and 20Document5 pagesChapter 19 and 20maferNo ratings yet
- Articles of ConfederationDocument4 pagesArticles of ConfederationAaron AndujoNo ratings yet
- 06 Overview 20 21 US StudentsDocument10 pages06 Overview 20 21 US StudentsDenisa Alexandra AdamNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review Sheet - U.S. History A Unit 1: Continuity vs. ChangeDocument15 pagesFinal Exam Review Sheet - U.S. History A Unit 1: Continuity vs. Changebhr856No ratings yet
- The 20th Century Begins Battle of IdeasDocument13 pagesThe 20th Century Begins Battle of Ideasюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- The Beginnig of The Cold War To 1953Document42 pagesThe Beginnig of The Cold War To 1953Luzyka SioNo ratings yet
- Ecological CityDocument2 pagesEcological CityЕмина РустемоскаNo ratings yet
- Three Widows Who Trusted GodDocument9 pagesThree Widows Who Trusted GodSolomon IyamNo ratings yet
- Contracts Outline 2022 v1Document63 pagesContracts Outline 2022 v1AmandaNo ratings yet
- Clog On Redemption - A Property Law II Project - Jay SingheeDocument22 pagesClog On Redemption - A Property Law II Project - Jay Singheejay1singheeNo ratings yet
- TSO C155bDocument6 pagesTSO C155bHosein AlaviNo ratings yet
- Pdic-Invitation To Bid March012019Document1 pagePdic-Invitation To Bid March012019JhinFritzNo ratings yet
- Tumen Buzdar Tribal Area: List of Candidates For Appointment As Sepoy Tribal Area, Baloch Levy, D.G.KhanDocument66 pagesTumen Buzdar Tribal Area: List of Candidates For Appointment As Sepoy Tribal Area, Baloch Levy, D.G.Khanمحمد عمران راناNo ratings yet
- 1060Document8 pages1060jbkmailNo ratings yet
- Adb-200 - Project Constraints With AttachmentsDocument80 pagesAdb-200 - Project Constraints With AttachmentsM KamranNo ratings yet
- Blackburn: of Determinism. What Is Being Ruled Out Is The Rule For Individual Will. What Is Happening Is TheDocument3 pagesBlackburn: of Determinism. What Is Being Ruled Out Is The Rule For Individual Will. What Is Happening Is TheSagar AroraNo ratings yet
- Jde CRM Sales Order MGMT DsDocument4 pagesJde CRM Sales Order MGMT DsAmiiiNo ratings yet
- 7.1.4 Transfer of Work Worksheet Template and Checklists 1OCT2016Document12 pages7.1.4 Transfer of Work Worksheet Template and Checklists 1OCT2016cover filterNo ratings yet
- DIAZ and TIMBOL Vs Sec of Finance and CIRDocument2 pagesDIAZ and TIMBOL Vs Sec of Finance and CIRBrylle Deeiah TumarongNo ratings yet
- Casino Labor Association Vs CADocument11 pagesCasino Labor Association Vs CAAnsai CaluganNo ratings yet
- Unenforceable ContractsDocument10 pagesUnenforceable ContractsGolaNo ratings yet
- Mfa700 ExamDocument5 pagesMfa700 ExamThomas T.R HokoNo ratings yet
- AY Program For June 18th 2016Document6 pagesAY Program For June 18th 2016Darnelle Allister-CelestineNo ratings yet
- De Leon, Nicole Franchezka G. Case Opao, Gabrielle V. Prof. Randy SarmientoDocument4 pagesDe Leon, Nicole Franchezka G. Case Opao, Gabrielle V. Prof. Randy SarmientoNicole Franchezka De LeonNo ratings yet
- Anticipation GuideDocument1 pageAnticipation Guideapi-259906298No ratings yet
- Sujeet Yadav 2022Document6 pagesSujeet Yadav 2022Akshit JainNo ratings yet
- Standards of Auditing NotesDocument101 pagesStandards of Auditing NotesRocky Rk100% (4)
- Cada IntmgtAcctg3Exer1Document7 pagesCada IntmgtAcctg3Exer1KrishNo ratings yet
- Quote Identification For To Kill A MockingbirdDocument2 pagesQuote Identification For To Kill A MockingbirdJacjac BattsNo ratings yet
- ##Cell - Sec - 4 Easy Ways To Block Robocalls - Cyberguy - Com:how-To:4-Easy-Ways-To-Block-Robocalls-FastDocument7 pages##Cell - Sec - 4 Easy Ways To Block Robocalls - Cyberguy - Com:how-To:4-Easy-Ways-To-Block-Robocalls-Fastwise222No ratings yet
- DLL Esp 7 W1 Q2Document1 pageDLL Esp 7 W1 Q2Winsome Nena CaumboNo ratings yet
- Muskan Legal NoticeDocument5 pagesMuskan Legal NoticeAdv. Shashaank SharmaNo ratings yet
- MN CDMQXDocument260 pagesMN CDMQXJackson Dias RochaNo ratings yet
- Federal Register / Vol. 70, No. 199 / Monday, October 17, 2005 / NoticesDocument2 pagesFederal Register / Vol. 70, No. 199 / Monday, October 17, 2005 / NoticesJustia.comNo ratings yet