Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advanced Communications Matlab-1
Uploaded by
AdiseshuMiddeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced Communications Matlab-1
Uploaded by
AdiseshuMiddeCopyright:
Available Formats
Advance Communications Lab Manual
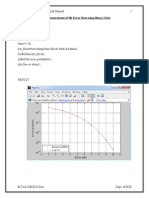
1. Measurement of Bit Error Rate using Binary Data
n=23;
k=12;
dmin=7;
ebno=1:10;
ber_block=bercoding(ebno,'block','hard',n,k,dmin);
berfit(ebno,ber_block)
ylabel('bit error probability');
title('ber vs eb/no');
RESULT:
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
2. Verification of minimum distance in Hamming Code
m=3;
n=2^m-1;
k=4;
msg=[0 0 0 0; 0 0 0 1; 0 0 1 0; 0 0 1 1; 0 1 0 0; 0 1 0 1; 0 1 1 0; 0 1 1 1];
code1 =encode(msg,n,k,'hamming/binary');
code2 =num2str(code1);
code= bin2dec(code2);
number1= [];
for i=1:8
for j=i+1:8
[number]=biterr(code(i),code(j),7);
number1=[number1 number];
end
end
minidistance = min(number1)
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
3. Determination of output of convolutional Encoder for a given sequence
%convolution encoder;input=1bit output=2bits with 3 memory elements,code
%rate=1/2.
function[encoded_sequence]=convlenc(message)
message=[ 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 ];
enco_mem=[ 0 0 0]; %no.of memory elments=3
encoded_sequence=zeros(1,(length(message))*2);
enco_mem(1,3)=enco_mem(1,2);
enco_mem(1,2)=enco_mem(1,1);
enco_mem(1,1)=message(1,1);
temp=xor(enco_mem(1),enco_mem(2));
O1=xor(temp,enco_mem(3));%gener.polynomial=111
O2=xor(enco_mem(1),enco_mem(3));%gener.polynomial=101
encoded_sequence(1,1)=O1;
encoded_sequence(1,2)=O2;
msg_len=length(message);
c=3;
for i=2:msg_len
enco_mem(1,3)=enco_mem(1,2);
enco_mem(1,2)=enco_mem(1,1);
if(i<=msg_len)
enco_mem(1,1)=message(1,i);
else
enco_mem(1,1)=0;
end
temp=xor(enco_mem(1),enco_mem(2));
O1=xor(temp,enco_mem(3));
O2=xor(enco_mem(1),enco_mem(3));
encoded_sequence(1,c)=O1;%01 generated polynomial(1,1,1)
c=c+1;
encoded_sequence(1,c)=O2;%02 generated polynomial(1,0,1)
c=c+1;
end
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
RESULT:
ans =
Columns 1 through 17
Columns 18 through 34
ans =
Columns 1 through 17
Columns 18 through 34
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
4. Determination of output of convolutional Decoder for a given sequence
tb=2;
t=poly2trellis([3],[7,5]);
encoded_sequence=[ 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 ];
decoded=vitdec(encoded_sequence,t,tb,'trunc','hard')
RESULTS:
decoded =
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
5. Efficiency of DS Spread Spectrum Technique
%direct sequence spread spectrum
clc
clear all;
%generating the bit pattern with each bit 6 samples long
b=round(rand(1,20));
pattern=[];
for k=1:20
if b(1,k)==0
sig=zeros(1,6);
else
sig=ones(1,6)
end
pattern=[pattern sig];
end
plot(pattern);
axis([-1 130 -0.5 1.5]);
title('\bf\it original bit sequenece');
%generating the psedorandom bit pattern for spreading
spread_sig=round(rand(1,120));
figure,plot(spread_sig);
axis([-1 130 -0.5 1.5]);
title('\bf\it psedorandom bit sequenece');
%xoring the pattern with spread signal
hopped_sig=xor(pattern,spread_sig);
%modulating the hopped signal
dsss_sig=[];
t=[0:100];
fc=0.1;
c1=cos(2*pi*fc*t);
c2=cos(2*pi*fc*t+pi);
for k=1:120
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
if hopped_sig(1,k)==0;
dsss_sig=[dsss_sig c1]
else
dsss_sig=[dsss_sig c2]
end
end
figure,plot([1:12120],dsss_sig);
axis([-1 12120 -1.5 1.5]);
title('\bf\ it dss signal');
%plotting the fft of dsss signal
figure,plot([1:12120],abs(fft(dsss_sig)));
RESULT:
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
10
6. Simulation of Frequency Hopping (FH) system
clear all;
s=round(rand(1,20));
signal=[];
carrier=[];
t=[0:10000];
fc=.01;
for k=1:20
if s(1,k)==0
sig= -ones(1,10001);
else
sig=ones(1,10001);
end
c=cos(2*pi*fc*t);
carrier=[carrier c];
signal=[signal sig];
end
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(signal);
axis([-1 200050 -1.5 1.5]);
title('/bf/it original bit sequence');
%BPSK modulation of signal
bpsk_sig=signal.*carrier;
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(bpsk_sig);
axis([-1 200050 -1.5 1.5]);
title('/bf/it BPSK modulated signal');
%FFT plot of BPSK modulated signal
figure, plot([1:200020],abs(fft(bpsk_sig)));
title('/bf/it FFT of BPSKmodulated signal');
%preparation of six carrier frequencies
fc1=.01; fc2=.02; fc3=.03;
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
11
fc4=.04; fc5=.05; fc6=.06;
c1=cos(2*pi*fc1*t);c2=cos(2*pi*fc2*t);c3=cos(2*pi*fc3*t);
c4=cos(2*pi*fc4*t);c5=cos(2*pi*fc5*t);c6=cos(2*pi*fc6*t);
%random frequencies hoops to form a spread signal
spread_sig =[];
for n=1:20
c=randint(1,1,[1 6]);
switch(c)
case(1)
spread_sig=[spread_sig c1];
case(2)
spread_sig=[spread_sig c2];
case(3)
spread_sig=[spread_sig c3];
case(4)
spread_sig=[spread_sig c4];
case(5)
spread_sig=[spread_sig c5];
case(6)
spread_sig=[spread_sig c6];
end
end
figure,plot([1:200020],abs(fft(spread_signal)));
freq_hopped_sig=bpsk_sig.*spread_signal;
figure,plot([1:200020],abs(fft(freq_hopped_sig)));
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
12
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
13
7. Histogram of a Image
clc;
clear all;
f=imread('cameraman.tif');
figure,imshow(f);
title('Input Image');
h=imhist(f);
h1=h(1:10:256);
horz=1:10:256;
figure,bar(horz,h1);
figure,plot(horz,h1);
title('Histogram Equalized Image');
Z=adapthisteq(f,'cliplimit',0.9,'distribution','uniform');
imview(Z);
b=imhist(f);
figure,imshow(b);
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
14
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
15
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
16
8. Verification of various Transforms - FT
RGB=imread('peppers.png');
I=rgb2gray(RGB);
J=fft2(I);
k=ifft2(J);
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(RGB);
title('original image');
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I);
title('gray scale image');
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(J);
title('DFT');
subplot(2,2,4);imshow(k,[0 255]);
title('IDFT');
RESULT:
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
17
9. Verification of various Transforms - DCT
x=imread('lena.png');
subplot(4,1,1);
imshow(x);
title('input image');
%convert rgb to BW image
a=im2bw(x);
subplot(4,1,2);
imshow(a);
title('input BW image')
%convert bw to rgb
b=bw2gray(a);
subplot(4,1,3);
imshow(b);
title('bw to rgb image');
%DCT
d=dct2(a);
subplot(4,1,4);
imshow(d);
title('DCT image');
%Inverse dct
i=idct2(d);
subplot(4,1,5);
h=imshow(i,[0 255]);
title('IDCT image');
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
18
10. Detection techniques using derivative operators - Edge
i=imread('coins.png');
imshow(i);
j=edge(i,'sobel');
figure, imshow(j)
k=edge(i,'prewitt');
figure, imshow(k)
l=edge(i,'robert');
figure, imshow(l)
h=edge(i, 'log');
figure, imshow(h)
RESULT:
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
19
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
20
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
21
Detection techniques using derivative operators - Point
%point detection%
I=imread('circuit.tif');
H=[1 1 1; 1 -8 1; 1 1 1];
B=imfilter(I,H);
subplot(1,2,1),imshow(I),title('Original image');
subplot(1,2,2),imshow(B),title('Point detection');
Detection techniques using derivative operators - Line
f= imread('coins.png');
imshow(f)
g= edge(f,'horizontal');
h= edge(f,'vertical');
figure, imshow(g)
figure, imshow(h)
k=g+h;
figure,imshow(k)
l=g-h;
figure,imshow(l)
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
22
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
23
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
24
11. Implementation of FIR filter
N=60;
R=0.5;
b=firnyquist(N,4,R,0,'nonnegative');
h=firrcos(N,0.25,R,2,'rolloff');
hfvt=fvtool(b,1,h,1);
set(hfvt,'color', [1 1 1]);
legend(hfvt,'FIR NYQUIST DESIGN','FIR RCOS DESIGN');
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
M.Tech DECS II Sem
25
Dept. of ECE
Advance Communications Lab Manual
26
12. Implementation of IIR filter
clc;
N=10; %UNCONSTRAINED NUMERATOR ORDER
M=10; %UNCONSTRAINED DENOMINATOR ORDER
F=[0 0.4 0.5 1]; %FREQUENCY VECTOR
E=F; %FREQUENCY EDGES
A=[1 1 0 0]; %MAGNITUDE VECTOR
W=[1 1 100 100]; %WEIGHT VECTOR
Nc=12; %CONSTRAINED NUMERATOR ORDER
Mc=12; %CONSTRAINED DENOMINATOR ORDER
R=0.92;
[b,a,err,sos,g]=iirlpnorm(N,M,F,E,A,W);
[bc,ac,errc,sosc,gc]=iirlpnormc(Nc,Mc,F,E,A,W,R);
H(1)=dfilt.df1sos(sos,g);
H(2)=dfilt.df1sos(sosc,gc);
[z,p,k]=zpk(H(2)); %FINDS THE POLES AND ZEROS OF CONSTRAINED FILTER
sqrt(real(p).^2+imag(p).^2) %RADII OF ALL POLES
hfvt=fvtool(H);
legend(hfvt,'IIR unconstrained design','IIR constrained design');
set(hfvt,'color',[1 1 1]);
M.Tech DECS II Sem
Dept. of ECE
You might also like
- Advance Communications MatlabDocument26 pagesAdvance Communications MatlabPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Exp - No.5: Study and Implement The CDMA Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Technique Using MATLABDocument8 pagesExp - No.5: Study and Implement The CDMA Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Technique Using MATLABPriya RanjanNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Bit Error Rate: Rat 'Overall'Document24 pagesMeasurement of Bit Error Rate: Rat 'Overall'Muhammed HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- WC Lab FileDocument30 pagesWC Lab FilekannNo ratings yet
- 7 To 10Document11 pages7 To 10Ayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Signal Coding and Estimation Theory PracticalDocument11 pagesSignal Coding and Estimation Theory Practicalrohit_vishwakarma786100% (2)
- Simulation Experiments-Com LabDocument14 pagesSimulation Experiments-Com LabSanjana M PNo ratings yet
- All DC ExprimentDocument8 pagesAll DC Exprimentatharvaingole11903No ratings yet
- DSP Lab ManualDocument62 pagesDSP Lab Manuall_wondersNo ratings yet
- DIP LAB Record III - CSDocument16 pagesDIP LAB Record III - CSAnand PrintNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lab Manual Exercise ProblemsDocument38 pagesVLSI Lab Manual Exercise ProblemsPrakhar Kumar100% (1)
- Exp - No.4 DSSSDocument2 pagesExp - No.4 DSSSSowmiyaNo ratings yet
- 27 Tanmay CNS Exp1-5Document21 pages27 Tanmay CNS Exp1-5Tanmay JoshiNo ratings yet
- Name: Rahul Tripathy Reg No.: 15bec0253Document22 pagesName: Rahul Tripathy Reg No.: 15bec0253rahulNo ratings yet
- 22bce20019. Lab Report-DldDocument40 pages22bce20019. Lab Report-Dldrockstarguy2005No ratings yet
- Lab Results VlsiDocument18 pagesLab Results Vlsipankaj rangareeNo ratings yet
- Ver I Log ExamplesDocument22 pagesVer I Log ExamplesDayanand Gowda KrNo ratings yet
- DC Lab 07Document7 pagesDC Lab 07Affra NazirNo ratings yet
- LDPC Hardcoding Bec 52Document8 pagesLDPC Hardcoding Bec 52Heman ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 4-PSK Code: All AllDocument2 pages4-PSK Code: All AllEysha qureshiNo ratings yet
- 21BCT0093 VL2022230504083 Ast08Document15 pages21BCT0093 VL2022230504083 Ast08Srinivasan UmaNo ratings yet
- Eda LabrecordDocument71 pagesEda Labrecordteja roopNo ratings yet
- Report04Document34 pagesReport04anjan joyNo ratings yet
- Ber For BPSKDocument2 pagesBer For BPSKVenuGopal KavuluruNo ratings yet
- Algorithm: Wireless Communication Experiments Ex. No. 1 AimDocument16 pagesAlgorithm: Wireless Communication Experiments Ex. No. 1 Aimseedr eviteNo ratings yet
- Nithin AssignmentDocument36 pagesNithin Assignmentmohammadakram99gmailNo ratings yet
- Dataflow ModellingDocument30 pagesDataflow ModellingMayur NayakaNo ratings yet
- VHDL Code For Half Adder by Data Flow ModellingDocument14 pagesVHDL Code For Half Adder by Data Flow ModellingPrateekKumar96% (24)
- Print Lab 11 - AllDocument22 pagesPrint Lab 11 - AllLord GamerNo ratings yet
- Vlsi 1Document48 pagesVlsi 1Prasanna ECE 46No ratings yet
- 'Enter The Domain Length:' '/nenter The Number of Grid Points:'Document2 pages'Enter The Domain Length:' '/nenter The Number of Grid Points:'Sanket ShahNo ratings yet
- Combinational - Circuits-Verilog CodesDocument6 pagesCombinational - Circuits-Verilog CodesTheVerseNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Script For A Binary ASK With Two Amplitude LevelsDocument3 pagesMATLAB Script For A Binary ASK With Two Amplitude LevelsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- DSP File 2003Document25 pagesDSP File 2003ANAKJNo ratings yet
- Record - Aarkum ManasilavillaDocument45 pagesRecord - Aarkum ManasilavillaAdarsh HNo ratings yet
- Software Lab Assignment (Ayushi Manoria-0101EC181037)Document11 pagesSoftware Lab Assignment (Ayushi Manoria-0101EC181037)eiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 & 2 (MST) : Submitted by - Name - Shailendra Yadav - (21DR0165)Document5 pagesAssignment-1 & 2 (MST) : Submitted by - Name - Shailendra Yadav - (21DR0165)Shailendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Sns Lab 4Document12 pagesSns Lab 4Zarafsha AbbasNo ratings yet
- MatLab Complete File PDFDocument54 pagesMatLab Complete File PDFHardik GargNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: # 2D Linear Convolution, Circular Convolution Between Two 2D MatricesDocument21 pagesPractical 1: # 2D Linear Convolution, Circular Convolution Between Two 2D MatricesJustin Sebastian100% (1)
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument16 pagesPulse Code ModulationKissi MissiNo ratings yet
- TASK-5 V Sarvesh Prasanth 19BEC0394: %modulationDocument6 pagesTASK-5 V Sarvesh Prasanth 19BEC0394: %modulationvipul kumarNo ratings yet
- FHMA 1 FHMA SIMU MergedDocument3 pagesFHMA 1 FHMA SIMU Mergedakashkumarswain213No ratings yet
- Digital SignalDocument3 pagesDigital SignalAnonymous YYeqtuNo ratings yet
- 17-34764-2 Lab Final CodeDocument3 pages17-34764-2 Lab Final CodeTanjirul Islam PrinceNo ratings yet
- Python Programming Code For PracticeDocument6 pagesPython Programming Code For Practiceshutup bruhNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer GraphicsDocument32 pagesAdvance Computer Graphicsnamank999No ratings yet
- 20bec1075 3.3 AdclabDocument18 pages20bec1075 3.3 Adclabk15No ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Codes For EnggDocument17 pagesDigital Image Processing Codes For EnggRohit GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Matlab CodeDocument9 pagesMatlab CodeAhmed AbuelfutuhNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Adc 18f0535Document28 pagesLab 10 Adc 18f0535f180535 SajjadAhmadNo ratings yet
- Practical: 03: REG NO: 2021BEC511 Roll No: A72 Name: Vrushabha R Bagde Sub: Digital CommunicationDocument4 pagesPractical: 03: REG NO: 2021BEC511 Roll No: A72 Name: Vrushabha R Bagde Sub: Digital CommunicationSAGAR SANTOSH MORENo ratings yet
- Dynamic ProgrammingDocument28 pagesDynamic ProgrammingAmisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chandrakant HDocument33 pagesChandrakant HJayanth V 19CS045No ratings yet
- DSP Lab 1 TaskDocument18 pagesDSP Lab 1 TaskMuhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Error Control Codes Using Matlab: EX - NO: DateDocument4 pagesSimulation of Error Control Codes Using Matlab: EX - NO: DateSubhashini MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Ivp 3Document28 pagesLab Manual Ivp 3Pratik ChavhanNo ratings yet
- DVB 043 HuttlDocument9 pagesDVB 043 HuttlStarLink1No ratings yet
- Ece4001exp1 6Document43 pagesEce4001exp1 6Dev MehtaNo ratings yet
- Program 8queensDocument1 pageProgram 8queensAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Lecture25 PDFDocument13 pagesLecture25 PDFJunaid RajputNo ratings yet
- Basic Matrix Operations On A DSP Array Architecture: September 2000Document9 pagesBasic Matrix Operations On A DSP Array Architecture: September 2000AdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Various Memory Circuits Used in Digital VLSIDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Various Memory Circuits Used in Digital VLSIAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- AC 4th Unit Receiver PDFDocument21 pagesAC 4th Unit Receiver PDFAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Antennas PropagationDocument40 pagesAntennas PropagationSafura BegumNo ratings yet
- Radio Ranges Radar NotesDocument7 pagesRadio Ranges Radar NotesAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- AC 4th Unit Receiver PDFDocument21 pagesAC 4th Unit Receiver PDFAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- AWP (Antenna Measurement) PDFDocument94 pagesAWP (Antenna Measurement) PDFAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument32 pages7.3 Antennas and Wave PropagationAdiseshuMidde0% (1)
- Critical RegionDocument7 pagesCritical RegionmustafaNo ratings yet
- Field Programmable Gate ArrayDocument1 pageField Programmable Gate ArrayAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Newdoc 1Document1 pageNewdoc 1AdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- .Model Small .Stack 200 .Code Start: Mov Ax, 1111h Mov BX, 1111h Add Ax, BX Int 03h End StartDocument1 page.Model Small .Stack 200 .Code Start: Mov Ax, 1111h Mov BX, 1111h Add Ax, BX Int 03h End StartAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Modern CommunicationDocument1 pageModern CommunicationAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Run A Program On FPGA BoardDocument11 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Run A Program On FPGA BoardAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- PTSP Qus BankDocument6 pagesPTSP Qus BankAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Run A Program Xilinix On FPGA BoardDocument11 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Run A Program Xilinix On FPGA BoardAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Advantages of NwellDocument1 pageAdvantages of NwellAdiseshuMidde100% (2)
- Stack Full OperationDocument1 pageStack Full OperationAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Docu KLMDocument1 pageDocu KLMAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Message Contain Either Audio or Video or Picture InformationDocument1 pageMessage Contain Either Audio or Video or Picture InformationAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- SsstacDocument1 pageSsstacAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document1 pageUntitled 1AdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Stack Full Out OperationDocument1 pageStack Full Out OperationAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Final Documentation For ThesisDocument1 pageFinal Documentation For ThesisAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Overal Final Documentation For ThesisDocument1 pageOveral Final Documentation For ThesisAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Integrated Circuit - Ic Vlsi-Very Large Scale IntegrationDocument1 pageIntegrated Circuit - Ic Vlsi-Very Large Scale IntegrationAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Ic 123Document1 pageIc 123AdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- SVC Manual C2670 EngDocument146 pagesSVC Manual C2670 EngAnonymous 1lbWGmNo ratings yet
- 2 Related Topics Automatic IrrigationDocument13 pages2 Related Topics Automatic IrrigationSftvsn Giovanni TandogNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Electric Industrial Robots: Communication Middleware (Melfarxm - Ocx) Instruction ManualDocument152 pagesMitsubishi Electric Industrial Robots: Communication Middleware (Melfarxm - Ocx) Instruction ManualRafael GagoNo ratings yet
- TSM SmokeDocument2 pagesTSM SmokeSudin AmatyaNo ratings yet
- California Bearing Ratio, Evaluation and Estimation: A Study On ComparisonsDocument4 pagesCalifornia Bearing Ratio, Evaluation and Estimation: A Study On ComparisonsAmyra MiaNo ratings yet
- 38 Meter Wind Turbine Blade Design PDFDocument47 pages38 Meter Wind Turbine Blade Design PDFWalid MohammedNo ratings yet
- CND - Clinical Round ChecklistDocument2 pagesCND - Clinical Round ChecklistMona Ismail AlsomaliNo ratings yet
- A35 Ostetricia Ginecologia PDFDocument8 pagesA35 Ostetricia Ginecologia PDFAarthiNo ratings yet
- Transistor IRFP350Document7 pagesTransistor IRFP350MiguelAngelCedanoBurrolaNo ratings yet
- Week4 Divide and ConquerDocument15 pagesWeek4 Divide and ConquerHg0% (1)
- Synopsis of Power FactorDocument10 pagesSynopsis of Power FactorRavi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Material 1 HOUSEHOLD CHORES PICTURE DICTIONARYDocument12 pagesMaterial 1 HOUSEHOLD CHORES PICTURE DICTIONARYnerepeichNo ratings yet
- Is 1786Document5 pagesIs 1786Jeevan ShendreNo ratings yet
- Spirex": Onepiece Spiral Flexible CouplingDocument1 pageSpirex": Onepiece Spiral Flexible CouplingHazim HazimNo ratings yet
- 09 Technical TablesDocument8 pages09 Technical TablesRuban Vijaya SinghNo ratings yet
- M2.2.9 Critical Review and Selection of NDT MethodsDocument13 pagesM2.2.9 Critical Review and Selection of NDT MethodsAldy Bagus PratamaNo ratings yet
- 312 Excavators Hydraulic System: Component ListDocument2 pages312 Excavators Hydraulic System: Component ListRr hardiyantoNo ratings yet
- Analysis Procedure K2co3 PDFDocument3 pagesAnalysis Procedure K2co3 PDFPiyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Supriya 113418799Document4 pagesSupriya 113418799Kewl JstNo ratings yet
- Control Panel STD Design PDFDocument71 pagesControl Panel STD Design PDFDuy ThaiNo ratings yet
- Plastic Coatings: Advanced Polymer Technologies ForDocument13 pagesPlastic Coatings: Advanced Polymer Technologies ForFazlul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Uk Fat 2017Document178 pagesUk Fat 2017Christopher J MillsNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 783Document2 pagesDatasheet 783veertulNo ratings yet
- Astm B446 - 2003 - 2008Document5 pagesAstm B446 - 2003 - 2008isaque300984No ratings yet
- Physics 02-07 Centripetal Force and Banked CurvesDocument2 pagesPhysics 02-07 Centripetal Force and Banked CurveslatteNo ratings yet
- Amadeus Web ServicesDocument2 pagesAmadeus Web ServicesBoris ChoiNo ratings yet
- PCMX Data Eng 01Document13 pagesPCMX Data Eng 01spamNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Stainless SteelsDocument5 pagesCorrosion of Stainless Steelsparasite0167% (3)
- The PA Bible Addn 03 Microphones PDFDocument4 pagesThe PA Bible Addn 03 Microphones PDFjosiasns5257100% (1)
- A Business Intelligence Framework For The FutureDocument10 pagesA Business Intelligence Framework For The Futuremcalbala100% (1)